Professional Documents
Culture Documents
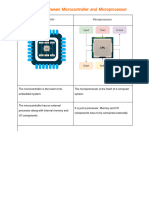
Sub: Microcontrollers (18ECC21) Microprocessors Vs Microcontrollers S.no. Microprocessor Microcontroller
Uploaded by
revanth0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageMicrocontrollers are used in embedded systems while microprocessors are used in general purpose computers. Microcontrollers have a processor, memory, and I/O components integrated on a single chip, making the circuit smaller and less expensive than a microprocessor system. Microcontrollers are commonly used in devices that run on batteries like MP3 players and washing machines due to their low power consumption.
Original Description:
Original Title
MPVSMC.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMicrocontrollers are used in embedded systems while microprocessors are used in general purpose computers. Microcontrollers have a processor, memory, and I/O components integrated on a single chip, making the circuit smaller and less expensive than a microprocessor system. Microcontrollers are commonly used in devices that run on batteries like MP3 players and washing machines due to their low power consumption.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageSub: Microcontrollers (18ECC21) Microprocessors Vs Microcontrollers S.no. Microprocessor Microcontroller
Uploaded by
revanthMicrocontrollers are used in embedded systems while microprocessors are used in general purpose computers. Microcontrollers have a processor, memory, and I/O components integrated on a single chip, making the circuit smaller and less expensive than a microprocessor system. Microcontrollers are commonly used in devices that run on batteries like MP3 players and washing machines due to their low power consumption.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Sub: Microcontrollers (18ECC21)
Microprocessors vs Microcontrollers
S.no. Microprocessor Microcontroller
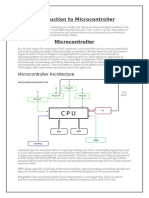
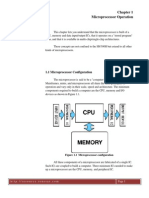
1. Microprocessor is the heart of Computer Micro Controller is the heart of an
system. embedded system.
2. It is only a processor, so memory and I/O Micro Controller has a processor along
components need to be connected with internal memory and I/O
externally components.
3. Memory and I/O has to be connected Memory and I/O are already present, and
externally, so the circuit becomes large. the internal circuit is small.
4.
You can’t use it in compact systems You can use it in compact systems.
5.
Cost of the entire system is high Cost of the entire system is low
6. Due to external components, the total As external components are low, total
power consumption is high. Therefore, it power consumption is less. So it can be
is not ideal for the devices running on used with devices running on stored
stored power like batteries. power like batteries.
7. Most of the microprocessors do not have Most of the microcontrollers offer
power saving features. power-saving mode.
8. It is used mainly in a washing machine,
It is mainly used in personal computers.
MP3 players, and embedded systems.
9. Microprocessor has a smaller number of
Microcontroller has more register. Hence
registers, so more operations are
the programs are easier to write.
memory-based.
10. Microprocessors are based on Von Micro controllers arc based on Harvard
Neumann model architecture
11. It is a by-product of the development of
It is a central processing unit on a single
microprocessors with a CPU along with
silicon-based integrated chip.
other peripherals.
12. It has a CPU along with RAM, ROM, and
It has no RAM, ROM, Input-Output units,
other peripherals embedded on a single
timers, and other peripherals on the chip.
chip.
13. It uses an external bus to interface to
It uses an internal controlling bus.
RAM, ROM, and other peripherals.
14. Microprocessor-based systems can run at Microcontroller based systems run up to
a very high speed because of the 200MHz or more depending on the
technology involved. architecture.
15. It’s used for general purpose
applications that allow you to handle It’s used for application-specific systems.
loads of data.
16. It’s complex and expensive, with a large It’s simple and inexpensive with less
number of instructions to process. number of instructions to process.
You might also like
- How A CPU WorksDocument11 pagesHow A CPU Workshwa890No ratings yet
- Microprocessor System Syllabus OBEDocument7 pagesMicroprocessor System Syllabus OBEGilCuajuncoNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors Vs MicrocontrollersDocument40 pagesMicroprocessors Vs MicrocontrollersNgaa SiemensNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument25 pagesMicroprocessor and MicrocontrollerHafizuddin Mohamad100% (1)
- Intel Case StudyDocument19 pagesIntel Case StudyJonathan100% (1)
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesFrom EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesNo ratings yet
- Soal Try Out BHS Inggris Paket ADocument12 pagesSoal Try Out BHS Inggris Paket AMuhamad Tikal KartikalNo ratings yet
- CSC 101 (3) Sa 37870Document3 pagesCSC 101 (3) Sa 37870Bohtyar KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 - Microprocessor & ControllersDocument7 pagesLecture-2 - Microprocessor & ControllersVivekananda BtechNo ratings yet
- Difference Between MP&MC and C&Embedded - CDocument4 pagesDifference Between MP&MC and C&Embedded - ChrishipisalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Learning MaterailDocument52 pagesUnit 2 - Learning MaterailPILLARISETTY KARTHIK 2021-CSE UGNo ratings yet
- Arm Embedded Systems & Arm Processor Fundamentals: Microprocessors Versus MicrocontrollersDocument34 pagesArm Embedded Systems & Arm Processor Fundamentals: Microprocessors Versus MicrocontrollersShresth sahNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Vs MicrocontrollerDocument8 pagesMicroprocessor Vs MicrocontrollerMohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- MP Vs MCDocument6 pagesMP Vs MCAyushi SavaniNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Microcontroller and MicroprocessorDocument2 pagesDifference Between Microcontroller and MicroprocessorSanjay ParelkarNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument5 pagesDifference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerAngel CatangayNo ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller Hardware: 128 Addressable BitsDocument6 pages8051 Microcontroller Hardware: 128 Addressable BitsTakbir mahmudNo ratings yet
- Embedded System NotesDocument66 pagesEmbedded System NotesChetnaNo ratings yet
- Real Mode MicroprocessorDocument3 pagesReal Mode MicroprocessorSaqib RaoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Introduction To Embedded SystemsDocument23 pagesUnit - 1 Introduction To Embedded Systemssrinivasarao vuppanapalliNo ratings yet
- Embedded (Practical)Document18 pagesEmbedded (Practical)Devika KachhawahaNo ratings yet
- Micro-Controller: Embedded: Designing & Programming Using ArduinoDocument18 pagesMicro-Controller: Embedded: Designing & Programming Using ArduinoSatyjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- VBNVCBNBVNDocument16 pagesVBNVCBNBVNGunjan MudgalNo ratings yet
- DR Somashekhar: Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai - 600 036Document16 pagesDR Somashekhar: Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai - 600 036Gunjan MudgalNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesDifference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerMOUNI VARMANo ratings yet
- 1 Course Material - All Chapter 04-01-2024Document148 pages1 Course Material - All Chapter 04-01-2024RU MATH GamerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-v3 ARM - 3Document35 pagesChapter 1-v3 ARM - 3Weehao SiowNo ratings yet
- About MicrocontrollerDocument18 pagesAbout MicrocontrollerPrakhar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Pic 16f84a ManualDocument62 pagesPic 16f84a ManualjpatrNo ratings yet
- Difference in MP & MCDocument1 pageDifference in MP & MCvirendra.aryaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Vs MicrocontrollersDocument5 pagesMicroprocessor Vs MicrocontrollersRamesh KesavanNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Programming: Prof. Dr. Hassan AlansaryDocument10 pagesEmbedded Systems Programming: Prof. Dr. Hassan AlansaryAbdallah AdelNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument1 pageDifference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerNeela MuraliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document24 pagesChapter 2wondimu bantihunNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument27 pagesEmbedded Systemsnavneet100% (1)
- Micro-Controller Basics 1: Nasif MDocument24 pagesMicro-Controller Basics 1: Nasif MMd.Rakibul IslamNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Overview of Embedded Systems Characteristics of Embedded SystemsDocument51 pagesUnit - I Overview of Embedded Systems Characteristics of Embedded SystemsKushal RajvanshiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrocontrollerDocument5 pagesIntroduction To MicrocontrollerSongNo ratings yet
- Topic 1-Intro To Es - Part 1Document39 pagesTopic 1-Intro To Es - Part 1hadimustaffa00No ratings yet
- 00 Lec 1Document11 pages00 Lec 1fatima20031014ailNo ratings yet
- Giao Trinh He Thong Nhung - VDK H8Document193 pagesGiao Trinh He Thong Nhung - VDK H8gaikieuucNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Overview of Mechatronics: Lesson 1: Microcontrollers, Microprocessors, and Embedded ComputersDocument18 pagesModule 1: Overview of Mechatronics: Lesson 1: Microcontrollers, Microprocessors, and Embedded ComputersCerealNo ratings yet
- EEAC 110 Learning Material 1Document11 pagesEEAC 110 Learning Material 1Krizel Joyce C. NullarNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller VS MicroprocessorDocument3 pagesMicrocontroller VS MicroprocessorSuryaCharanPaidipalliNo ratings yet
- MP Vs MC 111Document2 pagesMP Vs MC 111Ali ZahidNo ratings yet
- 5-Microcontrollers 8051Document8 pages5-Microcontrollers 8051Dhiraj ShahNo ratings yet
- Intro - Embedded SystremsDocument15 pagesIntro - Embedded SystremsDr-Samson ChepuriNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors Microcontrollers: Cisc RiscDocument3 pagesMicroprocessors Microcontrollers: Cisc RiscSyed HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Microcomputer System - Peripheral DesignDocument70 pagesChapter 1 Microcomputer System - Peripheral DesignJevithaNo ratings yet
- Abraham Microprocessor - 084452Document4 pagesAbraham Microprocessor - 084452RICHARD OTIENONo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Embedded System and Pic Programming in C: Learning OutcomesDocument33 pages1 Introduction To Embedded System and Pic Programming in C: Learning OutcomesAlya SyakirahNo ratings yet
- Arm Processor: by Neha Dewangan Guest Faculty Sos in Electronics & Photonics, PrsuDocument14 pagesArm Processor: by Neha Dewangan Guest Faculty Sos in Electronics & Photonics, PrsuNeha DewanganNo ratings yet
- PDR - Unit IDocument16 pagesPDR - Unit IMUKILANNo ratings yet
- Micro 1Document8 pagesMicro 1Zuhaib AyazNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor V/s Micro ControllerDocument2 pagesMicroprocessor V/s Micro ControllerMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Basics of MicrocontrollerDocument11 pagesBasics of Microcontrollerpavi1402No ratings yet
- Home AutomationDocument54 pagesHome AutomationSmartselect ShyamlaNo ratings yet
- ES QA NotesDocument91 pagesES QA NotesPratik PatilNo ratings yet
- Lec (1) Microprocessor Applications: Lecturer: Arwa Alaaeldin Mursi Elamin 2020Document19 pagesLec (1) Microprocessor Applications: Lecturer: Arwa Alaaeldin Mursi Elamin 2020abdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- 1.new - Introducing Embedded Systems and The MicrocontrollersDocument23 pages1.new - Introducing Embedded Systems and The MicrocontrollersBlaser TacticalNo ratings yet
- PIC16F877A DocDocument41 pagesPIC16F877A DocKamal Ra JNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Micro ControllerDocument1 pageMicroprocessor Micro ControllerKarthik MurganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1Arpana B MNo ratings yet
- 00 2Document25 pages00 2أمير سليمان Amir solimanNo ratings yet
- Physical Computing: Exploring Computer Vision in Physical ComputingFrom EverandPhysical Computing: Exploring Computer Vision in Physical ComputingNo ratings yet
- "Introduction To PIC MCU": AV-314 Digital Systems-Embedded SystemDocument15 pages"Introduction To PIC MCU": AV-314 Digital Systems-Embedded SystemMuhammad EhtishamNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Subhradeep Mitra & Debanjan MukherjeeDocument32 pagesPresented By: Subhradeep Mitra & Debanjan MukherjeeAkhilesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller 8051Document72 pagesMicrocontroller 8051vaibhav sharmaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Introduction To The Microprocessor and ComputerDocument154 pagesCHAPTER 1 Introduction To The Microprocessor and ComputerMira AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 06 Lab Mp2 Microprocessor ApplicationsDocument3 pages06 Lab Mp2 Microprocessor ApplicationsGulbanu KarimovaNo ratings yet
- MP Vs MCDocument6 pagesMP Vs MCAyushi SavaniNo ratings yet
- MPI Unit 1Document26 pagesMPI Unit 1Dishant RathiNo ratings yet
- HMC+and+Firmware+AIX+VUG Feb+2011Document99 pagesHMC+and+Firmware+AIX+VUG Feb+2011myssa91No ratings yet
- 8086 Microprocesser InstructionsDocument22 pages8086 Microprocesser InstructionsSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- 1Document43 pages1Geonell AgustinNo ratings yet
- Sisteme Integrate Ver4Document129 pagesSisteme Integrate Ver4Adrian-Laurențiu RădulescuNo ratings yet
- Cpu2006 20170626 47262Document5 pagesCpu2006 20170626 47262ll_lvl4st3r_llNo ratings yet
- Science and Research Policy at The End of Moore'S Law: PerspectiveDocument8 pagesScience and Research Policy at The End of Moore'S Law: PerspectiveMd Zawadul IslamNo ratings yet
- 195Document11 pages195sabatino123No ratings yet
- Tech Guide 1 Hardware: TG1.1 Components of A Computer SystemDocument25 pagesTech Guide 1 Hardware: TG1.1 Components of A Computer SystemmwandidaNo ratings yet
- Motorola MPX5010DPIntegrated Pressure Sensor DatasheetDocument10 pagesMotorola MPX5010DPIntegrated Pressure Sensor DatasheetdimasrenatoNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki VishwavidyalayaDocument2 pagesRajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki VishwavidyalayaDinesh NagarNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Protocol StackDocument24 pagesBluetooth Protocol StackCuong PhamNo ratings yet
- Viva Questions For MP LabDocument9 pagesViva Questions For MP LabMithun MohanNo ratings yet
- MPMCDocument10 pagesMPMCrs newNo ratings yet
- Apple CaseDocument13 pagesApple Casevinayak nNo ratings yet
- 1 Embedded SystemsDocument24 pages1 Embedded SystemsRoopesh BadalaNo ratings yet
- Rotary Screw Compressor Units: "Mini" Microprocessor ControlDocument20 pagesRotary Screw Compressor Units: "Mini" Microprocessor ControlChrise5502No ratings yet
- BDocument19 pagesBHareesh HarshaNo ratings yet
- What Is An MCU? SCM Is Going To Be Out of Date?Document15 pagesWhat Is An MCU? SCM Is Going To Be Out of Date?mengxiangNo ratings yet