Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7.05 - Total Internal Reflection
Uploaded by
...0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views5 pagesThe document defines critical angle and total internal reflection, explaining that total internal reflection occurs when light travels from an optically dense medium to a less dense one at an angle greater than the critical angle. It provides examples of total internal reflection in reflecting prisms and optical fibers, noting their uses include high-speed telecommunication and various medical applications like endoscopes.
Original Description:
Original Title
7.05 - Total internal reflection
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines critical angle and total internal reflection, explaining that total internal reflection occurs when light travels from an optically dense medium to a less dense one at an angle greater than the critical angle. It provides examples of total internal reflection in reflecting prisms and optical fibers, noting their uses include high-speed telecommunication and various medical applications like endoscopes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views5 pages7.05 - Total Internal Reflection
Uploaded by
...The document defines critical angle and total internal reflection, explaining that total internal reflection occurs when light travels from an optically dense medium to a less dense one at an angle greater than the critical angle. It provides examples of total internal reflection in reflecting prisms and optical fibers, noting their uses include high-speed telecommunication and various medical applications like endoscopes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
7.
05: Total internal reflection
Textbook: 148 - 149
Objective
Defining: Critical angle & Total internal reflection
Reflecting prisms
Optical fibres
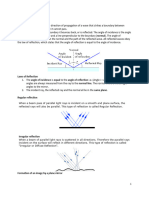
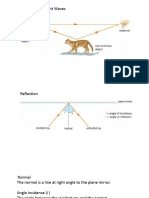
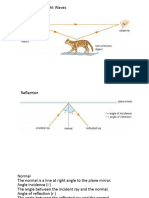
Critical angle:
The angle at which the ray passes along the plane.
The angle of incidence (less dense to more dense) or
angle of refraction (more dense to less dense) is 90°.
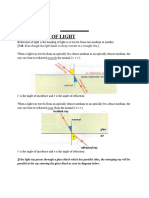
Total internal reflection:
When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, the ray
will get reflected back into the same medium called total internal
reflection.
Total internal reflection occurs due to two reasons,
Angle of incidence should be greater than the
critical angle.
The light ray must travel from more dense to less
dense medium.
Reflecting prisms:
In the below examples, the inside faces of prisms are being used
as mirrors.
Total internal reflection occurs because the angle of incidence on
the face (45°) is greater than the critical angle for glass or acrylic
plastic.
Optical fibres:
Optical fibre are very thin, flexible rods made of special glass or
transparent plastic.
Light out in one end is total internally reflected until it comes out of the
other end.
Uses of total internal reflection
1. Telecommunication: High speed data transfer.
2. In medical fields: Extensive use in medicine (endoscopes, inside-body
flexible cameras)
You might also like
- Total Internal Reflection of LightDocument13 pagesTotal Internal Reflection of LightMadesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Refraction and TIRDocument3 pagesRefraction and TIRsurvival vlogsNo ratings yet
- Total Internal Reflection Meblu Sanand Tom AU1920155Document3 pagesTotal Internal Reflection Meblu Sanand Tom AU1920155YakovNo ratings yet
- Light PUREDocument9 pagesLight PUREtalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- Humara Nam Ravi HaiDocument8 pagesHumara Nam Ravi HaiRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- CH12 PPT 1Document49 pagesCH12 PPT 1kaungforgameNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument26 pagesFiber OpticsAmol DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- WP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2Document11 pagesWP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2matsweamogelang89No ratings yet
- Pusat Tuition Makrifat Chapter 6.2 F.4.PhyDocument6 pagesPusat Tuition Makrifat Chapter 6.2 F.4.PhyBazil BoliaNo ratings yet
- Notes For IGCSE Grade 10 - From 7.04 To 7.09: Refraction of LightDocument9 pagesNotes For IGCSE Grade 10 - From 7.04 To 7.09: Refraction of LightRAMAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- 5.applications of TIRDocument4 pages5.applications of TIRnwvzdpmms6No ratings yet
- What Is Reflection of Light?Document3 pagesWhat Is Reflection of Light?MD: Rabiul Awal ShuvoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Light (1) (1) - 2Document10 pages3.1 Light (1) (1) - 2Dark VariantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Refraction of LightDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Refraction of LightAryan YadavNo ratings yet
- Lec 25Document31 pagesLec 25Tika NuraeniNo ratings yet
- Jashmeet Physics Project File PDF Made by Lallu DadaDocument12 pagesJashmeet Physics Project File PDF Made by Lallu Dadalalit palNo ratings yet
- Phy ADocument20 pagesPhy AShardul Singh 11 S1 DPSKNo ratings yet
- CH12 PPT 1Document49 pagesCH12 PPT 1kaungforgameNo ratings yet
- 53B LIGHT Refraction Total Internal ReflectionDocument20 pages53B LIGHT Refraction Total Internal ReflectionSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument31 pagesOpticsRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic InstrumentsDocument117 pagesOphthalmic Instrumentsmaf manNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Total Internal Reflection. Course Code: PHY 104Document13 pagesPresentation On Total Internal Reflection. Course Code: PHY 104Jesmin ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Total Internal ReflectionDocument15 pagesTotal Internal Reflectionayenjayalmonte7No ratings yet
- Physics Project On Total Internal ReflectionDocument8 pagesPhysics Project On Total Internal Reflectionharnaek singhNo ratings yet
- Nota Light - Total Internal ReflectionDocument26 pagesNota Light - Total Internal ReflectionmaiyaaNo ratings yet
- Note Slide Total Internal ReflectionDocument18 pagesNote Slide Total Internal ReflectionMastura MohamadNo ratings yet
- Project OSCAR: Total Internal ReflectionDocument8 pagesProject OSCAR: Total Internal ReflectionHARSHIT shuklaNo ratings yet
- Ifferent Ariants of Icroscope: DR Uttam Kumar Das PGT-1 Dept of Pathology BSMC BankuraDocument114 pagesIfferent Ariants of Icroscope: DR Uttam Kumar Das PGT-1 Dept of Pathology BSMC BankuraHadi AdamNo ratings yet
- Class 2 PPT 3 Unit 1Document53 pagesClass 2 PPT 3 Unit 1ece Ms.G.BhargaviNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 5: Light: Prepared By: Sharvinder SinghDocument28 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 5: Light: Prepared By: Sharvinder SinghSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics IP ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics IP ProjectHimanshu yadavNo ratings yet
- Ray Theory: by Deepa MathewDocument16 pagesRay Theory: by Deepa MathewDeepa JerinNo ratings yet
- Physic Project 3Document13 pagesPhysic Project 3Jesmin ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibers Module IIIDocument17 pagesOptical Fibers Module IIIRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Light - Free Exam AcademyDocument20 pagesLight - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- Applications of Total Internal ReflectionDocument2 pagesApplications of Total Internal ReflectionAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics: Refraction of LightDocument51 pagesRay Optics: Refraction of LightAbishek ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Physics Tir (Total Internal ReflectionDocument7 pagesPhysics Tir (Total Internal ReflectionHarsheet ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Physics RefractionDocument15 pagesPhysics RefractionFelicity O' MalleyNo ratings yet
- LightDocument17 pagesLightAhmad ZebNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Bright DICDocument24 pagesMicroscopy Bright DICSüzShñtä ÅykpmNo ratings yet
- Slide Micro Teaching 5.3Document18 pagesSlide Micro Teaching 5.3Mastura MohamadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 OFCDocument14 pagesChapter 2 OFCShining StarNo ratings yet
- SA & Pore Analysis - 14 - 17 - 19 Aug 2015Document33 pagesSA & Pore Analysis - 14 - 17 - 19 Aug 2015sharmatanima23No ratings yet
- Ray OpyicsDocument56 pagesRay OpyicsDhruv JainNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticDocument14 pagesFiber Optic080bei010.asmitNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: - An Optic Fiber Consists of A Core That Is Surrounded by A Cladding Which Is NormallyDocument4 pagesExperiment 1: - An Optic Fiber Consists of A Core That Is Surrounded by A Cladding Which Is NormallyAJINKYA PINDAWALANo ratings yet
- OI - Unit 5Document25 pagesOI - Unit 5Krunal ParmarNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument76 pagesFiber OpticsHariom RavatNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument75 pagesFiber OpticsPriya KumariNo ratings yet
- TirDocument3 pagesTircharlottechoiNo ratings yet
- Total Internal Reflection - PhyDocument16 pagesTotal Internal Reflection - PhyRishabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Large Mode AreaDocument37 pagesLarge Mode AreaĐặng Thái NhậtNo ratings yet
- 14 Snells LawDocument8 pages14 Snells Lawapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument11 pagesRay OpticsTatvamasiNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics - 2Document7 pagesRay Optics - 2jiluNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS - PROJECT - FINAL by K BharadwajDocument13 pagesPHYSICS - PROJECT - FINAL by K BharadwajKannuri BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vii Fiber Optics Engineering PhysicsDocument12 pagesUnit - Vii Fiber Optics Engineering PhysicsKallur SandilyaNo ratings yet
- Optic ىلولا ا ةرضاحمل ا: Dr.Hasanain Al ShibanyDocument19 pagesOptic ىلولا ا ةرضاحمل ا: Dr.Hasanain Al ShibanySaif HassanNo ratings yet
- Optigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationFrom EverandOptigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument7 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/23Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/23...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Chemistry 2017 45 MinutesDocument16 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Chemistry 2017 45 Minutes...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: 0625/42 PhysicsDocument24 pagesCambridge International Examinations: 0625/42 Physics...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology For Examination From 2020 1 HourDocument10 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology For Examination From 2020 1 Hour...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62...No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62...No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education...No ratings yet