Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AIAS-FinalsRodjeanSimballa (Answer)
Uploaded by
Rodjean SimballaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AIAS-FinalsRodjeanSimballa (Answer)
Uploaded by
Rodjean SimballaCopyright:
Available Formats
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
AIAS
NAME: RODJEAN A. SIMBALLA BSIT 3D
STUDENT NO. 19-05453
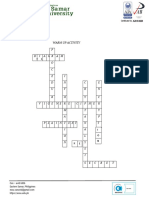
WARM UP ACTIVITY
P
1. 1
D I A G R A M
E I
D N C E
U F R N
R O Y C
V I G E N E R E C I P H E R
M T Y
A A P
P L A I N T E X T N T
I A I
O L O
N Y N
K E
S
S E C R E T
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
EXERCISE 7:
A.
1. Describe the different categories of symmetric encryption algorithms.
Asymmetric encryption: in this encryption two different keys are used namely
public key and private key.
ANSWER: Sender used his own private key to encrypt the data, receiver use sender public key
to decrypt the data.
Different categories of asymmetric encryption:
1. Rivest-shamir-adleman (RSA) algorithm
2. Diffie-hellman algorithm
3. Elliptic curve
RSA algorithm:
In RSA algorithm, private key and private key both are consisting numbers because these
numbers should generated by large prime numbers. These large prime numbers perform
modular operations to produce the public key and private key.
Diffie-hellman algorithm:
In diffie-hellman algorithm shared secret key is the main aspect. Every participant performs
multiplication operation with their private key and other's public key to produce the shared
secret key.
Elliptic cureve:
Elliptic curve is similar to the diffie-hellman algorithm. Shared secret key, every participant
multiplying secret key with the other's published product.
2.Outline the symmetric encryption process and explain the components involved
in the process.
ANSWER: The process which involved in symmetric encryption is first the user process the
plain text in which we apply secret key and algorithm and then cipher text is produces after this
the cipher text data is send to the receiver in which he decrypt the data by using the same
secret key which the user has used and retrieves ...
3.What is cryptanalysis? Give an example of a cryptanalytic problem.
ANSWER: Cryptanalysis refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to
understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic
security systems and gain access to the contents of encrypted messages, even if the
cryptographic key is unknown.Other types of cryptanalytic attacks can include techniques for
convincing individuals to reveal their passwords or encryption keys, developing Trojan horse
programs that steal secret keys from victims' computers and send them back to the
cryptanalyst, or tricking a victim into using a weakened cryptosystem.
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
B. Look for the following topics on the internet:
1.The Data Encryption Standard under computer-based encryption.
ANSWER:The data encryption standard (DES) defined by US NIST performs encryption in
hardware thereby speeding up the encryption and decryption operation. Additional features of
DES are: 1. ... A unique 56-bit key is used to encrypt each block of plaintext into a 64-bit block
of ciphertext.
2. The Advanced Encryption Standard.
ANSWER: The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a symmetric block cipher chosen by
the U.S. government to protect classified information. AES is implemented in software and
hardware throughout the world to encrypt sensitive data. It is essential for government computer
security, cybersecurity and electronic data protection.
3.The Effects of Ciphertext Errors.
ANSWER: A single bit error in a ciphertext block affects the decryption of all subsequent
blocks. Rearrangement of the order of the ciphertext blocks, for example, can cause the
decryption process to become corrupted.
4.File Encryption Software.
ANSWER: Is a software that uses cryptology in order to prevent unauthorized access to
sensitive data. The software helps to streamline the movement of data, keeps the content of
your files secure, and eliminates the need for using alternative vulnerable methods.
5. Digital Rights Management under Encrypting Files.
ANSWER: Encryption or digital rights management technology (DRM) can be used to control
access to information. ... DRM and encryption may be beneficial when information is highly
confidential, or if intellectual property is involved, but risks accompany their use.
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
Warm Up Activity (Word Search)
*REKEYING
*CRYPTONETS
*SIGNATURE
*CUTE
*CRYPTO PERIOD
E C B Y C U T E S K F D O P S
G V R S T E K N Y E S N Q K I
N X U Y R I Y F R B E R C L G
I Q L C P Z R L H W Z A C N N
Y I E F N T Y G A V T L T R A
E S V F M K O Y E T Z Y W X T
K U W K R U H N A T H M Q L U
E B Y I J A E Y E Y N H X X R
R G J Z S T A K W T T I D P E
J A Z H K D I N R X S I C H S
G A B Y H Y E K C I L B U P S
X O A T U U P C K N X U R J B
P C R Y P T O P E R I O D S O
T I C O D D R L P L S W A F R
B I V N T J C V W I Q F A C O
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
EXERCISE 8
1.Summarize the challenges of key management.
ANSWER: Key management is the important aspect in cryptosystem, which is used to
generating, distributing, storing the cryptographic keys.
These cryptographic keys are used to maintain the protection to the transfer files, which is
transmitted from one to another.
Challenges in key management:
• The main aim for this key management is to distribute the keys to the authorized people
only, don't distribute to the unauthorized people.
• Generate the keys, which is can't guess by the intruder. For example, in RSA algorithm
large prime numbers should be chosen to generate the keys.
• The last challenge of the key management is maintain the key integrity. That is intruder
shouldn't intercept those keys.
2.If we need enough entropy for a 16-byte key, why should we hash a 20-byte (or
larger) passphrase?
ANSWER: Hashing is the function, where arbitrary length input message is converted into the
fixed length output. User should have larger passphrase to produce the enough entropy. ...
Therefore, user should use 20-byte or larger passphrase to produce the 16-byte entropy key.
3.Explain the reused key stream problem.
ANSWER: Reused key stream is the concept that uses same key in multiple times to encrypt
the data. That is same key is used to encrypt the different messages. ... Then intruder easily
decrypt the messages, which are transmitted later.
4.Describe the role of the nonce in preventing reused key streams when using the
same passphrase to encrypt different files.
ANSWER: Nonce is used in the file' header and nonce combined with the passphrase. That
can create a high random key. This random key should generate each time of encryption of the
file.
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
5.Describe how key wrapping may be applied to file encryption.
ANSWER: Key wrapping is the technique, that encrypts the key itself using the passphrase. ...
KEK is used to produce the passphrase. When CEK is encrypted with the KEK, then wrapped
key is produced.
EXERCISE 9
1.Explain the difference between file encryption and volume encryption.
ANSWER: File encryption is just that one file at a time rather slow and unnecessary with
VeraCrypt unless it's so sensitive a file that the NSA is actively looking for it. Volume encryption
is just what it sounds like. Encrypt a volume and anything stored in it is encrypted with the
volume as a whole.
2.Explain the fundamental difference between block and stream ciphers.
ANSWER: The main difference between a Block cipher and a Stream cipher is that a block
cipher converts the plain text into cipher text by taking plain text's block at a time. ... Stream
Cipher Converts the plain text into cipher text by taking 1 byte of plain text at a time. 2.
3.Describe the steps performed in a typical block cipher.
ANSWER: Divide the key schedule into subsections, one per round. - For each subsection,
perform a round: For the first round, take the plaintext as the input text; for the remaining
rounds, take the output of the previous round as the input text.
4.What is a drive controller (look on the internet)?
ANSWER: The disk controller is the controller circuit which enables the CPU to communicate
with a hard disk, floppy disk or other kind of disk drive. It also provides an interface between the
disk drive and the bus connecting it to the rest of the system.
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
5.What is drive locking and unlocking (look on the internet)?
ANSWER: Predator, a free Windows program, turns your USB drive into a key that locks your
computer when it's removed. To unlock your computer, you'll have to plug the USB drive back
in. (Talk about having secret-agent-style security.)
Anyone who attempts to access your computer without the USB flash drive will be hit with an
epic "Access Denied" message. To get started, follow this guide:
Step 1: Download and install Predator.
Step 2: Once Predator launches, plug in your USB flash drive. None of the contents of the drive
will be deleted or altered in any way, so feel free to use your primary thumbdrive.When you
insert the drive, a dialog box will appear asking you to create a password. Click OK to continue.
Step 3: In the Preferences window, take note of a few key settings. First, enter a secure, unique
password in the "New password" field. If you lose your USB drive, you'll use it to unlock your
computer.If you'd like, you can check the Always Required box and you'll be asked to enter the
password each time you use your thumbdrive to unlock your PC.
Finally, in the section under Flash Drives, ensure that the correct USB flash drive is selected.
When you're done, click "Create key" and then OK
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
Warm Up Activity
Across
*EMAIL
*EMAIL PROTOCOL
*INTERNET
Down
*CLOUD SERVICE
*DELIVERY
E M A I L
E M A I L P R O T O C O L
V D
I N T E R N E T
C L
E I
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
EXERCISE 14
1.Describe the structure of an email message. Identify typical header fields. How
does the format mark the end of a message’s regular headers?
ANSWER: A message begins with several headers, which are formatted lines beginning with a
header identifier, followed by a colon and a space, followed by the contents of the header. Many
standard header identifiers are specified in RFC 822 and follow-up RFCs. Any other header
used for non-standard purposes may be created of the form X-headername:After the headers
comes a blank line, followed by the message body (which doesn’t concern us).Your E-mail
software, by default, will only display a subset of the headers found in a typical message,
because the rest aren’t normally important to you. In order to figure out where a message came
from, however, you need to look at the Received: headers.
2.Explain the purpose and use of MIME in an email message.
ANSWER: The MIME stands for Multi-Purpose Internet Mail Extensions. As the name
indicates, it is an extension to the Internet email protocol that allows it's users to exchange
different kinds of data files over the Internet such as images, audio, and video. The MIME is
required if text in character sets other than ASCII.
3.Describe a typical strategy for formatting an email message with text features
not found in a plaintext file.
ANSWER: OPTIMIZE YOUR PLAIN-TEXT EMAILS Most email service providers (ESPs) will
send in multi-part MIME automatically, or walk you through setting this up as an option.
However, these auto-generated plain-text versions are usually unorganized and difficult to read.
4.Explain the role of mailbox protocols.
ANSWER: Email protocol is a method by which a communication channel is established
between two computers and email is transferred between them. ... One computer sends the
mail and the other one receives it. The mail server stores the mail and lets the receiving device
access it and download it if needed.
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
5.Describe how all three types of network switching (message, circuit, and
packet) are used in the email system.
ANSWER: The store-and-forward switching method
In this method, the switch waits till all bits of the frame are received. After receiving all bits of the
frame, the switch verifies whether the received frame is error-free. If the received frame is error-
free, the switch forwards the frame from the selected port or ports. If the received frame
contains errors, the switch discards the frame.
To know the condition of a frame, the switch uses the FCS (frame check sequence) field of the
frame. The FCS field contains a value known as the CRC value. The CRC value allows a
receiving device to know whether the frame is exactly in the same state as the source packed it
or it has been damaged or tempered in the middle.
After creating a frame, the sender or the source device runs the CRC (Cyclic Redundancy
Check) algorithm on it. The value produced by this algorithm is known as the CRC value. The
CRC value is stored in the FCS field of the frame. After storing the CRC value, the sender
device loads the frame on the media.
Upon receiving the frame, the receiver or destination device runs the CRC algorithm on the
frame and compares the result with the CRC value stored in the FCS field of the frame. If the
result and the CRC value are the same, the frame is considered error-free. If they are not the
same, the frame is considered as the damaged frame.
store and forward method
In this method, a switch only forwards error-free frames. This method provides the highest level
of accuracy but at the cost of speed. If we compare all three methods of switching, this method
respectively stands at the first and the last positions in terms of accuracy and speed.The cut-
through switching method
In this method, the switch starts the third phase as soon as the forward port is determined. An
Ethernet frame stores the destination MAC address in the third field. To forward a frame, a
switch only needs the destination MAC address of the frame. Since the destination MAC
address occurs very early in the Ethernet frame, a switch can start forwarding the received bits
of the frame before receiving all bits of the frame.
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
[Type text]
[Type text]
Certificate No. AJA19-0226
Ethernet frame destination address
In this method, the switch does not check the condition of the frame before forwarding it. This
reduces the latency, but it also propagates errors. From all three switching methods, this is the
fastest method of switching. But it provides speed at the cost of having forwarded some frames
that contain errors.cut and through switching method
The fragment-free switching method
In this method, after determining the forward port, the switch waits till the first 64 bytes of the
frame are received. The 64 bytes is the minimum legal size of an Ethernet frame. An Ethernet
frame that is smaller than 64 bytes is known as the runt frame. A runt frame is a corrupt frame.
fragment-free switching method
This method is the modified version of the cut-through switching method. This method reduces
the number of runt frames that are being switched. Sometimes this method is also known as the
modified cut-through or runtless switching method.
Can – avid 6806
Eastern Samar, Philippines
You might also like
- TCPIP Professional Reference GuideDocument258 pagesTCPIP Professional Reference GuideneonavNo ratings yet
- Vuln WebDocument3 pagesVuln WebsandraNo ratings yet
- Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator Chfi v9Document5 pagesComputer Hacking Forensic Investigator Chfi v9harshadspatil0% (2)
- PMSDocument6 pagesPMSParixit DasNo ratings yet
- Attachment e Requirements Traceability Matrix 2Document117 pagesAttachment e Requirements Traceability Matrix 2vini100% (1)
- Name: Bsit 3N Student No.: Warm Up ActivityDocument13 pagesName: Bsit 3N Student No.: Warm Up ActivityRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Name: Josie C. Cesista Bsit 3N Student No.: Warm Up ActivityDocument13 pagesName: Josie C. Cesista Bsit 3N Student No.: Warm Up ActivityRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Improving Emotiona L QuotientDocument13 pagesImproving Emotiona L QuotientDuck HatNo ratings yet
- Edoc - Pub - Curso Cat 950 962g Steering Syst STMGDocument48 pagesEdoc - Pub - Curso Cat 950 962g Steering Syst STMGJhoncastilloNo ratings yet
- T.L.E 7 and 8 Week 5Document15 pagesT.L.E 7 and 8 Week 5Eleonor DistrajoNo ratings yet
- BSC Diploma CertificateDocument2 pagesBSC Diploma CertificaterishibarathiNo ratings yet
- Insurance in Risk Management: by V RamakrishnaDocument17 pagesInsurance in Risk Management: by V RamakrishnaVeena EstherNo ratings yet
- Cryptograpy and Network Security: Unit-1Document17 pagesCryptograpy and Network Security: Unit-1tatigutla thulasammaNo ratings yet
- CRUCIGRAMADocument1 pageCRUCIGRAMAPatricia BeltranNo ratings yet
- Computer Security Principles and Practice 3rd Edition Stallings Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesComputer Security Principles and Practice 3rd Edition Stallings Solutions Manualkeeling.grownzqrhqv93% (15)
- Steven V Cooper-TransactionFlow-TXN - BrnBagDocument50 pagesSteven V Cooper-TransactionFlow-TXN - BrnBagMahesh JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Sopa de LetrasDocument1 pageSopa de LetrasBrayan Edigio Parra ParraNo ratings yet
- Aias Assessment FinalsDocument10 pagesAias Assessment FinalsLexy Ira CapaoNo ratings yet
- Grand AssignmentDocument4 pagesGrand AssignmentAnsa MalikNo ratings yet
- Juego - CrucigramaDocument1 pageJuego - CrucigramaErick Franz Belzu PonceNo ratings yet
- EtymologyDocument9 pagesEtymologyJesiah PascualNo ratings yet
- Exam GGDocument8 pagesExam GGbeeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Applicants FormDocument1 pageApplicants FormW-CUBAO PWR SALESNo ratings yet
- Organ I GramaDocument1 pageOrgan I GramaPedro CasaverdeNo ratings yet
- Network Security - Cryptography: AbstractDocument11 pagesNetwork Security - Cryptography: Abstractapi-19799369No ratings yet
- Effect Bell: Project: Continental Management Hotel 311 Amansari System: Conventional Fire Alarm SystemDocument6 pagesEffect Bell: Project: Continental Management Hotel 311 Amansari System: Conventional Fire Alarm Systemnorazlina_a_rahimNo ratings yet
- Simer Rim Ppt2Document12 pagesSimer Rim Ppt2ashokb2009No ratings yet
- LaRon Walker - Cryptology ConceptsDocument6 pagesLaRon Walker - Cryptology ConceptsLaRon WalkerNo ratings yet
- Jobs Word SearchDocument2 pagesJobs Word SearchChiew N Pang100% (1)
- Jobs Word Search (Keys)Document2 pagesJobs Word Search (Keys)Chiew N PangNo ratings yet
- Workshop Translation and GuidelinesDocument10 pagesWorkshop Translation and GuidelinesOscar BaccaNo ratings yet
- Brilliant Smoke ADocument6 pagesBrilliant Smoke ApaultcoltNo ratings yet
- Gemmw: Mathematics in The Modern World Module 5: Cryptography Learning OutcomesDocument15 pagesGemmw: Mathematics in The Modern World Module 5: Cryptography Learning OutcomesDANINo ratings yet
- Seven R'S of Logistics: Right ProductDocument1 pageSeven R'S of Logistics: Right ProductKatherine BernalNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 5 Workshop Getting Started As A TranslatorDocument9 pagesEvidencia 5 Workshop Getting Started As A TranslatorSusiNo ratings yet
- 11 Actividad #4 Crucigrama Contabilidad VDocument3 pages11 Actividad #4 Crucigrama Contabilidad VMaria F OrtizNo ratings yet
- TiempoDocument2 pagesTiempoLUIS ALFREDO LEMUS RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- 1 1 WordsearchVOLCANOLOGY Sci9 Yourfamilyname 9section 06mar2023Document1 page1 1 WordsearchVOLCANOLOGY Sci9 Yourfamilyname 9section 06mar2023Hans Rondave PlagaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.2: Across DownDocument1 pageActivity 2.2: Across DownThabang LeseleNo ratings yet
- Mid TermDocument6 pagesMid Termmizta devan1No ratings yet
- Layemar WSDocument5 pagesLayemar WS118466No ratings yet
- Worksheet VirusDocument2 pagesWorksheet VirusKaleNo ratings yet
- MultimediainformationDocument43 pagesMultimediainformationCaren Tajale PacomiosNo ratings yet
- Actividad de Aprendizaje 5 Evidencia 5: Workshop: Getting Started As A TranslatorDocument10 pagesActividad de Aprendizaje 5 Evidencia 5: Workshop: Getting Started As A TranslatorDaniela LopezNo ratings yet
- Final Examination in IT22: S B A I A CDocument8 pagesFinal Examination in IT22: S B A I A CJb MejiaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation & Maintenance Electrical Installation & MaintenanceDocument23 pagesElectrical Installation & Maintenance Electrical Installation & MaintenanceMichael AnoraNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts Word Search: Name: DateDocument2 pagesMicroscope Parts Word Search: Name: DateAnonymous K3WNW5ZopNo ratings yet
- Perniagaan T4: Cari Kata Bab 1 Ting 4Document1 pagePerniagaan T4: Cari Kata Bab 1 Ting 4Irwana YusufNo ratings yet
- Stars: Sedan For TheDocument16 pagesStars: Sedan For TheAmit198474No ratings yet
- Activity Sheets MAPEHDocument11 pagesActivity Sheets MAPEHIzzabella Mustacisa100% (3)
- T o R T o I S e W L FDocument2 pagesT o R T o I S e W L FYamile NasiraNo ratings yet
- Input Output1-IctDocument22 pagesInput Output1-IctyusairriNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 5Document9 pagesEvidencia 5Angel ThomasNo ratings yet
- Degree Certificate SIBADocument1 pageDegree Certificate SIBAvccabinbbsrNo ratings yet
- WeatherDocument1 pageWeatherNatasha TaylorNo ratings yet
- ParadiseFoundtheCradleoftheHumanRaceattheNorthPole 10033988Document538 pagesParadiseFoundtheCradleoftheHumanRaceattheNorthPole 10033988Mariem KawanaNo ratings yet
- Insects HardDocument2 pagesInsects HardNishalini SandramoganNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument8 pagesAnswer KeyAndrew PeriodicoNo ratings yet
- 2 Preliminary Examination Tle Garments 10 Name: - Section: - DateDocument4 pages2 Preliminary Examination Tle Garments 10 Name: - Section: - DateGingerann Ignacio CataquisNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Crossword PuzzleDocument2 pagesActivity 2 - Crossword PuzzleHailla GuiralNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Puzzle in ICT Grade 10Document2 pagesReviewer Puzzle in ICT Grade 10Felix BrimonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Activity 2Document2 pagesLesson 1 - Activity 2DE BELEN JEFFREYNo ratings yet
- MarketingnUnitn1n1184e8n616329c4nnn35646cd29ee68e0nnnnnn7864834beae3e3cnnn 15648860e446720Document1 pageMarketingnUnitn1n1184e8n616329c4nnn35646cd29ee68e0nnnnnn7864834beae3e3cnnn 15648860e446720Valentina Martinez VargasNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Coatings and Thin Films 1991From EverandMetallurgical Coatings and Thin Films 1991G.E. McGuireNo ratings yet
- Mobile Security: Question and Answer Format Name: Date: Grade: Course & Section: TopicDocument1 pageMobile Security: Question and Answer Format Name: Date: Grade: Course & Section: TopicRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1&2 in Data ScienceDocument5 pagesAssessment 1&2 in Data ScienceRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- IT Elective I Advance Database SystemDocument70 pagesIT Elective I Advance Database SystemRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- AIAS-FinalsMorallosJanrelKent (Answer) - WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesAIAS-FinalsMorallosJanrelKent (Answer) - WPS OfficeRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Barangay Management Information System: Background of The StudyDocument6 pagesBarangay Management Information System: Background of The StudyRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Unit VI - Routing Fundamentals: Learning OutcomesDocument13 pagesUnit VI - Routing Fundamentals: Learning OutcomesRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Mobile AppDocument14 pagesLesson 3 Mobile AppRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Pg. 51 Evaluating LearningDocument4 pagesPg. 51 Evaluating LearningRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions/Activity I. Write The Letter of The Correct Answer Before The StatementDocument5 pagesGuide Questions/Activity I. Write The Letter of The Correct Answer Before The StatementRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Exercise MultiplicationDocument1 pageExercise MultiplicationRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Integrative ProgrammingDocument3 pagesIntegrative ProgrammingRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Comp 121 Computer Programming II: Laboratory Manual inDocument15 pagesComp 121 Computer Programming II: Laboratory Manual inRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To HistoryDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To HistoryRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Project (Essay) IN Readings in Philippine History: Roden O. MugasDocument1 pageMidterm Project (Essay) IN Readings in Philippine History: Roden O. MugasRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Rjpot WorksheetDocument52 pagesRjpot WorksheetRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- John Errol Ausa... MC-chapter1 - Questions& AnswersDocument5 pagesJohn Errol Ausa... MC-chapter1 - Questions& AnswersRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- AIAS Module FinalsDocument31 pagesAIAS Module FinalsRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Rescued Document 1Document4 pagesRescued Document 1Rodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Computerized Budgeting System of Barangay 04, Can-Avid Eastern SamarDocument17 pagesComputerized Budgeting System of Barangay 04, Can-Avid Eastern SamarRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- UNIT II. Controlling FilesDocument13 pagesUNIT II. Controlling FilesRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Data Flow Diagram: Admin (Librarian)Document10 pagesData Flow Diagram: Admin (Librarian)Rodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Memory Management: IT 311: Applied Operating SystemDocument44 pagesLesson 2: Memory Management: IT 311: Applied Operating SystemRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1. Controlling A ComputerDocument15 pagesUNIT 1. Controlling A ComputerRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: File Management: IT 311: Applied Operating SystemDocument58 pagesLesson 5: File Management: IT 311: Applied Operating SystemRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: MS-DOS, Windows 10 and Linux OS: IT 311: Applied Operating SystemDocument96 pagesLesson 6: MS-DOS, Windows 10 and Linux OS: IT 311: Applied Operating SystemRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Process Management: IT 311: Applied Operating SystemDocument64 pagesLesson 3: Process Management: IT 311: Applied Operating SystemRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: I/O DEVICES Management: IT 311: Applied Operating SystemDocument45 pagesLesson 4: I/O DEVICES Management: IT 311: Applied Operating SystemRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Overview of Operating SystemDocument57 pagesLesson 1: Overview of Operating SystemRodjean SimballaNo ratings yet
- What Is GitHubDocument4 pagesWhat Is GitHubabirje0No ratings yet
- Archer Vr300 Ug Rev1.20.0Document99 pagesArcher Vr300 Ug Rev1.20.0Nassif HawaNo ratings yet
- Design For Security and ComplianceDocument27 pagesDesign For Security and Compliancetunguyen.itsysNo ratings yet
- OB - Here Are The Important Links To KnowDocument6 pagesOB - Here Are The Important Links To KnowRaquel Mendoza HernandezNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Cyber CrimesDocument23 pagesModule 5 Cyber CrimesHridya sNo ratings yet
- SIP Test ToolsDocument2 pagesSIP Test Toolswin_ramanNo ratings yet
- Domain Name SystemDocument39 pagesDomain Name SystemRavi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Santo: J. Acácio Santana Partitura: Ronaldo E. LemeDocument1 pageSanto: J. Acácio Santana Partitura: Ronaldo E. LemeRonaldo Egevarth LemeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AJAXDocument43 pagesIntroduction To AJAXMohamed Ossama AbdallahNo ratings yet
- PSP Assignment1Document25 pagesPSP Assignment1B BasitNo ratings yet
- Yuzu Installer2Document2 pagesYuzu Installer2Alexander GaticaNo ratings yet
- Activation Error CodesDocument2 pagesActivation Error CodesrightmyankleNo ratings yet
- RecaptchaDocument5 pagesRecaptchaMian Zaigham AslamNo ratings yet
- ProDigiSign CPSDocument72 pagesProDigiSign CPSPrakash N RamaniNo ratings yet
- Configure Docker Registry On Dev ServerDocument6 pagesConfigure Docker Registry On Dev ServerMuhammad IkbalNo ratings yet
- HC110110027 Access Control ListsDocument14 pagesHC110110027 Access Control ListsDimitris FergadiotisNo ratings yet
- HyconnectDocument2 pagesHyconnectChris EkohNo ratings yet
- WebSphere Application Server Step by StepDocument23 pagesWebSphere Application Server Step by StepimamitohmNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 22 Chapter 20 - FirewallsDocument5 pagesCryptography and Network Security Chapter 22 Chapter 20 - FirewallsPrasannaBhagavathNo ratings yet
- Netstat Liste NewDocument26 pagesNetstat Liste NewCsabiNo ratings yet
- Release Notes v6.20.2Document9 pagesRelease Notes v6.20.2Max MannNo ratings yet
- INTERNET ARCHIVE - Old Website Pages Still in CyberspaceDocument3 pagesINTERNET ARCHIVE - Old Website Pages Still in CyberspaceKintyre On Record100% (1)
- Dairy and Food Process and Products Technology - Course ProgressDocument2 pagesDairy and Food Process and Products Technology - Course ProgressNitheesh Kumar100% (1)
- Advanced Stealth Mitm Attack in Wpa2Document5 pagesAdvanced Stealth Mitm Attack in Wpa2Nurul AtikahNo ratings yet
- Trend in ICTDocument2 pagesTrend in ICTSheena BarreraNo ratings yet