Professional Documents
Culture Documents
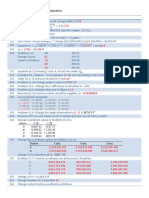
Point of Selection: Table4 Measurement Data On Travel Distance Error Unit: MM
Uploaded by
Mohit Sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageThe document presents measurement data for the travel distance error of a ball screw over a reference travel distance of 9 m/500 mm. The data shows small errors between the commanded position and actual travel distance, fluctuating between -0.019 mm and +0.001 mm. A graph of the measurement data depicts the positioning error and a representative travel distance line, with a representative travel distance error of -7 μm and fluctuation of 8.8 μm.
Original Description:
Original Title
Ball Screw Accuracy 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document presents measurement data for the travel distance error of a ball screw over a reference travel distance of 9 m/500 mm. The data shows small errors between the commanded position and actual travel distance, fluctuating between -0.019 mm and +0.001 mm. A graph of the measurement data depicts the positioning error and a representative travel distance line, with a representative travel distance error of -7 μm and fluctuation of 8.8 μm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pagePoint of Selection: Table4 Measurement Data On Travel Distance Error Unit: MM
Uploaded by
Mohit SharmaThe document presents measurement data for the travel distance error of a ball screw over a reference travel distance of 9 m/500 mm. The data shows small errors between the commanded position and actual travel distance, fluctuating between -0.019 mm and +0.001 mm. A graph of the measurement data depicts the positioning error and a representative travel distance line, with a representative travel distance error of -7 μm and fluctuation of 8.8 μm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
512E´
Point of Selection
Accuracy of the Ball Screw
Example: When the lead of a Ball Screw manufactured is measured with a target value for the refer-
ence travel distance of 9 m/500 mm, the following data are obtained.
Table4 Measurement Data on Travel Distance Error Unit: mm
Command position (A) 0 50 100 150
Travel distance (B) 0 49.998 100.001 149.996
Travel distance error (AB) 0 0.002 +0.001 0.004
Command position (A) 200 250 300 350
Travel distance (B) 199.995 249.993 299.989 349.985
Travel distance error (AB) 0.005 0.007 0.011 0.015
Command position (A) 400 450 500
Travel distance (B) 399.983 449.981 499.984
Travel distance error (AB) 0.017 0.019 0.016
The measurement data are expressed in a graph as shown in Fig.2.
The positioning error (A-B) is indicated as the actual travel distance while the straight line represent-
ing the tendency of the (A-B) graph refers to the representative travel distance.
The difference between the reference travel distance and the representative travel distance appears
as the representative travel distance error.
Ball Screw
Fig.2 Measurement Data on Travel Distance Error
[Measurements]
Representative travel distance error: -7 m
Fluctuation: 8.8 m
You might also like
- Deflection of Beams Laboratory: 1. ObjectivesDocument8 pagesDeflection of Beams Laboratory: 1. ObjectivesBenjamin OpokuNo ratings yet
- EC340 DEC150 Assign1Document3 pagesEC340 DEC150 Assign1Cholwe Essau MbilimaNo ratings yet
- Planchas TopoDocument102 pagesPlanchas Toposaul100% (2)
- 1d - Refix (Procedure& Calculation)Document23 pages1d - Refix (Procedure& Calculation)muhamadfarris100% (3)
- Control Mean 4Document1 pageControl Mean 4Carlos MartinezNo ratings yet
- THK PresisonDocument13 pagesTHK PresisonadolfovolumetricNo ratings yet
- Buckling TestDocument16 pagesBuckling TestAhmed ElqazazNo ratings yet
- Ore Reserve, 1,2021Document5 pagesOre Reserve, 1,2021Rajulapati VinodkumarNo ratings yet
- Ball Screw AccuracyDocument1 pageBall Screw AccuracyMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Levelling ManualDocument57 pagesLevelling ManualAddisu melakNo ratings yet
- ME 350 Lab 1Document5 pagesME 350 Lab 1Joseph (Ryan) Haas100% (1)
- Ballscrew Product Specifications 7 8Document2 pagesBallscrew Product Specifications 7 8harryNo ratings yet
- Surveying I Group AssignmentDocument2 pagesSurveying I Group AssignmentSolomon DanielNo ratings yet
- Result & Analysis - Indeterminate BeamDocument7 pagesResult & Analysis - Indeterminate Beamnasrul najmiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: Chapter 02 Trigonometrical LevellingDocument2 pagesTutorial 1: Chapter 02 Trigonometrical Levellingmukesh kafleNo ratings yet
- Sagar Institute of Science & Technology (Sistec) Department of Civil EngineeringDocument8 pagesSagar Institute of Science & Technology (Sistec) Department of Civil EngineeringASHISH SINGH SENGARNo ratings yet
- Traverse Calculation ExampleDocument7 pagesTraverse Calculation ExamplePalikaNo ratings yet
- Highway Assignment Week 9Document3 pagesHighway Assignment Week 9Farell TanNo ratings yet
- ME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Document6 pagesME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Kumar RajeshNo ratings yet
- Column Design Ecp203 VS Aci VS BS8110Document37 pagesColumn Design Ecp203 VS Aci VS BS8110MANo ratings yet
- 18BM60142 - Abhishek Tiwary - Assignment 6Document6 pages18BM60142 - Abhishek Tiwary - Assignment 6Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Intersections 2Document5 pagesIntersections 2junaidsurveyorNo ratings yet
- Stadia DisrDocument1 pageStadia DisrZabdiel Jairus AustriaNo ratings yet
- Moment Area MethodDocument9 pagesMoment Area MethodHammad RiazNo ratings yet
- Results & DiscussionDocument6 pagesResults & DiscussionSung Tze LauNo ratings yet
- MMME2053-DefBeams Lab Sheet Data CollectionDocument8 pagesMMME2053-DefBeams Lab Sheet Data CollectionBenjamin OpokuNo ratings yet
- University of Mines and Technology, TarkwaDocument2 pagesUniversity of Mines and Technology, TarkwaIsha IssahNo ratings yet
- ME51 429 R01a PDFDocument8 pagesME51 429 R01a PDFseb_dominiqueNo ratings yet
- Buckling TestDocument16 pagesBuckling TestAhmed ElqazazNo ratings yet
- G2 - Highway CW1-Marzuq UpdatedDocument35 pagesG2 - Highway CW1-Marzuq UpdatedsharvinNo ratings yet
- Ass (2) LevellingDocument3 pagesAss (2) LevellingMohamed HeshamNo ratings yet
- Lecture1b ConvCadastralRefixation Procedure and CalculationDocument25 pagesLecture1b ConvCadastralRefixation Procedure and CalculationHafidz NajmiNo ratings yet
- Ordinates and Angles ExampleDocument16 pagesOrdinates and Angles ExampleethjetjetNo ratings yet
- Camera Calibration ReportDocument5 pagesCamera Calibration ReportadintNo ratings yet
- C2a SiDocument1 pageC2a SihidayahazranNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Gls554Document3 pagesLab 4 Gls554Vanilla BartNo ratings yet
- Indeterminate BeamDocument12 pagesIndeterminate Beamnasrul najmiNo ratings yet
- University of MauritiusDocument4 pagesUniversity of MauritiusAkshay BundhooNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMAS FILTRACION LydiaaDocument5 pagesPROBLEMAS FILTRACION LydiaaAna Cristina SnchzNo ratings yet
- Road Alignment Calculation V 104Document227 pagesRoad Alignment Calculation V 104Bilal Ahmed BarbhuiyaNo ratings yet
- Surveying PDFDocument6 pagesSurveying PDFremster OñateNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3 Deflected Shape of A Simply Supported Overhanging BeamDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 3 Deflected Shape of A Simply Supported Overhanging BeamJihadinita El HajjiNo ratings yet
- Agisoft Photoscan Project ReportDocument7 pagesAgisoft Photoscan Project ReportAndi Putra ParlindunganNo ratings yet
- 09-Traverse SurveyingDocument26 pages09-Traverse SurveyingKristine DizonNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric He IghtingDocument1 pageTrigonometric He IghtingtanjiayiNo ratings yet
- GGE 1205 Surveying 1 2021 Main Exam PrintDocument5 pagesGGE 1205 Surveying 1 2021 Main Exam PrintlucyNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Surveying PRDocument5 pagesToaz - Info Surveying PRjek vinNo ratings yet
- UME 408 Machine Design-1 Redesign of An Angle Cutter/grinder A - 1 Force AND Stress Analysis OF Bevel Gear & Selection of BearingDocument8 pagesUME 408 Machine Design-1 Redesign of An Angle Cutter/grinder A - 1 Force AND Stress Analysis OF Bevel Gear & Selection of Bearingbalreet singhNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Range FindersDocument4 pagesUltrasonic Range Finders277192No ratings yet
- Two Hills A and C Have Elevations of 675 MDocument1 pageTwo Hills A and C Have Elevations of 675 MKian Kevin BautistaNo ratings yet
- Errata in 5th Edition of Adjustment ComputationsDocument2 pagesErrata in 5th Edition of Adjustment ComputationsdayatsajaNo ratings yet
- Levelling - Lab (216) 0000Document7 pagesLevelling - Lab (216) 0000mohammedNo ratings yet
- ReadingsDocument4 pagesReadingsMohafisto SofistoNo ratings yet
- Body Dimensions: Group 2Document20 pagesBody Dimensions: Group 2george georgeNo ratings yet
- nFINAL TUTORIAL FOR ALLDocument12 pagesnFINAL TUTORIAL FOR ALLkefapaul21No ratings yet
- Kelompok 28 - 02 - Muhammad Arvarefo Aulia RahmanDocument8 pagesKelompok 28 - 02 - Muhammad Arvarefo Aulia RahmanrefoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4. Direct ShearDocument4 pagesProblem Set 4. Direct ShearGerald MoaresNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering: Ce1014E SurveyingDocument2 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering: Ce1014E Surveyingjakharviru009No ratings yet
- Ball Screw Accuracy 8Document1 pageBall Screw Accuracy 8Mohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ball Screw Accuracy-2Document1 pageBall Screw Accuracy-2Mohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ball Screw AccuracyDocument1 pageBall Screw AccuracyMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 512E 15BallScrewDocument434 pages512E 15BallScrewMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bill Taxi Format - PDFDocument18 pagesBill Taxi Format - PDFMohit SharmaNo ratings yet