Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differents Encoding Techniques: 1. Analog Data To Analog Signals
Uploaded by
maximo gabilan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThe document discusses four different encoding techniques: 1) Analog data to analog signals which is how analog copiers work, 2) Analog data to digital signals which makes digital transmission of information more reliable than analog, 3) Digital data to analog signals which is how digital audio can be transmitted over phone lines, and 4) Digital data to digital signals known as digital-to-digital encoding which is how computers transmit binary data as voltage pulses over wires such as in pulse amplitude modulation.
Original Description:
wertvertycryy
Original Title
ertaewrtc3r
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses four different encoding techniques: 1) Analog data to analog signals which is how analog copiers work, 2) Analog data to digital signals which makes digital transmission of information more reliable than analog, 3) Digital data to analog signals which is how digital audio can be transmitted over phone lines, and 4) Digital data to digital signals known as digital-to-digital encoding which is how computers transmit binary data as voltage pulses over wires such as in pulse amplitude modulation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageDifferents Encoding Techniques: 1. Analog Data To Analog Signals
Uploaded by
maximo gabilanThe document discusses four different encoding techniques: 1) Analog data to analog signals which is how analog copiers work, 2) Analog data to digital signals which makes digital transmission of information more reliable than analog, 3) Digital data to analog signals which is how digital audio can be transmitted over phone lines, and 4) Digital data to digital signals known as digital-to-digital encoding which is how computers transmit binary data as voltage pulses over wires such as in pulse amplitude modulation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
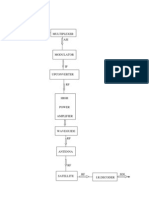
Differents encoding techniques
1. Analog data to analog signals- is the analog signal's representation
of analog information. It is a procedure in which the carrier wave's
characteristic is changed in response to the modulating signal's
instantaneous amplitude.
My example is photocopier because the fine powder in the toner is
attracted to a sheet of paper that is likewise charged with static electricity.
When the small toner dust particles roll off the drum, they fuse to the
paper. The final product is then pushed out by the copier.
2. Analog data to digital signal- is an electrical procedure that converts
a continuously variable (analog) signal into a multi-level (digital) signal
without changing its basic content.
My example is computer because Digital computers are a more reliable
form of transmitting information because an error in the amplitude or
frequency value would have to be very large in order to cause a jump to a
different value.
3. Digital data to analog signal- The process of converting digital
signals which contain a binary state to analog signals is known as digital-
to-analog conversion DAC, which theoretically have an infinite number of
states.
For example, turns digital computer data into analog audio-frequency
signals that may be sent via telephone lines.
4. Digital data to digital signal- is known as digital-to-digital encoding.
The process of converting binary 1s and 0s created by a computer into a
sequence of voltage pulses that can be transmitted across a wire is known
as digital-to-digital encoding.
For example is pulse train, a pulse amplitude modulated signal, a
sequence of fixed-width square wave electrical pulses or light pulses, each
occupying one of a discrete number of levels of amplitude.
You might also like
- IT2004 - Introduction To Data Communication & NetworksDocument73 pagesIT2004 - Introduction To Data Communication & NetworksRamya AththanayakeNo ratings yet
- C2 FC Stud AUG31 Sept2Document12 pagesC2 FC Stud AUG31 Sept2Ravi RoshanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 NotesDocument25 pagesUNIT 3 NotesmansiNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks - Mod1Document29 pagesComputer Networks - Mod1Gitto George ThomasNo ratings yet
- EI Assignment 1 PDFDocument6 pagesEI Assignment 1 PDFFirozNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Analogue N Digital SignalsDocument40 pagesPresentation On Analogue N Digital SignalsnancykapoorNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & Computer Networks: Week # 05Document41 pagesData Communication & Computer Networks: Week # 05mr nNo ratings yet
- Presented by Omkar TendulkarDocument12 pagesPresented by Omkar TendulkarOmkar TendulkarNo ratings yet
- Final Analog Vs DigitalDocument15 pagesFinal Analog Vs DigitalPuri AshutoshNo ratings yet
- A Level PracticeDocument2 pagesA Level PracticeRakotoarison Louis FrederickNo ratings yet
- Internet WorkingDocument4 pagesInternet Workinglin_guardianangelNo ratings yet
- 1 Lesson2 DigitalCommunicationDocument10 pages1 Lesson2 DigitalCommunicationQhadija JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Communications 2: Modulation and Coding TechniquesDocument9 pagesCommunications 2: Modulation and Coding Techniquesbecy welbaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No9Document15 pagesAssignment No9Nadia BatoolNo ratings yet
- SDI ASI Encoder MultiplexerDocument41 pagesSDI ASI Encoder MultiplexerChristie MillerNo ratings yet
- Digital CircuitsDocument44 pagesDigital CircuitssjbloomsNo ratings yet
- Unit1-Chapter1 - CS-2-uddar SirDocument147 pagesUnit1-Chapter1 - CS-2-uddar SirRaghu BNo ratings yet
- TelecommunicationsDocument31 pagesTelecommunicationstuhafenijason05No ratings yet
- An Analogue Signal Uses Some Attribute of The Medium To Convey The SignalDocument3 pagesAn Analogue Signal Uses Some Attribute of The Medium To Convey The SignalJoyce BuelaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 - Introduction To Digital ElectronicsDocument25 pagesUnit - 1 - Introduction To Digital ElectronicsAvinash SharmaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Digital CommunicationDocument14 pagesUNIT 5 Digital CommunicationSunithaNo ratings yet
- Mixed Signals and SensorsDocument27 pagesMixed Signals and SensorsT ENGANo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital SignalsDocument2 pagesAnalog and Digital SignalsMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication PPT Aditya BaraskarDocument8 pagesDigital Communication PPT Aditya Baraskar6163 Tharun pNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document7 pagesPresentation 1Ira FitriyaniNo ratings yet
- Digital and Analog Signals: Figure 1a: Analog SignalDocument3 pagesDigital and Analog Signals: Figure 1a: Analog Signaljomabi1753No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 1 Physical LayerDocument30 pagesChapter 3 - 1 Physical Layerhenok metaferiaNo ratings yet
- Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM) Is A Method Used ToDocument8 pagesPulse-Code Modulation (PCM) Is A Method Used ToMwesigye KennethNo ratings yet
- DC CheatsheetDocument2 pagesDC CheatsheetRashi SinghNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument8 pagesPPTMD IshakNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Sonal HarshNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication - Quick GuideDocument72 pagesDigital Communication - Quick GuideVIKASH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Comms ReviewerDocument124 pagesComms Reviewergelai 2No ratings yet
- 1.fundamental Concepts of Digital Communications - Part1of2Document136 pages1.fundamental Concepts of Digital Communications - Part1of2Gianne ObusanNo ratings yet
- Analog-to-Digital-Convesion v2 - StudentDocument43 pagesAnalog-to-Digital-Convesion v2 - StudentJysh MamusogNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication - Analog To DigitalDocument4 pagesDigital Communication - Analog To DigitalDilip PanchalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemDheeraj RajNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Baseband ModulationDocument65 pagesSampling and Baseband ModulationAbdul Qawi AnsariNo ratings yet
- Multimedia PresentationDocument16 pagesMultimedia PresentationHusain PoonawalaNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document42 pagesCH 08engaydiNo ratings yet
- Ca2 Ec503Document7 pagesCa2 Ec503amit BeraNo ratings yet
- CS6304 PDFDocument155 pagesCS6304 PDFßharath SparkyNo ratings yet
- Analogue vs. Digital: Nicole Sánchez Figueroa 3° Bac. DDocument16 pagesAnalogue vs. Digital: Nicole Sánchez Figueroa 3° Bac. DNicole Sanchez FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocument17 pagesAnalog and Digital CommunicationeceelectroNo ratings yet
- 1-Digital Comm.Document15 pages1-Digital Comm.عقيل سعدNo ratings yet
- 2020 Seo Analog Signals Vs Digital Signals - r1.0Document7 pages2020 Seo Analog Signals Vs Digital Signals - r1.0PeterNo ratings yet
- DDC ReviewerDocument15 pagesDDC ReviewerKimmy WadeNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital SystemDocument13 pagesAnalog and Digital SystemBorse RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Data TransmissionDocument13 pagesChapter I Data TransmissionMohamedLashabNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConversionDocument37 pagesAnalog To Digital ConversionSharanya VaidyanathNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication - Prelim ReviewerDocument13 pagesDigital Communication - Prelim ReviewerXexa Red0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To CommDocument32 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To CommhaftamunigusNo ratings yet
- Signals Carried Over The NetworkDocument15 pagesSignals Carried Over The NetworkAgma Tinoe MauludyNo ratings yet
- Data Acquisition SystemDocument14 pagesData Acquisition SystemAditi Saha33% (3)
- CHAPTER 7 Digital Communications TechniquesDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 7 Digital Communications TechniquesPatrick GarciaNo ratings yet
- Power Point Presentation On (Topic: Methods of Signal Conversion) Presented byDocument10 pagesPower Point Presentation On (Topic: Methods of Signal Conversion) Presented bySUBHAJIT DHARANo ratings yet
- DCNotes PDFDocument75 pagesDCNotes PDFUttam ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)