Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Proceso de La Motivación en Las Organizaciones
Uploaded by
Armand IAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Proceso de La Motivación en Las Organizaciones
Uploaded by
Armand IACopyright:
Available Formats
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning
experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
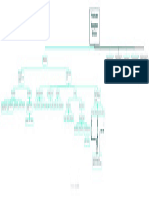
Satisfaction with Perceived Search for Turnover
Experience
Past Performance Personal Inputs Better Job Absenteeism
Self-esteem Effort-performance Perceived
Self-efficacy Expectancy Inputs and Lowered
Outcomes of Job
Attractiveness
Skill Training Referent Others Dissatisfaction
of Job
Communication Effort Age
Actual Situation
from Others Ability Seniority
Psychological Arousal Education
Attention Organizational Psychological
Perceived Amount Consider:
Persistence Loyalty Withdrawal
that Rewards 1. Changing Future
Attractiveness of Past Performance Poor Physical
Performance-outcome Should Be Performance
Outcomes Health
Expectancy 2. Strike
(valence) Poor Mental
3. Grievance
Health
Level of Job
Difficulty Perceived Job
Timespan Characteristics
Personal Goals,
Responsibility
Values, Attitudes,
and Needs if
Intrinsic Equity dissatisfied
Internal vs. External Rewards Determination
Locus of Control
Goal Characteristics:
difficulty
specificity Organizational Perceived Redefined Tasks Present
Organizational Organizational Perceived Overall
intensity Requirements on Requirements from Organization Work Behavior Performance Facet Satisfaction
Needs and Goals Resources Rewards Satisfaction
acceptance Individual from Organization and Person (Accomplishment)
commitment
Degree of Goal
Job Design (autonomy and feedback) Extrinsic Accomplishment
Decision acceptance and ownership Rewards
Leadership Style Perceived Outcomes
Group Relations of Referent Others
Pay and Promotions
Rewards and Punishments
CHAPTER 18 • Employee Motivation
KEY (only primary aspects highlighted; overlaps exist):
Expectancy Reinforcement Satisfaction
Goal Theory Need Theory
Theory Theory
Equity Theory
Relationships
Main process—“performance properly rewarded leads to satisfaction”
FIGURE 18.10 The motivation process in organizations.
Based on E. E. Lawler, III, Motivation in Work Organizations (Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole, 1973); E. A. Locke and G. P. Latham, Goal Setting: A Motivational Technique that Works! (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1984); L. W. Porter,
E. E. Lawler, III, and J. R. Hackman, Behavior in Organizations (NY McGraw-Hill, 1975); Van Fleet, D. D. & Peterson, T. O. Contemporary Management, 3rd ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 1994); Van Fleet, D. D. Behavior in Organizations, Boston:
Houghton Mifflin, 1991; and Van Fleet, D. D., “The individual, the organization, and motivation: propositions, proposals, and implications”; In D. F. Ray & T. B. Green (eds.), Managing the Changing Organization (Atlanta: Southern Management
Association, November, 1974), 169–176.
385
You might also like
- Balance Sheet Eng 05-06Document1 pageBalance Sheet Eng 05-06sashdreamNo ratings yet
- Performance Manage MenDocument1 pagePerformance Manage MenmariaaltammamNo ratings yet
- Maintain Safe Work EnvironmentDocument3 pagesMaintain Safe Work EnvironmentSana buttNo ratings yet
- Module 2 AssessmentDocument3 pagesModule 2 AssessmentSheela AliNo ratings yet
- STUDENT GUIDE FOR COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING NC IIDocument11 pagesSTUDENT GUIDE FOR COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING NC IIAireen Letana SiagaNo ratings yet
- Value-Map TM DeloitteDocument1 pageValue-Map TM DeloitteHugo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Exalted 3rd Edition Charm Cascades Legend: Any Five Essence 2+ Performance Charms ???Document1 pageExalted 3rd Edition Charm Cascades Legend: Any Five Essence 2+ Performance Charms ???merashinNo ratings yet
- Deloitte Wireless Industry Value MapDocument1 pageDeloitte Wireless Industry Value MapDiogo Pimenta Barreiros0% (1)
- Group Performance CHPT 13Document1 pageGroup Performance CHPT 13Şterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Report Akreditasi Batch Mbt in Branch Batch 124 2024-04-04 08 48 26Document2 pagesReport Akreditasi Batch Mbt in Branch Batch 124 2024-04-04 08 48 26Muhammad Agung PratamaNo ratings yet
- Ag2018 GBK Aqu 100 V3Document1 pageAg2018 GBK Aqu 100 V3Event Safety Management ServiceNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Services Jobs and Skills by LocationDocument6 pagesInfrastructure Services Jobs and Skills by LocationtarunmduNo ratings yet
- Kanban Core Practices VisualizedDocument1 pageKanban Core Practices VisualizedRodrigo PintoNo ratings yet
- Consolidado de Notas - Secundaria: Eddy Iv BimestreDocument2 pagesConsolidado de Notas - Secundaria: Eddy Iv BimestreEmprendedores Del FuturoNo ratings yet
- Struktur Harvesting Per 18 Nov 2021 (Target Kiriman 10000 Ton)Document7 pagesStruktur Harvesting Per 18 Nov 2021 (Target Kiriman 10000 Ton)Eshika PrawitasariNo ratings yet
- HR Recruiting and Hiring WorkflowDocument1 pageHR Recruiting and Hiring WorkflowPhone SSBNo ratings yet
- Teacher Evaluation Measure T1Document2 pagesTeacher Evaluation Measure T1shehnaz khanNo ratings yet
- Issued: CARRIE DACANAY YUSON Architects Builder IncDocument1 pageIssued: CARRIE DACANAY YUSON Architects Builder IncCristinaB.DanglaCruzNo ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 5: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 5: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- (Exemplo) Matriz de Treinamento GEDocument1 page(Exemplo) Matriz de Treinamento GEpauloNo ratings yet
- Gambar Perencaan Promosindo Group Rev 1 PDFDocument54 pagesGambar Perencaan Promosindo Group Rev 1 PDFFadilah Putri100% (2)
- Reliability Web 5 Sources of Defects SecureDocument1 pageReliability Web 5 Sources of Defects SecureHaitham YoussefNo ratings yet
- Proposed 100 PE Small Sewerage Treatment SystemDocument1 pageProposed 100 PE Small Sewerage Treatment SystemArman ManNo ratings yet
- Resume File: Health Care Cert. Full-Time Part-Time Remote Worker Future HireDocument1 pageResume File: Health Care Cert. Full-Time Part-Time Remote Worker Future HireAbdullah FasehNo ratings yet
- Kurikulum Jadwal Vs Target 2018Document46 pagesKurikulum Jadwal Vs Target 2018Sidik AkbarNo ratings yet
- ITIL Edition 2011 - COBIT 5 - Mapping-22Document1 pageITIL Edition 2011 - COBIT 5 - Mapping-22Jeovanny MeraNo ratings yet
- Basic Competencies Basic CompetenciesDocument8 pagesBasic Competencies Basic CompetenciesLloydie LopezNo ratings yet
- Value TreeDocument1 pageValue TreeMaisaa NajiNo ratings yet
- Consolidado de Notas - Secundaria: Carolina Iv BimestreDocument2 pagesConsolidado de Notas - Secundaria: Carolina Iv BimestreEmprendedores Del FuturoNo ratings yet
- The Basic Balanced Scorecard TemplateDocument2 pagesThe Basic Balanced Scorecard TemplateomzoerNo ratings yet
- Simops MatrixDocument17 pagesSimops MatrixthinkpadNo ratings yet
- Purpose: IIM Sambalpur Fill RateDocument1 pagePurpose: IIM Sambalpur Fill RateKrati JainNo ratings yet
- Purpose: IIM Sambalpur Fill RateDocument1 pagePurpose: IIM Sambalpur Fill RateKrati JainNo ratings yet
- Acute Adult Mental Health Integrated Care Pathway - Service MapDocument1 pageAcute Adult Mental Health Integrated Care Pathway - Service MapBernewsAdminNo ratings yet
- Jsu T5 Bi K1Document1 pageJsu T5 Bi K1MOHD FAHMI BIN ABD ALIAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Local Governemnt Development PackageDocument3 pagesLocal Governemnt Development PackageYousaf Khalid KhaulaNo ratings yet
- 1 WSF Risk Management PlanDocument7 pages1 WSF Risk Management PlanYong Kim100% (1)
- Crepes and Waffles Corporate Strategy AnalysisDocument1 pageCrepes and Waffles Corporate Strategy AnalysisOladayo AyodejiNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Safety ChecklistDocument2 pagesWarehouse Safety ChecklistOmkar BhavleNo ratings yet
- TNA - Monthly Training Report Kelas Paralel - 2020 - Subcont - PUPDocument1 pageTNA - Monthly Training Report Kelas Paralel - 2020 - Subcont - PUPMuhamad Rizki AzisNo ratings yet
- Online Edition - Digital AccessDocument1 pageOnline Edition - Digital Access18aw2708No ratings yet
- The PMBOK® Guide NotesDocument90 pagesThe PMBOK® Guide NotesSafa SlimNo ratings yet
- SO KSO MPS - Rev1Document8 pagesSO KSO MPS - Rev1RACHMATNo ratings yet
- Second Seniority List AP Teachers 2017Document26 pagesSecond Seniority List AP Teachers 2017S V PRASADNo ratings yet
- 0202 Microsoft Team System Roles and SecurityDocument1 page0202 Microsoft Team System Roles and Securitypradeepku.bNo ratings yet
- DENY or ALLOW - Who wins with TFS security profilesDocument1 pageDENY or ALLOW - Who wins with TFS security profilesJorge Enrique Rico MarulandaNo ratings yet
- Competencies Basic Competencies Common Competencies Core CompetencyDocument2 pagesCompetencies Basic Competencies Common Competencies Core Competencylara joey datoyNo ratings yet
- First Floor: Statue of OnenessDocument1 pageFirst Floor: Statue of OnenessSufyan AhmadNo ratings yet
- BBS and HSE Scorecard RecordsDocument1 pageBBS and HSE Scorecard RecordsAl - AminNo ratings yet
- Training MatrixDocument1 pageTraining MatrixRohitNo ratings yet
- Order Management Ecommerce WorkflowDocument1 pageOrder Management Ecommerce WorkflowElena EnacheNo ratings yet
- Construction SpecificationsDocument1 pageConstruction SpecificationsDJNo ratings yet
- 08 Annex 7 Pac Validation Report 2Document4 pages08 Annex 7 Pac Validation Report 2City Hope GrivialdeNo ratings yet
- Customer Service Collections Processing WorkflowDocument1 pageCustomer Service Collections Processing WorkflowJancy KattaNo ratings yet
- 12 PSPO - APAC - MayDocument1 page12 PSPO - APAC - Maychellappan29No ratings yet
- Reasoning Target Types: Inductive, Deductive, Comparative & EvaluativeDocument6 pagesReasoning Target Types: Inductive, Deductive, Comparative & Evaluativebaronganjennalynpsu.edu.ph psu san carlosNo ratings yet
- WBHO Training Matrix 24.02.2020Document1 pageWBHO Training Matrix 24.02.2020Edson Mauro Thomas NobregaNo ratings yet
- HR Applicant Screening and Interview WorkflowDocument1 pageHR Applicant Screening and Interview WorkflowPhone SSBNo ratings yet
- Structural Notes: Seaoil Filling StationDocument1 pageStructural Notes: Seaoil Filling StationCasmir TayagNo ratings yet
- 00 - RPL (A) Planning MatrixDocument10 pages00 - RPL (A) Planning Matrixa245fsNo ratings yet
- Entrega Fase 3 - InglesDocument5 pagesEntrega Fase 3 - InglesMiguel OspitiaNo ratings yet
- Tos Pretest Pe and Health G11Document107 pagesTos Pretest Pe and Health G11Jero MenaleNo ratings yet
- Case Study BDocument5 pagesCase Study BAwa SannoNo ratings yet
- Less Stress More CareDocument28 pagesLess Stress More CareSyrel Santos100% (1)
- Gita Summary in AcronymsDocument47 pagesGita Summary in Acronymsastrokpm100% (2)
- DLL - Mapeh 3 - Q2 - W3Document3 pagesDLL - Mapeh 3 - Q2 - W3Maricon ChicanoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 - Stages of Child Learning DevelopmentDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 10 - Stages of Child Learning DevelopmentErica100% (1)
- Understanding Motivation and Emotion Through Physiological and Psychological FactorsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Motivation and Emotion Through Physiological and Psychological FactorsnowellstanNo ratings yet
- sAMPLE DLL FOR COT KRA 2Document3 pagessAMPLE DLL FOR COT KRA 2Tamz Bokz100% (1)
- Action Research Test ResultsDocument3 pagesAction Research Test Resultsrussel100% (1)
- Communication Elements and Types ExplainedDocument104 pagesCommunication Elements and Types ExplainedArianne FloresNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Nursing 3BScN 23082012 1437Document25 pagesMental Health Nursing 3BScN 23082012 1437Subhada GosaviNo ratings yet
- "Tell Me and I Forget. Teach Me and I May Remember. Involve Me and I Will Learn." Benjamin FranklinDocument5 pages"Tell Me and I Forget. Teach Me and I May Remember. Involve Me and I Will Learn." Benjamin FranklinKirby C. LoberizaNo ratings yet
- Robert Tannenbaum & Warren H Schmidt: Carlo Widjaja Chin Chiang ChenDocument15 pagesRobert Tannenbaum & Warren H Schmidt: Carlo Widjaja Chin Chiang ChenCarlo WidjajaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Semiotics - Deely, John N. - 4077Document164 pagesBasics of Semiotics - Deely, John N. - 4077Silvana TorresNo ratings yet
- Training Methods A Review and Analysis PDFDocument26 pagesTraining Methods A Review and Analysis PDFSyed MujahidNo ratings yet
- Burnout SyndromeDocument2 pagesBurnout SyndromeAlina NeagoeNo ratings yet
- Leadership and Management For Service IndustriesDocument17 pagesLeadership and Management For Service IndustriesOanaa ComanNo ratings yet
- Course Code: MEM 602 Course Description: Educational Leadership Presenter: Krizza Joy S. Peduca Professor: Jinefer Favila-ButuDocument9 pagesCourse Code: MEM 602 Course Description: Educational Leadership Presenter: Krizza Joy S. Peduca Professor: Jinefer Favila-ButuKrizza Joy PeducaNo ratings yet
- The Media TriangleDocument7 pagesThe Media TriangleMichalis KarakatsanisNo ratings yet
- Experiencing the Teaching-Learning Process in ActionDocument8 pagesExperiencing the Teaching-Learning Process in ActionJeffrey Lois Sereño MaestradoNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of EducationDocument2 pagesPhilosophies of Educationedenfiel100% (1)
- Coach Job Skills and Help Colleagues ImproveDocument43 pagesCoach Job Skills and Help Colleagues ImproveMk ሐበሻ100% (1)
- Organisational Behaviour: Assignment On: Organisational ClimateDocument5 pagesOrganisational Behaviour: Assignment On: Organisational ClimateShravani RathodNo ratings yet
- Burnout Self Care Outreach PresentationDocument16 pagesBurnout Self Care Outreach PresentationBilly AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Systemic ThinkingDocument15 pagesSystemic Thinkingpchng94% (16)
- The Design and Dynamics of Cities As Self-Organizing SystemsDocument23 pagesThe Design and Dynamics of Cities As Self-Organizing SystemsamarelobassNo ratings yet
- Arts and Creative LiteracyDocument66 pagesArts and Creative LiteracyshivauneamarioNo ratings yet
- Science Forward Planning DocumentDocument5 pagesScience Forward Planning Documentapi-280948150No ratings yet
- Change ManagementDocument18 pagesChange ManagementMehjabin PatelNo ratings yet