Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Equity and Poverty - Global - POVEQ - MYS
Uploaded by
al fatehOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Equity and Poverty - Global - POVEQ - MYS
Uploaded by
al fatehCopyright:
Available Formats
Poverty & Equity Brief
East Asia & Pacific
Malaysia
April 2020
Malaysia is an upper middle income country with a GNI per capita of nearly US$ 31,000 (2011 PPP). The national poverty line is
approximately US$ 4.00 (2011 PPP) per person per day, and has not increased in real terms since 1977, despite the country's
rapid economic development. As a result, only 0.4 percent of households live below the current national poverty line. At the
WBG's Upper Middle Income Class poverty line of US$ 5.50 (2011 PPP), poverty has declined from 16.7 percent of the
population in 2008 to 2.7 percent in 2015. Malaysia introduced a national multidimensional poverty index (MPI) in 2015, and by
that measure 0.9 percent of Malaysian households were estimated to be multidimensionally poor in 2015. Based on the World
Bank's Multidimensional Poverty Measure, only 0.2 percent of Malaysians were multidimensionally poor as of 2015.
Annual growth of the bottom 40 percent's mean household income per capita was 8.3 percent from 2011 to 2015, which was
2.4 percentage points faster than the corresponding growth for the country's total population. Median household income per
capita grew at 7.1 percent per year, also outpacing the growth in mean income. The inclusive pattern of growth has led to
significant reductions in relative income inequality, with relative Gini index decreasing from 43.9 in 2011 to 41.0 by 2015. Even
so, public discourse and policy statements have tended to focus on the continued increase in absolute income gaps, as the
absolute Gini index has increased by 17 percent from 2011 to 2015.
Malaysia's economy is projected to contract in 2020 because of the COVID-19 pandemic and associated economic disruptions,
with GDP forecast to decline in the range of 0.1 to 4.6 percent. As a result, the poverty rate at the US$ 5.50 (2011 PPP) poverty
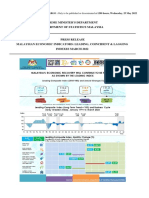
Number of Poor Rate
POVERTY (thousand) (%)
Period
National Poverty Line 122.9 0.4 2015
International Poverty Line
3.1 0.0 2015
3.3 in Malaysian ringgit (2015) or US$1.90 (2011 PPP) per day per capita
Lower Middle Income Class Poverty Line
71.0 0.2 2015
5.6 in Malaysian ringgit (2015) or US$3.20 (2011 PPP) per day per capita
Upper Middle Income Class Poverty Line
810.9 2.7 2015
9.6 in Malaysian ringgit (2015) or US$5.50 (2011 PPP) per day per capita
Multidimentional Poverty Measure 0.2 2015
SHARED PROSPERITY
Annualized Income Growth per capita of the bottom 40 percent 8.30 2011-2015
INEQUALITY
Gini Index 41.0 2015
Shared Prosperity Premium = Growth of the bottom 40 - Average Growth 2.35 2011-2015
GROWTH
Annualized GDP per capita growth 3.88 2011-2015
Annualized Income Growth per capita from Household Survey 5.95 2011-2015
MEDIAN INCOME
Growth of the annual median income/consumption per capita 7.14 2011-2015
Sources: WDI for GDP, National Statistical Offices for national poverty rates, POVCALNET as of Feburary 2020, and Global Monitoring Database for the rest.
Poverty Economist: Kenneth Simler
POVERTY HEADCOUNT RATE, 2008-2015 INEQUALITY TRENDS, 2008-2015
Gini Index
50.0
18 30
45.0
16
25 40.0
14
35.0
12 20
30.0
10
15 25.0
8
20.0
6 10 15.0
4 10.0
5
2 5.0
0 0 0.0
2008 2010 2012 2014 2008 2010 2012 2014
Poverty International Poverty Line Lower Middle IC Line GDP per
rate Upper Middle IC Line National Poverty Line capita
(%) GDP (Thousand)
Source: World Bank using HIS/EAPPOV/GMD Source: World Bank using HIS/EAPPOV/GMD
KEY INDICATORS
Upper Middle Income line(%) Relative group (%)
Distribution among groups: 2015 Multidimensional Poverty Measures (% of people): 2015
Non-Poor Poor Bottom 40 Top 60
Urban population 99 1 33 67 Monetary poverty (Income)
Rural population 93 7 64 36 Daily income less than US$1.90 per person 0.0
Males 97 3 40 60 Education
Females 97 3 40 60 At least one school-aged child is not enrolled in school 0.6
0 to 14 years old 95 5 52 48 No adult has completed primary education 0.7
15 to 64 years old 98 2 36 64 Access to basic infrastructure
65 and older 99 1 33 67 No access to limited-standard drinking water 1.6
Without education (16+) 95 5 54 46 No access to limited-standard sanitation 13.2
Primary education (16+) 97 3 49 51 No access to electricity 0.6
Secondary education (16+) 98 2 40 60
Tertiary/post-secondary education (16+) 99 1 15 85
Source: World Bank using HIS/EAPPOV/GMD Source: World Bank using HIS/EAPPOV/GMD
Notes: N/A missing value, N/A* value removed due to less than 30 observations
POVERTY DATA AND METHODOLOGY
The Department of Statistics Malaysia (DOSM) produces national poverty estimates. The estimates are income-based, using data from household surveys conducted
every 2.5 years. Official statistics and results from the 2019 household survey are expected to be released in May 2020. The method roughly follows the Cost of Basic
Needs methodology, with a food component based on nutritional requirements and a nonfood component based on consumption behavior of poor and near-poor
households. Tens of thousands of household-specific poverty lines are calculated, tailored to the location (state and rural/urban) and the age and gender composition of
each surveyed household. Because DOSM's methods sometimes diverge from those commonly used for international comparisons, particularly with regard to
equivalence scales and weighting, DOSM's published results often differ from those published by the World Bank or other international organizations even when using
the same primary data. For example, DOSM's published poverty rates refer to the proportion of households—not the more conventional proportion of the
population—living below the poverty line. Similarly, the official published Gini index uses total household income as the welfare aggregate, without normalization for
household size or composition, and calculates inequality across households. The resulting Gini index estimates are 2.0 to 2.5 percentage points lower than those
calculated by the more common approach that uses household income per capita and population weights.
HARMONIZATION
The numbers presented in this brief are based on the EAPPOV database. EAPPOV is a database of socio-economic statistics constructed using microdata from household
surveys in the East Asia and the Pacific (EAP) region and is managed by the East Asia & Pacific Team for Statistical Development (EAPTSD). As of January 2019, the
collection includes 19 countries and 93 surveys. Harmonized surveys in the EAPPOV database are compiled into 4 modules following Global Monitoring Database (GMD)
Harmonization guidelines. A subset of the harmonized variables form the basis of the GMD collection, including the welfare aggregate which is used for Global Poverty
Monitoring. Terms of use of the data adhere to agreements with the original data producers.
East Asia & Pacific povertydata.worldbank.org
Malaysia www.worldbank.org/poverty
You might also like
- Pakistan: Poverty & Equity BriefDocument2 pagesPakistan: Poverty & Equity BriefAwais AliNo ratings yet
- Philippines: Poverty & Equity BriefDocument2 pagesPhilippines: Poverty & Equity BriefCarollinne LeeNo ratings yet
- Indonesia's poverty rate falls to record low 9.2Document2 pagesIndonesia's poverty rate falls to record low 9.2Bella NovitaNo ratings yet
- Global_POVEQ_KENDocument2 pagesGlobal_POVEQ_KENLumin ONo ratings yet
- Vietnam: Poverty & Equity BriefDocument2 pagesVietnam: Poverty & Equity BriefAnnisa KhairaniNo ratings yet
- Global Poveq ZafDocument2 pagesGlobal Poveq ZafKevin FlynnNo ratings yet
- IACFM Presentations Feb 2020 PDFDocument51 pagesIACFM Presentations Feb 2020 PDFZack StraussNo ratings yet
- Global Poveq RusDocument2 pagesGlobal Poveq RusDina OsamaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Poverty Through Dimensions and MeasuresDocument41 pagesUnderstanding Poverty Through Dimensions and MeasuresダニエルNo ratings yet
- CBRE VN - ILS Quarterly Market Update (June 20)Document52 pagesCBRE VN - ILS Quarterly Market Update (June 20)Galih AnggoroNo ratings yet
- The Situation of Children in AlgeriaDocument8 pagesThe Situation of Children in AlgeriaSamraNo ratings yet
- JapanDocument4 pagesJapanMaria BuereNo ratings yet
- SPAIN Trade Investment Statistical Country NoteDocument10 pagesSPAIN Trade Investment Statistical Country Notelockleong93No ratings yet
- Arup Raha - Indonesia in A Covid-19 WorldDocument10 pagesArup Raha - Indonesia in A Covid-19 WorldMikesNo ratings yet
- Compiled Economic Survey English 2019/20Document256 pagesCompiled Economic Survey English 2019/20Hanu ManNo ratings yet
- Poverty Stuty Asia - Comparison of CountriesDocument16 pagesPoverty Stuty Asia - Comparison of Countriesjudith patnaanNo ratings yet
- Global POVEQ NGADocument2 pagesGlobal POVEQ NGABonifaceNo ratings yet
- Resilient Economy: Average Economic Decade Wise 2001 - 2010 4.81 %Document2 pagesResilient Economy: Average Economic Decade Wise 2001 - 2010 4.81 %Varshil DesaiNo ratings yet
- Brazil Paper AnalysisDocument60 pagesBrazil Paper AnalysisJella SantillanaNo ratings yet
- A Broken Social Elevator?: How To Promote Social MobilityDocument22 pagesA Broken Social Elevator?: How To Promote Social MobilityMohd Abu AjajNo ratings yet
- Financial GAPsDocument5 pagesFinancial GAPsGabriel FernandesNo ratings yet
- Causes and Consequences of Increasing Inequality in IndonesiaDocument24 pagesCauses and Consequences of Increasing Inequality in IndonesiaFaisal AnasNo ratings yet
- Comparing The Economic Indicators of Mali, Bangladesh and United StatesDocument4 pagesComparing The Economic Indicators of Mali, Bangladesh and United StatesShaikh Saifullah KhalidNo ratings yet
- Poverty Line IndonesiaDocument2 pagesPoverty Line IndonesiaDonny MeirantikaNo ratings yet
- Colombia: Growth Performance, Inequality and Environment Indicators: ColombiaDocument4 pagesColombia: Growth Performance, Inequality and Environment Indicators: ColombiaFelipe MoraNo ratings yet
- Greece Trade Investment Statistical Country NoteDocument10 pagesGreece Trade Investment Statistical Country NoteJake QuakeNo ratings yet
- Roadmap and Demographic TrendsDocument27 pagesRoadmap and Demographic TrendsSiti Hadijah Aspan, M.PHNo ratings yet
- Cushman & Wakefield - Presentation - THE ROLE OF SOUTHERN VIETNAM IN GLOBAL SUPPLY CHAINS - ENDocument28 pagesCushman & Wakefield - Presentation - THE ROLE OF SOUTHERN VIETNAM IN GLOBAL SUPPLY CHAINS - ENTrang DaoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Role of Mining in Philippines National SecurityDocument22 pagesStrategic Role of Mining in Philippines National Securitymonkeybike88No ratings yet
- LAC CFS 2017 Ecuador ENDocument4 pagesLAC CFS 2017 Ecuador ENMichaelNo ratings yet
- Interest Rates: Yield Curve Flattening Yield Curve FlatteningDocument2 pagesInterest Rates: Yield Curve Flattening Yield Curve FlatteningNishtha KaushikNo ratings yet
- Indonesia IEP June 2021 SlidesDocument17 pagesIndonesia IEP June 2021 Slidesfrisdian97No ratings yet
- 2015 Bakery and Cereals Market PDFDocument83 pages2015 Bakery and Cereals Market PDFashchua21No ratings yet
- Mohammed Alfalasi - Quiz 2Document3 pagesMohammed Alfalasi - Quiz 2mahamshoaib1No ratings yet
- Economic Survey 2019 - 20201125024153Document342 pagesEconomic Survey 2019 - 20201125024153Himani100% (1)
- Resumer Du MemoireDocument10 pagesResumer Du Memoirerita tamohNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka Economic Outlook: Fiscal Deficits, Debt and TradeDocument22 pagesSri Lanka Economic Outlook: Fiscal Deficits, Debt and TradeMecon Sri LankaNo ratings yet
- The Distributional Impact of Fiscal PolicyDocument28 pagesThe Distributional Impact of Fiscal PolicyFirst_LastNo ratings yet
- Edhie - IR4UHC Learning JkkiDocument29 pagesEdhie - IR4UHC Learning JkkiImam RizaldiNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Recent Monetary Policy and What It Entails For The Nigerian Economy - Ugochukwu AnthonyDocument10 pagesUnderstanding The Recent Monetary Policy and What It Entails For The Nigerian Economy - Ugochukwu Anthonyabdulbasitabdulazeez30No ratings yet
- Rural WellBeing HungaryDocument3 pagesRural WellBeing HungaryMaria C.No ratings yet
- Masa Depan Ekonomi Politik Pasca Covid 19: Perspektif Anak MudaDocument13 pagesMasa Depan Ekonomi Politik Pasca Covid 19: Perspektif Anak MudaBadrulArifinIINo ratings yet
- 2017 10 20 Realtor University Speaker Series Lavaughn Henry Income Saving Debt Patterns Among Young Adults Presentation Slides 10-30-2017Document29 pages2017 10 20 Realtor University Speaker Series Lavaughn Henry Income Saving Debt Patterns Among Young Adults Presentation Slides 10-30-2017National Association of REALTORS®No ratings yet
- Citn Presentation DR Olusegun Omisakin 2021Document12 pagesCitn Presentation DR Olusegun Omisakin 2021Rasheed LawalNo ratings yet
- Comm Sec Budget 2011Document20 pagesComm Sec Budget 2011peter_martin9335No ratings yet
- Bridgewater ReportDocument12 pagesBridgewater Reportw_fibNo ratings yet
- States and Their TaxesDocument2 pagesStates and Their TaxesCity Limits (New York)No ratings yet
- Consumer Insights Brochure-2016Document44 pagesConsumer Insights Brochure-2016JunnLRNo ratings yet
- Day1 Session2 DR - Joung Kyoung Eun Korea Labour and Society InstituteDocument28 pagesDay1 Session2 DR - Joung Kyoung Eun Korea Labour and Society InstitutemulyophNo ratings yet
- Italy's Macroeconomic OverviewDocument19 pagesItaly's Macroeconomic OverviewSatvikNo ratings yet
- Potential Inflationary PressuresDocument5 pagesPotential Inflationary PressuresKamran BayramovNo ratings yet
- Poverty and Inequality#Seventh Five Year Plan FY2016 - FY2020Document25 pagesPoverty and Inequality#Seventh Five Year Plan FY2016 - FY2020avi69No ratings yet
- LLIN Market and Supply Update April 2013Document7 pagesLLIN Market and Supply Update April 2013shuai liNo ratings yet
- Mgt-201 Assignment International Trade, Trends in World Trade and Overview of India'S TradeDocument21 pagesMgt-201 Assignment International Trade, Trends in World Trade and Overview of India'S TradeGable kaura L-2020 -A-16-BIVNo ratings yet
- Jing - Poverty and Subjective Poverty in Rural ChinaDocument25 pagesJing - Poverty and Subjective Poverty in Rural ChinaNova TambunanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Chile.Document23 pagesAnalysis of Chile.Estefanía Cardona UsmaNo ratings yet
- Haveman CausesofPoverty1Document37 pagesHaveman CausesofPoverty1Marcus CasillasNo ratings yet
- Technology Incentive Plan - TECHIP: Year 2019-20Document4 pagesTechnology Incentive Plan - TECHIP: Year 2019-20vikasarya044No ratings yet
- Schimbări Macroeconomice in RomaniaDocument19 pagesSchimbări Macroeconomice in Romaniachiratcu.valyNo ratings yet
- Vehicles Outnumber People in Malaysia - NSTDocument7 pagesVehicles Outnumber People in Malaysia - NSTal fatehNo ratings yet
- Celcom-Axiata Market Analysis & Qualitative JudgementDocument12 pagesCelcom-Axiata Market Analysis & Qualitative Judgemental fateh100% (1)
- 5 Most Important Things To Know About Malaysian Employment Laws - Career ResourcesDocument4 pages5 Most Important Things To Know About Malaysian Employment Laws - Career Resourcesal fatehNo ratings yet
- Malaysia: BTI 2022 Country ReportDocument39 pagesMalaysia: BTI 2022 Country Reportal fatehNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Economic Indicators - Leading, Coincident & Lagging Indexes March 2022Document2 pagesMalaysian Economic Indicators - Leading, Coincident & Lagging Indexes March 2022al fatehNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Foreign Direct Investment in Malaysia, 2021Document2 pagesStatistics of Foreign Direct Investment in Malaysia, 2021al fatehNo ratings yet
- Global InequalityDocument3 pagesGlobal InequalitymestrumNo ratings yet
- 32.do We Need HR - Repositioning People Management For SuccessDocument299 pages32.do We Need HR - Repositioning People Management For SuccessChan Myae MoeNo ratings yet
- Mso 3 em PDFDocument6 pagesMso 3 em PDFFirdosh Khan100% (2)
- Chapter 3 - Socio Economic ProblemDocument26 pagesChapter 3 - Socio Economic ProblemRaiiSyaNo ratings yet
- Rising Inequalities and New Vulnerabilities in Globalizing IndiaDocument40 pagesRising Inequalities and New Vulnerabilities in Globalizing IndiasumitromiNo ratings yet
- Ethics of Job Discrimination Chapter 7Document28 pagesEthics of Job Discrimination Chapter 7faqeersahibNo ratings yet
- Budget Equity ToolDocument22 pagesBudget Equity ToolEd PraetorianNo ratings yet
- Matrix Highlighting The Claims/Descriptions or Arguments of The 4 Major Classic Theories of DevelopmentDocument6 pagesMatrix Highlighting The Claims/Descriptions or Arguments of The 4 Major Classic Theories of DevelopmentMELANY A. MANRIZANo ratings yet
- Brelsford Et Al-Heretogeneity and Scale of Sustainable Development in CitiesDocument6 pagesBrelsford Et Al-Heretogeneity and Scale of Sustainable Development in CitiesIgnacio CancinoNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Sir Christian F. Choco: Final Examination in NSTP 2 (NSTPN02G)Document3 pagesPrepared By: Sir Christian F. Choco: Final Examination in NSTP 2 (NSTPN02G)Christian F. ChocoNo ratings yet
- Constructing A Democratic Developmental State in South AfricaDocument336 pagesConstructing A Democratic Developmental State in South Africadon_h_manzano100% (1)
- Vocabulary - Lists ExamplesDocument4 pagesVocabulary - Lists ExamplesTansëri MikãNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Poverty and Educational Inequality in Uttar PradeshDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Poverty and Educational Inequality in Uttar PradeshEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- The Arab Uprising: Causes, Prospects and ImplicationsDocument10 pagesThe Arab Uprising: Causes, Prospects and Implicationssak_akNo ratings yet
- Motivation LetterDocument2 pagesMotivation LetterMuhammad IqhrammullahNo ratings yet
- m3 Swat AnalysiDocument10 pagesm3 Swat Analysiapi-504223947No ratings yet
- Friedman tHE RIGHT TO THE cITY PDFDocument17 pagesFriedman tHE RIGHT TO THE cITY PDFcybermonchingNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.: Sociological Analysis of Visual TextsDocument55 pagesUnit 3.: Sociological Analysis of Visual TextsAllysa Marie SilbolNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document24 pagesWeek 3Clowie Anne CatenaNo ratings yet
- Experience Sociology 2Nd Edition Croteau Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument56 pagesExperience Sociology 2Nd Edition Croteau Test Bank Full Chapter PDFthoabangt69100% (11)
- Dimensions of GlobalizationDocument3 pagesDimensions of Globalizationshahbaz anjumNo ratings yet
- Literary Work-My Children Have Faces by Carol CampbellDocument3 pagesLiterary Work-My Children Have Faces by Carol CampbellHelena SELVA GALLEGONo ratings yet
- Why China Cannot Become Global Economic Leader - New FormatDocument16 pagesWhy China Cannot Become Global Economic Leader - New FormatThayabaran MunusamyNo ratings yet
- 12 Economics Case StudyDocument9 pages12 Economics Case StudyconnorNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Social Science - Outcomes of DemocracyDocument6 pagesPadhle 10th - Social Science - Outcomes of DemocracyAnuj Jangra100% (1)
- Ruth Lister - Defining PovertyDocument25 pagesRuth Lister - Defining PovertyDaniel Errázuriz Silva33% (3)
- PAD104 AssignmentDocument14 pagesPAD104 Assignmentadriana adlin100% (1)
- What Are The Effects of CorruptionDocument1 pageWhat Are The Effects of CorruptionBhirawa Ananditya WicaksanaNo ratings yet
- Rethinking Public ServicesDocument23 pagesRethinking Public ServicesCivilServiceWorldNo ratings yet
- Economics Course Chapters and AssignmentsDocument22 pagesEconomics Course Chapters and AssignmentsDanielleNo ratings yet