Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippines
Uploaded by
Tom Cuenca0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views5 pagesOriginal Title
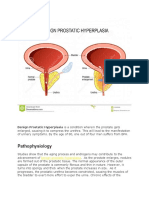
Patient E NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views5 pagesPrioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippines
Uploaded by
Tom CuencaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
FATHER SATURNINO URIOS UNIVERSITY
San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippines
Nursing Program
PRIORITIZATION OF PROBLEMS
Rank Problem Identified
1 Impaired Urinary Elimination related to neuromuscular
impairment as evidenced by increasing urinary frequency and
urgency
2 Self-care Deficit related to neuromuscular impairments,
decreased strength and endurance, and motor impairment as
evidenced by numbness and weakness of the right arm and
inability to hold objects
3 Risk for Ineffective Coping related to physiological changes,
anxiety, and fear
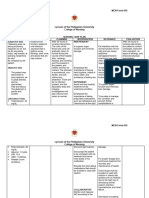
NURSING CARE PLAN #1
By A.T., Cuenca, FSUU, SN
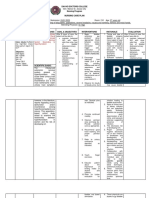
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation
Subjective data: Impaired Within 8 hours of nursing INDEPENDENT After 8 hours of nursing
No statements were Urinary intervention, the patient will 1. Note reports of urinary - Provides information about the intervention, the patient
verbalized by the Elimination be able to: frequency, urgency, burning, degree of interference with was able to:
patient related to incontinence, nocturia, and size or elimination or may indicate a
neuromuscular • Demonstrate behaviors force of the urinary stream. Palpate bladder infection. Fullness over • Demonstrate behaviors
Objective data: impairment as or techniques to bladder after voiding. bladder following void is indicative of or techniques to
• Increasing evidenced by prevent or minimize inadequate emptying or retention prevent or minimize
urinary increasing infection and requires intervention. infection
frequency and urinary • Be free of urine 2. Review drug regimen, including - A number of medications such as • Be free of urine
urgency frequency and leakage, achieve prescribed, over-the-counter some antispasmodics, leakage, achieve
• Episodes of eye urgency normal elimination (OTC), and street. antidepressants, and narcotic normal elimination
fuzziness pattern, and empty analgesics; OTC medications with pattern, and empty
associated with bladder complete and anticholinergic or alpha agonist bladder complete and
diplopia and regularly properties; or recreational drugs regularly
flashes of such as cannabis may interfere with
brightness bladder emptying. Goal met.
• Ascending 3. Encourage adequate fluid - Sufficient hydration promotes November 6, 2021
numbness and intake, avoiding caffeine and use urinary output and aids in preventing 11:00 AM
weakness of the of aspartame, and limiting intake infection. Note: When the patient is
right arm during the late evening and at taking sulfa drugs, sufficient fluids
• Inability to hold bedtime. Recommend use of are necessary to ensure adequate
objects cranberry juice/ vitamin C. excretion of the drug, reducing the
• Rapid risk of cumulative effects. Note: A.T., Cuenca, FSUU, SN
progression of Aspartame, a sugar substitute (e.g.,
weakness in the Nutrasweet), may cause bladder
legs irritation leading to bladder
dysfunction.
No vital signs data 4. Institute bladder training - Helps restore adequate bladder
were recorded program or timed voidings as functioning; lessens the occurrence
appropriate. of incontinence and bladder
infection.
5. Promote continued mobility. - Decreases risk of developing UTI.
6. Recommend good hand - Reduces skin irritation and the risk
washing and proper perineal care. of ascending infection.
7. Obtain periodic urinalysis and - Monitors renal status. Colony
urine culture and sensitivity as count over 100,000 indicates the
indicated. presence of infection requiring
treatment.
8. Encourage patient to observe - Indicative of infection requiring
for sediments or blood in urine, foul further evaluation or treatment.
odor, fever, or unexplained
increase in MS symptoms.
9. Teach self-catheterization and - Helps patient maintain autonomy
instruct in the use and care of the and encourages self-care. An
indwelling catheter. indwelling catheter may be required,
depending on the patient’s abilities
and degree of the urinary problem.
COLLABORATIVE
10. Refer to urinary continence - Helpful for developing an
specialist as indicated. individual plan of care to meet
patient’s specific needs using the
latest techniques, continence
products.
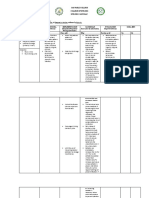
NURSING CARE PLAN #2
By A.T., Cuenca, FSUU, SN
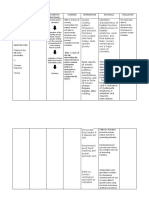
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation
Subjective data: Self-care Within 8 hours of nursing INDEPENDENT After 8 hours of nursing
No statements were Deficit related intervention, the patient will 1. Determine the current activity - Provides information to develop a intervention, the patient
verbalized by the to be able to: level and physical condition. plan of care for rehabilitation. Note: was able to:
patient neuromuscular Assess degree of functional Motor symptoms are less likely to
impairments, • Demonstrate impairment using a 0–4 scale. improve than sensory ones. • Demonstrate
Objective data: decreased techniques and lifestyle 2. Encourage patient to perform - Promotes independence and techniques and lifestyle
• Increasing strength and changes to meet self- self-care to the maximum of ability sense of control; may decrease changes to meet self-
urinary endurance, care needs as defined by the patient. Do not feelings of helplessness. care needs
frequency and and motor • Perform self-care rush the patient. • Perform self-care
urgency impairment as activities within level of 3. Assist according to the degree - Participation in own care can ease activities within level of
• Episodes of eye evidenced by own ability of disability; allow as much the frustration over the loss of own ability
fuzziness numbness and autonomy as possible. independence.
associated with weakness of 4. Encourage patient input in the - Patient’s quality of life is enhanced Goal met.
diplopia and the right arm planning schedule and encourage when desires and likes are November 6, 2021
flashes of and inability to scheduling activities early in the considered in daily activities. 3:35 PM
brightness hold objects day or during the time when the Patients with MS expend a great
• Ascending energy level is best. deal of energy to complete ADLs,
numbness and increasing the risk of fatigue, which
weakness of the often progresses through the day.
right arm 5. Note presence of fatigue. - Fatigue experienced by patients A.T., Cuenca, FSUU, SN
• Inability to hold with MS can be very debilitating and
objects greatly impact the ability to
• Rapid participate in ADLs. The subjective
progression of nature of reports of fatigue can be
weakness in the misinterpreted by healthcare
legs providers and family, leading to
conflict and the belief that the
No vital signs data patient is “manipulative” when, in
were recorded fact, this may not be the case.
6. Allot sufficient time to perform - Decreased motor skills and
tasks, and display patience when spasticity may interfere with the
movements are slow.
ability to manage even simple
activities.
7. Encourage stretching and - Helps decrease spasticity and its
toning exercises and use of effects.
medications, cold packs, and
splints and maintenance of proper
body alignment, when indicated.
8. Problem-solve ways to meet - Provides for adequate intake and
nutritional and fluid needs. enhances the patient’s feelings of
independence or self-esteem.
9. Provide assistive devices and - Reduces fatigue, enhancing
aids as indicated: shower chair, participation in self-care.
elevated toilet seat with arm
supports.
COLLABORATIVE
10. Consult with a physical and/or - Useful in identifying devices
occupational therapist. and/or equipment to relieve spastic
muscles, improve motor functioning,
prevent and reduce muscular
atrophy and contractures, promoting
independence and an increasing
sense of self-worth.
You might also like
- Apurba S Sastry-Essentials of Medical Microbiology 3E Rev ReprintDocument1 pageApurba S Sastry-Essentials of Medical Microbiology 3E Rev ReprintSandra Ann Biju100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis of Prostate CancerDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis of Prostate CancerSyafiqAzizi100% (1)
- #PROJECT50 Project Created by State of MindDocument3 pages#PROJECT50 Project Created by State of Mindameera leilaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics-III For Pharmacy Technician 2nd Year BookDocument30 pagesPharmaceutics-III For Pharmacy Technician 2nd Year BookAttari Express YT88% (8)
- CCTV CONSENTDocument2 pagesCCTV CONSENTGam SaiiNo ratings yet
- Vietnam Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare Report - Q3 2022 - Shared by WorldLine TechnologyDocument62 pagesVietnam Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare Report - Q3 2022 - Shared by WorldLine Technologylebaosip100% (3)
- Group-5 NCM-107 NCPDocument4 pagesGroup-5 NCM-107 NCPbulok netflakes100% (1)
- Pancreatitis Group 3 NCM 116Document21 pagesPancreatitis Group 3 NCM 116Diana Jane LauretaNo ratings yet
- NCP BPHDocument1 pageNCP BPHyasiraNo ratings yet
- NCP Metro San JoseDocument8 pagesNCP Metro San JosePrincess NavarroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Denise GabatoNo ratings yet
- Activity On NCM MakingDocument4 pagesActivity On NCM MakingJollan Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypokalemia: Monitoring and Maintaining Serum Potassium LevelsDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hypokalemia: Monitoring and Maintaining Serum Potassium LevelsDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationRODERICK FELICIANO JR.No ratings yet
- Silvaqueenie Rose Multiple SclerosisDocument5 pagesSilvaqueenie Rose Multiple SclerosisQueenie SilvaNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence in Elderly: DefinitionDocument13 pagesUrinary Incontinence in Elderly: DefinitionTarek AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesCerebral Palsy Nursing Care PlanAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- NCP Urinary RetentionDocument3 pagesNCP Urinary RetentionKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence: Pathophysiology and Management OutlineDocument6 pagesUrinary Incontinence: Pathophysiology and Management OutlineNgurah AndhikaNo ratings yet
- NCP Urine RetentionDocument4 pagesNCP Urine RetentionKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- KUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE ConstipationDocument2 pagesKUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE Constipationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermDocument3 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- NCP Pedia RotDocument5 pagesNCP Pedia RotGian kyle AradillosNo ratings yet
- Davao Doctors College Nursing Program Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesDavao Doctors College Nursing Program Nursing Care PlanPRINCESS KOBAYASHINo ratings yet
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument3 pagesDiarrheaBert GasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Drug Study: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Drug Study: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationteejay andradaNo ratings yet
- CONSTIPATIONDocument4 pagesCONSTIPATIONKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- Prostate Nrsg. ManagementDocument7 pagesProstate Nrsg. ManagementKim RamosNo ratings yet
- College Drug Study Details Pregnancy DeliveryDocument1 pageCollege Drug Study Details Pregnancy DeliveryMarjorie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN FOR DIARRHEADocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN FOR DIARRHEAKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Neurogenic Bladder: Mobility Clinic Case-Based Learning ModuleDocument11 pagesNeurogenic Bladder: Mobility Clinic Case-Based Learning ModuleJamaicaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Cervical Cancer PatientDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for Cervical Cancer PatientJeanessa Delantar QuilisadioNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanatation Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanatation Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- Alteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesDocument3 pagesAlteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Plan of Care Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Plan of Care Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDawn TobiasNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy Villapando Ivan Concept MapDocument8 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Villapando Ivan Concept MapIvan VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Managing Urinary Incontinence in Older PeopleDocument5 pagesManaging Urinary Incontinence in Older PeopleSarah Naura IrbahNo ratings yet
- Triptico ITUDocument2 pagesTriptico ITUClaudi Tperez0% (1)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. NCM 109Document16 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia. NCM 109Niña Jean Tormis AldabaNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesProstate Cancer Nursing Care PlanShakour El seifyNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan - AgeDocument7 pagesNursing-Care-Plan - AgePanda JocyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment, Plan, Interventions & Evaluation for Postpartum ConstipationDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment, Plan, Interventions & Evaluation for Postpartum ConstipationCayla Mae CarlosNo ratings yet
- ConstipationDocument4 pagesConstipationprincess_bee100% (1)
- Constipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BDocument2 pagesConstipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BShafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- ConstipationDocument3 pagesConstipationmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- NCP ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP ConstipationFaith Bingan Remiscal67% (6)
- Discharge Planning and NCP SDocument8 pagesDischarge Planning and NCP SRainier RamosNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Urinary IncontinenceDocument38 pagesGeriatric Urinary IncontinenceStarr NewmanNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Types and Causes of Urinary IncontinenceDocument9 pagesTypes and Causes of Urinary Incontinencehussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Advincula NCP LiverDocument2 pagesAdvincula NCP LiverErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis and Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis and Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: Ma - Alicia Grace S. Kaimo, RN, ManDocument17 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Ma - Alicia Grace S. Kaimo, RN, ManYongNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPbulok netflakesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Constipation and Establishing Normal Bowel FunctionDocument1 pageUnderstanding Constipation and Establishing Normal Bowel FunctionLoverMind CabaronNo ratings yet
- Bowel Incontinence ConstipationDocument3 pagesBowel Incontinence ConstipationMatty-b AskalaniNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument3 pagesCase StudyLouel VicitacionNo ratings yet
- Chronic Constipation: Guest Editor: Bhim S. PandhiDocument5 pagesChronic Constipation: Guest Editor: Bhim S. PandhiAndreea PopescuNo ratings yet
- Ob NCP and Drug StudyDocument3 pagesOb NCP and Drug StudyRomhea MatmyrNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of ConstipationDocument8 pagesEvaluation of ConstipationAndrea GallegoNo ratings yet
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - UTI NCP - NCM 112 Lec PDFDocument3 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - UTI NCP - NCM 112 Lec PDFGen Paulo EstoyaNo ratings yet
- Consti Pati On: Evaluati On and Management: by Bhairvi Jani, MD & Elizabeth Marsicano, MDDocument5 pagesConsti Pati On: Evaluati On and Management: by Bhairvi Jani, MD & Elizabeth Marsicano, MDsavitri geminiNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Failure: Diagnosis, Management and TransplantationFrom EverandIntestinal Failure: Diagnosis, Management and TransplantationAlan LangnasNo ratings yet
- Previous BON Files (Foundation of Professional Nursing Practice)Document16 pagesPrevious BON Files (Foundation of Professional Nursing Practice)Tom Cuenca100% (1)
- Previous BON Files (Leadership, Management, Bioethics and Research)Document11 pagesPrevious BON Files (Leadership, Management, Bioethics and Research)Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Previous BON Files (MCHN)Document13 pagesPrevious BON Files (MCHN)Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Tiktok Pilit-PilitDocument1 pageTiktok Pilit-PilitTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Previous BON Files (Community Health Nursing)Document10 pagesPrevious BON Files (Community Health Nursing)Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Daily Objectives KyangDocument1 pageDay 1 Daily Objectives KyangTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- HEALTH CARE ETHICS MIDTERMS TELEOLOGICAL ETHICSDocument1 pageHEALTH CARE ETHICS MIDTERMS TELEOLOGICAL ETHICSTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (HCE) Prelims Trans 4Document1 page(HCE) Prelims Trans 4Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Previous BON Files (Medical-Surgical Nursing)Document14 pagesPrevious BON Files (Medical-Surgical Nursing)Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Extra Major PageDocument2 pagesExtra Major PageTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (GN) Introduction To AgingDocument3 pages(GN) Introduction To AgingTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Extra Minor PageDocument2 pagesExtra Minor PageTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (CUENCA) Reliability Analysis InterpretationDocument1 page(CUENCA) Reliability Analysis InterpretationTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (GN) (Cuenca) E-ProjectDocument12 pages(GN) (Cuenca) E-ProjectTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Prioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument5 pagesPrioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (CUENCA) Connecting The Lines...Document2 pages(CUENCA) Connecting The Lines...Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Endorsement of Aling Anna Day 6Document1 pageEndorsement of Aling Anna Day 6Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Prioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument5 pagesPrioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Neck Cancer PhysiosynthesisDocument1 pageNeck Cancer PhysiosynthesisTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument4 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (CUENCA) Assessing Qualitative Data (Elaborate)Document1 page(CUENCA) Assessing Qualitative Data (Elaborate)Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Mang Raul Case StudyDocument3 pagesMang Raul Case StudyTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Disturbances in Ileostomy PatientsDocument1 pageElectrolyte Disturbances in Ileostomy PatientsTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- ALING MARITES CASE STUDY: HYDRATION AND BLOOD TRANSFUSIONDocument4 pagesALING MARITES CASE STUDY: HYDRATION AND BLOOD TRANSFUSIONTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Team 1A: Alaba, Bagares, Bonghanoy, Cuenca, Goma, Rosales: Holy Roman EmpireDocument1 pageTeam 1A: Alaba, Bagares, Bonghanoy, Cuenca, Goma, Rosales: Holy Roman EmpireTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Endorsement of Aling AnnaDocument2 pagesEndorsement of Aling AnnaTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (Prelims Trans 1) Historical Antecedents of Science and TechnologyDocument3 pages(Prelims Trans 1) Historical Antecedents of Science and TechnologyTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Timeline Page 1Document1 pageTimeline Page 1Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- MDG 2015 Rev (July 1)Document75 pagesMDG 2015 Rev (July 1)yensyNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis 1Document4 pagesCase Analysis 1Anne Caryl Cabral AfableNo ratings yet
- External Otitis TreatmentDocument28 pagesExternal Otitis TreatmentGuardito PequeñoNo ratings yet
- Chair-Side Generated Posterior Lithium Disilicate CrownsDocument10 pagesChair-Side Generated Posterior Lithium Disilicate CrownsNelson BarakatNo ratings yet
- Bacterial STIs: Gonorrhoea, Chlamydia & SyphilisDocument77 pagesBacterial STIs: Gonorrhoea, Chlamydia & SyphilisJohir ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Dr.B.R. Ambedkar Medical CollegeDocument1 pageDr.B.R. Ambedkar Medical CollegeRakeshKumar1987No ratings yet
- OphthalmologyDocument15 pagesOphthalmologyAnusha VaranasiNo ratings yet
- Derm Quiz True/False: Venous Ulcers, Arterial Ulcers, Neuropathic Ulcers, and DermatomyositisDocument7 pagesDerm Quiz True/False: Venous Ulcers, Arterial Ulcers, Neuropathic Ulcers, and DermatomyositisOccamsRazorNo ratings yet
- IVT RenewalDocument3 pagesIVT RenewalHarbyNo ratings yet
- JHA Risk Assesment 1Document6 pagesJHA Risk Assesment 1leonardo GaraisNo ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDocument4 pagesReflection PaperMary Lyn BesmonteNo ratings yet
- CAB ManagementDocument21 pagesCAB ManagementTery'sNo ratings yet
- The 7 Principles of Naturopathic MedicineDocument7 pagesThe 7 Principles of Naturopathic MedicineBiol. Miguel Angel Gutiérrez Domínguez0% (1)
- Bahasa Inggris SOALDocument20 pagesBahasa Inggris SOALAyu Nita PangestuNo ratings yet
- Convulsion Neo Flujograma 11 NicusDocument8 pagesConvulsion Neo Flujograma 11 NicusYolanda RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Week 13 CD COURSE TASK 7. Dengue Fever, Filariasis, Malaria and EncephalitisDocument5 pagesWeek 13 CD COURSE TASK 7. Dengue Fever, Filariasis, Malaria and EncephalitisRogelyn PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Tentative CML 2017 - Not Updated - 02.01.2018Document870 pagesTentative CML 2017 - Not Updated - 02.01.2018drgnans36% (11)
- Health Services and Delivery ResearchDocument152 pagesHealth Services and Delivery ResearchThierry UhawenimanaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Safety Climate and Workplace Violence Among Primary Healthcare Workers in MalaysiaDocument10 pagesOrganizational Safety Climate and Workplace Violence Among Primary Healthcare Workers in MalaysiaIJPHSNo ratings yet
- What Is The Importance of Demodex Folliculorum in Behcet DiseaseDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Importance of Demodex Folliculorum in Behcet DiseaseRoxana SurliuNo ratings yet
- PDS Benefit Overview - Dentist 2019Document4 pagesPDS Benefit Overview - Dentist 2019jentotheskyNo ratings yet
- Ante - Natal Case ProformaDocument4 pagesAnte - Natal Case Proformakavya sriNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Structure 2020Document10 pagesLaboratory Structure 2020kaseera musaNo ratings yet
- EFNS Guideline - Mild Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument8 pagesEFNS Guideline - Mild Traumatic Brain InjuryAnce NdapaoleNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Disease in PregnancyDocument24 pagesCardiac Disease in PregnancyJoshua Kingsley OkechiNo ratings yet
- Types and causes of common sleep disordersDocument2 pagesTypes and causes of common sleep disordersnics comiaNo ratings yet