Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edited - Sanaa Anderson - Module 8 Lesson 1 #2 Assignment
Uploaded by
Sanaa AndersonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Edited - Sanaa Anderson - Module 8 Lesson 1 #2 Assignment
Uploaded by
Sanaa AndersonCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 8
Cellular Energy
1 How Organisms Obtain Energy
BEFORE YOU READ WHAT YOU’LL LEARN
Think about the objects in your home that use energy. On the • the two laws of
lines below, describe the ways that these objects get energy. Then thermodynamics
read about how organisms obtain energy. • the difference between
anabolic and catabolic
My lamp gets energy from the outlet and the pathways
outlet gets its energy from wind, but depending • how ATP works in a cell
on where you are it might come from natural gas,
water, or coal
READ TO LEARN
⊳ FOCUS
Transformation of Energy After you read this lesson,
Cells need energy. They need energy to move molecules across create a quiz based on what
you have learned. Be sure to
membranes and to make and break down molecules. Energy is
answer the quiz questions.
the ability to do work. Thermodynamics is the study of how
energy flows and changes in the universe.
What are the laws of thermodynamics?
Two laws of thermodynamics explain the flow of energy. The
first law states that energy can change form, but it cannot be
created or destroyed. For example, your body changes the
chemical energy in food into a more useable form. Then when
you move, your body changes that energy into mechanical energy.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education
The second law of thermodynamics states that systems change
from states of order to states of disorder on their own. This
disorder is known as entropy (EN truh pee). Entropy is always THINK IT OVER
increasing. This means that when your body changes energy into 1. State the first law of
another form, some of the energy is lost as heat. The energy is still thermodynamics.
present, but it can no longer be used. The first law of
thermodynamics
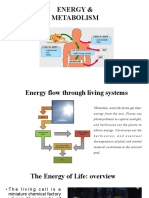
How do organisms get energy from the Sun?
is that energy can
Nearly all the energy for life on Earth comes from the Sun.
change form, but
Some organisms make their own food. Some autotrophs use
it can’t be created
inorganic substances as a source of energy. Other autotrophs
or destroyed.
change light energy from the Sun into chemical energy. Plants
and some bacteria are autotrophs.
Reading Essentials • Cellular Energy
83
Heterotrophs get their energy by eating food. Heterotrophs get
energy from the Sun indirectly. They do this by eating autotrophs.
Animals are heterotrophs. The figure below shows the
relationship between autotrophs and heterotrophs.
TAKE A LOOK
2. Circle the organism that
makes its own food.
Sunlight Autotroph Heterotroph Heterotroph
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that go on inside a cell are known
as the cell’s metabolism. A series of reactions in which the
product of one reaction becomes the reactant for the next
reaction is called a metabolic pathway.
What are the two types of metabolic pathways?
THINK IT OVER
3. Compare what happens to There are two types of metabolic pathways: catabolic (ka tuh
energy in anabolic and BAH lik) pathways and anabolic (a nuh BAH lik) pathways. In
catabolic pathways. catabolic pathways, energy is released by breaking larger
In catabolic pathways, energy is molecules into smaller molecules. In anabolic pathways, the
released by breaking larger energy released by catabolic pathways is used to build larger
molecules into smaller molecules from smaller molecules.
molecules and the energy
released is used to build larger Energy flows between the metabolic pathways of organisms in
molecules from smaller an ecosystem. Photosynthesis is an anabolic pathway. Cellular
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education
molecules which is called respiration is a catabolic pathway. These pathways work together
anabolic pathways to meet the energy needs of cells.
How is energy changed during photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a series of reactions that change light energy
from the Sun into chemical energy that can be used by the cell.
During photosynthesis, light energy, carbon dioxide, and water
are changed into organic molecules and oxygen. The energy
stored in organic molecules made during photosynthesis can be
passed to other organisms. When an animal eats a plant, the
plant’s stored energy is passed to the animal.
Reading Essentials • Cellular Energy
84
What happens during cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of reactions that break down
organic molecules into carbon dioxide, water, and energy. The
energy is used by the cell. The processes of cellular respiration
and photosynthesis form a cycle, which is shown in the figure
below. The products of photosynthesis are the reactants for TAKE A LOOK
cellular respiration, and the products of cellular respiration 4. Identify Draw a circle
around the anabolic
are the reactants for photosynthesis. process and a square
around the catabolic
process.
Sunlight
Photosynthesis
(autotrophs)
CO2 + H2O O2 + Glucose
Cellular respiration
(heterotrophs)
ATP: The Unit of Cellular Energy
Cells store chemical energy in biological molecules. The most
important biological molecule is adenosine triphosphate (uh
DEN uh seen • tri FAHS fayt), or ATP.
How does ATP store energy?
ATP is the most abundant energy-storing molecule. It is found
in all kinds of organisms. The structure of ATP is shown below. It
is made of an adenine base, a ribose sugar, and three phosphate
groups.
ATP releases energy when the bond between the second and
third phosphate groups is broken, forming a molecule called
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education
adenosine diphosphate (ADP). ADP can be changed back into
ATP by adding a phosphate group. TAKE A LOOK
ATP 5. Identify Circle the high-
Triphosphate energy bond that is broken
group
Adenine P P P + H2O
when ATP is converted to
ADP.
Ribose
Energy
Energy
ADP
Diphosphate
group
Adenine P P + P
Ribose
Reading Essentials • Cellular Energy
85
You might also like
- Life Science 012208Document2 pagesLife Science 012208EdenNo ratings yet
- Block 4. Metabolism SciencJournalDocument4 pagesBlock 4. Metabolism SciencJournalfernanda barragan torresNo ratings yet
- Mil4ch31 (Energy and Enzymes)Document9 pagesMil4ch31 (Energy and Enzymes)Muhammad AsadkhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Biochemistry and ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Biochemistry and ThermodynamicsMamamiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Atkins PDFDocument49 pagesChapter 1 Atkins PDFAndi Haswinar Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- 1.3a Energy Transformations 1 12BIODocument20 pages1.3a Energy Transformations 1 12BIOedensatire21No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document47 pagesChapter 3alphabequalNo ratings yet
- Week 4.1 AdvancedDocument21 pagesWeek 4.1 AdvancedAaron MostNo ratings yet
- 00 Cells Energy2 2Document8 pages00 Cells Energy2 2Hendra du NantNo ratings yet
- Topic: Bioenergetics: Living OrganismsDocument9 pagesTopic: Bioenergetics: Living OrganismsNaiomiNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 3 Student NotesDocument46 pagesAP Biology Unit 3 Student NotesJ15No ratings yet
- Energy in BiologyDocument15 pagesEnergy in BiologyJay BetaizarNo ratings yet
- Advance Biology: Quarter 3: Cell MetabolismDocument4 pagesAdvance Biology: Quarter 3: Cell MetabolismEmmanuel AzoresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 PDFDocument48 pagesLecture 6 PDFSugamNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Biomolecules, Thermodynamics & Properties of WaterDocument31 pagesIntroduction, Biomolecules, Thermodynamics & Properties of WaterMUHAMMAD ZHARIF MOHD RAZIMANNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Chemical EnergyDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Chemical EnergyInned NylNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Bioenergetics: Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Bioenergetics: Review QuestionsBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Metabilism and EnergyDocument40 pagesMetabilism and EnergyKisra MahdereNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Module Test 2Document7 pagesThermochemistry: Module Test 2Dobal PunioNo ratings yet
- 3 Principles of Cell MetabolismDocument53 pages3 Principles of Cell MetabolismKristine Claire TarucNo ratings yet
- Bio EnergeticsDocument3 pagesBio EnergeticsJobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- Energy - MetabolismDocument45 pagesEnergy - MetabolismAngel GustasianaNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of Cells: A.2.1 Matter and EnergyDocument13 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cells: A.2.1 Matter and EnergyRovina Narayan DiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1a Biochemistry and Organization of CellsDocument38 pagesChapter 1a Biochemistry and Organization of CellsSyahirah FazialNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesThermodynamicsGalvez Glaiza ElaineNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To MetabolismDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To MetabolismsamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bio462 NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Bio462 Notesdaniel AfiqNo ratings yet
- 2 7 Atp-AdpDocument27 pages2 7 Atp-Adpıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- Bio 201 pt.1Document43 pagesBio 201 pt.1Vivian WuNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 - 12 Q2 0701 PF FDDocument43 pagesBio 11 - 12 Q2 0701 PF FDrasheika ducosNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Chapter Six An Introduction To MetabolismDocument13 pagesAP Bio Chapter Six An Introduction To Metabolismpink123123No ratings yet
- Bio1 11 - 12 Q2 0701 FDDocument21 pagesBio1 11 - 12 Q2 0701 FDSketch the FilterNo ratings yet
- How Ecosystems WorkDocument8 pagesHow Ecosystems WorkyjnhtgrfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Section 1 SciDocument3 pagesChapter 9 Section 1 SciThere is only 2 Genders100% (1)
- Assign1b 204Document27 pagesAssign1b 204Maii AlaarajNo ratings yet
- Ess Topic 1.3Document8 pagesEss Topic 1.3areenaNo ratings yet
- Green Minimalist The Environtment PresentationDocument11 pagesGreen Minimalist The Environtment PresentationJimmy Q MadroneroNo ratings yet
- General Biology Themes in Biology 115Document36 pagesGeneral Biology Themes in Biology 115RifdahTsabitaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Energy and MetabolismDocument29 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Energy and MetabolismClaire WeerepasNo ratings yet
- C7 Generation of Biochemical EnergyDocument22 pagesC7 Generation of Biochemical EnergySoraya D. Al-ObinayNo ratings yet
- Cell Processes and EnergyDocument36 pagesCell Processes and EnergyCarolinaNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Ebook 2020Document29 pagesBioenergetics Ebook 2020MjNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument25 pagesEnergyMaejean Capito DamianNo ratings yet
- A. Chapter 4-Lesson 4.1-Energy For Life-PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesA. Chapter 4-Lesson 4.1-Energy For Life-PhotosynthesisIntan Putri FebriyonNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument5 pagesMetabolismjasmineNo ratings yet
- Sci8 - EnergyDocument36 pagesSci8 - Energytchr keiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Energy & Enzymes: Isolated System Closed System Open SystemDocument2 pagesLecture 4: Energy & Enzymes: Isolated System Closed System Open SystemAsherNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Part 2 ReportingDocument10 pagesGen Bio Part 2 ReportingMj DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Phy105 ch1 1Document24 pagesPhy105 ch1 1Ruben GavidiaNo ratings yet
- 01 INTRO To BIOCHEMDocument6 pages01 INTRO To BIOCHEMJoshua CoNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Lecture Outline 6Document6 pagesAP Biology Lecture Outline 6jenbutts1977No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Metabolism: Lecture OutlineDocument12 pagesAn Introduction To Metabolism: Lecture Outlinehaha_le12No ratings yet
- Classification of Energy PDFDocument9 pagesClassification of Energy PDFSOFIA REYES RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Learners Copy Phys Scie Mod 4Document16 pagesLearners Copy Phys Scie Mod 4Lynlyn ClorNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics KOMDocument4 pagesBioenergetics KOMGayathri potnuru JioNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Week 13 16 2Document16 pagesEarth and Life Science Week 13 16 2asleahgumama6No ratings yet
- Science Revision Cheat SheetDocument24 pagesScience Revision Cheat SheetEmber LinNo ratings yet
- Biologi Medis. #6Document31 pagesBiologi Medis. #6MuhammadYusroNo ratings yet
- Module 1. IntroductionDocument26 pagesModule 1. IntroductionmimiNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte Ga b85m Ds3h A r10 PDFDocument30 pagesGigabyte Ga b85m Ds3h A r10 PDFMartha Lorena TijerinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Concepts About Educational TechnologyDocument17 pagesLesson 1 Concepts About Educational TechnologyMarvin ContigaNo ratings yet
- WoundVite®, The #1 Most Comprehensive Wound, Scar and Post-Surgical Repair Formula Receives Amazon's Choice High RatingsDocument3 pagesWoundVite®, The #1 Most Comprehensive Wound, Scar and Post-Surgical Repair Formula Receives Amazon's Choice High RatingsPR.comNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Strategic Management BarbosaDocument11 pagesSustainable Strategic Management BarbosapurwawardhaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment in Family Nursing PracticeDocument22 pagesNursing Assessment in Family Nursing PracticeHydra Olivar - PantilganNo ratings yet
- Iso Iec 25030 2007 eDocument44 pagesIso Iec 25030 2007 eAngélica100% (1)
- Introduction: Meaning of HypothesisDocument8 pagesIntroduction: Meaning of HypothesisMANISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- The Determinants of Corporate Dividend PolicyDocument16 pagesThe Determinants of Corporate Dividend PolicyRutvikNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Short-Circuit Current (Isc) at Any Point Within A LV Installation - Electrical Installation GuideDocument6 pages3-Phase Short-Circuit Current (Isc) at Any Point Within A LV Installation - Electrical Installation GuideYuukinoriNo ratings yet
- 2017LR72 - SUMMARY REPORT Final 03052020Document72 pages2017LR72 - SUMMARY REPORT Final 03052020Dung PhamNo ratings yet
- LP Pe 3Q - ShaynevillafuerteDocument3 pagesLP Pe 3Q - ShaynevillafuerteMa. Shayne Rose VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Democracy or Aristocracy?: Yasir MasoodDocument4 pagesDemocracy or Aristocracy?: Yasir MasoodAjmal KhanNo ratings yet
- Penelitian Tindakan Kelas - Alberta Asti Intan Sherliana 20220049Document25 pagesPenelitian Tindakan Kelas - Alberta Asti Intan Sherliana 20220049Asti SherlyanaNo ratings yet
- EDAG0007Document5 pagesEDAG0007krunalNo ratings yet
- 2023 2024 Syllabus PDFDocument23 pages2023 2024 Syllabus PDFRika DianaNo ratings yet
- Dragons ScaleDocument13 pagesDragons ScaleGuilherme De FariasNo ratings yet
- NamalDocument5 pagesNamalAyusnab KarkiNo ratings yet
- 3E Hand Over NotesDocument3 pages3E Hand Over NotesAshutosh MaiidNo ratings yet
- Gandhi and The Non-Cooperation MovementDocument6 pagesGandhi and The Non-Cooperation MovementAliya KhanNo ratings yet
- Eng03 Module Co4Document14 pagesEng03 Module Co4Karl Gabriel ValdezNo ratings yet
- Debate Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesDebate Brochure PDFShehzada FarhaanNo ratings yet
- Rare Watches (Christie's) 16. 05. 2016.Document236 pagesRare Watches (Christie's) 16. 05. 2016.Simon LászlóNo ratings yet
- Structure of NABARD Grade ADocument7 pagesStructure of NABARD Grade ARojalin PaniNo ratings yet
- ING C1 CO JUN2016 CorrectorDocument6 pagesING C1 CO JUN2016 CorrectoraciameNo ratings yet
- Banin Cawu 1: Panitia Ujian Perguruan Islam Mathali'Ul FalahDocument4 pagesBanin Cawu 1: Panitia Ujian Perguruan Islam Mathali'Ul FalahKajen PatiNo ratings yet
- Matutum View Academy: (The School of Faith)Document14 pagesMatutum View Academy: (The School of Faith)Neil Trezley Sunico BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- Nascsa - Sponsor Solicitation List: January 06, 2021Document35 pagesNascsa - Sponsor Solicitation List: January 06, 2021Prasoon SimsonNo ratings yet
- Setting and Plot: Old YellerDocument8 pagesSetting and Plot: Old YellerWalid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 20: TroubleshootingDocument12 pagesUnit 20: TroubleshootingDongjin LeeNo ratings yet
- Level I 2018 2019 Program Changes PDFDocument2 pagesLevel I 2018 2019 Program Changes PDFMuhammad BurairNo ratings yet