Dr.
Sudhir Chandra Sur Institute of Technology & Sports Complex
540, Dumdum Road,
Surermath,Kolkata - 700074
Department of Automobile Engineering
Automobile Engineering Lab - I (Engine & Chassis Component Lab)
Experiment Number: PC AUE 592/02
Title of Experiment: Study of Frames used for Heavy Commercial Vehicle (HCV), Car, Two & Three
Wheelers
Objective: To classify the chassis in different types and also understand their Construction & Application.
Function: The main functions of the Frame in vehicles are
To support the vehicle's mechanical components and body.
To deal with static and dynamic loads, without undue deflection or distortion.
These includes:
Weight of the body, passengers, and cargo loads.
Vertical and torsional twisting transmitted by going over uneven surfaces.
Transverse lateral forces caused by road conditions, side wind, and steering the vehicle.
Torque from the engine and transmission.
Longitudinal tensile forces from starting and acceleration, as well as compression from
braking.
Sudden impacts from collisions.
Theory: A vehicle frame, also known as its chassis, is the main supporting structure of a motor vehicle to
which all other components are attached, comparable to the skeleton of an organism. Until the 1930s,
virtually every car had a structural frame separate from its body. This construction design is known
as body-on-frame. Over time, nearly all passenger cars have migrated to unibody construction, meaning
their chassis and bodywork have been integrated into one another. Nearly all trucks, buses, and
most pickups continue to use a separate frame as their chassis.
Classification of Frame: According to the Construction the Vehicle Body Frame mainly classified into four
types these are;
Ladder Frame
Monocoque Frame
Tubular Frame
Backbone Frame
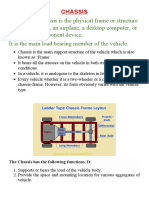
�Ladder Frame:
The Ladder frame is one of the simplest and oldest of all designs. It consists of two symmetrical
beams, rails, or channels running the length of the vehicle, and several transverse cross members
connecting them.
This Design offers good beam resistance because of its continuous rails from front to rear, but poor
resistance to torsion, so that the cross members are used.
The vehicle's overall height will be greater due to the floor pan sitting above the frame instead of
inside it.
This type of frame is mostly used in Heavy Commercial and Light Commercial Vehicles.
Monocoque Frame:
A Monocoque frame is a structure which integrates body and chassis together to form a composite
structure which has better stiffness as well as low weight.
In Monocoque frame the stress generated by the vehicle during motion is being distributed among
the structure and does not form localized stress, which may causes the deformation of the frame.
Monocoque is a one piece structure which defines the overall shape of the car. All most all high
performance cars use Monocoque design.
�Tubular Space Frame:
Tube (structure), a structure is designed to act like a three –dimensional hollow tube so to resist
lateral loads.
Tubular space frame employs dozens of circular, rectangular etc section tube position in different
directions to provide the mechanical strength against force from anywhere.
Space frame or space structure, a truss-like, lightweight rigid structure constructed from
interlocking struts in a geometric pattern.
These tubes are welded and form a very complex structure and very much used in Racing Cars and
All Terrain Vehicles.
In order to maximize rigidity and minimize weight, the design makes maximum use of triangles,
and all the forces in each strut are either tensile or compressive, never bending, so they can be kept
as thin as possible.
�Backbone Frame:
Backbone tube chassis is a type of automobile construction chassis that is similar to the body-on-
frame design. Instead of a two-dimensional ladder-type structure, it consists of a strong tubular
backbone (usually rectangular in cross section) that connects the front and
rear suspension attachment areas. A body is then placed on this structure.
This type of chassis has been used in numerous sports cars. It does not provide protection
against side collisions, and thus has to be combined with a body that would compensate for this
shortcoming.
Vehicle Frame Channel Section can be classified into three types and these are,
Box Section
Channel Section
Tubular Section
� Box Section: It provides the good resistance to both bending and Torsion and it is used in short
members of the frame.
Channel Section: It provides the good resistance to bending and it is used in long members of the
frame.
Tubular Section: It provides the good resistance to torsion and it is used in these days in three
wheelers, scooters, matadors and in Pickup Trucks.
Conclusion: Students will have to write this
Related Questions:
1) What are the functions are served by the Vehicle Body Frame?
2) What are the differences between Ladder Frame and Monocoque Frame?
3) What are the advantages and disadvantages of Ladder Frame, Tubular space Frame,
Monocoque Frame and Backbone Frame?
4) Why two symmetrical channels are used in Ladder Frame?