Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arm Embedded Systems & Arm Processor Fundamentals: Microprocessors Versus Microcontrollers
Uploaded by
Shresth sahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arm Embedded Systems & Arm Processor Fundamentals: Microprocessors Versus Microcontrollers
Uploaded by
Shresth sahCopyright:
Available Formats
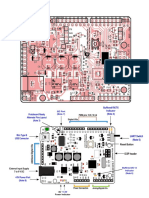
MODULE – 1
ARM EMBEDDED SYSTEMS & ARM PROCESSOR FUNDAMENTALS
MICROPROCESSORS versus MICROCONTROLLERS:
A microprocessor is an electronic component that is used by a computer to do its work. It is a
central processing unit on a single integrated circuit chip containing millions of very small
components including transistors, resistors, and diodes that work together.
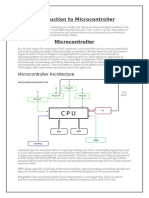
A microcontroller is a compact integrated circuit designed to govern a specific operation in an
embedded system. A typical microcontroller includes a processor, memory and input/output (I/O)
peripherals on a single chip.
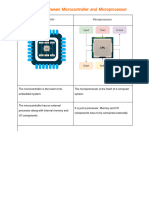
Microprocessors Microcontrollers
Microprocessors generally does not have RAM, Microcontroller is ‘all in one’ processor, with
ROM and I/O pins. RAM, I/O ports, all on the chip.
Microprocessors usually use its pins as a bus to Controlling bus is internal and not available to
interface to RAM, ROM, and peripheral the board designer.
the controlling bus is
devices. Hence,
expandable at the board level.
Microprocessors are generally capable of being Microcontrollers are usually used for more
built into bigger general purpose applications. dedicated applications.
Microprocessors, generally do not have power Microcontrollers have power saving system,
saving system. like idle mode or power saving; mode so
overall it uses less power.
The overall cost of systems made with Microcontrollers are made by using
Microprocessors is high, because of the high complementary metal oxide semiconductor
number of external components required. technology; so they are far cheaper than
Microprocessors.
Processing speed of general microprocessors is Processing speed of Microcontrollers is about 8
above 1 GHz; so it works much faster than MHz to 50 MHz.
Microcontrollers.
Microprocessors are based on von-Neumann Microcontrollers are based on Harvard
model; where, program and data are stored in architecture; where, program memory and data
same memory module. memory are separate.
You might also like
- Lecture-2 - Microprocessor & ControllersDocument7 pagesLecture-2 - Microprocessor & ControllersVivekananda BtechNo ratings yet
- Sub: Microcontrollers (18ECC21) Microprocessors Vs Microcontrollers S.no. Microprocessor MicrocontrollerDocument1 pageSub: Microcontrollers (18ECC21) Microprocessors Vs Microcontrollers S.no. Microprocessor MicrocontrollerrevanthNo ratings yet
- Embedded (Practical)Document18 pagesEmbedded (Practical)Devika KachhawahaNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument27 pagesEmbedded Systemsnavneet100% (1)
- Unit 2 - Learning MaterailDocument52 pagesUnit 2 - Learning MaterailPILLARISETTY KARTHIK 2021-CSE UGNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument5 pagesDifference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerAngel CatangayNo ratings yet
- MP Vs MCDocument6 pagesMP Vs MCAyushi SavaniNo ratings yet
- Embedded System NotesDocument66 pagesEmbedded System NotesChetnaNo ratings yet
- Micro 1Document8 pagesMicro 1Zuhaib AyazNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors Microcontrollers: Cisc RiscDocument3 pagesMicroprocessors Microcontrollers: Cisc RiscSyed HussainNo ratings yet
- CSC 101 (3) Sa 37870Document3 pagesCSC 101 (3) Sa 37870Bohtyar KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-v3 ARM - 3Document35 pagesChapter 1-v3 ARM - 3Weehao SiowNo ratings yet
- EEAC 110 Learning Material 1Document11 pagesEEAC 110 Learning Material 1Krizel Joyce C. NullarNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Programming: Prof. Dr. Hassan AlansaryDocument10 pagesEmbedded Systems Programming: Prof. Dr. Hassan AlansaryAbdallah AdelNo ratings yet
- PDR - Unit IDocument16 pagesPDR - Unit IMUKILANNo ratings yet
- Real Mode MicroprocessorDocument3 pagesReal Mode MicroprocessorSaqib RaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrocontrollerDocument5 pagesIntroduction To MicrocontrollerSongNo ratings yet
- 1 Course Material - All Chapter 04-01-2024Document148 pages1 Course Material - All Chapter 04-01-2024RU MATH GamerNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Overview of Embedded Systems Characteristics of Embedded SystemsDocument51 pagesUnit - I Overview of Embedded Systems Characteristics of Embedded SystemsKushal RajvanshiNo ratings yet
- DR Somashekhar: Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai - 600 036Document16 pagesDR Somashekhar: Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai - 600 036Gunjan MudgalNo ratings yet
- MP Vs MC 111Document2 pagesMP Vs MC 111Ali ZahidNo ratings yet
- Micro Controller:: Applications of MicrocontrollersDocument3 pagesMicro Controller:: Applications of MicrocontrollersLokesh DahiyaNo ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller Hardware: 128 Addressable BitsDocument6 pages8051 Microcontroller Hardware: 128 Addressable BitsTakbir mahmudNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document18 pagesModule 1Rohit AnejaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - L Notes - Introduction To MicrocontrollerDocument53 pagesUnit 4 - L Notes - Introduction To MicrocontrollerAKSHANSH MATHUR100% (1)
- 5-Microcontrollers 8051Document8 pages5-Microcontrollers 8051Dhiraj ShahNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Microcontroller and MicroprocessorDocument2 pagesDifference Between Microcontroller and MicroprocessorSanjay ParelkarNo ratings yet
- Basics of MicrocontrollerDocument11 pagesBasics of Microcontrollerpavi1402No ratings yet
- Microprocessor Part2Document84 pagesMicroprocessor Part2مهند عدنان الجعفريNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Understanding The Concept of Microprocessor and MicrocomputerDocument5 pagesChapter 1 - Understanding The Concept of Microprocessor and MicrocomputerFaizur FarihaNo ratings yet
- Micro-Controller: Embedded: Designing & Programming Using ArduinoDocument18 pagesMicro-Controller: Embedded: Designing & Programming Using ArduinoSatyjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- VBNVCBNBVNDocument16 pagesVBNVCBNBVNGunjan MudgalNo ratings yet
- PIC16F877A DocDocument41 pagesPIC16F877A DocKamal Ra JNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesDifference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerMOUNI VARMANo ratings yet
- Benm 2123 Microprocessor Technology: Chapter 1: Introduction To MicroprocessorDocument24 pagesBenm 2123 Microprocessor Technology: Chapter 1: Introduction To MicroprocessorDeva RaguNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Vs MicrocontrollersDocument5 pagesMicroprocessor Vs MicrocontrollersRamesh KesavanNo ratings yet
- Mpi Unit 1Document27 pagesMpi Unit 1godhanipriyank8No ratings yet
- Zeeshan Ahmed WarraichDocument10 pagesZeeshan Ahmed Warraich5682 AatqaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument25 pagesMicroprocessor and MicrocontrollerHafizuddin Mohamad100% (1)
- Assignment 1 ESMP: Syed Nouman Zaidi L1f08bscs2074Document5 pagesAssignment 1 ESMP: Syed Nouman Zaidi L1f08bscs2074Syed AtharNo ratings yet
- MPU & MCU 8 X Lessons NotesDocument233 pagesMPU & MCU 8 X Lessons NotesserjaniNo ratings yet
- Nptel - Ac.in Aeronautical Microprocessors and Software Engineering FinalDocument148 pagesNptel - Ac.in Aeronautical Microprocessors and Software Engineering FinalMani KumarNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesFrom EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Interfacing TechniquesDocument17 pagesMicroprocessor Interfacing TechniquesAbdul Rehman KhanNo ratings yet
- MP Vs MC - InterviewDocument2 pagesMP Vs MC - InterviewProf.Monika JainNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Vs MicrocontrollerDocument8 pagesMicroprocessor Vs MicrocontrollerMohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument72 pagesUnit Ivfishatsion09No ratings yet
- Microcontroller 8051 NotesDocument17 pagesMicrocontroller 8051 NotesPretty FibberNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors NotesDocument65 pagesMicroprocessors NoteswizardvenkatNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineering B.E III Year Embedded Systems: Unit-TWO Microcontroller and Programming Lesson - 1Document18 pagesBiomedical Engineering B.E III Year Embedded Systems: Unit-TWO Microcontroller and Programming Lesson - 1REKHA SENCHA gs0801bm161043No ratings yet
- Microcontroller - Wikipedia..Document7 pagesMicrocontroller - Wikipedia..452bobNo ratings yet
- Unit 1B Typical Emb SysDocument52 pagesUnit 1B Typical Emb SysNandan BallaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrocontrollersDocument13 pagesIntroduction To MicrocontrollerssvirkomartinkoNo ratings yet
- Types of IcDocument2 pagesTypes of IcEdbert CatapangNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv: Intel 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument42 pagesUnit-Iv: Intel 8051 MicrocontrollerAtchut MarleyNo ratings yet
- 3 MicrocontrollersDocument28 pages3 MicrocontrollersRynefel ElopreNo ratings yet
- 1 AlDocument10 pages1 Aleba girmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microprocessor MicroprocessorDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Microprocessor MicroprocessorAltayeb AbdulhameedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Embedded Systems ByshibukvDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Embedded Systems ByshibukvNyein NyeinNo ratings yet
- Implement Canny Edge Detector in Python Using OpenCVDocument13 pagesImplement Canny Edge Detector in Python Using OpenCVShresth sahNo ratings yet
- Apurv SBDocument16 pagesApurv SBShresth sahNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: Jnana Sangama, Belagavi-590018Document11 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: Jnana Sangama, Belagavi-590018Shresth sahNo ratings yet
- Ball Tracking SystemDocument13 pagesBall Tracking SystemShresth sahNo ratings yet