Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul Digital 10b SPS-hedy-Tapis Pasif Analog
Uploaded by
Ade Maulana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pages1. Band-pass filters pass all frequencies within a band between a lower cutoff frequency (fc1) and upper cutoff frequency (fc2), attenuating frequencies outside the band. The bandwidth is defined as fc2 - fc1.
2. Band-stop filters reject all frequencies within a band between a lower (fc1) and upper (fc2) cutoff frequency, passing frequencies outside the band.
3. An example band-pass filter with a center frequency of 15kHz and bandwidth of 1kHz has a quality factor (Q) of 15, making it a narrow-band filter. If the Q was doubled, the bandwidth would be halved.
Original Description:
Original Title
Modul Digital 10b SPS-hedy-Tapis pasif analog
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Band-pass filters pass all frequencies within a band between a lower cutoff frequency (fc1) and upper cutoff frequency (fc2), attenuating frequencies outside the band. The bandwidth is defined as fc2 - fc1.
2. Band-stop filters reject all frequencies within a band between a lower (fc1) and upper (fc2) cutoff frequency, passing frequencies outside the band.
3. An example band-pass filter with a center frequency of 15kHz and bandwidth of 1kHz has a quality factor (Q) of 15, making it a narrow-band filter. If the Q was doubled, the bandwidth would be halved.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesModul Digital 10b SPS-hedy-Tapis Pasif Analog
Uploaded by
Ade Maulana1. Band-pass filters pass all frequencies within a band between a lower cutoff frequency (fc1) and upper cutoff frequency (fc2), attenuating frequencies outside the band. The bandwidth is defined as fc2 - fc1.
2. Band-stop filters reject all frequencies within a band between a lower (fc1) and upper (fc2) cutoff frequency, passing frequencies outside the band.
3. An example band-pass filter with a center frequency of 15kHz and bandwidth of 1kHz has a quality factor (Q) of 15, making it a narrow-band filter. If the Q was doubled, the bandwidth would be halved.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1
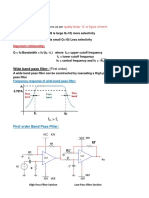
X. TAPIS PASIF ANALOG
10.3. Band-pass Filters
• All frequencies lying within a band between a lower (fc1) and upper (fc2) frequency limit are
passed.
• All other frequencies outside band (lower or upper) are significantly attenuated.
• Bandwidth (BW) is defined as (BW=fc2 - fc1).
• Center Frequency (f0): the geometric mean of cut-off frequencies, center frequency of pass
band.
• Quality Factor (Q): Ratio of f0 with bandwidth (BW)= f0/BW.
• Q determines selectivity of a filter: Higher value of Q shows better selectivity and narrow
bandwidth for a given f0.
• Band-pass => Narrow band (Q>10); Wide-band (Q<10).
• Cut-off frequencies are always at -3dB or 70.7%.
• Example: if a band-pass filter is required across center frequency of 15kHz with bandwidth
(BW=1kHz), what is its Q factor?.
Figure 6.14.
• Q=fo/BW = 15k/1k = 15.
• Thus, it’s a narrow-band filter.
• What will be BW if Q is doubled?.
9.4. Band-stop Filters
• All frequencies lying within a band between a lower (fc1) and upper (fc2) frequency limit are
rejected.
• All other frequencies outside band (lower or upper) are passed.
• Bandwidth (BW) is defined as (BW=fc2 - fc1).
(Hedy Aditya Baskhara).
2
Figure 6.15.
(Hedy Aditya Baskhara).
You might also like
- Chapter 5 Active FilterDocument55 pagesChapter 5 Active Filterlutfi sulthonNo ratings yet
- Filters QCMDocument15 pagesFilters QCMMary-Joe SemaaniNo ratings yet
- Signal Conditioning FiltersDocument41 pagesSignal Conditioning FiltersSaleem Haddad100% (1)
- Active FiltersDocument11 pagesActive FiltersJean Paul RousselinNo ratings yet
- Active FilterDocument55 pagesActive FilterEdgar PeninsulaNo ratings yet
- SPECAIAL NOTES ON ACTIVE - FILTERS CoepDocument29 pagesSPECAIAL NOTES ON ACTIVE - FILTERS Coeponkarsinare1No ratings yet
- Active FiltersDocument31 pagesActive FiltersAbdirahman Elmi GureNo ratings yet
- Electronics - Ii: Active FilterDocument55 pagesElectronics - Ii: Active FilterASD DSANo ratings yet
- Engineering Electronics & Design ميمصتو ةيسدنه تاينورتكلا: Dr. Mugahid Omer HajeltoumDocument36 pagesEngineering Electronics & Design ميمصتو ةيسدنه تاينورتكلا: Dr. Mugahid Omer Hajeltoumأبو هشامNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics 1: Active FiltersDocument17 pagesAnalog Electronics 1: Active FiltersAnonymous elrSyA30No ratings yet
- 4 Am ReceiverDocument8 pages4 Am Receivermohammed229No ratings yet
- Filter PDFDocument21 pagesFilter PDFNugraha PratamaNo ratings yet
- Rangkaian Filter 1Document14 pagesRangkaian Filter 1Fathur RizkyNo ratings yet
- New Active FiltersDocument73 pagesNew Active FiltersPradip GhorpadeNo ratings yet
- Notch FilterDocument2 pagesNotch Filterlmorales74No ratings yet
- Active Filter (Part 1)Document40 pagesActive Filter (Part 1)Vickneswaran KalerwananNo ratings yet
- EE303Sp09 L05 FiltersDocument23 pagesEE303Sp09 L05 FiltersAzul NogalesNo ratings yet
- QualityFactor For A DigitalFilter NSPDocument6 pagesQualityFactor For A DigitalFilter NSPAnonymous O5byxZ29fbNo ratings yet
- Op Amps27Document1 pageOp Amps27lecuellarq85gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Filters TypesDocument27 pagesFilters TypesRyan SomervilleNo ratings yet
- Active Filter by Floyd 2021pptorigDocument48 pagesActive Filter by Floyd 2021pptorigEos BanaNo ratings yet
- Active Filter (Slide)Document24 pagesActive Filter (Slide)ASD DSANo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Active-FiltersDocument39 pagesChapter 6 Active-FiltersIs Mohd100% (1)
- Chapter 15Document10 pagesChapter 15Yug VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Active Band Stop Filter-1Document13 pagesActive Band Stop Filter-1nutanpimpalkar150No ratings yet
- Filter LicDocument37 pagesFilter LicSamadhan ThokalNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - Active FilterDocument84 pagesCH 3 - Active FilterNURUL NADHIRAH ROSDINo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document30 pagesLecture 7Martian 07No ratings yet
- Elp 311Document9 pagesElp 311Srijan SinghNo ratings yet
- Band Pass Filtersstudents PDFDocument6 pagesBand Pass Filtersstudents PDFRajesh KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- Butter Worth Filter DesignDocument4 pagesButter Worth Filter DesignCan ÇamlıkNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Active FiltersDocument41 pagesUnit-5 Active FiltersAnvesh MagantiNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 5 - (Filter) StudentDocument79 pagesTOPIC 5 - (Filter) StudentAR de SouzaNo ratings yet
- PART 4-Elec Buk (Final)Document18 pagesPART 4-Elec Buk (Final)Mizhar Layosa GerardoNo ratings yet
- Active Lowpass, Highpass and BandpassDocument5 pagesActive Lowpass, Highpass and BandpassSANNo ratings yet
- D98e11b2 1639639863331Document75 pagesD98e11b2 1639639863331Ashish kumarNo ratings yet
- ADC Lab3 PDFDocument11 pagesADC Lab3 PDFFarhan NitrateNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan FIlter AktifDocument19 pagesPengenalan FIlter Aktifade yulianiNo ratings yet
- Cycle 2 Second HalfDocument8 pagesCycle 2 Second HalfNithyashree MNo ratings yet
- Filters (Autosaved)Document93 pagesFilters (Autosaved)Madipelli HimaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment #4-Active Filters: Hands-On RadioDocument2 pagesExperiment #4-Active Filters: Hands-On RadiomathurashwaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 FiltersDocument74 pagesUnit 5 FiltersAbhishek YadavNo ratings yet
- Below Frequency Response of A 2nd Order Band Pass FilterDocument11 pagesBelow Frequency Response of A 2nd Order Band Pass FilterNurul FathiaNo ratings yet
- LIC Bandpass BandrejectDocument6 pagesLIC Bandpass BandrejectNikhil AsraniNo ratings yet
- ADC Lab 2Document6 pagesADC Lab 2Danish Habib Habib MasihNo ratings yet
- (MRK) Active Filter Design PDFDocument130 pages(MRK) Active Filter Design PDFDharmveer ModiNo ratings yet
- Band Pass FiltersDocument5 pagesBand Pass FiltersHeraNo ratings yet
- Electronics Exp 8Document24 pagesElectronics Exp 8Mohammad NamiqNo ratings yet
- Basic Opamp ApplicationsDocument10 pagesBasic Opamp ApplicationsNorbertNo ratings yet
- EE301 Electronic Circuit Chapter 5 - FILTERSDocument48 pagesEE301 Electronic Circuit Chapter 5 - FILTERSWann Fariera100% (4)
- FiltersDocument28 pagesFiltersAiza GhanchiNo ratings yet
- Experiment RC FiltersDocument11 pagesExperiment RC FiltersingeniouNo ratings yet
- Lab CircuitDocument7 pagesLab Circuit201012No ratings yet
- Active Filters StudyDocument19 pagesActive Filters StudyTo Dinh DuNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (B) Active FiltersDocument24 pagesModule 4 (B) Active Filterskaranphutane2254No ratings yet
- Filters in Control Systems: Figure 1 Passive Low-Pass Filter Circuit DiagramDocument5 pagesFilters in Control Systems: Figure 1 Passive Low-Pass Filter Circuit Diagramahmet şahinNo ratings yet
- What Is A FilterDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Filtermuhammad irfanNo ratings yet
- 2-RC Filter Circuits and LCR Resonance CircuitsDocument13 pages2-RC Filter Circuits and LCR Resonance CircuitsaxelNo ratings yet
- Chebyshev Stepped Impedance Filter: BW W W W W WDocument3 pagesChebyshev Stepped Impedance Filter: BW W W W W WALEX_125No ratings yet