Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edunxt-The Institute of Learning
Edunxt-The Institute of Learning
Uploaded by
ashh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pages1) The document provides test questions on gas laws and the preparation of hydrogen gas. It includes questions on the reactions of potassium, aluminum, and lead with water or other substances, molecular equations, collection methods for hydrogen, and conditions for producing water gas.
2) It also asks about defining and applying Boyle's law, Charles' law, and relating the Kelvin and Celsius temperature scales. Gas laws are defined as how gases behave in relation to pressure, volume, temperature, and amount.
3) Questions are asked about calculating gas properties based on changes in temperature, pressure, and volume according to the gas laws, such as tripling the volume of a gas with no pressure change or calculating volumes at standard temperature and
Original Description:
Original Title
...
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document provides test questions on gas laws and the preparation of hydrogen gas. It includes questions on the reactions of potassium, aluminum, and lead with water or other substances, molecular equations, collection methods for hydrogen, and conditions for producing water gas.
2) It also asks about defining and applying Boyle's law, Charles' law, and relating the Kelvin and Celsius temperature scales. Gas laws are defined as how gases behave in relation to pressure, volume, temperature, and amount.
3) Questions are asked about calculating gas properties based on changes in temperature, pressure, and volume according to the gas laws, such as tripling the volume of a gas with no pressure change or calculating volumes at standard temperature and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesEdunxt-The Institute of Learning
Edunxt-The Institute of Learning
Uploaded by
ashh1) The document provides test questions on gas laws and the preparation of hydrogen gas. It includes questions on the reactions of potassium, aluminum, and lead with water or other substances, molecular equations, collection methods for hydrogen, and conditions for producing water gas.
2) It also asks about defining and applying Boyle's law, Charles' law, and relating the Kelvin and Celsius temperature scales. Gas laws are defined as how gases behave in relation to pressure, volume, temperature, and amount.
3) Questions are asked about calculating gas properties based on changes in temperature, pressure, and volume according to the gas laws, such as tripling the volume of a gas with no pressure change or calculating volumes at standard temperature and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
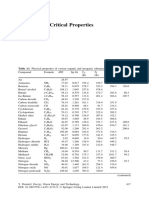
EduNXT-The Institute Of Learning 2021-
22
Test Series - Chemistry –: Hydrogen _Gas Laws
A) Answer the following
a. Write the equation for the following-
1. Potassium with cold water
2. Aluminium with steam
b. Name the element which reacts very vigorously when treated with cold water
c. Write the molecular equation for the following-
1. Lead and sodium hydroxide
2. Magnesium and hydrochloric acid
d. What are the precautions to be taken while collecting the hydrogen gas
e. Name the method used in the collection of hydrogen in lab method.
1. How is hydrogen purified
2. Name the drying agent used to remove moisture from the hydrogen
f. Under what conditions is the water gas produced. Mention its constituents
g. Give the reaction on how the hydrogen gas is liberated from water gas
h. Name the catalysts used in the preparation of hydrogen through bosch process
i. How are the following impurities removed- carbon dioxide and carbon
monoxide from the bosch process
j. How does the hydrogen react when a burning splint is introduced in to the jar
k. What happen when hydrogen is exposed to air
l. “When stating the volume of a gas, the pressure and temperature should
also be given”. Why?
m. Define or state: Boyle’s law
n. Define or state: Charle’s law
o. In Charle’s law, how do we relate Kelvin[absolute} and Celsius scale of
temperature.
p. What are “Gas Laws”? How do we define them?
B) Give reasons for the following:
a. Gas unlike the solids and liquids exert pressure in all directions.
b. Gases have lower densities as compared to solids or liquids
c. All temperatures on the Kelvin scale are in positive figures.
d. Lead cant be used in the preparation of hydrogen.
C) Calculate the following:
EduNXT-The Institute Of Learning 2021-
22
a. Calculate the temperature to which a gas must be heated, so that the
volume triples without any change in pressure. The gas is originally at
57⁰C and having a volume of 150cc.
b. A gas ‘X’ at -33⁰C is heated to 127⁰C at constant pressure. Calculate the %
increase in the volume of the gas.
c. Calculate the volume of a gas ‘A’ at s.t.p., if at 37⁰C and 775 mm of
mercury pressure, it occupies a volume of 9 ½ litres.
d. Calculate the temperature at which a gas ‘A’ at 20⁰C having a volume of
550 cc will occupy a volume of 250 cc.
e. The temperature at which 500cc of a gas ‘X’ at temp. 293K occupies half
its original volume [pressure remaining constant].
f. The volume at s.t.p. occupied by a gas ‘Y’ originally occupying 760 cc at
300K and 70mm pressure of Hg.
You might also like
- Phat (Necro) Ho - 5-00 Gases Unit Pack - 2021Document8 pagesPhat (Necro) Ho - 5-00 Gases Unit Pack - 2021Just an Abnormal SIMPNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 First LawDocument179 pagesChapter 02 First LawWen Hsiao100% (31)
- Comparison Between Trent 1000 and GenxDocument8 pagesComparison Between Trent 1000 and GenxRatnendra Singh100% (1)
- The Leading Edge by Goro Tamai - Complete IndexDocument8 pagesThe Leading Edge by Goro Tamai - Complete IndexBentley PublishersNo ratings yet
- Safe Isolation and Reinsinment of PlantDocument85 pagesSafe Isolation and Reinsinment of PlantPradeep JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Test for Gases答案Document5 pagesTest for Gases答案Mary JewelNo ratings yet
- 4thqrtly Sience10 2017 18Document11 pages4thqrtly Sience10 2017 18gerald100% (1)
- AP Gases WorksheetDocument4 pagesAP Gases Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- 4Q-SCIENCE-10-PT RemedialDocument4 pages4Q-SCIENCE-10-PT RemedialRichard Jay TaalaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Gases Quiz: Name: DIRECTIONS: Read Each Question Carefully and Choose The Best AnswerDocument5 pagesCH 4 - Gases Quiz: Name: DIRECTIONS: Read Each Question Carefully and Choose The Best Answerapi-393155483No ratings yet
- Chemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 1Document6 pagesChemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 1maxime namaNo ratings yet
- Second Term ExaminationDocument5 pagesSecond Term ExaminationAriyo olawaleNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Document3 pagesGas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Nikhil Singh100% (1)
- Fourth Quarter Final Exam G9 and G10Document17 pagesFourth Quarter Final Exam G9 and G10Sylvs EnongNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Worksheet - Matter in Our Surroundings - 1Document2 pagesClass 9 Science Worksheet - Matter in Our Surroundings - 1Sumedha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Tutorial+5-+States of Matter 2022-23Document2 pagesTutorial+5-+States of Matter 2022-23Damz RtgNo ratings yet
- The Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsDocument29 pagesThe Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsabcdefNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam III Chap5-6Document4 pagesPractice Exam III Chap5-6Jovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- 14 ThermochemistryDocument6 pages14 ThermochemistryizabelNo ratings yet
- JH EcampusUpload SubjectNote STUDY of GAS LAWSDocument2 pagesJH EcampusUpload SubjectNote STUDY of GAS LAWSdiamehta1410No ratings yet
- General Chemistry Homework 2015/11/27Document2 pagesGeneral Chemistry Homework 2015/11/27eliotshowNo ratings yet
- Physics Thermodynamics MCQsDocument2 pagesPhysics Thermodynamics MCQsMohammad Umair100% (1)
- Test Ch.10: Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesTest Ch.10: Multiple ChoiceMj LeeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision Assignment 1Document5 pagesChemistry Revision Assignment 1Aditya PandeyNo ratings yet
- GASES Free Response WorksheetDocument4 pagesGASES Free Response WorksheetJJNo ratings yet
- Austrian 25Document13 pagesAustrian 25Vo Tung LamNo ratings yet
- REF 2 SCIENCES EE - Answer KeyDocument4 pagesREF 2 SCIENCES EE - Answer KeyJevan SoberanoNo ratings yet
- The Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsDocument29 pagesThe Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsMinh TieuNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Answer Key ChemDocument5 pagesExam 3 Answer Key Chemalbert jeffersonNo ratings yet
- 24.physical ChemistryDocument15 pages24.physical ChemistryJames BalanaNo ratings yet
- Stem - GC11DL 48 POWERPOINTDocument19 pagesStem - GC11DL 48 POWERPOINTFabeliña GavinNo ratings yet
- Homework 11-AnswersDocument8 pagesHomework 11-AnswersMiranda Murielle Keith CuenoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering-I Part-A QDocument4 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering-I Part-A Qleela2008No ratings yet
- Previous Hse Questions and Answers of The Chapter "States of Matter"Document10 pagesPrevious Hse Questions and Answers of The Chapter "States of Matter"arshaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Fuels and Combustion - NotesDocument19 pagesModule 6 - Fuels and Combustion - NotesFalguni IyerNo ratings yet
- Previous Hse Questions and Answers of The Chapter "States of Matter"Document12 pagesPrevious Hse Questions and Answers of The Chapter "States of Matter"3093 Ayoob NNo ratings yet
- I. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Blacken The Letter of The Correct Answer On A Separate Answer Sheet ProvidedDocument3 pagesI. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Blacken The Letter of The Correct Answer On A Separate Answer Sheet ProvidedMJ LizadaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledAbyssNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Sample Paper-05: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 12Document12 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Sample Paper-05: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 12WE ARE CRaZyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9Document3 pagesWorksheet - Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9Random AccNo ratings yet
- Gases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryDocument20 pagesGases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryAshley Marie ChildersNo ratings yet
- 52th IMO - 1st Tour - ProblemsDocument8 pages52th IMO - 1st Tour - ProblemsPhạm Gia KhánhNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Chapter 11 ReviewDocument15 pagesAP Chemistry Chapter 11 ReviewRemar Jhon PaineNo ratings yet
- Chemistry EUEE 2013 (14) - 151269132054Document12 pagesChemistry EUEE 2013 (14) - 151269132054mintesnot udessa100% (1)
- Chemistry QuestionsDocument71 pagesChemistry QuestionsNnaer Ortiz NasupmilacNo ratings yet
- Chemistry QP in English Set 2Document4 pagesChemistry QP in English Set 2Annesha MondalNo ratings yet
- Practice FRQDocument4 pagesPractice FRQKrystal LiNo ratings yet
- Physics-Xii Heat TEST N0:01Document3 pagesPhysics-Xii Heat TEST N0:01Farid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Baltic Chemistry Olymipiad On 2007Document5 pagesBaltic Chemistry Olymipiad On 2007Muhammad GhifariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Context 6Th Edition American Chemical Society Acs Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesChemistry in Context 6Th Edition American Chemical Society Acs Test Bank Full Chapter PDFelise.green301100% (14)
- 2324 Level L (Gr10 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 4 NotesDocument6 pages2324 Level L (Gr10 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 4 Noteslaithobeidat7981No ratings yet
- Set A - Experiment 1 Calibration of Bomb Calorimeter: Annenberg Foundation (2017)Document6 pagesSet A - Experiment 1 Calibration of Bomb Calorimeter: Annenberg Foundation (2017)Noreen Beth AlbertoNo ratings yet
- KMT ws2Document10 pagesKMT ws2Troy MateoNo ratings yet
- Test ReviewDocument2 pagesTest ReviewgraceNo ratings yet
- 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center V 515-294-6624 V Sistaff@iastate - Edu V HTTP://WWW - Si.iastate - EduDocument5 pages1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center V 515-294-6624 V Sistaff@iastate - Edu V HTTP://WWW - Si.iastate - EduRhod Jayson RicaldeNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving 1Document4 pagesProblem Solving 1Raphael Pizarro ArceoNo ratings yet
- Vivek High School Sector 38, Chandigarh NAME - Class: Xi Date: SUBJECT: Chemistry (Revision) TOPIC: Chap1 and 2Document5 pagesVivek High School Sector 38, Chandigarh NAME - Class: Xi Date: SUBJECT: Chemistry (Revision) TOPIC: Chap1 and 2manseeratNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Context Applying Chemistry To Society 8Th Edition American Chemical Society Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesChemistry in Context Applying Chemistry To Society 8Th Edition American Chemical Society Test Bank Full Chapter PDFjulianna.washington847100% (12)
- Department of Education Region VII, Central Visayas Division of Talisay City Talisay City, CebuDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education Region VII, Central Visayas Division of Talisay City Talisay City, CebuElue Sañal EtnaledNo ratings yet
- (AdU Special Topics) PhyChm and ChEThermo ProblemsDocument4 pages(AdU Special Topics) PhyChm and ChEThermo ProblemsRyan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Molecular Physics, Thermodynamics, Atomic and Nuclear Physics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandMolecular Physics, Thermodynamics, Atomic and Nuclear Physics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Pumpjack: Above Ground Down-Hole Water Well Pumpjacks See Also References External LinksDocument5 pagesPumpjack: Above Ground Down-Hole Water Well Pumpjacks See Also References External LinksBenjamin KonjicijaNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document2 pagesTut 1GUNJAN MUDGALNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual For Gas TrainDocument2 pagesOperating Manual For Gas TrainynmoihcppwlkaizbciNo ratings yet
- 4a's Lesson PlanDocument2 pages4a's Lesson PlanRowenickNo ratings yet
- Eor Ior Course T AhmedDocument298 pagesEor Ior Course T AhmedMiguel Angel ValladaresNo ratings yet
- NozzlesDocument2 pagesNozzlesAlmukhtar AlkinanyNo ratings yet
- Nordtec ProposalDocument15 pagesNordtec Proposaluzair khan100% (1)
- HAZID - Saraswati Oil Field DevelopmentDocument26 pagesHAZID - Saraswati Oil Field Developmentjithin shankarNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow Part III Viscous FlowDocument59 pagesCH 6 Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow Part III Viscous FlowMujtaba Rizvi100% (1)
- Journal of Environmental Science, Computer Science and Engineering & TechnologyDocument6 pagesJournal of Environmental Science, Computer Science and Engineering & Technologypete pansNo ratings yet
- GS ExercisesDocument88 pagesGS ExercisesCristian Cutipa MendozaNo ratings yet
- Safe Reduction of LK-853 FENCE at High Pressure: Matt Wishman, EITDocument10 pagesSafe Reduction of LK-853 FENCE at High Pressure: Matt Wishman, EITGrootNo ratings yet
- SPE-178368-MS (August, 2015)Document25 pagesSPE-178368-MS (August, 2015)lulut falaNo ratings yet
- UNIT - SeparatorDocument39 pagesUNIT - SeparatorRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-A2 PhysicsDocument12 pagesLesson 4-A2 PhysicsShiu Ping Wong0% (1)
- PETRONAS Distributor Price List - W.E.F 10-10-23Document2 pagesPETRONAS Distributor Price List - W.E.F 10-10-23Mujeeb SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Steam Trap Selection GuideDocument1 pageSteam Trap Selection GuidelatshareNo ratings yet
- ModuleDocument35 pagesModuleAlvin RazoNo ratings yet
- P and H Chapter 3Document42 pagesP and H Chapter 3Noor UL AaienNo ratings yet
- Ozone and Global WarmingDocument8 pagesOzone and Global WarmingCamilleKingNo ratings yet
- Gas Lift - Unloading (Leslie Thompson)Document59 pagesGas Lift - Unloading (Leslie Thompson)Reza RamadhanNo ratings yet
- DENSITYDocument9 pagesDENSITYJonaver RebiteNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki Genset Green - BrochureDocument8 pagesKawasaki Genset Green - BrochureFerozeNo ratings yet
- 2012 BookMatter EnergyDocument88 pages2012 BookMatter EnergyLutfi ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Tech Specs HDF 120Document2 pagesTech Specs HDF 120Vijay Pawar Innovative TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Norme-Osobna Zaštitna OpremaDocument41 pagesNorme-Osobna Zaštitna Opremadona2005No ratings yet
- EFX Dewpoint Control Plants PresentationDocument44 pagesEFX Dewpoint Control Plants PresentationAditya DubeyNo ratings yet