Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Example 11: Successful Outcomes Totalnumber of Outcomes
Example 11: Successful Outcomes Totalnumber of Outcomes
Uploaded by
Thif EngliusOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Example 11: Successful Outcomes Totalnumber of Outcomes
Example 11: Successful Outcomes Totalnumber of Outcomes
Uploaded by
Thif EngliusCopyright:
Available Formats
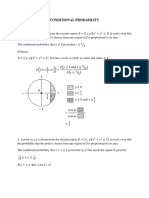
Example 11
A bag of candy contains candies of different fruit flavors. Four candies are strawberry-, eight are
lemon-, and three are cherry-flavored. If two candies are picked at random without replacement,
what is the probability that they both will have the same flavor?
Solution :
Step 1 (Identify the experiment, an outcome, and what constitutes a successful outcome)
Experiment : Picking two candies
An outcome : The two flavors picked
A successful outcome : The flavors are the same
Step 2 (Count the total number of outcomes)
Use the counting principle
15 ×14=210 different ways
Step 3 (Find the number of successful outcomes)
Find the number of ways we can pick two candies of each flavor
Strawberry candies : 4 ×3=12 ways
Lemon candies : 8 ×7=56 ways
Cherry candies : 3 ×2=6 ways
Add all of the number of ways of each flavor
12+56+6=74 ways
Step 4 (Define the probability)
successful outcomes 74
=
total number of outcomes 210
37
We can reduce it, so we get
105
Or, to the nearest percent, the answer is 35 %
37
∴ So, the probability will have the same flavor of two candies is or 35 % .
105
Example 12
A card is drawn from an ordinary deck of 52 playing crads and replaced in the deck. A second
card is then drawn. What is the probability that both are picture cards?
Solution :
We can solve that problem by a different use of the counting principle
1. First way
Step 1 (Identify the experiment, an outcome, and what constitutes a successful
outcome)
Experiment : Pick two card
An outcome : The types of cards picked
A successful outcome : The two cards are picture cards (jacks, queens, or kings not
necessarily the same)
Step 2 (Count the total number of outcomes)
52 ×52=2704 different ways
Step 3 (Find the number of successful outcomes)
Because in the deck there are 12 picture, so the number of successful outcomes is
12 ×12=144 ways
Step 4 (Define the probability)
successful outcomes 144
=
total number of outcomes 2704
9
We can reduce it, so we get
169
Or, to the nearest percent, the answer is 5 %
2. Second way
Specifically, it states : The probability of an event is equal to the product of the
probabilities of being successful at each stage of the experiment.
12 3
The probability of picking a picture card at each stage is or
52 13
Therefore, the probability of picking two picture cards is found simply by
3 3 9
× =
13 13 169
9
∴ So, the probability will have the picture cards of two cards is or 5 %.
169
You might also like
- Numerical Methods Using MATLAB 4ed Solution ManualDocument171 pagesNumerical Methods Using MATLAB 4ed Solution Manualnoobispriest2343% (23)
- SouthclawDocument40 pagesSouthclawFellype BrayanNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Mid 1 PaperDocument6 pagesBlockchain Mid 1 PaperDr-Anwar ShahNo ratings yet
- Binomial Probability DistributionDocument7 pagesBinomial Probability Distribution99210041290No ratings yet
- Probability DRV Mean and Variance of DRVDocument87 pagesProbability DRV Mean and Variance of DRVLemonadeNo ratings yet
- Unlock Your Academic Potential With Our Expert Statistics Assignment Help!Document7 pagesUnlock Your Academic Potential With Our Expert Statistics Assignment Help!statisticsassignmenthelpNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesLecture Notes For Introductory ProbabilityDocument218 pagesLecture NotesLecture Notes For Introductory Probabilityمهند عدنان الجعفريNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Introductory ProbabilityDocument218 pagesLecture Notes For Introductory ProbabilitySohail AfridiNo ratings yet
- Mat ADocument111 pagesMat Awnjue001No ratings yet
- Probability Review 2 SolutionsDocument4 pagesProbability Review 2 SolutionscmisaacNo ratings yet
- Take Home QuizDocument5 pagesTake Home QuizAlthia Joy AlisingNo ratings yet
- Simple Predictions of Events With Problem Solving: Name Grade Level Learning Area/Quarter DateDocument2 pagesSimple Predictions of Events With Problem Solving: Name Grade Level Learning Area/Quarter DateChel CalejaNo ratings yet
- Probability-2Document15 pagesProbability-2yasuo192427No ratings yet
- Quiz 2 PDFDocument4 pagesQuiz 2 PDFConrad Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Math 117 Ex 2 Samples OlDocument7 pagesMath 117 Ex 2 Samples OlhagostadesseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ProbabilityDocument57 pagesChapter 3 ProbabilitySittie Lyca MopacNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Data Handling Probability Statistics inDocument13 pagesGrade 8 Data Handling Probability Statistics inShweta RawatNo ratings yet
- Probability Notes: My Career StudyDocument7 pagesProbability Notes: My Career StudyMANOJ100% (1)
- Probability p2Document28 pagesProbability p2Hana ElfarNo ratings yet
- Q4 Math 5 Week7Document4 pagesQ4 Math 5 Week7JustVisitingNo ratings yet
- W1-3 Q3 Math-8B Simple-ProbabilityDocument6 pagesW1-3 Q3 Math-8B Simple-ProbabilityShanelle SantillanaNo ratings yet
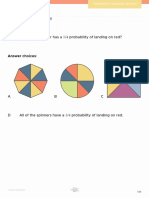
- 1/4 Probability of Landing On Red?Document6 pages1/4 Probability of Landing On Red?Isaque SilvaNo ratings yet
- PPT8Document47 pagesPPT8clayorder147No ratings yet
- Broñola - Statistics & Probability (Activity)Document11 pagesBroñola - Statistics & Probability (Activity)[STEM - 21] Alexander BroñolaNo ratings yet
- STATISTICS and PROBABILITY PPT2Document11 pagesSTATISTICS and PROBABILITY PPT2Armand James OcliasoNo ratings yet
- Counting and ProbabilityDocument40 pagesCounting and ProbabilityJazel David100% (1)
- Lecture 22binomial DistributionDocument15 pagesLecture 22binomial DistributionRajesh KabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Statistics, Probability & Counting Methods QDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Statistics, Probability & Counting Methods QSapa PynGNo ratings yet
- GECMAT Assignment #3Document7 pagesGECMAT Assignment #3Sunny EggheadNo ratings yet
- Probability - Easy AnsDocument48 pagesProbability - Easy AnsAbuNo ratings yet
- Math 2320 Assignment 2 SolutionDocument6 pagesMath 2320 Assignment 2 Solutionkitty100% (2)
- Probability 2024Document11 pagesProbability 2024Given MteweleNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory: "Equally Likely". The Terms Experiment', Event' and Equally Likely' Are Defined As FollowsDocument13 pagesProbability Theory: "Equally Likely". The Terms Experiment', Event' and Equally Likely' Are Defined As FollowshareshtankNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ProbabilityDocument42 pagesIntroduction To ProbabilitylittlemakzmathNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 3 Mathematics of ChancesDocument18 pagesChapter # 3 Mathematics of ChancesAmal K ANo ratings yet
- Multiplying Fractions 2 2. Dividing Fractions 5Document8 pagesMultiplying Fractions 2 2. Dividing Fractions 5indyglowNo ratings yet
- Probability Repeated TrialsDocument6 pagesProbability Repeated Trialsapi-3730369100% (1)
- StatsB TheBinomialDistributionDocument4 pagesStatsB TheBinomialDistributionShane LambertNo ratings yet
- 8.1, 8.2 & 8.3 Theoretical Probability: Probability of An Event OccurringDocument3 pages8.1, 8.2 & 8.3 Theoretical Probability: Probability of An Event OccurringEugenio CapielloNo ratings yet
- Pad - Wee 3Document10 pagesPad - Wee 3May JavellanaNo ratings yet
- Mutually Inclusive EventsDocument7 pagesMutually Inclusive EventsMuhammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: SolutionDocument6 pagesStatistics and Probability: SolutionNery GranadaNo ratings yet
- 2 Discrete Random Variable Probability Distributions 2Document28 pages2 Discrete Random Variable Probability Distributions 2William TsuiNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics and ProbabilityDocument25 pagesCombinatorics and ProbabilityHedi mar NecorNo ratings yet
- Probability of Compound Events 1Document23 pagesProbability of Compound Events 1David PalugaNo ratings yet
- MATH 109 Basic ProbabilityDocument5 pagesMATH 109 Basic ProbabilitySam CunananNo ratings yet
- Important-Question-Class-8-Maths-Chapter-6 Cubes and Cube RootsDocument6 pagesImportant-Question-Class-8-Maths-Chapter-6 Cubes and Cube Rootsnirmal krisnaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and Position (Ungrouped Data) : Lesson 3Document9 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and Position (Ungrouped Data) : Lesson 3Gemver Baula BalbasNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 1 in MMW, Ch3Document16 pagesLearning Material 1 in MMW, Ch3Princess Angie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument14 pagesProbabilitySriNo ratings yet
- Conditional ProbabilityDocument29 pagesConditional ProbabilityAkhilNo ratings yet
- A Review of ProbabilityDocument18 pagesA Review of ProbabilityJanine LerumNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Probability Hand OutsDocument8 pagesThird Quarter Probability Hand Outsgianlesternaelgas69No ratings yet
- Probabilistic Robotics Exam, Spring 2012: 4 PointsDocument7 pagesProbabilistic Robotics Exam, Spring 2012: 4 PointseetahaNo ratings yet
- General Aptitude: Trainer: Sujata MohiteDocument64 pagesGeneral Aptitude: Trainer: Sujata Mohitesmkcoolllll-10No ratings yet
- GECMAT Assignment 3Document9 pagesGECMAT Assignment 3Rheysalyn Mae DespiNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument33 pagesProbabilityayush valechaNo ratings yet
- Probability and Tree Diagrams: Wjec MathematicsDocument18 pagesProbability and Tree Diagrams: Wjec MathematicsGim ReyesNo ratings yet
- 13-6 Probabilities of Mutually Exclusive EventsDocument3 pages13-6 Probabilities of Mutually Exclusive EventsKynard PatrickNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probability Miscellaneous ExerciseDocument16 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probability Miscellaneous Exerciseanjalishukla2729No ratings yet
- Job - 1 - Percobaan Dasar Input - Output Menggunakan Led Dan MicroswitchDocument5 pagesJob - 1 - Percobaan Dasar Input - Output Menggunakan Led Dan MicroswitchIkomang PartasanjayaputraNo ratings yet
- Programming 1A: (PROG5121)Document13 pagesProgramming 1A: (PROG5121)Dzudzi ManyuhaNo ratings yet
- 26-Synchronization in JavaDocument12 pages26-Synchronization in Javapratigya gNo ratings yet
- Coding Interview Java (PART-2)Document207 pagesCoding Interview Java (PART-2)Ankush TiwariNo ratings yet
- M.3 - Move Constructors and Move Assignment - Learn C++Document16 pagesM.3 - Move Constructors and Move Assignment - Learn C++njb25bcnqfNo ratings yet
- Tax Fraud Detection Through Neural NetworksDocument14 pagesTax Fraud Detection Through Neural NetworksNuttaphon CharuvajanaNo ratings yet
- TE Computer Engg 2019 Course Syllabus Draft 23may2021Document100 pagesTE Computer Engg 2019 Course Syllabus Draft 23may2021Mayur SarodeNo ratings yet
- Yacht Club and Linea CalcDocument16 pagesYacht Club and Linea CalcTibyanNo ratings yet
- Slow Learns Question BankDocument2 pagesSlow Learns Question BankSatwik KrishnaNo ratings yet
- ComProg Module - M5 FinalDocument6 pagesComProg Module - M5 FinalLEO JR GREFALDONo ratings yet
- Pointers Examples: Page 1 of 7Document7 pagesPointers Examples: Page 1 of 7Laxman KuddemmiNo ratings yet
- 15 Vertical Order Traversal 09-02-2024Document19 pages15 Vertical Order Traversal 09-02-2024cybersyndicatenftNo ratings yet
- Unit-2.3 Local Search Algo and Optimization ProblemsDocument18 pagesUnit-2.3 Local Search Algo and Optimization Problemsmani111111No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Graph McqsDocument6 pagesUnit 4 Graph McqsFatherNo ratings yet
- Rabin-Karp AlgorithmDocument3 pagesRabin-Karp Algorithmkrishna16kkumawatNo ratings yet
- Lower Bounds in Computer ScienceDocument38 pagesLower Bounds in Computer ScienceMirza AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Distributed Computing System (DCS) Solved MCQs (Set-4)Document6 pagesDistributed Computing System (DCS) Solved MCQs (Set-4)YilmaNo ratings yet
- IMPLEMENTATION OF MACRO PROCESSOR System Software Lab ProgramDocument2 pagesIMPLEMENTATION OF MACRO PROCESSOR System Software Lab ProgramBalaji Shanmugam0% (1)
- OS Record Cover Page Bonafide and Index SEC ADocument4 pagesOS Record Cover Page Bonafide and Index SEC AKaarthik RajaNo ratings yet
- Where, In, Logical, Like OperatorDocument12 pagesWhere, In, Logical, Like OperatorSatyam TiwariNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Knowledge ManagementDocument2 pagesMCQ On Knowledge ManagementtanubajpaNo ratings yet
- Maths Ist SemDocument6 pagesMaths Ist SemSutapa Pawar100% (1)
- Java Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesJava Course SyllabusAbdul Hakeem ShaikNo ratings yet
- C++ NotesDocument4 pagesC++ Notesvaibhav bhuwaniaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C 4Th Edition Weiss Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument13 pagesEbook Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C 4Th Edition Weiss Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmenaionemperilgtod26100% (12)
- Lesson 5 Python For Loops While LoopsDocument7 pagesLesson 5 Python For Loops While LoopsAzira TeamNo ratings yet
- SP Lab ManualsDocument52 pagesSP Lab Manualsayesha hassanNo ratings yet