Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippines
Uploaded by
Tom Cuenca0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Patient F NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views5 pagesPrioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippines
Uploaded by
Tom CuencaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
FATHER SATURNINO URIOS UNIVERSITY
San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippines
Nursing Program
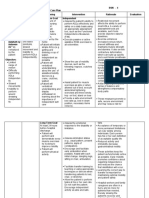
PRIORITIZATION OF PROBLEMS
Rank Problem Identified
1 Impaired physical mobility related to cognitive impairment
secondary to subacute sclerosing panencephalitis as evidenced by
limited range of motion
2 Disturbed (Altered) thought process related to changes in the
level of consciousness as evidenced by cognitive deficits
3 Self-care deficit related to the inability to perform activities of daily
living as evidenced by impaired motor functions
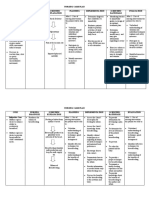
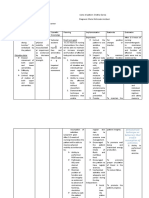
NURSING CARE PLAN #1
By A.T., Cuenca, FSUU, SN
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation
Subjective data: Impaired Within 8 hours of nursing INDEPENDENT After 8 hours of nursing
No statements were physical intervention, the patient will 1. Check for functional level of - Understanding the particular level, intervention, the patient
verbalized by the mobility be able to: mobility. guides the design of best possible was able to:
patient. related to management plan.
cognitive • Maintain position of 2. Assess for impediments to - Identifying barriers to mobility (e.g., • Maintain position of
Objective data: impairment function and skin mobility. chronic arthritis versus stroke versus function and skin
• Inability to secondary to integrity as evidenced pain) guides design of an optimal integrity as evidenced
perform activities subacute by absence of treatment plan. by absence of
of daily living sclerosing contractures, footdrop, 3. Assess the strength to perform - This assessment provides data on contractures, footdrop,
independently panencephalitis decubitus, etc. ROM to all joints. extent of any physical problems and decubitus, etc.
• Loss of motor as evidenced • Demonstrate guides therapy. Testing by a physical • Demonstrate
function by paralysis techniques and therapist may be needed. techniques and
• Limited range of and limited behaviors that enable 4. Assess input and output record - Pressure ulcers build up more behaviors that enable
motion range of motion safe repositioning and and nutritional pattern and monitor rapidly in patients with a nutritional safe repositioning and
• Cognitive safety measures to nutritional needs as they relate to insufficiency. Good nutrition also safety measures to
impairment minimize potential for immobility. gives required energy for minimize potential for
• Past health injury participating in an exercise or injury
history of rehabilitative activities.
measles at 11 5. Evaluate the need for assistive - Correct utilization of wheelchairs, Goal met.
months of age devices. canes, transfer bars, and other November 11, 2021
assistance can enhance activity and 9:45 AM
No vital signs data lessen the danger of falls.
were recorded 6. Assist patient for muscle - Adds to gaining enhanced sense of
exercises as able or when allowed balance and strengthens
out of bed; execute abdominal- compensatory body parts.
tightening exercises and knee A.T., Cuenca, FSUU, SN
bends; hop on foot; stand on toes.
7. Present a safe environment: bed - These measures promote a safe,
rails up, bed in a down position, secure environment and may reduce
important items close by. risk for falls.
8. Show the use of mobility devices, - These devices can compensate for
such as the following: trapeze, impaired function and enhance level
crutches, or walkers. of activity. The goals of using such
aids are to promote safety, enhance
mobility, avoid falls, and conserve
energy.
9. Keep limbs in functional - This avoids footdrop and too much
alignment with one or more of the plantar flexion or tightness. Maintain
following: pillows, sandbags, feet in dorsiflexed position.
wedges, or prefabricated splints.
10. Set goals with patient or - This enhances sense of anticipation
Significant Other for cooperation in of progress or improvement and
activities or exercise and position gives some sense of control or
changes. independence.
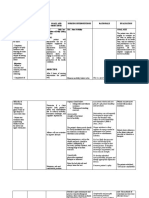
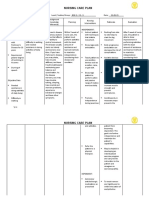
NURSING CARE PLAN #2
By A.T., Cuenca, FSUU, SN
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation
Subjective data: Disturbed Within 8 hours of nursing INDEPENDENT After 8 hours of nursing
No statements were (Altered) intervention, the patient will 1. Identify factors present - Identifying factors present is intervention, the patient
verbalized by the thought be able to: [acute/chronic brain syndrome important to know the was able to:
patient. process (recent stroke, Alzheimer’s causative/contributing factors.
related to • Maintain reality disease), brain injury or increased • Maintain reality
Objective data: changes in the orientation and intracranial pressure, anoxic event, orientation and
• Inability to level of communicate clearly acute infections, malnutrition, sleep communicate clearly
perform activities consciousness with others or sensory deprivation, chronic with others
of daily living as evidenced • Interacts and mental illness (schizophrenia)]. • Interacts and
independently by cognitive cooperates with staff in 2. Review laboratory values for - Monitoring laboratory values aids in cooperates with staff in
• Loss of motor deficits the hospital setting abnormalities such as metabolic identifying contributing factors. the hospital setting
function alkalosis, hypokalemia, anemia,
• Limited range of elevated ammonia levels, and signs Goal met.
motion of infection. November 11, 2021
• Cognitive 3. Interview SO or caregiver to - This is to provide baseline for 11:20 AM
impairment determine patient’s usual thinking comparison.
• Past health ability, changes in behavior, length
history of of time problem has existed, and
measles at 11 other pertinent information.
months of age 4. Perform periodic - Early recognition of changes A.T., Cuenca, FSUU, SN
neurological/behavioral promotes proactive modifications to
No vital signs data assessments, as indicated, and plan of care.
were recorded compare with baseline. - Cognition/thinking often improves
5. Assist with treatment for with treatment/correction of
underlying problems, such as medical/psychiatric problems.
anorexia, brain injury/increased
intracranial pressure, sleep
disorders, biochemical imbalances.
6. Provide safety measures (e.g., - It is always necessary to consider
side rails, padding, as necessary; the safety of the patient.
close supervision, seizure
precautions), as indicated.
7. Maintain a pleasant and quiet - Patient may respond with anxious
environment and approach patient or aggressive behaviors if startled or
in a slow and calm manner. overstimulated.
8. Reduce provocative stimuli, - This is to avoid triggering fight/flight
negative criticism, arguments, and responses.
confrontations.
9. Schedule structured activity and - This provides stimulation while
rest periods. reducing fatigue.
10. Provide nutritionally well- - These enhance intake and general
balanced diet, incorporating well-being.
patient’s preferences as able.
Encourage patient to eat. Provide
pleasant environment and allow
sufficient time to eat.
You might also like
- Brain Breakthrough: The Art of Neurological Rehabilitation: Easy and Innovative Techniques, #1From EverandBrain Breakthrough: The Art of Neurological Rehabilitation: Easy and Innovative Techniques, #1No ratings yet
- Case IcuDocument5 pagesCase IcuTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- NCP - PoliomyelitisDocument4 pagesNCP - PoliomyelitisCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan TophiDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan TophiAndrea Isabel U. O'DellNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDeanne Carla DalilisNo ratings yet
- Nag Lilinis NG Sugat Ko, Hindi Ko Kasi Kaya. Mahina Kasi Kalahati NG Katawan Ko" AsDocument4 pagesNag Lilinis NG Sugat Ko, Hindi Ko Kasi Kaya. Mahina Kasi Kalahati NG Katawan Ko" AsNursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Care of Elderly - NCP1Document2 pagesCare of Elderly - NCP1ROGEN KATE AZARCONNo ratings yet
- Rabanal, Lovely Jane A. Bsn-Ii Benner MCN Final Exam Case 2Document3 pagesRabanal, Lovely Jane A. Bsn-Ii Benner MCN Final Exam Case 2mark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Hip DysplasiaDocument4 pagesNCP - Hip DysplasiaCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature: Motor Vehicle AccidentDocument8 pagesReview of Related Literature: Motor Vehicle AccidentJ. TSNo ratings yet
- NCP - OsteoporosisDocument4 pagesNCP - OsteoporosisCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Geria NCP, Dela CruzDocument7 pagesGeria NCP, Dela CruzStephany Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalGeralyn KaeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cues24 PAULINO ALDRIN MUJARNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: This Is A Good Tool For TheDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: This Is A Good Tool For TheAvery SandsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsChristine Lebico100% (1)
- Subjective Data: Baseline Data of Client.: Reference: Nurse's Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Interventions, and RationalesDocument4 pagesSubjective Data: Baseline Data of Client.: Reference: Nurse's Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Interventions, and RationalesJor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: "Maglisod Man Kog Short Term: Independent: - Establish RapportDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: "Maglisod Man Kog Short Term: Independent: - Establish RapportSergi Lee OrateNo ratings yet
- III. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Intervention EvaluationDocument4 pagesIII. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Intervention EvaluationSTEPHANIE JOSUENo ratings yet
- NCP Case PresDocument5 pagesNCP Case Pressyd19No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Hip Fracture Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For Hip Fracture Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentAce Khiel PeraltaNo ratings yet
- NCP PagetsDocument6 pagesNCP PagetsDarla JoyceNo ratings yet
- NCP (BD)Document5 pagesNCP (BD)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- Spinal Bifida Ncp-Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesSpinal Bifida Ncp-Impaired Physical MobilityNicole cuencos50% (2)
- NCP ImmobilityDocument1 pageNCP ImmobilityBcoi QuilacioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalkuroroexileNo ratings yet
- NCP For Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesNCP For Impaired Physical MobilityPrincess Averin Navarro50% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument15 pagesNursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationEina TandincoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goal Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Impaired Physical Mobility Related ToDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goal Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Impaired Physical Mobility Related ToMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesMultiple Sclerosis Nursing Care PlanCHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- Subjective: The PatientDocument2 pagesSubjective: The PatientRoscoe ParaanNo ratings yet
- Day 3 Activity: Nursing Care Plan: College of Health SciencesDocument6 pagesDay 3 Activity: Nursing Care Plan: College of Health SciencesAngelica Charisse BuliganNo ratings yet
- NCP of Impaired MobilityDocument3 pagesNCP of Impaired MobilityHazel Cabrera0% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMa Virginia Nathalia CreerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKatrene Lequigan100% (1)
- CACHO NCP NeuromuscularDocument3 pagesCACHO NCP NeuromuscularJaymee CachoNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke NCPDocument11 pagesIschemic Stroke NCPJohannah DaroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument18 pagesNursing Care PlanElla Grace PradoNo ratings yet
- NCP OrthoDocument1 pageNCP Orthoroger0% (1)
- Compre Notes!!!!!!!!!!!Document12 pagesCompre Notes!!!!!!!!!!!Cyenel DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Surgical, Indiv Patient)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan (Surgical, Indiv Patient)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For StrokeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Strokerusseldabon24No ratings yet
- Names: MANIRAHO Cyprien Reg. Numbers: 020/04/GN/933 Individual AssignimentDocument70 pagesNames: MANIRAHO Cyprien Reg. Numbers: 020/04/GN/933 Individual AssignimentCyprien Silencer ManirahoNo ratings yet
- Assess Ment Nursing Diagnos IS Plannin G Nursing Interve Ntion Rationa LE Evaluat IONDocument2 pagesAssess Ment Nursing Diagnos IS Plannin G Nursing Interve Ntion Rationa LE Evaluat IONStephany Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Dementia NCPDocument2 pagesDementia NCPkaloydiaz09No ratings yet
- ABUEVA GULFAN NCP 1 Primary AldosteronismDocument2 pagesABUEVA GULFAN NCP 1 Primary AldosteronismAmy Rose AbuevaNo ratings yet
- NCP Formulation (Older Adult)Document3 pagesNCP Formulation (Older Adult)maria khalifa0% (1)
- FHP & NCP - FractureDocument14 pagesFHP & NCP - FractureFrancis AdrianNo ratings yet
- Hindlimb Stretching Alters Locomotor Function After Spinal Cord Injury in The Adult RatDocument10 pagesHindlimb Stretching Alters Locomotor Function After Spinal Cord Injury in The Adult RatRafliNo ratings yet
- 2018 5 Practiacs para El Abordaje Muscuesqueletico GeneralDocument2 pages2018 5 Practiacs para El Abordaje Muscuesqueletico GeneralNahuel GomezNo ratings yet
- Cva NCP 1Document3 pagesCva NCP 1MarcieNo ratings yet
- Dialysis NCPDocument2 pagesDialysis NCPJennifer AlamonNo ratings yet
- Length Tension Testing Book 1, Lower Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesFrom EverandLength Tension Testing Book 1, Lower Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Previous BON Files (MCHN)Document13 pagesPrevious BON Files (MCHN)Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Previous BON Files (Community Health Nursing)Document10 pagesPrevious BON Files (Community Health Nursing)Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Extra Minor PageDocument2 pagesExtra Minor PageTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Previous BON Files (Foundation of Professional Nursing Practice)Document16 pagesPrevious BON Files (Foundation of Professional Nursing Practice)Tom Cuenca100% (1)
- Day 1 Daily Objectives KyangDocument1 pageDay 1 Daily Objectives KyangTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Previous BON Files (Leadership, Management, Bioethics and Research)Document11 pagesPrevious BON Files (Leadership, Management, Bioethics and Research)Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Tiktok Pilit-PilitDocument1 pageTiktok Pilit-PilitTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Previous BON Files (Medical-Surgical Nursing)Document14 pagesPrevious BON Files (Medical-Surgical Nursing)Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (HCE) Prelims Trans 4Document1 page(HCE) Prelims Trans 4Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (GN) (Cuenca) E-ProjectDocument12 pages(GN) (Cuenca) E-ProjectTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Extra Major PageDocument2 pagesExtra Major PageTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (CUENCA) Assessing Qualitative Data (Elaborate)Document1 page(CUENCA) Assessing Qualitative Data (Elaborate)Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (HCE) Prelims Trans 5Document1 page(HCE) Prelims Trans 5Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Prioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument5 pagesPrioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (GN) Introduction To AgingDocument3 pages(GN) Introduction To AgingTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Prioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument5 pagesPrioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument4 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (Prelims Trans 1) Historical Antecedents of Science and TechnologyDocument3 pages(Prelims Trans 1) Historical Antecedents of Science and TechnologyTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Endorsement of Aling Anna Day 6Document1 pageEndorsement of Aling Anna Day 6Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (CUENCA) Connecting The Lines...Document2 pages(CUENCA) Connecting The Lines...Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- (CUENCA) Reliability Analysis InterpretationDocument1 page(CUENCA) Reliability Analysis InterpretationTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Neck Cancer PhysiosynthesisDocument1 pageNeck Cancer PhysiosynthesisTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Research: EBR #1 Name: April Tom O. CuencaDocument1 pageEvidence Based Research: EBR #1 Name: April Tom O. CuencaTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Endorsement of Aling AnnaDocument2 pagesEndorsement of Aling AnnaTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- MDG 2015 Rev (July 1)Document75 pagesMDG 2015 Rev (July 1)yensyNo ratings yet
- Timeline Page 1Document1 pageTimeline Page 1Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Mang Raul Case StudyDocument3 pagesMang Raul Case StudyTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Aling Marites Case Study:: Endorsement ForDocument4 pagesAling Marites Case Study:: Endorsement ForTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Team 1A: Alaba, Bagares, Bonghanoy, Cuenca, Goma, Rosales: Holy Roman EmpireDocument1 pageTeam 1A: Alaba, Bagares, Bonghanoy, Cuenca, Goma, Rosales: Holy Roman EmpireTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Lesson 1Document4 pagesModule 3 Lesson 1Rickie Marx RonamoNo ratings yet
- The Leadership Effectiveness and Adaptability Descriptor Tool AnalysisDocument4 pagesThe Leadership Effectiveness and Adaptability Descriptor Tool Analysisashlesha_ganatra100% (8)
- Diarrhea New Edited 2Document82 pagesDiarrhea New Edited 2bharathNo ratings yet
- Survey Method Statement For Construction Under PASSDocument28 pagesSurvey Method Statement For Construction Under PASSMustakim AnsaryNo ratings yet
- Youth Camp Registration Form-2022Document1 pageYouth Camp Registration Form-2022FlerkNo ratings yet
- Lead Better, Start Younger: The Course DescriptionDocument4 pagesLead Better, Start Younger: The Course DescriptionBfp Rsix Maasin FireStationNo ratings yet
- Tanishqa Jogani - TAPMIDocument3 pagesTanishqa Jogani - TAPMITanishqa JoganiNo ratings yet
- CS Form No - 6, Revised 2020 (Application For Leave) (Fillable) - 1Document3 pagesCS Form No - 6, Revised 2020 (Application For Leave) (Fillable) - 1ben carlo ramos srNo ratings yet
- Personal Development: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Persons and Careers (Career Basic Concepts)Document3 pagesPersonal Development: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Persons and Careers (Career Basic Concepts)Lovely Joy ValdezNo ratings yet
- Denatured Fuel Ethanol: Material Safety Data SheetDocument14 pagesDenatured Fuel Ethanol: Material Safety Data SheetElder Andrades MartinezNo ratings yet
- Siddha Dossier CCRS Chennai 1Document104 pagesSiddha Dossier CCRS Chennai 1Dr.kali.vijay kumkar100% (1)
- Portfolio in Gender and Society: Jennifer D. RoseteDocument7 pagesPortfolio in Gender and Society: Jennifer D. RoseteDmzjmb SaadNo ratings yet
- Andreas Tigor 22010112130144 Lap Kti Bab7Document19 pagesAndreas Tigor 22010112130144 Lap Kti Bab7Zia NajlaNo ratings yet
- Red Cross CPR Guidelines PDFDocument31 pagesRed Cross CPR Guidelines PDFandrewh3No ratings yet
- Tenants Pathology-Update Uploads 329 SEBASTIAN Roche ePoster+FINALDocument1 pageTenants Pathology-Update Uploads 329 SEBASTIAN Roche ePoster+FINALsanderssebastianNo ratings yet
- Al-Okshi Et Al 2019Document9 pagesAl-Okshi Et Al 2019Ayman AlOkshiNo ratings yet
- Continuing Education Certificate: ACLS Instructor UpdateDocument1 pageContinuing Education Certificate: ACLS Instructor UpdateJorgeSolórzanoNo ratings yet
- Memorix Anatomy 2Document1 pageMemorix Anatomy 2Sreedhar Tirunagari100% (1)
- Neonatal and Pediatric Mechanical Ventilation - 2020Document88 pagesNeonatal and Pediatric Mechanical Ventilation - 2020Ahmed YasserNo ratings yet
- Managing School OperationsDocument15 pagesManaging School OperationsAmberShanty TalerNo ratings yet
- QA On Conformity Assessment Procedures For PPE and MD - v2.0 - 10 July 2020Document9 pagesQA On Conformity Assessment Procedures For PPE and MD - v2.0 - 10 July 2020flojanas3858No ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument214 pagesCombinepdfAl Ther JumadilNo ratings yet
- MicroSilver BG PDFDocument16 pagesMicroSilver BG PDFBoblea LaviniaNo ratings yet
- Nyvad 1999Document9 pagesNyvad 1999Felipe Maldonado ArayaNo ratings yet
- Informative Speech TextDocument2 pagesInformative Speech TextadzwinjNo ratings yet
- CV Dr. ErwadiDocument3 pagesCV Dr. ErwadiErwadi ErwadiNo ratings yet
- (Template) BEED CHAPTER 3 MODULE 3 - Sci 1Document6 pages(Template) BEED CHAPTER 3 MODULE 3 - Sci 1Regilyn GalasNo ratings yet
- P6022MAB.000.51S.085 - Confined Space EntryDocument34 pagesP6022MAB.000.51S.085 - Confined Space EntrybabjihanumanthuNo ratings yet
- Sysmex XW - 100: Instructions For Use ManualDocument32 pagesSysmex XW - 100: Instructions For Use ManualNahom BalchaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Assignment SolutionDocument8 pagesBiotechnology Assignment SolutionPiyush RajNo ratings yet