Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fuel Supply System To The Low-Pressure Stage
Uploaded by
cotin006Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fuel Supply System To The Low-Pressure Stage
Uploaded by
cotin006Copyright:
Available Formats
78 Fuel supply system to the low-pressure stage Overview
Fuel supply system to the low-pressure stage
The function of the fuel supply system is Overview
to store and filter the required fuel, and to
provide the fuel-injection system with fuel The fuel-supply system comprises the follow-
at a specific supply pressure in all operating ing main components (Figs. 1, 2, 3):
conditions. For some applications, the fuel 쐌 Fuel tank
return flow is also cooled. 쐌 Pre-filter
쐌 Control unit cooler (optional)
Essentially, the fuel-supply system differs 쐌 Presupply pump (optional, also in-tank
greatly, depending on the fuel-injection pump on cars)
system used, as the following figures for 쐌 Fuel filter
radial-piston pump, common-rail system and 쐌 Fuel pump (low-pressure)
passenger-car UIS show. 쐌 Pressure-control valve (overflow valve)
쐌 Fuel cooler (optional)
쐌 Low-pressure fuel lines
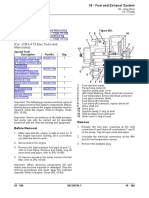
1 Fuel system on a fuel-injection system with radial-piston pump
Fig. 1
11 Fuel tank 7
12 Pre-filter 6
13 Presupply pump
14 Fuel filter 8
15 Low-pressure fuel
line
9
5
16 Radial-piston pump
with integrated
supply pump 4
17 High-pressure 11
delivery line
18 Nozzle-and-holder
1 10
æ UMK1970-2Y
assembly
19 Glow-plug 3 EDC 16
10 ECU 2
11 Fuel return line
2 Fuel system on a common-rail fuel-injection system
Fig. 2
11 Fuel tank
12 Pre-filter 8
13 Presupply pump 7
14 Fuel filter 7
15 Low-pressure fuel
6 10
lines 9
16 High-pressure pump
17 High-pressure fuel
lines 10 12 13
18 Fuel rail 11
19 Nozzle 5 EDC 16
10 Fuel return line 4
æ UMK2009-1Y
11 Fuel-temperature 5
1
sensor
12 ECU 3
13 Sheathed-element 2
glow plug
K. Reif (Ed.), Diesel Engine Management, Bosch Professional Automotive Information,
DOI 10.1007/978-3-658-03981-3_8, © Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden 2014
Fuel supply system to the low-pressure stage Overview 79
Fuel tank Diesel fuel filter
The fuel tank stores the fuel. It must be corro- Fuel-injection equipment for diesel engines
sion-resistant and leakproof at double the op- are manufactured with great precision and
erating pressure, but at least at 0.3 bar. Any are sensitive to the slightest contamination
gauge pressure must be relieved automatically in the fuel. The fuel filter has the following
by suitable vents or safety valves. When the functions:
vehicle is negotiating corners, inclines or 쐌 Reduce particulate impurities to avoid
bumps, fuel must not escape past the filler particulate erosion
cap or leak out of the pressure-relief vents or 쐌 Separate emulgated water from free water
valves. to avoid corrosion damage
The fuel tank must be separated from the
engine to prevent the fuel from igniting in The fuel filter must be adapted to the fuel-
case of an accident. injection system.
Fuel lines Fuel-supply pump
Besides metallic tubes, flexible, flame-retar- The fuel-supply pump draws fuel from the
dant tubes reinforced with braided-steel fuel tank and conveys it continuously to the
armoring can be used in the low-pressure high-pressure pump. The fuel pump is inte-
stage. They must be routed so as to avoid grated in the high-pressure pump on axial-
contact with moving components that might piston and radial-piston distributor pumps,
damage them and in such a way that any leak and in a few instances in common-rail sys-
fuel or evaporation cannot collect or ignite. tems.
The function of the fuel lines must not be im- Alternatively, an additional fuel pump can
paired by twisting of the chassis, movement be provided as a presupply pump.
of the engine or any other similar effects.
All fuel-conveying parts must be protected
against heat that may affect their proper
operation. On buses, fuel lines may not be
routed though the passenger cabin or the
driver’s cab. Fuel may not be gravity-fed.
3 Fuel system on a UIS fuel-injection system (passenger car)
11
8
9 R
7 6 Z
Fig. 3
10 11 Fuel tank
5 12 Presupply pump
13 Fuel cooler
4 3 14 ECU
15 Fuel filter
EDC 16
16 Fuel supply line
1 17 Fuel return line
æ UMK1971-2Y
18 Tandem pump
19 Fuel-temperature
2
sensor
10 Glow-plug
11 Nozzle
You might also like
- SMS Tips Technology 2013 Nr72 en 57601Document5 pagesSMS Tips Technology 2013 Nr72 en 57601jorjNo ratings yet
- 2. Forsthoffer's Rotating Equipment Handbooks: PumpsFrom Everand2. Forsthoffer's Rotating Equipment Handbooks: PumpsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- SchemaDocument14 pagesSchemaMarcelo MalagoNo ratings yet
- 114 Engine S&FDocument30 pages114 Engine S&Fivan alvesNo ratings yet
- Syslem: GenerolDocument6 pagesSyslem: GenerolAwliya TaqwaNo ratings yet
- SISEMUS5Document5 pagesSISEMUS5WillNo ratings yet
- Signature and Isx cm870 Fuel System Cummins Ontario TrainDocument16 pagesSignature and Isx cm870 Fuel System Cummins Ontario TrainHung Hua Nhu100% (8)
- Commissioning ChecklistDocument16 pagesCommissioning ChecklistLaiqNo ratings yet
- Engine HPCR 39 HalDocument39 pagesEngine HPCR 39 HalDian Idawati100% (2)
- 5-1 Steering SystemDocument7 pages5-1 Steering SystemSumitomo Laos Sumitomo LaosNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Mining Excavator CAT 6040: 03. SuperstructureDocument21 pagesHydraulic Mining Excavator CAT 6040: 03. Superstructure----100% (1)
- 2-1. EngineDocument14 pages2-1. EngineSumitomo ExcavatorNo ratings yet
- 2000 m72M013023 - 02EDocument42 pages2000 m72M013023 - 02EDimas Saputro100% (1)
- Hydraulic Mining Excavator CAT 6040: 03. SuperstructureDocument20 pagesHydraulic Mining Excavator CAT 6040: 03. SuperstructureJorby CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Commercial N67 220 132 KWDocument2 pagesCommercial N67 220 132 KWEnzo SovittiNo ratings yet
- Engine structure, systems and componentsDocument7 pagesEngine structure, systems and componentsЕвгений СолдатовNo ratings yet
- QSB QSL CM2250 - Fuel SystemsDocument49 pagesQSB QSL CM2250 - Fuel SystemsMussard100% (4)
- Manual Servicio Grand VitaraDocument34 pagesManual Servicio Grand Vitarajulio diazNo ratings yet
- 2.CRDi Diagnosis Expert - KMCDocument82 pages2.CRDi Diagnosis Expert - KMCAhmad Nashrullah100% (4)
- Great-Wall-Wingle-5 2016 en Manual de Taller 76a3f09b84 (394-510)Document117 pagesGreat-Wall-Wingle-5 2016 en Manual de Taller 76a3f09b84 (394-510)Brändön LänfräncöNo ratings yet
- Range Rover Fuel Tank SpecsDocument65 pagesRange Rover Fuel Tank Specsshafeek mshahNo ratings yet
- Mantenimiento QSX 15Document71 pagesMantenimiento QSX 15Wilfredo Gaince Parada100% (1)
- 03 - 2 - Service - Tests 107Document32 pages03 - 2 - Service - Tests 107domis007100% (2)
- GP200FDocument4 pagesGP200FAmane LexNo ratings yet
- HL740-9 2-1Document7 pagesHL740-9 2-1REMZONANo ratings yet
- Engine Assembly: 1. Major Components in Engine and Engine CompartmentDocument11 pagesEngine Assembly: 1. Major Components in Engine and Engine CompartmentchamNo ratings yet
- System Description Section 20: 737 Flight Crew Operations ManualDocument5 pagesSystem Description Section 20: 737 Flight Crew Operations ManualWilliam XavierNo ratings yet
- SECOND4Document3 pagesSECOND4WillNo ratings yet
- 8.edc 17 9 Aug 2016Document34 pages8.edc 17 9 Aug 2016iqbal husseinNo ratings yet
- Engine SummaryDocument53 pagesEngine Summaryhydeer 13100% (1)
- Fuel System JTEC ChryslerDocument56 pagesFuel System JTEC ChryslerkeiwerkasNo ratings yet
- Fsi Injection Part 1 PDFDocument20 pagesFsi Injection Part 1 PDFHenkNo ratings yet
- BS IV Common Rail SystemDocument151 pagesBS IV Common Rail SystemNM GroupNo ratings yet
- 6-Speed Automatic Gearbox 09GDocument23 pages6-Speed Automatic Gearbox 09GGloria VelaNo ratings yet
- 6M33 Training Document EPA - FA R01Document71 pages6M33 Training Document EPA - FA R01Daniel Ardila100% (1)
- Technical Training SeriesDocument8 pagesTechnical Training SeriesMubashiryyy mehmoodNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Large CRI EnginesDocument26 pagesStructure and Function of Large CRI EnginesTeguh Imam Adri100% (3)
- JCB 4.4 T3 Fuel Injection Pump RemovalDocument1 pageJCB 4.4 T3 Fuel Injection Pump RemovalKetutNo ratings yet
- 82.5 To 125 KVA PDFDocument53 pages82.5 To 125 KVA PDFMohammad Aslam100% (1)
- Common Rail Injection - Technical Overview - UnlockedDocument60 pagesCommon Rail Injection - Technical Overview - UnlockedPaula SousaNo ratings yet
- Cummins ISX Fuel System 02 05 PDFDocument18 pagesCummins ISX Fuel System 02 05 PDFJose juli100% (3)
- Jeep+2.5 TD PDFDocument38 pagesJeep+2.5 TD PDFMiguel ChaconNo ratings yet
- Chota ChilliDocument1 pageChota ChilliRishu ranaNo ratings yet
- Tech Data Sheet 6622Document1 pageTech Data Sheet 6622Shubhankar MenonNo ratings yet
- About The Trainer (VH-HCT-02) PDFDocument8 pagesAbout The Trainer (VH-HCT-02) PDFErwinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - MR FuelDocument75 pagesLesson 4 - MR FuelJaime castroNo ratings yet
- 05-737-800 Ramp & Transit FuelDocument90 pages05-737-800 Ramp & Transit FuelNicolas SalNo ratings yet
- 82 5KVAto125KVADocument53 pages82 5KVAto125KVALU YONo ratings yet
- 2.engine Fuel SystemDocument16 pages2.engine Fuel SystemSoeAyeNo ratings yet
- MC 10152915 9999Document10 pagesMC 10152915 9999Daniel Dario Greig SalazarNo ratings yet
- SPICA Fuel Supply Diagnostic Guide Nov 2004Document14 pagesSPICA Fuel Supply Diagnostic Guide Nov 2004oliver.staufferNo ratings yet
- Zaude ModrnDocument47 pagesZaude ModrnZewdeneh AsemieNo ratings yet
- Edc VolvoDocument20 pagesEdc VolvoAlex San Tana100% (1)
- Q145 WML 202Document11 pagesQ145 WML 202Sebastian Guzman camachoNo ratings yet
- SLU 1/2/3 Shank lubricator technical specificationDocument2 pagesSLU 1/2/3 Shank lubricator technical specificationMax RojasNo ratings yet
- 2 1 4 PDFDocument7 pages2 1 4 PDFAndre STANo ratings yet
- AE 04a EDC7 en GesamtDocument92 pagesAE 04a EDC7 en GesamtMJNo ratings yet
- NJ-ASHRAE FOS Pumping 3-6-2012Document47 pagesNJ-ASHRAE FOS Pumping 3-6-2012Hai PhanNo ratings yet
- Model 59503 C L Regulator InstructionsDocument4 pagesModel 59503 C L Regulator InstructionsmasNo ratings yet
- V1-Part A-09.0 Procedure For Trolley Emergency OperationDocument13 pagesV1-Part A-09.0 Procedure For Trolley Emergency Operationcotin006No ratings yet
- IR2101 DatasheetzDocument14 pagesIR2101 Datasheetzcotin006No ratings yet
- Tad1641ge PDFDocument2 pagesTad1641ge PDFjuanNo ratings yet
- C2e34580 Fe84 4e81 Bde2 15d8aaddd4b7 XDT14 PB Breakdown XDT14M, R, ZDocument3 pagesC2e34580 Fe84 4e81 Bde2 15d8aaddd4b7 XDT14 PB Breakdown XDT14M, R, Zcotin006No ratings yet
- TOEZVS 656DC5EnclosureInstallationManualDocument26 pagesTOEZVS 656DC5EnclosureInstallationManualcotin006No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment ExampleDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment Examplecotin006No ratings yet
- GP-PRO/PBIII Device Connection Manual for Yaskawa PLCsDocument16 pagesGP-PRO/PBIII Device Connection Manual for Yaskawa PLCscotin006No ratings yet
- Ge1 Ge2-GbDocument3 pagesGe1 Ge2-Gbcotin006No ratings yet
- Isc 2SC1114: Silicon NPN Power TransistorDocument2 pagesIsc 2SC1114: Silicon NPN Power Transistorcotin006No ratings yet
- Iso-8859-1 Sol 936Document1 pageIso-8859-1 Sol 936cotin006No ratings yet
- Fast Acting RectifiersDocument1 pageFast Acting Rectifierscotin006No ratings yet
- Single-Direction Thrust Ball BearingsDocument4 pagesSingle-Direction Thrust Ball Bearingscotin006No ratings yet
- 150MM Cordless Metal Cutter Parts ListDocument3 pages150MM Cordless Metal Cutter Parts Listcotin006No ratings yet
- Variable Pitch SheavesDocument2 pagesVariable Pitch Sheavescotin006No ratings yet
- Brake Motors FFB: Maintenance Guide Maintenance GuideDocument24 pagesBrake Motors FFB: Maintenance Guide Maintenance Guidecotin006No ratings yet
- U35000 - Motor - Brakes NORDDocument20 pagesU35000 - Motor - Brakes NORDany3000No ratings yet
- FFB Brake Motors Brochure Leroy-SomerDocument52 pagesFFB Brake Motors Brochure Leroy-Somercotin006No ratings yet
- MTU 12V4000 DS1550: Diesel Generator SetDocument5 pagesMTU 12V4000 DS1550: Diesel Generator SetTran PhuocNo ratings yet
- TORO 301 High Lift PDFDocument2 pagesTORO 301 High Lift PDFpressisoNo ratings yet
- IC Engine PDFDocument40 pagesIC Engine PDFDiyar NezarNo ratings yet
- Steam BoilerDocument62 pagesSteam BoilerLofi RadioNo ratings yet
- P1169 P0089 Rough Run FixDocument2 pagesP1169 P0089 Rough Run FixYuting NgNo ratings yet
- N54 Engine.: Aftersales Training - Product InformationDocument68 pagesN54 Engine.: Aftersales Training - Product InformationOmar Khaled Haggag100% (2)
- Sany Machinery Spare Parts List Shop Manual DiagramDocument24 pagesSany Machinery Spare Parts List Shop Manual Diagrammargaretsexton230990egs100% (108)
- BiodieselDocument31 pagesBiodieselAravind Zyx50% (2)
- Lab Report EngineDocument9 pagesLab Report EngineasyrafNo ratings yet
- 50T - Rt600eDocument20 pages50T - Rt600eangel lozadaNo ratings yet
- Ex - No 1 Dismantling of Piston EngineDocument9 pagesEx - No 1 Dismantling of Piston EngineesakkimuthuNo ratings yet
- Marine Engine Selection GuideDocument114 pagesMarine Engine Selection GuideMahmoud ElsherifNo ratings yet
- Walt Pyle - Solar Hydrogen ChroniclesDocument273 pagesWalt Pyle - Solar Hydrogen ChroniclesBelabaNo ratings yet
- Proper Sizing of Boiler Feedwater SystemsDocument3 pagesProper Sizing of Boiler Feedwater SystemsCarlos WayNo ratings yet
- J1171 Ignition Proof StandardDocument2 pagesJ1171 Ignition Proof StandardTan Akuma100% (1)
- MME 2010 Contents and Introduction PDFDocument13 pagesMME 2010 Contents and Introduction PDFAmaraaZoyaNo ratings yet
- Service Program A Service Program A Service Program A Service Program ADocument3 pagesService Program A Service Program A Service Program A Service Program ApeterNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Orion EngineDocument5 pagesMitsubishi Orion Enginenew0% (3)
- Manual on Handling and Storage of CoalDocument94 pagesManual on Handling and Storage of CoalSamrin NaazNo ratings yet
- JU6H-UF94 ProposalDocument10 pagesJU6H-UF94 ProposalRaúl Antonio MacíasNo ratings yet
- Om615 616 617 PDFDocument221 pagesOm615 616 617 PDFAnonymous wpUyixsj100% (1)
- D4204T5 EngineDocument52 pagesD4204T5 EngineCristian100% (7)
- Alternator replacement guide for agricultural and construction equipmentDocument6 pagesAlternator replacement guide for agricultural and construction equipmentEdwin CañonNo ratings yet
- Lincoln: MODEL 82054 Air Operated Chassis Pump Series "J"Document8 pagesLincoln: MODEL 82054 Air Operated Chassis Pump Series "J"Bram YudistiraNo ratings yet
- Technical (Modified) Agreement For 750HP Truck Mounted Drilling RigDocument12 pagesTechnical (Modified) Agreement For 750HP Truck Mounted Drilling Rigchtoil2020100% (1)
- S - Fa/Rs: Owners ManualDocument18 pagesS - Fa/Rs: Owners ManualbachstradNo ratings yet
- Model 3402E Specs & Operation GuideDocument43 pagesModel 3402E Specs & Operation GuideAlexis ValleNo ratings yet
- Dimsport Race2000 - Tuning - Ing - 06 PDFDocument39 pagesDimsport Race2000 - Tuning - Ing - 06 PDFBogdan CodoreanNo ratings yet
- Electric Veichle Presentation (Autosaved)Document19 pagesElectric Veichle Presentation (Autosaved)Raj DasNo ratings yet
- Manual Repair Nissan QuestDocument18 pagesManual Repair Nissan QuestALONDRA NATALI GONAZLEZ CANCHENo ratings yet