Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Depreciation Explained
Uploaded by
Priyank JainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Depreciation Explained
Uploaded by
Priyank JainCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPRECIATION
What is Depreciation?
Depreciation is the reduction in the value of assets due to wear and tear,
effluxion of time and obsolescence.
Every asset is subject to wear and tear in the ordinary course of its use and
with the effluxion or passage of time. Reduction in the value of asset may
also take place due to obsolescence. The cost of the asset is allocated over
time and considered as expense.
It is applied on long term assets which give benefits for many years. For
example, on Plant & Machinery, Vehicles, Computers, Furniture, Building
etc. Land is not subject to wear and tear and thus depreciation is not levied
on Land but applicable on a Building.
Considering depreciation as an expense is very much required for successful
financial management. For example, a driver gives his car for tourism
purpose, he must consider the fact that car has a limited useful life and he
needs to replace that after some years. For that, while calculating its
operation cost, he must consider the cost of car, its life, the resale value
after useful life and add it to other expenses for calculating total cost.
Depreciation is also allowed as an expense as per Income Tax Act and also
as per Companies Act.
Common Methods or Types of Depreciation
Straight Line Method (SLM)
In this method, equal amount of depreciation is charged on the asset over
its useful life. For Example – Asset is purchased for ₹1,00,000 and useful
life is 10 years with salvage value of Rs. 10,000 then depreciation is charged
at Rs. 9,000 for each of the 10 years. (1,00,000 – 10,000)/10 Years.
𝑪𝒐𝒔𝒕 𝒐𝒇 𝑨𝒔𝒔𝒆𝒕+𝑰𝒏𝒔𝒕𝒂𝒍𝒍𝒂𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏 𝑪𝒉𝒂𝒓𝒈𝒆𝒔−𝑬𝒔𝒕𝒊𝒎𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒅 𝑺𝒄𝒓𝒂𝒑 𝑽𝒂𝒍𝒖𝒆
Formula= 𝑵𝒐. 𝒐𝒇 𝑼𝒔𝒆𝒇𝒖𝒍 𝒀𝒆𝒂𝒓𝒔 𝒐𝒇 𝑳𝒊𝒇𝒆
Written Down Value (WDV) Method
WDV method is the most commonly used method of depreciation. Also, in
Income Tax Act, depreciation is allowed as per WDV method only.
In this method depreciation is charged on the book value of asset and book
value is decreased each year by the depreciation. For e.g.- Asset is
purchased at ₹1,00,000 and depreciation rate is 10% then first year
depreciation is ₹10,000(10% of ₹1,00,000), second year depreciation is
Prof. Dr. (CA) Ameya Tanawade Page 1
₹9,000 (10% of 90,000 [1,00,000 – 10,000]) and third year depreciation is
₹8,100 ( 10% of ₹81,000 [90,000 – 9,000]).
This method is also called as Reducing Balance Method or Diminishing
Balance Method. In the WDV method, the amount of depreciation goes on
decreasing with time. An asset gives more value to a business in initial years
than later year, therefore, this method is considered as the most logical
method of depreciation.
There are also other methods of depreciation but they are not often used
such as Depreciation on the basis of Units of Production, Sum of years
Method, Sinking Fund Method etc.
Specimen Journal Entries
Sr.
Transaction Journal Entry
No.
1 Purchase of Asset Asset A/c………….……………………….…Dr.
To Cash/Bank A/C
2 Depreciation of Asset Depreciation A/c………….…………….….Dr.
To Asset A/C
3 Sale of Asset at Profit Cash/Bank A/c………………………….…Dr.
To Asset A/C
To Profit & Loss A/c
4 Sale of Asset at Loss Cash/Bank A/c…………………………….Dr.
Profit & Loss A/c…………………………..Dr.
To Asset A/C
5 Balance at the end of Profit & Loss A/c……………………….….Dr.
the year in Depreciation To Depreciation A/c
Account transferred to
Profit & Loss Account
Thus, depreciation is shown as an Indirect expense in the debit side of Profit
and Loss Account and Asset’s value is to be shown after the reduction of
depreciation in the balance sheet.
Difference between Depreciation amount under SLM & WDV
For e.g. Company purchases Machinery for ₹1,00,000/- having useful life of 10
years but not having scrap value and rate applicable for depreciation is 10%.
Calculate depreciation under SLM and WDV methods.
SLM (Depreciation Rate 10%) WDV (Depreciation Rate
10%)
At the end of Year
Book Depreciation Book Depreciation
Value Amount Value Amount
1 100000 10000 100000 10000
2 90000 10000 90000 9000
3 80000 10000 81000 8100
4 70000 10000 72900 7290
5 60000 10000 65610 6561
Prof. Dr. (CA) Ameya Tanawade Page 2
6 50000 10000 59049 5904.90
7 40000 10000 53144.10 5314.41
8 30000 10000 47829.69 4782.97
9 20000 10000 43046.72 4304.67
10 10000 10000 38742.05 3874.21
Benefits/Need of charging depreciation
1. Tax Benefit – Depreciation is allowed as an expense under Income Tax and
therefore it is important to consider it to save Income Tax.
2. Mandatory under Companies Act – It is compulsory to charge depreciation in
Profit and Loss account in Companies Act, 2013.
3. Real Profit – If it is not considered then expenditure on behalf of fixed assets
is not considered and the profit may be shown as a high number especially
in industries required large plant and machinery. Also, this may lead to high
distribution of earnings to shareholders and thus non-availability of funds
when business is in need to replace the asset.
Problems
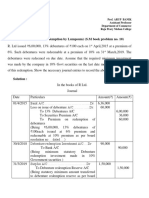
Q1.
Turn hill Corporation a Limited company purchased Machinery worth ₹4,90,000 on
1st April 2012. They spent ₹10,000 on its installation. On 1st October 2012, they
Purchased another Machine costing ₹2,30,000 and spent ₹20,000 on its
installation. On 31st December 2014 they sold, the Machine purchased on 1 st
October 2012 for ₹1,90,000. On the same day they Purchased another Machine
costing ₹ 2,80,000 and paid ₹20,000 on installation of the same.
You are required to:
Prepare Machinery Account for the FY 2012-13, 2013-14, 2014-15
charging Depreciation @ 10% on Straight Line Method Basis. Working
Notes will form a part of your answer.
Solution:
Working Note:
Particulars 1 2 3
2012-13
Purchased on 1/4/2012 500000
Purchased on 1/10/2012 250000
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2013 50000 12500
WDV on 31/3/2013 450000 237500
2013-14
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2014 50000 25000
WDV on 31/3/2014 400000 212500
2014-15
Less: Depreciation up to 31/12/2014 (9M) 18750
WDV as on 31/12/2014 193750
Less: Sold for 190000
Loss on Sale 3750
Purchased on 31/12/2014 300000
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2015 50000 7500
WDV on 31/3/2015 350000 292500
Prof. Dr. (CA) Ameya Tanawade Page 3
Dr. Machinery A/c Cr.
Date Particulars Amt (₹) Date Particulars Amt (₹)
1/4/12 To Bank A/c 500000 31/3/13 By Depreciation A/c 62500
1/10/12 To Bank A/c 250000 31/3/13 By Balance C/d 687500
750000 750000
1/4/13 To Balance B/d 687500 31/3/14 By Depreciation A/c 75000
31/3/14 By Balance C/d 612500
687500 687500
1/4/14 To Balance B/d 612500 31/12/14 By Depreciation A/c 18750
31/12/14 To Bank A/c 300000 31/12/14 By Bank A/c 190000
31/12/14 By P & L A/c 3750
31/3/15 By Depreciation A/c 57500
31/3/15 By Balance C/d 642500
912500 912500
Q2.
Magnum Logistics Purchased 4 Motor Trucks worth ₹12,00,000 each for
their newly started Transport Business. These were purchased on 1st April,
2005. On 30th June 2006 they purchased 2 more trucks costing ₹12,50,000
each and expanded their fleet. On 1st October 2007, one of the trucks
Purchased on 1st April 2005, met with an accident and the insurance
company paid a claim of ₹9,00,000 against it.
The company replaced this truck with another truck costing ₹13,00,000 on
the same day.
You are required to:
Prepare Motor Truck Account & Depreciation Account for the
years 2005-06, 2006-07, 2007-08, charging Depreciation @10%
on SLM basis. Working Notes shall form a part of your answer.
Solution:
Particulars 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
2005-06
Purchase on 1200000 1200000 1200000 1200000
1/4/2005
(-) Depn on 120000 120000 120000 120000
31/3/2006
WDV on 1080000 1080000 1080000 1080000
31/3/2006
2006-07
Purchase on - - - - 1250000 1250000
30/6/2006
(-) Depn on 120000 120000 120000 120000 93750 93750
31/3/2007
WDV on 960000 960000 960000 960000 1156250 1156250
31/3/2007
2007-08
(-) Depn on 60000
1/10/2007
WDV on 900000
1/10/2007
(-) Insurance 900000
Claim
Profit/Loss Nil
Prof. Dr. (CA) Ameya Tanawade Page 4
Purchased on 1300000
1/10/2007
(-) Depn on - 120000 120000 120000 125000 125000 65000
31/3/2008
WDV on - 840000 840000 840000 1031250 1031250 1235000
31/3/2008
Dr. Truck A/c Cr.
Date Particulars Amt (₹) Date Particulars Amt (₹)
1/4/05 To Bank A/c 4800000 31/3/06 By Depn. A/c 480000
31/3/06 By Balance C/d 4320000
4800000 4800000
1/4/06 To Balance B/d 4320000 31/3/07 By Depn. A/c 667500
30/6/06 To Bank A/c 2500000 31/3/07 By Balance C/d 6152500
6820000 6820000
1/4/07 To Balance B/d 6152500 1/10/07 By Depn. A/c 60000
1/10/07 To Bank A/c 1300000 1/10/07 By Bank A/c 900000
31/3/08 By Depn. A/c 675000
31/3/08 By Balance C/d 5817500
7452500 7452500
Dr. Depreciation A/c Cr.
Date Particulars Amt (₹) Date Particulars Amt (₹)
31/3/06 To Truck A/c 480000 31/3/06 By P & L A/c 480000
480000 480000
31/3/07 To Truck A/c 667500 31/3/07 By P & L A/c 667500
667500 667500
1/10/07 To Truck A/c 60000
31/3/08 To Truck A/c 675000 31/3/08 By P & L A/c 735000
735000 735000
Q3.
Hilton India Limited purchased Machinery worth amount ₹19,00,000 on 1st
July 2009. They spent ₹1,00,000 on its installation. On 1st April 2010, they
Purchased another Machine costing ₹5,00,000 and spent ₹50,000 on its
installation. On 31st December 2011 they scrapped half the Machine
purchased on 1st July 2009 for ₹7,50,000 that was damaged due to fire
beyond repairs. However, on the same day they Purchased another Machine
costing ₹14,00,000 and paid ₹1,00,000 on installation of the same.
You are required to:
Prepare Machinery Account for the 2009-10, 2010-11, 2011-12
charging Depreciation @ 10% on Reducing Balance Method Basis.
Working Notes will form a part of your answer.
Prof. Dr. (CA) Ameya Tanawade Page 5
Solution:
Working Note:
Particulars 1 2 3
50% 50%
2009-10
Purchased on 1/7/2009 1000000 1000000
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2010 75000 75000
(9 Months)
WDV on 31/3/2010 925000 925000
2010-11
Purchased on 1/4/2010 550000
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2011 92500 92500 55000
WDV on 31/3/2011 832500 832500 495000
2011-12
Less: Depreciation on 62438
31/12/2011 (9 Months)
WDV on 31/12/2011 770062
Less: Sale 750000
Loss 20062
Purchased on 31/12/2011 - 1500000
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2012 - 83250 49500 37500
WDV on 31/3/2012 - 749250 445500 1462500
Dr. Machinery A/c Cr.
Date Particulars Amt (₹) Date Particulars Amt (₹)
1/7/2009 To Bank A/c 2000000 31/3/2010 By Depn. A/c 150000
31/3/2010 By Bal. C/d 1850000
2000000 2000000
1/4/2010 To Bal. B/d 1850000 31/3/2011 By Depn. A/c 240000
1/4/2010 To Bank A/c 550000 31/3/2011 By Bal. C/d 2160000
2400000 2400000
1/4/2011 To Bal. B/d 2160000 31/12/2011 By Depn. A/c 62438
31/12/2011 To Bank A/c 1500000 31/12/2011 By Bank A/c 750000
31/12/2011 By P & L A/c 20062
31/3/2012 By Depn. A/c 170250
31/3/2012 By Bal. C/d 2657250
3660000 3660000
Q4.
Excellent Ventures Limited is a Software manufacturer and distributor. The
company Purchased Fixed Assets worth ₹4,80,000 for its efficient working
and spent ₹20,000 on its installation on 1st October 2013. The company
acquired additional Fixed Assets valued at ₹3,50,000 and spent ₹10,000 on
its installation on January 01, 2014. On 1st April 2014 ¼th of the Assets
acquired on 1st October 2013 were damaged and had to be scrapped for
₹75,000. These assets were replaced by another lot of purchases worth
₹2,00,000.
Prof. Dr. (CA) Ameya Tanawade Page 6
Required:
You are required to prepare, Fixed Assets Account & Depreciation
Account using DBM charging depreciation at 20% p.a. and
showing detailed working notes to substantiate your calculation
for a period of 2013-14 and 2014-15.
Solution:
Working Note:
Particulars 1 2 3
2013-14 ¼ ¾
Purchased on 1/10/2013 125000 375000
Purchased on 1/1/2014 360000
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2014 12500 37500 18000
WDV on 31/3/2014 112500 337500 342000
2014-15
Less: Sale 75000
Loss on Sale 37500
Purchased on 1/4/2014 200000
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2015 - 67500 68400 40000
WDV on 31/3/2015 - 270000 273600 160000
Dr. Fixed Assets A/c Cr.
Date Particulars Amt (₹) Date Particulars Amt (₹)
1/10/13 To Bank A/c 500000 31/3/14 By Depn. A/c 68000
1/1/14 To Bank A/c 360000 31/3/14 By Bal. C/d 792000
860000 860000
1/4/14 To Bal. B/d 792000 1/4/14 By Bank A/c 75000
1/4/14 To Bank A/c 200000 1/4/14 By P & L A/c 37500
31/3/15 By Depn. A/c 175900
31/3/15 By Bal. C/d 703600
992000 992000
Dr. Depreciation A/c Cr.
Date Particulars Amt (₹) Date Particulars Amt (₹)
31/3/14 To Fixed Asset A/c 68000 31/3/14 By P & L A/c 68000
68000 68000
31/3/15 To Fixed Asset A/c 175900 31/3/15 By P & L A/c 175900
175900 175900
Prof. Dr. (CA) Ameya Tanawade Page 7
Classwork Exercise:
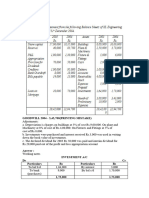
Q5.
New look Foundry acquired a Blast Furnace costing ₹25,00,000 on 1st April
2010. On 1st July 2011, another Blast Furnace was acquired for ₹12,00,000.
On 31st December 2012 the furnace acquired on 1st July 2011 was sold for
₹10,50,000. On the same day company acquired another small furnace
costing ₹10,00,000.
Required to prepare:
Blast Furnace Account
Depreciation Account charging 10% Depreciation using DBM
Show proper working notes
Solution:
Working Note:
Particulars 1 2 3
2010-11
Purchased on 1/4/2010 2500000
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2011 250000
WDV on 31/3/2011 2250000
2011-12
Purchased on 1/7/2011 1200000
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2012 225000 90000
WDV on 31/3/2012 2025000 1110000
2012-13
Less: Depreciation on 31/12/2012 83250
(9 Months)
WDV on 31/12/2012 1026750
Less: Sale 1050000
Profit on Sale 23250
Purchased on 31/12/2012 1000000
Less: Depreciation on 31/3/2013 202500 25000
WDV on 31/12/2013 1822500 975000
Prof. Dr. (CA) Ameya Tanawade Page 8
Dr. Furnace A/c Cr.
Date Particulars Amt (₹) Date Particulars Amt (₹)
1/4/10 To Bank A/c 2500000 31/3/11 By Depn. A/c 250000
31/3/11 By Bal. C/d 2250000
2500000 2500000
1/4/11 To Bal. B/d 2250000 31/3/12 By Depn. A/c 315000
1/7/11 To Bank A/c 1200000 31/3/12 By Bal. C/d 3135000
3450000 3450000
1/4/12 To Bal. B/d 3135000 31/12/12 By Depn. A/c 83250
31/12/12 To P & L A/c 23250 31/12/12 By Bank A/c 1050000
31/12/12 To Bank A/c 1000000 31/3/13 By Depn. A/c 227500
31/3/13 By Bal. C/d 2997500
4158250 4158250
Dr. Depreciation A/c Cr.
Date Particulars Amt (₹) Date Particulars Amt (₹)
31/3/11 To Furnace A/c 250000 31/3/11 By P & L A/c 250000
250000 250000
31/3/12 To Furnace A/c 315000 31/3/12 By P & L A/c 315000
315000 315000
31/12/12 To Furnace A/c 83250
31/3/13 To Furnace A/c 227500 31/3/13 By P & L A/c 310750
310750 310750
Journal Entry for Sale of Furnace
Date Particulars J/F Dr. (Rs.) Cr. (Rs.)
31/12/12 Bank A/c------------------------------Dr. 1050000
To Furnace A/c 1026750
To Profit & Loss A/c 23250
(Being Furnace purchased on
1/7/2011 sold at profit)
Prof. Dr. (CA) Ameya Tanawade Page 9
You might also like
- A Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific: Fifth EditionFrom EverandA Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific: Fifth EditionNo ratings yet
- Depreciation-2Document9 pagesDepreciation-2divya shindeNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument21 pagesDepreciationxvfidxwmgNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Accountingformanager - AnanduDocument52 pagesUnit 2 - Accountingformanager - Ananducraziestidiot31No ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument3 pagesDepreciationSumanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Depreciation and Its AccountingDocument4 pagesDepreciation and Its AccountingSatish SheoranNo ratings yet
- Unit-3Document27 pagesUnit-3v9510491No ratings yet
- CCP302Document13 pagesCCP302api-3849444No ratings yet
- Depreciation AccountingDocument22 pagesDepreciation AccountingRajat srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Calculate Depreciation Using Different MethodsDocument4 pagesCalculate Depreciation Using Different MethodsowaisNo ratings yet
- Depreciation AccountingDocument12 pagesDepreciation Accountingshreyu14796No ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument21 pagesDepreciationDark XYNo ratings yet
- Discount Bank Illustrations Calculate RebateDocument7 pagesDiscount Bank Illustrations Calculate RebateAikya GandhiNo ratings yet
- Problem - 2 (Redemption by Lumpsum) (S.M Book Problem No. 10)Document5 pagesProblem - 2 (Redemption by Lumpsum) (S.M Book Problem No. 10)Gopal DasNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Accounting for Class 11 StudentsDocument19 pagesDepreciation Accounting for Class 11 StudentsMithraNo ratings yet
- Journal Date Description Post REF. DebitDocument20 pagesJournal Date Description Post REF. DebitKanika SharmaNo ratings yet
- 11 Accountancy Notes ch05 Depreciation Provision and Reserves 02 PDFDocument18 pages11 Accountancy Notes ch05 Depreciation Provision and Reserves 02 PDFVigneshNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument7 pagesBudgetvasanthgurusamynsNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Lease TutorialDocument9 pagesTopic 3 Lease TutorialHakim AzmiNo ratings yet
- Classes Unit 4 Commerce DepreciationDocument25 pagesClasses Unit 4 Commerce Depreciationhappy lifeNo ratings yet
- Facultyid 4 Depreciation 1672490717Document50 pagesFacultyid 4 Depreciation 1672490717Dhanaseelan thailandNo ratings yet
- Aidcom Financial Accounting AnalysisDocument17 pagesAidcom Financial Accounting AnalysisAjmal K HussainNo ratings yet
- Depr Fixed AssetDocument6 pagesDepr Fixed AssetRanib Bhakta SainjuNo ratings yet
- Acc PoojaDocument7 pagesAcc PoojaMemer BabaNo ratings yet
- II PU AccountsDocument30 pagesII PU AccountsJanani Priya100% (2)
- Depreciation Provision ReservesDocument60 pagesDepreciation Provision ReservesjonesmbNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of AccountingDocument3 pagesBasic Principles of Accounting22ba045No ratings yet
- Commerce Paathshaala: Pu-Ii Annual Examination April-May-2022 Accountancy Key Answers Section A (1 Mark Answers)Document12 pagesCommerce Paathshaala: Pu-Ii Annual Examination April-May-2022 Accountancy Key Answers Section A (1 Mark Answers)Ashok dore Ashok doreNo ratings yet
- Revaluation Problems Part 2Document32 pagesRevaluation Problems Part 2XNo ratings yet
- HIRE PURCHASE AND INSTALLAMENT SYSTEM (Autosaved)Document16 pagesHIRE PURCHASE AND INSTALLAMENT SYSTEM (Autosaved)Mujieh NkengNo ratings yet
- DEPRECIATIONDocument11 pagesDEPRECIATIONsiddhartha RajNo ratings yet
- Gerry's classes on partnership liquidationDocument6 pagesGerry's classes on partnership liquidationgankNo ratings yet
- Project Name - HR Connect # 5 Create A Project BudgetDocument3 pagesProject Name - HR Connect # 5 Create A Project BudgetShowri ReddyNo ratings yet
- Reading of Ledger AccountDocument18 pagesReading of Ledger Accountneeru79200050% (2)
- Christ CIA FM MidtermDocument6 pagesChrist CIA FM MidtermKSHITIZ CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Far510 Test Dec 2020 SSDocument6 pagesFar510 Test Dec 2020 SS2022478048No ratings yet
- Test Far510 Sept 2019 SSDocument4 pagesTest Far510 Sept 2019 SS2022478048No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ACCA F3Document12 pagesChapter 6 ACCA F3siksha100% (1)
- G. S. College of Commerce & Economics, Nagpur: Fundamentals of Accounting StandardsDocument3 pagesG. S. College of Commerce & Economics, Nagpur: Fundamentals of Accounting StandardsRanjhana SahuNo ratings yet
- AFA End Examination 2021-2022Document6 pagesAFA End Examination 2021-2022sebastian mlingwaNo ratings yet
- Internal Reconstruction Part-IIDocument13 pagesInternal Reconstruction Part-IIINTER SMARTIANSNo ratings yet
- Kts g11 - Principles of Accounts Final AdjustmentsDocument16 pagesKts g11 - Principles of Accounts Final AdjustmentsBupe Banda100% (1)
- Problem - 7: Problem On Redemption by Annual DrawingDocument5 pagesProblem - 7: Problem On Redemption by Annual DrawingGopal DasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document9 pagesAssignment 2PoommalarNo ratings yet
- Hra 11J1919Document5 pagesHra 11J1919إسماعيل البلوشيNo ratings yet
- Income StatementDocument3 pagesIncome StatementBiswajit SarmaNo ratings yet
- CA Foundation Accounts A MTP 2 Dec 2022Document11 pagesCA Foundation Accounts A MTP 2 Dec 2022shagana212005No ratings yet
- T 4Document3 pagesT 4Muntasir AhmmedNo ratings yet
- Islam Is RealDocument5 pagesIslam Is Realhussnainali shahNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument3 pagesDepreciationSarath kumar CNo ratings yet
- Cash and Credit ManagementDocument11 pagesCash and Credit Managementaoishic2025No ratings yet
- Solution Ultimate Sample Paper 4Document5 pagesSolution Ultimate Sample Paper 4Karthick KarthickNo ratings yet
- Basic Principle of AccountingDocument3 pagesBasic Principle of Accounting22ba045No ratings yet
- Depreciation SolutionsDocument14 pagesDepreciation SolutionsAyush MadurwarNo ratings yet
- XI Accountancy Model Set 2078Document38 pagesXI Accountancy Model Set 2078kevin bhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Goodwill 2004 - 3,43,700 (Printing Mistake)Document9 pagesGoodwill 2004 - 3,43,700 (Printing Mistake)vasanthgurusamynsNo ratings yet
- CCP302Document11 pagesCCP302api-3849444No ratings yet
- Project Report On General StoreDocument10 pagesProject Report On General StoreApplication's ManagerNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Question and Answers 2Document2 pagesDepreciation Question and Answers 2AMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNo ratings yet
- Strategic Accounting Ratios Help Fitness Club Improve PerformanceDocument12 pagesStrategic Accounting Ratios Help Fitness Club Improve PerformanceabhigoldyNo ratings yet
- RVV Yb 083Document136 pagesRVV Yb 083Priyank JainNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument2 pagesFinancial ManagementPriyank JainNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Cogno Ai Chatbot: Priyank Jain Roll No: 6617Document6 pagesAn Introduction To Cogno Ai Chatbot: Priyank Jain Roll No: 6617Priyank JainNo ratings yet
- What Was The Time When You Faced A Tough Challenge in Life and You Emerged Successfully ?Document1 pageWhat Was The Time When You Faced A Tough Challenge in Life and You Emerged Successfully ?Priyank JainNo ratings yet
- One PlusDocument98 pagesOne PlusPriyank JainNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Cogno Ai Chatbot: Priyank Jain Roll No: 6617Document6 pagesAn Introduction To Cogno Ai Chatbot: Priyank Jain Roll No: 6617Priyank JainNo ratings yet
- What Was The Time When You Faced A Tough Challenge in Life and You Emerged Successfully ?Document1 pageWhat Was The Time When You Faced A Tough Challenge in Life and You Emerged Successfully ?Priyank JainNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentPriyank JainNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info GD Pi Bible PRDocument69 pagesToaz - Info GD Pi Bible PRPriyank JainNo ratings yet
- Profitability IndexDocument1 pageProfitability IndexPriyank JainNo ratings yet
- MHRD Two Year Full Time Programme Course Structure and SyllabusDocument59 pagesMHRD Two Year Full Time Programme Course Structure and SyllabusPriyank JainNo ratings yet
- Ledger TemplateDocument7 pagesLedger TemplateIts SaoirseNo ratings yet
- LSE AC444 Analysis PDFDocument256 pagesLSE AC444 Analysis PDFHu HeNo ratings yet
- IFRS 8 Operating Segments GuideDocument18 pagesIFRS 8 Operating Segments GuideDaryll DecanoNo ratings yet
- COMEX1 TAX REVIEW Canvas-1Document18 pagesCOMEX1 TAX REVIEW Canvas-1Angel RosalesNo ratings yet
- North Mountain NurseryDocument1 pageNorth Mountain Nurserychandel08No ratings yet
- Accounting exam questions on corporate accounts and costingDocument3 pagesAccounting exam questions on corporate accounts and costingd.cNo ratings yet
- Income Statement Analysis of Ford Motor CompanyDocument5 pagesIncome Statement Analysis of Ford Motor CompanyMoses MachariaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Resources Notes FinalDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurship Resources Notes FinalHSFXHFHXNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER VI - Long-Term FinancingDocument55 pagesCHAPTER VI - Long-Term FinancingMan TKNo ratings yet
- Audit Investments ChapterDocument34 pagesAudit Investments ChapterMr.AccntngNo ratings yet
- Seasons Construction estimates and costs for building projectDocument5 pagesSeasons Construction estimates and costs for building projectCarlo ParasNo ratings yet
- Business License Fees for Tobacco, Wholesale, Retail, and Other IndustriesDocument2 pagesBusiness License Fees for Tobacco, Wholesale, Retail, and Other Industriesjason camachoNo ratings yet
- Proposed 51% Asset Purchase Structure for $823,140Document1 pageProposed 51% Asset Purchase Structure for $823,140SebiNo ratings yet
- YTL Corporation: Earnings Momentum To ContinueDocument17 pagesYTL Corporation: Earnings Momentum To Continuephantom78No ratings yet
- Annexure Form for MSE Loan ApplicationDocument24 pagesAnnexure Form for MSE Loan ApplicationShakeer HussainNo ratings yet
- Info 0824Document442 pagesInfo 0824Amal RoyNo ratings yet
- Project Report Format For Bank LoanDocument7 pagesProject Report Format For Bank LoanRaju Ramjeli70% (10)
- Analysis of Banking Industry & Janata Bank: An Internship ReportDocument71 pagesAnalysis of Banking Industry & Janata Bank: An Internship ReportTareq AlamNo ratings yet
- Ac2102 RaDocument9 pagesAc2102 RaNors PataytayNo ratings yet
- Market Makers' Methods of Stock ManipulationDocument4 pagesMarket Makers' Methods of Stock Manipulationhkless100% (3)
- Due Diligence Checklist For An ASSET PurchaseDocument2 pagesDue Diligence Checklist For An ASSET PurchaseDerek Noble50% (2)
- Banking BreakdownDocument2 pagesBanking Breakdownjnn sNo ratings yet
- 17C - Jollibee Foods Corporation Press Release For 2ndQ 2021 FinalDocument7 pages17C - Jollibee Foods Corporation Press Release For 2ndQ 2021 FinalElla HermonioNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: FAR Ocampo/Cabarles/Soliman/Ocampo Quiz No. 3 Set A OCTOBER 2019Document3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: FAR Ocampo/Cabarles/Soliman/Ocampo Quiz No. 3 Set A OCTOBER 2019ChjxksjsgskNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument10 pagesBusiness Planjoseph nsamaNo ratings yet
- CBZ Dividend AnnouncementDocument1 pageCBZ Dividend AnnouncementBusiness Daily ZimbabweNo ratings yet
- Sollution Accounting Chapter # 03 KeisoDocument79 pagesSollution Accounting Chapter # 03 KeisoUmair CHNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 03 - PPT (Supplementary To ISpace)Document43 pagesChapter - 03 - PPT (Supplementary To ISpace)kjw 2No ratings yet
- Fund Fact Sheets - Prosperity Index FundDocument1 pageFund Fact Sheets - Prosperity Index FundJohh-RevNo ratings yet
- Millennium Company - Projected Financial StatementDocument2 pagesMillennium Company - Projected Financial StatementKathleenCusipagNo ratings yet