Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 1
Uploaded by
M. Hamza Akhtar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesLecture 1
Uploaded by
M. Hamza AkhtarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
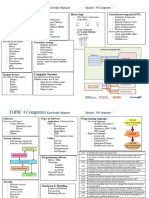
Device
- anything or any equipment that is used for a specific purpose
- 3 Types of Devices
- Input Devices
- the devices which recieve data/instruction
- Examples
- Keyboard
- mouse/trackball
- scanner
- microphone
- Simple Camera
- Joystick
- Stylus
- touchpad/pointing stick
- Output Devices
- the devices which send data/instruction
- Examples
- monitor
- speaker
- printer/plotters
- projector
- Peripheral Devices
- the devices which send and recieve data/instruction
- Examples
- Modem
- Routers/Hubs/Switches
- Smart Camera
- Fax Machine
- Touch Screens
- Telephone
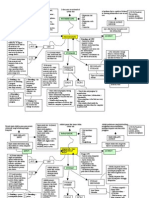
Memory
- the device which is used to temporarily hold the data
- 4 types of memories
- Registers
- smallest memory in the system
- it is located in the processor
- Genernal Purpose
- accumulator
- base
- counter
- data
- it is smaller in physical and memory size
- it is very expensive
- it is very fast
- it is in Bytes
- Cache Memory
- it is located in motherboard
- it is slower than registers
- it very expensive but cheaper than registers
- it is in smaller MBs
- ROM
- Read Only Memory
- Basic instructions are stored in ROM
- Sequential access
- Non-volatile
- Hard-wired
- RAM
- Random Access Memory
- Everything which we want to execute should be loaded into the
RAM first
- Volatile
- Flip-flops
- Requires addresses to access any location
- data is stored as long as the electricity is supplied to it
You might also like
- Basic Computer Skills Module 2 Software ConceptsDocument14 pagesBasic Computer Skills Module 2 Software ConceptsArthur CapawingNo ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technology Chapter 1: Types and Components of Computer SystemsDocument2 pagesInformation and Communication Technology Chapter 1: Types and Components of Computer SystemsKgomotso MonagengNo ratings yet
- CSC Note Chap 1Document6 pagesCSC Note Chap 1Dyia AfrinaNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer: Calera High School Dawn BoneDocument14 pagesBasic Computer: Calera High School Dawn BoneMohammed R.HusseinNo ratings yet
- 5 - HardwareDocument12 pages5 - Hardwaredatu.he078No ratings yet
- ITS Unit 3Document18 pagesITS Unit 3shakila shaikhNo ratings yet
- Intro To CSDocument4 pagesIntro To CSsmr529437No ratings yet
- 04 Computers Knowledge-OrganiserDocument5 pages04 Computers Knowledge-OrganiserNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- CC100 Module 3Document8 pagesCC100 Module 3Hassina 05No ratings yet
- ICT TheoryDocument38 pagesICT Theoryyoonmimikyaw2008No ratings yet
- Reviewer: Computer Fundamentals: Low Capacity Warehouse SectionDocument9 pagesReviewer: Computer Fundamentals: Low Capacity Warehouse SectionRecil Marie BoragayNo ratings yet
- ProcessorDocument2 pagesProcessorMrashdi OmarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To MicroproDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Intro To Microproellyshacb-wp21No ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument2 pagesComputer Hardwarereymilyn zuluetaNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument24 pagesComputer HardwareJan Henry JebulanNo ratings yet
- Components of The System UnitDocument4 pagesComponents of The System UnitAhnNo ratings yet
- Ringkasan ICT: - MotherboardDocument4 pagesRingkasan ICT: - MotherboardmelchiornolifeNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of A Computer SystemDocument23 pagesBasic Components of A Computer SystemRafat AnsariNo ratings yet
- CSS ReviewerDocument6 pagesCSS Reviewerjunghoseok1258No ratings yet
- Comp 1Document4 pagesComp 1cocomartinNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Part-I: Components of Computer SystemDocument29 pagesChapter Two: Part-I: Components of Computer SystemyoantanNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems: NCM 110 Nursing Information LabDocument4 pagesComputer Systems: NCM 110 Nursing Information Labpamela rasmoNo ratings yet
- Ch02 Interacting With Computer SystemDocument43 pagesCh02 Interacting With Computer SystemAli HaiderNo ratings yet
- Comp Definitions: Sequence of Their ExecutionDocument7 pagesComp Definitions: Sequence of Their ExecutionApoorv BelgundiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-HardwareDocument4 pagesChapter 2-HardwareMohammad HamdanNo ratings yet
- PLD L1Document2 pagesPLD L1Apple ManNo ratings yet
- Chapter I ContinuedDocument9 pagesChapter I Continuedking hiikeyNo ratings yet
- IntropptDocument16 pagesIntropptmalinaojerome151No ratings yet
- Power Point Presentation On Memory of ComputerDocument17 pagesPower Point Presentation On Memory of Computerarpita banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 HCI Edit 2021Document15 pagesChapter - 3 HCI Edit 2021Bekode YadesaNo ratings yet
- Types of Components and Objects To Be Measured.: Mind Map Jan Clifford PahigonDocument2 pagesTypes of Components and Objects To Be Measured.: Mind Map Jan Clifford PahigonJan Clifford PahigonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document38 pagesLesson 1Dianne Jiecel CasimoNo ratings yet
- F4t2wt1-Intro To Computers2-ADocument2 pagesF4t2wt1-Intro To Computers2-Alatoya andersonNo ratings yet
- Computer IntroDocument32 pagesComputer IntroIshika VohraNo ratings yet
- Input Output StorageDocument46 pagesInput Output StorageCatherine Flores Jimenez100% (1)
- Session 2 and 3Document6 pagesSession 2 and 3lucilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Overview of A Computer System: Csc118 Fundamentals of Algorithm DevelopmentDocument16 pagesChapter 1: Overview of A Computer System: Csc118 Fundamentals of Algorithm DevelopmentKhairil Izwan IsmailNo ratings yet
- Midterm It EraDocument3 pagesMidterm It EraJonna BellNo ratings yet
- Intro HDMDocument21 pagesIntro HDMleexxjannelapatNo ratings yet
- 5 RamDocument5 pages5 Rammikko balagtasNo ratings yet
- ICTnotesDocument4 pagesICTnotesNominee OnlineNo ratings yet
- Year 9 NotesDocument29 pagesYear 9 Notesolivecresent6No ratings yet
- Year 9 NotesDocument29 pagesYear 9 Notesolivecresent6No ratings yet
- ITB. 3 NewDocument30 pagesITB. 3 NewRb REJANNo ratings yet
- Module1 PDFDocument45 pagesModule1 PDFshejal naikNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics: CS 1 Introduction To Computers and Computer Technology Rick Graziani Fall 2007Document58 pagesComputer Basics: CS 1 Introduction To Computers and Computer Technology Rick Graziani Fall 2007Androgel AbalajonNo ratings yet
- ICT ICF Lesson Outline 2Document2 pagesICT ICF Lesson Outline 2lorenzo aoalinNo ratings yet
- ComputerDocument14 pagesComputerLilian May MalfartaNo ratings yet
- ICT Lecture 02updatedDocument58 pagesICT Lecture 02updatedUzair Ali ZahidNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Group 4 FinalDocument25 pagesPowerPoint Group 4 Finalangel albaricoNo ratings yet
- Storage & Input and Output: Understanding ComputersDocument50 pagesStorage & Input and Output: Understanding ComputersFarhan QadirNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Literacy: Basic Computer Training Program For LGU Bayawan City EmployeesDocument51 pagesBasic Computer Literacy: Basic Computer Training Program For LGU Bayawan City Employeesnick21070No ratings yet
- What's in A Computer?: - Logical or Functional Organization: "Architecture"Document8 pagesWhat's in A Computer?: - Logical or Functional Organization: "Architecture"Lakhvir SinghNo ratings yet
- Intro To IT Part 2Document8 pagesIntro To IT Part 2Marc Jancent BagasbasNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.3.1 - DocumentationDocument13 pagesInformation Sheet 1.3.1 - DocumentationJohn Kenley SerranoNo ratings yet
- Dgital Bab 5Document30 pagesDgital Bab 5Naseer AbdaljabarNo ratings yet
- Đề Cương TACNDocument6 pagesĐề Cương TACNĐặng M.TùngNo ratings yet
- Computer SystemDocument63 pagesComputer SystemEden Mae Sagadraca TabliagoNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Course - Management Information SystemDocument22 pagesWelcome To The Course - Management Information SystemLipika haldarNo ratings yet
- A Computer Computer Hardware: Input Processing Output Storage Input OutputDocument3 pagesA Computer Computer Hardware: Input Processing Output Storage Input Outputسلطان العولقيNo ratings yet
- While Loop Practice-1Document15 pagesWhile Loop Practice-1M. Hamza AkhtarNo ratings yet
- While Loop Practice-2Document3 pagesWhile Loop Practice-2M. Hamza AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Switch Statement in Java-2Document3 pagesSwitch Statement in Java-2M. Hamza AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ProblemsDocument26 pagesChapter 3 ProblemsM. Hamza AkhtarNo ratings yet
- The Switch Statement-Java-1Document6 pagesThe Switch Statement-Java-1M. Hamza AkhtarNo ratings yet
- For-Nested For - Practice-1Document6 pagesFor-Nested For - Practice-1M. Hamza AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Basic Problems For Practice #3Document419 pagesBasic Problems For Practice #3M. Hamza AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Hostel Management SystemDocument15 pagesHostel Management SystemM. Hamza AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Array Practice 1Document5 pagesArray Practice 1M. Hamza AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Embedded Lab II Mtech Arm7-R13Document47 pagesEmbedded Lab II Mtech Arm7-R13log4iqbalNo ratings yet
- LG R510 - Schematics PDFDocument42 pagesLG R510 - Schematics PDFLuiz LandtechNo ratings yet
- Embedded Controllers (18EC2205) Laboratory Manual 2019-2020: Course CoordinatorDocument13 pagesEmbedded Controllers (18EC2205) Laboratory Manual 2019-2020: Course CoordinatorRam MNo ratings yet
- Canon IR 3045Document8 pagesCanon IR 3045vijaiNo ratings yet
- Libro El Trueno de La JusticiaDocument5 pagesLibro El Trueno de La JusticiaJose Luis Pittau0% (1)
- Specsheet MP5000Document2 pagesSpecsheet MP5000Marisagarcia2014No ratings yet
- Superior Quality: F Ine DetailDocument2 pagesSuperior Quality: F Ine DetailMergeNo ratings yet
- Lec - 9 - Lec - 10 MDSDocument29 pagesLec - 9 - Lec - 10 MDSMehedi Hasan EmonNo ratings yet
- Pisa SpecDocument9 pagesPisa SpecCarlos do PradoNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design - OverviewDocument3 pagesCompiler Design - OverviewLet's FunNo ratings yet
- A Milbus BriefDocument2 pagesA Milbus BriefsivaramNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Unit V: DSP ProcessorDocument20 pagesDigital Signal Processing Unit V: DSP ProcessorKumar ManiNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Platform Management Interface Firmware, Upgrade: Operational InstructionDocument23 pagesIntelligent Platform Management Interface Firmware, Upgrade: Operational InstructionLayth WaellNo ratings yet
- Di1 (Si210) Elevator: Trouble ShootingDocument74 pagesDi1 (Si210) Elevator: Trouble ShootingArnaldo cordovaNo ratings yet
- Printer Canon MF3110Document176 pagesPrinter Canon MF3110huubachNo ratings yet
- The SIMATIC S7 System FamilyDocument31 pagesThe SIMATIC S7 System Familyhwhhadi100% (1)
- Presented By: Pankaj Jaiswal Branch: ITDocument15 pagesPresented By: Pankaj Jaiswal Branch: ITAkilaNo ratings yet
- 8080 Manual IntelDocument222 pages8080 Manual IntelM N GeethasreeNo ratings yet
- Programmable Interfacing Devices PDFDocument6 pagesProgrammable Interfacing Devices PDFkunalg293No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Components of A Computer SystemDocument12 pagesUnit 2 Components of A Computer SystemPanopio EnterpNo ratings yet
- N68-GS3 UCC - multiQIGDocument117 pagesN68-GS3 UCC - multiQIGLabargarNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8086 Addressing ModesDocument3 pagesMicroprocessor - 8086 Addressing ModesGaganBhayanaNo ratings yet
- Fifa 15Document1,037 pagesFifa 15David CocaNo ratings yet
- m900 SFF Platform SpecDocument1 pagem900 SFF Platform SpecRrrNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet-CHS NCIIDocument9 pagesInformation Sheet-CHS NCIIRenel CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- E-Studio 166 Op Manual Toshiba ViewerDocument164 pagesE-Studio 166 Op Manual Toshiba Viewerdieubimat100% (1)
- Detail Lesson Plan in Ict Computer 7Document5 pagesDetail Lesson Plan in Ict Computer 7Imee-leen Eusebio-MateoNo ratings yet
- Idealtech PricelistDocument4 pagesIdealtech PricelistfitriNo ratings yet
- Name: Soumendu Patra Student Code: BWU/BNC/21/067 Roll Number: 067 Subject: Hw&Os Lab Course Code: BNCSC192 Topic: Types of MemoryDocument14 pagesName: Soumendu Patra Student Code: BWU/BNC/21/067 Roll Number: 067 Subject: Hw&Os Lab Course Code: BNCSC192 Topic: Types of MemorySoumendu PatraNo ratings yet