Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4.2 ELASTIC DEFORMATION OF AN AXIALLY LOADED MEMBER
Uploaded by
hidayahazranOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4.2 ELASTIC DEFORMATION OF AN AXIALLY LOADED MEMBER
Uploaded by
hidayahazranCopyright:
Available Formats
4.
2 ELASTIC DEFORMATION OF AN AXIALLY LOADED 129
M EMBER
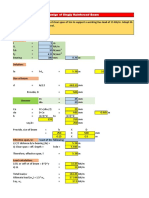
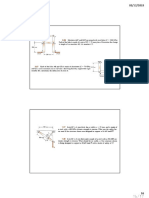
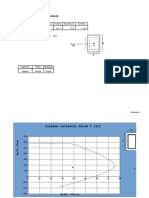
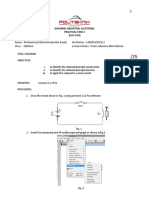
EXAMPLE 4.2
Rigid beam AB rests on the two short posts shown in Fig. 4–7a. AC is made of steel 90 k N
and has a diameter of 20 mm, and BD is made of aluminum and has a diameter of 200 mm
400
40 mm. Determine the displacement of point F on AB if a vertical load of 90 kN is mm
A B
applied over this point. Take Est = 200 GPa, Eal = 70 GPa.
F
300
mm
SOLUTION C D
Internal Force. The compressive forces acting at the top of each post are
determined from the equilibrium of member AB, Fig. 4–7b. These forces are (a)
equal to the internal forces in each post, Fig. 4–7c.
90 k N
Displacement. The displacement of the top of each post is 200 mm 4
400
mm
Post AC:
60 k N 30 k N
(b)
PACLAC [-60(10 3 ) N](0.300 m)
dA = = = -286(10 -6 ) m
A AC E st p(0.010 m)2[200(109) N>m2] 60 k N 30
kN
= 0.286 mm T
Post BD:
PBDL BD [-30(10 3)N](0.300 m)
dB = = = -102(10 )- 6m P AC = 60 k N
(c)
P B D = 30
A BDEal p(0.020 m)2[70(10 9) N>m 2] kN
= 0.102 mm T
A diagram showing the centerline displacements at A, B, and F on the
beam is shown in Fig. 4–7d. By proportion of the blue shaded triangle,
the displacement of point F is therefore
400 mm
dF = 0.102 mm + (0.184 mm) a b = 0.225 mm T Ans.
600 mm
600 mm
0.102
A F 400 B
mm mm
dF 0.102
0.184 mm
mm (d)
0.286
mm Fig. 4–7
You might also like
- 9P Equilibrium of RigidBodies 2D 2018Document25 pages9P Equilibrium of RigidBodies 2D 2018Ömer faruk SilNo ratings yet
- Singly Reinforced Beam ExcelDocument3 pagesSingly Reinforced Beam ExcelVEERKUMAR100% (3)
- MAK205 Chapter2 PDFDocument4 pagesMAK205 Chapter2 PDFdinish_813439106No ratings yet
- Column Foundation ConnectionDocument3 pagesColumn Foundation Connectionmdelacua2No ratings yet
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- Mechanicsofmaterialssi9theditionhibbelersolutionsmanual 180118182732 PDFDocument42 pagesMechanicsofmaterialssi9theditionhibbelersolutionsmanual 180118182732 PDFHassanImranNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids GTU PapersDocument17 pagesMechanics of Solids GTU Papersvaibhav shahNo ratings yet
- ColumnbaginDocument81 pagesColumnbagindhon escalanteNo ratings yet
- Review of Chapter 1-4Document16 pagesReview of Chapter 1-4Sabbir ZamanNo ratings yet
- BeamDocument3 pagesBeamLinoNo ratings yet
- DESIGN--REINFORCED RECTANGULAR BEAM AREA CALCULATIONDocument3 pagesDESIGN--REINFORCED RECTANGULAR BEAM AREA CALCULATIONHonorio Joshua P.No ratings yet
- 30m HL Mast Reinforcement DrawingDocument1 page30m HL Mast Reinforcement DrawingNavaraj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Column Design-Unaixial BendingDocument5 pagesColumn Design-Unaixial Bendingruchita jadhav100% (1)
- Design of StairDocument5 pagesDesign of StairWilfredoEnghoyNo ratings yet
- Design of Strap Foundation (3C-3D)Document5 pagesDesign of Strap Foundation (3C-3D)PraYush RajbhandariNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Tulangan Kolom: Pengaku (H 350mm)Document1 pagePerhitungan Tulangan Kolom: Pengaku (H 350mm)DonzNo ratings yet
- SOM Lecture 2-1Document8 pagesSOM Lecture 2-1dorothyagyeman24No ratings yet
- Design Data: CONNECTION DESIGN AS PER IS800-2007, IS4000-1992Document2 pagesDesign Data: CONNECTION DESIGN AS PER IS800-2007, IS4000-1992OmPrakashNo ratings yet
- Power Exercise No.2Document17 pagesPower Exercise No.2lobarbiojeassNo ratings yet
- Design of Rectangular Beam (B174, Entry Gate Level)Document1 pageDesign of Rectangular Beam (B174, Entry Gate Level)PraYush RajbhandariNo ratings yet
- I) Selecting Trial Footing DepthsDocument5 pagesI) Selecting Trial Footing DepthsPraYush RajbhandariNo ratings yet
- Rect Mom16Document64 pagesRect Mom16Jimmy Carranza PalominoNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall Design (IS 13920-2016)Document8 pagesShear Wall Design (IS 13920-2016)Sahil OzaNo ratings yet
- A. Material Properties: SC1 Base Plate Analysis and Design Project (Based On AISC LRFD - 2005) BuildingDocument8 pagesA. Material Properties: SC1 Base Plate Analysis and Design Project (Based On AISC LRFD - 2005) BuildingmaheshbandhamNo ratings yet
- Review ProblemsDocument3 pagesReview ProblemsJihan PacerNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 1Document5 pages1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 1onenoteforlocadNo ratings yet
- Corbel DesignDocument3 pagesCorbel DesignLim EcNo ratings yet
- MOM I - Module 45Document8 pagesMOM I - Module 45Muhammad HabibNo ratings yet
- Colom Interaksi - Int - Kolom 4 Sisi-AnalisaDocument24 pagesColom Interaksi - Int - Kolom 4 Sisi-AnalisaMarjoko SantosoNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Beam DesignDocument4 pagesRectangular Beam DesignsudipNo ratings yet
- 6 R Design 13.88 Section A-ADocument4 pages6 R Design 13.88 Section A-AsudipNo ratings yet
- Elective-II: Finite Element Method: B.E. (Mechanical Engineering) Eighth Semester (C.B.S.)Document4 pagesElective-II: Finite Element Method: B.E. (Mechanical Engineering) Eighth Semester (C.B.S.)Sufiyan RehmanNo ratings yet
- Example. A Reinforced Concrete Spandrel Beam Has Overall Dimensions of 250 X 460 and Is JoinedDocument4 pagesExample. A Reinforced Concrete Spandrel Beam Has Overall Dimensions of 250 X 460 and Is JoinedJames NeoNo ratings yet
- Beam Design DraftDocument5 pagesBeam Design DraftJohn Christopher BaquingNo ratings yet
- Design and analysis of reinforced concrete T-beamDocument9 pagesDesign and analysis of reinforced concrete T-beamAmit Kumar PaulNo ratings yet
- Flexión CompuestaDocument3 pagesFlexión CompuestaleoNo ratings yet
- Continuous Slab and Beam Design CalculationsDocument26 pagesContinuous Slab and Beam Design CalculationsRenne Jude RollorataNo ratings yet
- Analysis of T-Beam: Nos in Layer 1 Nos in Layer2Document9 pagesAnalysis of T-Beam: Nos in Layer 1 Nos in Layer2p_ignatiusNo ratings yet
- RCC11 Element DesignDocument6 pagesRCC11 Element DesignCioabla BogdanNo ratings yet
- Ce 401 Structural Design Lecture 12: Footing Design: Yaip K Telue Beng, Beng (Hons2A), PHD (Qut) Mie (Aust), Mie (PNG)Document10 pagesCe 401 Structural Design Lecture 12: Footing Design: Yaip K Telue Beng, Beng (Hons2A), PHD (Qut) Mie (Aust), Mie (PNG)Israel PopeNo ratings yet
- Gate - Psus: Civil EngineeringDocument20 pagesGate - Psus: Civil EngineeringSureshSawantNo ratings yet
- Design of Column Footings and Strap BeamDocument20 pagesDesign of Column Footings and Strap BeamAnish NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Elastic Deformation of Axially Loaded MembersDocument20 pagesElastic Deformation of Axially Loaded Membersmaria garridoNo ratings yet
- Strap Beam DesignDocument18 pagesStrap Beam DesignRabin BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- A. Structure Material: 1. End 2. MidDocument7 pagesA. Structure Material: 1. End 2. MidhendyNo ratings yet
- Project: Jobno: Description: DateDocument2 pagesProject: Jobno: Description: DateJONAS NGNo ratings yet
- Column & FootingDocument32 pagesColumn & FootingAmol potdarNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering, Iit Bombay: Tutorial Sheet 2Document6 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering, Iit Bombay: Tutorial Sheet 2Mat MatttNo ratings yet
- Pad Footing 1Document4 pagesPad Footing 1John SmithNo ratings yet
- Solutions To RC ProbsDocument16 pagesSolutions To RC ProbsJosephNo ratings yet
- Input Data:: 100 MM 100 MMDocument2 pagesInput Data:: 100 MM 100 MMAnonymous YakppP3vAnNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapter 2 (WǪ) PDFDocument16 pagesSolutions Chapter 2 (WǪ) PDF黃羿傑No ratings yet
- SLAB AND WALL DESIGN CALCULATIONSDocument7 pagesSLAB AND WALL DESIGN CALCULATIONSRameez Ahmed AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Diseño Biaxial de Zapata Medianera Con Viga Centradora: Acero MínimoDocument5 pagesDiseño Biaxial de Zapata Medianera Con Viga Centradora: Acero MínimoEdwar Perez HerreñoNo ratings yet
- Combined FootingDocument2 pagesCombined FootingAbu KhatriNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- 4ch1 1c Rms 20220303Document18 pages4ch1 1c Rms 20220303unknow nowwNo ratings yet
- Tac 12 CpaDocument27 pagesTac 12 CpaAlexandre BAUN TECNICO AUTOMACAONo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide: FeaturesDocument2 pagesQuick Start Guide: FeaturescwchowNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations - Daily Home Assignment 02 - (Udaan 2024)Document3 pagesQuadratic Equations - Daily Home Assignment 02 - (Udaan 2024)prachikatewa1No ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics IDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics INikash SubediNo ratings yet
- Series H20: DynaparDocument4 pagesSeries H20: DynaparJULIAN ANDRES ROJASNo ratings yet
- Specific gravity and water absorption of coarse aggregateDocument6 pagesSpecific gravity and water absorption of coarse aggregateshah fahadNo ratings yet
- 04ionic Equilibrium Set Test Final EDocument5 pages04ionic Equilibrium Set Test Final EBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- Catalogue C-Pac Asia W Mee15k019 RevDocument30 pagesCatalogue C-Pac Asia W Mee15k019 RevNguyễn Xuân Điệp100% (1)
- BS en 14511-3-2018 - (2021-05-20 - 12-47-53 PM)Document56 pagesBS en 14511-3-2018 - (2021-05-20 - 12-47-53 PM)Deepak JoyNo ratings yet
- 2021 J1 MYE H2 Chem Paper 2 - Suggested AnswersDocument16 pages2021 J1 MYE H2 Chem Paper 2 - Suggested AnswersPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- Bending Moment CoefficientsDocument2 pagesBending Moment CoefficientssabishanuNo ratings yet
- Carbonate ClassificationDocument5 pagesCarbonate ClassificationArpit UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Probability and Stochastic Processes (5~8장)Document151 pagesProbability and Stochastic Processes (5~8장)엄준현No ratings yet
- Industrial Electronic ReportDocument5 pagesIndustrial Electronic ReportAkmal HazimNo ratings yet
- KS D 3504: Steel bars for concrete reinforcementDocument36 pagesKS D 3504: Steel bars for concrete reinforcementTrọng Đẹp TraiNo ratings yet
- Linear Coefficients in Two VariablesDocument8 pagesLinear Coefficients in Two Variablesrishiko aquinoNo ratings yet
- Water TankDocument24 pagesWater Tankvishnumani3011No ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Revision Sheet (Part A) - Physics - Standard 10Document3 pagesCurrent Electricity - Revision Sheet (Part A) - Physics - Standard 10mNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 Quiz QP WITH ANSWERDocument5 pagesPhase 1 Quiz QP WITH ANSWERsureshkumarNo ratings yet
- Percubaan 2 Matematik SPM 09Document6 pagesPercubaan 2 Matematik SPM 09khai_83No ratings yet
- Study Habits Guide: Effective vs Ineffective TechniquesDocument30 pagesStudy Habits Guide: Effective vs Ineffective TechniquesJustin Dave TiozonNo ratings yet
- Vivek - Kohinoor Steel Power ResumeDocument3 pagesVivek - Kohinoor Steel Power ResumesambhuNo ratings yet
- Tarea 3 TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 3 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- KSB Hyamat VP LiteratureDocument48 pagesKSB Hyamat VP LiteratureMuhammad azeemNo ratings yet
- Prepp - In-Preparation Strategy For IAS UPSC CSE Electrical Engineering OptionalDocument6 pagesPrepp - In-Preparation Strategy For IAS UPSC CSE Electrical Engineering Optionalmojo xoxoNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument14 pagesChemistryHanna GalatiNo ratings yet
- Science Pre BoardDocument6 pagesScience Pre BoardvspkpracticalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 HWDocument2 pagesLesson 12 HWKatsu MatasuNo ratings yet
- Journal of Building Engineering: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesJournal of Building Engineering: Sciencedirectr3dh34rtNo ratings yet