Professional Documents
Culture Documents
First Esa Missions To Use Gallium Nitride (Gan) - A Disruptive Technology For Space-Based Payloads
Uploaded by
qh huang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThe document discusses the first use of gallium nitride (GaN) technology on European Space Agency missions. GaN provides significant improvements for space payloads, but developing reliable GaN components for space was challenging. The ESA launched a program in 2008 to develop space-qualified GaN transistors. This led to an X-band transmitter using GaN flying on the PROBA V mission since 2013. Building on this success, ESA then used GaN to develop a 240W amplifier for the Biomass mission. The document describes the benefits and qualification process, concluding that GaN has matured for use in future space applications.
Original Description:
CSmantech2015
Original Title
1.3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the first use of gallium nitride (GaN) technology on European Space Agency missions. GaN provides significant improvements for space payloads, but developing reliable GaN components for space was challenging. The ESA launched a program in 2008 to develop space-qualified GaN transistors. This led to an X-band transmitter using GaN flying on the PROBA V mission since 2013. Building on this success, ESA then used GaN to develop a 240W amplifier for the Biomass mission. The document describes the benefits and qualification process, concluding that GaN has matured for use in future space applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageFirst Esa Missions To Use Gallium Nitride (Gan) - A Disruptive Technology For Space-Based Payloads
Uploaded by
qh huangThe document discusses the first use of gallium nitride (GaN) technology on European Space Agency missions. GaN provides significant improvements for space payloads, but developing reliable GaN components for space was challenging. The ESA launched a program in 2008 to develop space-qualified GaN transistors. This led to an X-band transmitter using GaN flying on the PROBA V mission since 2013. Building on this success, ESA then used GaN to develop a 240W amplifier for the Biomass mission. The document describes the benefits and qualification process, concluding that GaN has matured for use in future space applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
First ESA missions to use gallium nitride (GaN) -
a disruptive technology for space-based payloads
A. R Barnes
Data Systems, Microelectronics and EEE Components Division, European Space Agency, ECSAT, UK
Email: Andrew.Barnes@esa.int
Keywords: GaN, space qualification, PROBA V, Biomass.
Abstract As a result of this flight heritage demonstration, a decision
This paper gives an overview on the methodology and was made by ESA to develop and qualify European,
results obtained from performing early in-orbit hermetically packaged, microwave power transistors for use
demonstration and space qualification of microwave in the Biomass P-band SAR interferometric mission, aimed
GaN technology for the European Space Agency PROBA at quantifying and mapping changes in the global forest
V and Biomass missions. carbon cycle, as illustrated in Fig. 2.
INTRODUCTION
Gallium Nitride (GaN) is a key strategic enabling
technology that has the potential to provide an order of
magnitude improvement in RF output power, is inherently
radiation hard and tolerates higher bus-voltages as well as
higher operational temperatures. These characteristics
promise to disrupt today’s state of the art design for space
affecting Telecommunications, Navigation, Science and
Earth Observation missions.
The main challenge for space application has been to
combine outstanding GaN performance figures and reliable
operation. To address this situation ESA launched its GaN
Reliability and Technology Transfer initiative (GREAT2) in
2008, with the aim of establishing a European supply chain
for the manufacture of high reliability, space compatible, Fig. 2. Schematic of ESA Biomass mission
GaN-based microwave transistors and integrated circuits,
free from any ITAR or end-user license restrictions.
This paper shall describe the outputs of the reliability The mission operating requirements for PROBA V and
improvements achieved, culminating in the first in-orbit Biomass shall be described along with the performance
demonstration of a GaN X-band telemetry transmitter on benefits achieved by using GaN technology for realization of
PROBA V, illustrated in Fig. 1. Since 2013, this satellite has (i) an X-band telemetry downlink transmitter and (ii) a
been used to map land cover and vegetation growth on a 240W solid state power amplifier (SSPA) respectively. In
daily basis. addition, the space qualification methodology and lessons
learned shall be discussed.
CONCLUSIONS
The results obtained are an important milestone and
illustrate that GaN technology has now matured rapidly and
offers significant benefits for realization of future space-
based payloads.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank all ESA colleagues and
industrial partners who contributed to the success of this
work.
Fig. 1. Overview of PROBA V spacecraft.
You might also like
- Ogre Classic CountersDocument6 pagesOgre Classic Countersgianduja100% (1)
- Test of Infant Motor Performance (TIMP)Document6 pagesTest of Infant Motor Performance (TIMP)Juan Pablo NavarroNo ratings yet
- AUSA Logistics Companies 226 Valid Leads Update ListDocument30 pagesAUSA Logistics Companies 226 Valid Leads Update ListAsr Naeem KhanNo ratings yet
- The Polygamous Sex - Esther VilarDocument205 pagesThe Polygamous Sex - Esther VilarFederico Deambrosi Algorta100% (1)
- Moment Distribution Method ExplainedDocument37 pagesMoment Distribution Method ExplainedSuleiman Yusuf JibrilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of Social ResearchDocument240 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of Social ResearchRob Londs100% (1)
- Neuropsychological Effects of Caffeine Is Caffeine Addictive 2161 0487 1000295 PDFDocument12 pagesNeuropsychological Effects of Caffeine Is Caffeine Addictive 2161 0487 1000295 PDFAli ShahNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Communication On OrganisatDocument12 pagesThe Impact of Communication On Organisatewrerwrew100% (1)
- Quality Assessment of The Topo Iberia CGPS Stations and Dat 2024 Geodesy andDocument11 pagesQuality Assessment of The Topo Iberia CGPS Stations and Dat 2024 Geodesy andTuğçe DemirciNo ratings yet
- Field Performance of A Novel Wideband Optically Transparent GNSS AntennaDocument2 pagesField Performance of A Novel Wideband Optically Transparent GNSS AntennaThiripurasundari DNo ratings yet
- Toyoshima 2019Document5 pagesToyoshima 2019Mahadev MetriNo ratings yet
- Estable 2022 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1226 012095Document9 pagesEstable 2022 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1226 012095ryangy0919No ratings yet
- CAN Implementation and Performance For Raman Laser Spectrometer (RLS) Instrument On Exomars 2020 MissionDocument10 pagesCAN Implementation and Performance For Raman Laser Spectrometer (RLS) Instrument On Exomars 2020 Missiondwi johdiNo ratings yet
- High-gain S-band Patch Antenna for Earth-observation CubesatsDocument4 pagesHigh-gain S-band Patch Antenna for Earth-observation CubesatsAshim ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Holographic Beam-Forming Metasurface Technology for Next Gen CubeSatsDocument4 pagesHolographic Beam-Forming Metasurface Technology for Next Gen CubeSatssagacious.ali2219No ratings yet
- Earthquake Research Advances: Yu LiDocument9 pagesEarthquake Research Advances: Yu LiFajri YantoNo ratings yet
- Aerospace 08 00169 v2Document27 pagesAerospace 08 00169 v2kirancallsNo ratings yet
- Aerospace: Modular Impulsive Green Monopropellant Propulsion System (Mimps-G) : For Cubesats in Leo and To The MoonDocument26 pagesAerospace: Modular Impulsive Green Monopropellant Propulsion System (Mimps-G) : For Cubesats in Leo and To The MoonJagannath Prasad SahooNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Network Geometry On Network RTK UsiDocument12 pagesThe Effects of Network Geometry On Network RTK Usiseba 19junioNo ratings yet
- LEO Satilite 2021Document16 pagesLEO Satilite 2021MadhanDhonianNo ratings yet
- Principle and Performance of Multi-Frequency and multi-GNSS PPP-RTKDocument11 pagesPrinciple and Performance of Multi-Frequency and multi-GNSS PPP-RTKveteg67000No ratings yet
- technicalseminarreportsudeepDocument22 pagestechnicalseminarreportsudeepsudeep.revankar13No ratings yet
- Quality Assessment of A Network-Based RTK GPS ServDocument13 pagesQuality Assessment of A Network-Based RTK GPS ServSergiy PogoryelovNo ratings yet
- Configuration and The Calculation of Link Budget For A Connection Via A Geostationary Satellite For Multimedia Application in The Ka BandDocument5 pagesConfiguration and The Calculation of Link Budget For A Connection Via A Geostationary Satellite For Multimedia Application in The Ka BandFiras ZekiNo ratings yet
- 04successful Depth Imaging at Banyu Urip FieldDocument9 pages04successful Depth Imaging at Banyu Urip FieldHerry SuhartomoNo ratings yet
- Publi 7315Document5 pagesPubli 7315Sriram TallapragadaNo ratings yet
- Leica AR25 White PaperDocument10 pagesLeica AR25 White PaperSergiy PogoryelovNo ratings yet
- COTS in Space From Novelty To Necessity White Paper PDFDocument10 pagesCOTS in Space From Novelty To Necessity White Paper PDFFath GruntNo ratings yet
- 04enhancing Fault Interpretation Through Broadband Processing and Diffraction Imaging The First and Successful Experience From Madura Offshore AreaDocument12 pages04enhancing Fault Interpretation Through Broadband Processing and Diffraction Imaging The First and Successful Experience From Madura Offshore AreaHerry SuhartomoNo ratings yet
- NASA's Evolutionary Xenon Thruster-Commerical (NEXT-C)Document2 pagesNASA's Evolutionary Xenon Thruster-Commerical (NEXT-C)Klaus-BärbelvonMolchhagenNo ratings yet
- Venus: An Electric Orbit Raising Stage For Vega G. Ascanio, C. Tuninetti, D. NicoliniDocument8 pagesVenus: An Electric Orbit Raising Stage For Vega G. Ascanio, C. Tuninetti, D. NicoliniAnatoly VovkNo ratings yet
- TDR Eco Solar BoatDocument11 pagesTDR Eco Solar BoatRagna RokNo ratings yet
- Integration of Satellites in 5G Through LEO ConstellationsDocument6 pagesIntegration of Satellites in 5G Through LEO ConstellationsExtreme DaysNo ratings yet
- High Quality Software For Planetary Science From SpaceDocument6 pagesHigh Quality Software For Planetary Science From SpaceFadil HudaNo ratings yet
- Status of Telecommunication in W-Band and Possible Applications: Satellite Broadband Connection and Networks of Mobile PhonesDocument20 pagesStatus of Telecommunication in W-Band and Possible Applications: Satellite Broadband Connection and Networks of Mobile PhonesMario SergioNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Neural Network TEC Forecasting Models Over Equatorial Low-Latitude Indian GNSS StationDocument10 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Neural Network TEC Forecasting Models Over Equatorial Low-Latitude Indian GNSS StationHistoric CreationsNo ratings yet
- 2009 Globecom Workshop - Feasibility AeronauticalDocument5 pages2009 Globecom Workshop - Feasibility AeronauticaldesmauroNo ratings yet
- B-Scan GPR Sar ImagingDocument7 pagesB-Scan GPR Sar ImagingKöksalİçözNo ratings yet
- Technical and Quality ManagementDocument12 pagesTechnical and Quality ManagementMritunjay SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Accelerating Dust Temperature With GrapichDocument7 pagesAccelerating Dust Temperature With GrapichAngga RyanNo ratings yet
- Probality Density Function Analysis of Multipath Fading With Phase Error Over Rayleigh and Rician Fading Channels in Equal Gain DiversityDocument7 pagesProbality Density Function Analysis of Multipath Fading With Phase Error Over Rayleigh and Rician Fading Channels in Equal Gain DiversityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Paper 7Document13 pagesPaper 7d20l211No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S167477552100113X MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S167477552100113X Mainchenyi liNo ratings yet
- Tao-2020-Predicting Soil Settlement With Quantified Uncertainties by Using Ensemble Kalman FilteringDocument14 pagesTao-2020-Predicting Soil Settlement With Quantified Uncertainties by Using Ensemble Kalman FilteringAojie FengNo ratings yet
- Dual Chemical Electric Propulsion System Design For Interplanetary CubesatsDocument13 pagesDual Chemical Electric Propulsion System Design For Interplanetary CubesatsSebastián ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Inflatable Antenna Technology With Preliminary ShuDocument7 pagesInflatable Antenna Technology With Preliminary ShudivyaNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Satellite Communication System Under The Shadowed-Rician Fading: A Stochastic Geometry ApproachDocument15 pagesPerformance Analysis of Satellite Communication System Under The Shadowed-Rician Fading: A Stochastic Geometry Approachstefan.panicNo ratings yet
- Development of A Low-Cost Solution For GPSGyro AttDocument11 pagesDevelopment of A Low-Cost Solution For GPSGyro AttCamacho Camacho RochaNo ratings yet
- Remote SensingDocument19 pagesRemote SensingMert BezcioğluNo ratings yet
- Amanaf 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 982 012029Document10 pagesAmanaf 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 982 012029Nada KnaniNo ratings yet
- CrossDocument8 pagesCrossNinda SyafaNo ratings yet
- Respond Areas in SpaceDocument277 pagesRespond Areas in SpaceArijit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Geophysical Modeling With Satellite GravityDocument17 pagesGeophysical Modeling With Satellite Gravitymimin ajaNo ratings yet
- tmp2DCD TMPDocument10 pagestmp2DCD TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Uncovering Misconceptions in GNSS Precise Point PositioningDocument10 pagesUncovering Misconceptions in GNSS Precise Point PositioningChethan Kumar RENo ratings yet
- Compressive Strength Prediction of Sprayed Concrete Lining in - 2022 - UndergroDocument16 pagesCompressive Strength Prediction of Sprayed Concrete Lining in - 2022 - UndergroGustavo MariduenaNo ratings yet
- Mars Ascent Vehicle System Studies and Baseline Conceptual DesignDocument13 pagesMars Ascent Vehicle System Studies and Baseline Conceptual DesignJuanJoNo ratings yet
- Computational Intelligence-Based Methodology For Antenna DevelopmentDocument11 pagesComputational Intelligence-Based Methodology For Antenna Developmentjeganece84No ratings yet
- Tarea 1 - 1. MecatrónicaDocument17 pagesTarea 1 - 1. MecatrónicaHanna FraustoNo ratings yet
- A Benchmark of Dual Constellations GNSS Solutions For Vehicle Localization in Container TerminalsDocument7 pagesA Benchmark of Dual Constellations GNSS Solutions For Vehicle Localization in Container TerminalsjfrasconNo ratings yet
- Application of Double GPS Multi-rotor UAV in the Investigation of High Slope Perilous Rock-Mass in An Open Pit Iron MineDocument8 pagesApplication of Double GPS Multi-rotor UAV in the Investigation of High Slope Perilous Rock-Mass in An Open Pit Iron MineCarlosNo ratings yet
- SB14Document4 pagesSB14renatogeo14No ratings yet
- Thermal, Structural, and Optical Analysis of A Balloon-Based Imaging SystemDocument31 pagesThermal, Structural, and Optical Analysis of A Balloon-Based Imaging Systemmohammad hosein benvidiNo ratings yet
- Applsci 11 02659 v2Document21 pagesApplsci 11 02659 v2Cristian BandilaNo ratings yet
- GIOVE-B Satellite & Payload OverviewDocument9 pagesGIOVE-B Satellite & Payload OverviewN467RX100% (1)
- The Next Generation of Beam Hopping Satellite Systems Dynamic Beam Illumination With Selective PrecodingDocument17 pagesThe Next Generation of Beam Hopping Satellite Systems Dynamic Beam Illumination With Selective PrecodingSriram TallapragadaNo ratings yet
- Bibliographical Paper CubeSat AntennaDocument5 pagesBibliographical Paper CubeSat AntennaAbrahamNo ratings yet
- Eecs 2018 66Document52 pagesEecs 2018 66qh huangNo ratings yet
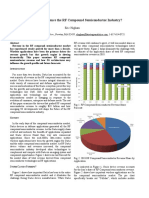
- How Will 5G Influence The RF Compound Semiconductor Industry?Document4 pagesHow Will 5G Influence The RF Compound Semiconductor Industry?qh huangNo ratings yet
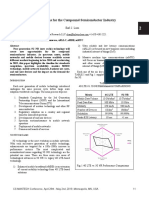
- 002.1 S2 P1 Lum PDFDocument4 pages002.1 S2 P1 Lum PDFYoav NatafNo ratings yet
- A Perspective On The Solutions and Needs of Iot, Utilities, and Smart CitiesDocument1 pageA Perspective On The Solutions and Needs of Iot, Utilities, and Smart Citiesqh huangNo ratings yet
- Form Follows Function: Mobile Use-Cases Dictates Electronic Design, Not The Other Way AroundDocument1 pageForm Follows Function: Mobile Use-Cases Dictates Electronic Design, Not The Other Way Aroundqh huangNo ratings yet
- Water Budget Equation Exercise Problems SolvedDocument10 pagesWater Budget Equation Exercise Problems SolvedSheeraz AhmedNo ratings yet
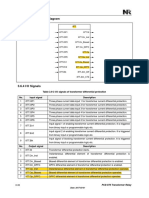
- 3.6.3 Function Block Diagram: 3 Operation TheoryDocument2 pages3.6.3 Function Block Diagram: 3 Operation TheoryAC DCNo ratings yet
- Office PoliticsDocument17 pagesOffice Politicsnasif al islamNo ratings yet
- Roots of EquationsDocument31 pagesRoots of EquationsGzim RamadaniNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in EDUC 6ADocument10 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in EDUC 6ARyan Jay Gaviola CalahatNo ratings yet
- Thermal Expansion of Iridium at High TemperaturesDocument5 pagesThermal Expansion of Iridium at High TemperaturesAntonio CamaranoNo ratings yet
- Solutions and Stoichiometry Worksheet (Sept, 17, 2021)Document2 pagesSolutions and Stoichiometry Worksheet (Sept, 17, 2021)Ahmed AlmossaweNo ratings yet
- Learning Task Part 1Document7 pagesLearning Task Part 1Francia Neil BasilioNo ratings yet
- Listening skills practice: Living online – exercisesDocument2 pagesListening skills practice: Living online – exercisesnavasfernando75100% (1)
- SMT0019-8.6 SynPAKDocument126 pagesSMT0019-8.6 SynPAKhadiNo ratings yet
- What Is PCB Busbar or PCB Stiffener Busbar in ElectronicsDocument13 pagesWhat Is PCB Busbar or PCB Stiffener Busbar in ElectronicsjackNo ratings yet
- Bolted Flanged Joint Creep/Relaxation Results at High TemperaturesDocument7 pagesBolted Flanged Joint Creep/Relaxation Results at High TemperaturesjlbarretoaNo ratings yet
- Math 5 - Pack 5Document42 pagesMath 5 - Pack 5Aneeza IftikharNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: My Hobbies Lesson 1: Getting Started-My Favourite HobbyDocument15 pagesUnit 1: My Hobbies Lesson 1: Getting Started-My Favourite HobbyLinhtram LêNo ratings yet
- 002 SillitoeDocument14 pages002 Sillitoesebastian tiriraNo ratings yet
- Cover LetterDocument2 pagesCover Letterapi-237243590No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Report 2Document4 pagesChemistry Lab Report 2Sahaj SinghNo ratings yet
- 05 Information LiteracyDocument11 pages05 Information LiteracyLaila Ismael SalisaNo ratings yet
- IISER Aptitude Test 2013: Syllabus ForDocument1 pageIISER Aptitude Test 2013: Syllabus ForSanthoshkumar RayavarapuNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of NCERT Booster Test Series - CoE NEET-2024 - 071157Document1 pageSyllabus of NCERT Booster Test Series - CoE NEET-2024 - 071157bishnuprasadmohapatra01No ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithms: Department of Computer Science, University of New Mexico, AlbuquerqueDocument4 pagesGenetic Algorithms: Department of Computer Science, University of New Mexico, AlbuquerqueESMAILNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization Using Bottom Ash and Areca Fiber: Experimental Investigations and Reliability AnalysisDocument11 pagesSoil Stabilization Using Bottom Ash and Areca Fiber: Experimental Investigations and Reliability AnalysisHugo Dario Machaca CondoriNo ratings yet