Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supports, Inotropes, Vasopressors
Supports, Inotropes, Vasopressors
Uploaded by
Mohamed Sayed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesThis document provides dosing guidelines for various inotropes and vasopressors used in hemodynamic support. It lists recommended dose ranges for adrenaline, noradrenaline, dobutamine, and dopamine. For each drug, it also briefly outlines their primary indications, advantages, and potential adverse effects. All drugs require dilution before administration and dose adjustments may be needed in certain patient populations like renal impairment.
Original Description:
Original Title
supports, inotropes, vasopressors
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides dosing guidelines for various inotropes and vasopressors used in hemodynamic support. It lists recommended dose ranges for adrenaline, noradrenaline, dobutamine, and dopamine. For each drug, it also briefly outlines their primary indications, advantages, and potential adverse effects. All drugs require dilution before administration and dose adjustments may be needed in certain patient populations like renal impairment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesSupports, Inotropes, Vasopressors
Supports, Inotropes, Vasopressors
Uploaded by
Mohamed SayedThis document provides dosing guidelines for various inotropes and vasopressors used in hemodynamic support. It lists recommended dose ranges for adrenaline, noradrenaline, dobutamine, and dopamine. For each drug, it also briefly outlines their primary indications, advantages, and potential adverse effects. All drugs require dilution before administration and dose adjustments may be needed in certain patient populations like renal impairment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
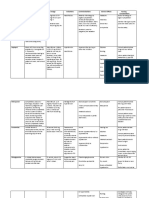
micrograms/mL).
Adrenalin 1 to 15 1 to 40 40 to 160 Initial vasopressor of
mcg/minute mcg/minute mcg/minute choice in anaphylactic
(0.01 to 0.5 (0.5 to 2 shock.
(0.01 to 0.2
mcg/kg mcg/kg Typically an add-on
mcg/kg/minute) /minute) agent to norepinephrine
/minute)
in septic shock when an
additional agent is
required to raise MAP to
target and occasionally
an alternative first-line
agent if norepinephrine
is contraindicated.
Increases heart rate;
may induce
tachyarrhythmias and
ischemia.
For inotropy, doses in
the higher end of the
suggested range is
needed
Elevates lactate
concentrations during
initial administration (ie,
may preclude use of
lactate clearance goal);
May decrease stroke
volume and cardiac
output in patients with
cardiac dysfunction.
May be given as bolus
dose of 50 to 100 mcg
to support blood
pressure during rapid
sequence intubation.
Must be diluted; eg, a
usual concentration is
10 mg in 250 mL D5W
or NS (40 mcg/mL).
Inotropin 2 to 5 mcg/kg 5 to 20 mcg/kg 20 to >50 An alternative to
/minute /minute mcg/kg norepinephrine in septic
/minute shock in highly selected
patients (eg, with
compromised systolic
function or absolute or
relative bradycardia and
a low risk of
tachyarrhythmias).
More adverse effects
(eg, tachycardia,
arrhythmias particularly
should be replacement for a first-
reserved for line vasopressor.
salvage Pure vasoconstrictor;
therapy may decrease stroke
volume and cardiac
output in myocardial
dysfunction or
precipitate ischemia in
coronary artery disease.
Must be diluted; eg, a
usual concentration is
25 units in 250 mL D5W
or NS (0.1 units/mL).
adrenergic)
Dobutrex 0.5 to 1 mcg/kg 2 to 20 mcg/kg 20 to 40 Initial agent of choice in
/minute /minute mcg/kg cardiogenic shock with
(alternatively, 2.5 /minute; low cardiac output and
mcg/kg/minute Doses >20 maintained blood
in more severe mcg/kg pressure.
cardiac /minute are Add-on to
decompensation) not norepinephrine for
recommended cardiac output
in heart failure augmentation in septic
and should be shock with myocardial
reserved for dysfunction (eg, in
Increases cardiac
contractility and
modestly increases
heart rate at high doses;
may cause peripheral
vasodilation,
hypotension, and/or
ventricular arrhythmia.
Renally cleared; dose
adjustment in renal
impairment needed.
Must be diluted; eg, a
usual concentration is
40 mg in 200 mL D5W
(200 micrograms/mL);
use of a commercially
available pre-diluted
solution is preferred.
es shown are for intravenous (IV) administration in adult patients. The initial doses
n this table may differ from those recommended in immediate post-cardiac arrest
ement (ie, advanced cardiac life support). For details, refer to the UpToDate topic
of post-cardiac arrest management in adults, section on hemodynamic
essors can cause life-threatening hypotension and hypertension, dysrhythmias, and
dial ischemia. They should be administered by use of an infusion pump adjusted
963 Version 15.0
You might also like
- Pharmacology Illustrated NotesDocument148 pagesPharmacology Illustrated NotesShikha Khemani90% (10)
- Aromatherapy Essential Oils ChartDocument6 pagesAromatherapy Essential Oils Chartamalya_84100% (9)
- Aherrera Notes PDFDocument213 pagesAherrera Notes PDFjampogaott100% (1)
- Pharmacology CardiacDocument1 pagePharmacology CardiacGrupo 4 CardiologiaNo ratings yet
- Botox HH TrainingDocument15 pagesBotox HH TrainingMohan J Reddy100% (5)
- Even Urologists Get Kidney Stones 1st PDFDocument205 pagesEven Urologists Get Kidney Stones 1st PDFIosub Lica-ClaudiuNo ratings yet
- Philips BV Endura Service Manual Frogenore PDFDocument5 pagesPhilips BV Endura Service Manual Frogenore PDFBashar Mohammad50% (6)
- Name of Drug Indication Contraindication Mechanism of Actions Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indication Contraindication Mechanism of Actions Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesLloyd Adrian GaffudNo ratings yet
- Tcs India Policy - Health InsuranceDocument42 pagesTcs India Policy - Health InsuranceSp Chandrashekarreddy100% (1)
- Drug Study - AmlodipineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - AmlodipineKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Responsibilities of First AiderDocument7 pagesResponsibilities of First AiderProject Director BFANo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument28 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study #2Document3 pagesDrug Study #2mharjoe pulmanoNo ratings yet
- Carvedilol - Drug StudyDocument1 pageCarvedilol - Drug StudyAcads useNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ORDocument3 pagesDrug Study ORIvan Jules P. PALMARESNo ratings yet
- Vaso PressorsDocument1 pageVaso PressorsJames BrownNo ratings yet
- Vasopressors and InotropesDocument4 pagesVasopressors and InotropesJayvee GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Intensive CareDocument9 pagesCardiac Intensive CareAlex AlexNo ratings yet
- QUINAPRILDocument2 pagesQUINAPRILTazkiaNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrilasi RATE CONTROL (Target HR 110 BPM)Document5 pagesAtrial Fibrilasi RATE CONTROL (Target HR 110 BPM)Melani NauritaNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument9 pagesDrug AnalysisKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- DobutamineDocument2 pagesDobutamineA.No ratings yet
- DobutamineDocument2 pagesDobutamineA.No ratings yet
- Drug Study 3Document5 pagesDrug Study 3jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument16 pagesEmergency DrugsDavid Hines LopezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study WengelDocument3 pagesDrug Study WengelWen SilverNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IcuDocument6 pagesDrug Study IcuJenny Juniora AjocNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CA.No ratings yet
- Drug Study Dopamine HCLDocument2 pagesDrug Study Dopamine HCLA.No ratings yet
- Acosta, Joyce Ara T. Week 7 & 8 Drug StudyDocument11 pagesAcosta, Joyce Ara T. Week 7 & 8 Drug StudyJoyce Ara Tumbaga AcostaNo ratings yet
- Jake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersDocument8 pagesJake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2023 1Document17 pagesDrug Study 2023 1Precious PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Cp201012 Learning Light-395Document2 pagesCp201012 Learning Light-395jyothiNo ratings yet
- Name of Drugs Mechanism of Action Dosage Indications Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations DigoxinDocument5 pagesName of Drugs Mechanism of Action Dosage Indications Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Digoxinjerwin01041No ratings yet
- Tuttle Mills 1975 Dobutamine Development of A New Catecholamine To Selectively Increase Cardiac ContractilityDocument12 pagesTuttle Mills 1975 Dobutamine Development of A New Catecholamine To Selectively Increase Cardiac ContractilityEli FATSAWONo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Part 2Document5 pagesPharmacology Part 2cherrymaemidoriNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blocking Agents: Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine)Document5 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking Agents: Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine)Montaser BadranNo ratings yet
- Product Manual ChronicDocument56 pagesProduct Manual ChronicsubhojitnayekNo ratings yet
- CGH Therapeutic Drug Monitoring GuidelinesDocument12 pagesCGH Therapeutic Drug Monitoring GuidelinesElaine100% (1)
- Management of Status EpilepticusDocument1 pageManagement of Status EpilepticusethainkeroNo ratings yet
- Medications at Red Zone: Sodium BicarbonateDocument13 pagesMedications at Red Zone: Sodium BicarbonateAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction NCPlapistolero33% (3)
- Dopamine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDopamine Drug StudyKwin Saludares100% (1)
- Heart FailureDocument3 pagesHeart FailurehawrazfarisNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument6 pagesHeart FailureAdnan RAHATNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument2 pagesAmiodaroneedemNo ratings yet
- DS NorepinephrineDocument4 pagesDS NorepinephrineReign RaineNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Atherosclerosis 1. Risk Factors of AtherosclerosisDocument5 pagesCase Study of Atherosclerosis 1. Risk Factors of AtherosclerosisCarly Beth Caparida LangerasNo ratings yet
- Reading C. Vasoactive Therapies.2015Document5 pagesReading C. Vasoactive Therapies.2015Mohamed AinacheNo ratings yet
- Drug Data Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindica Tion Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Data Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindica Tion Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesFlorante AnibanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Shaira May B. Luzadas BS Nursing Level 2-A Clinical Instructor: Mrs. Michelle AngDocument3 pagesShaira May B. Luzadas BS Nursing Level 2-A Clinical Instructor: Mrs. Michelle AngZoe Jisel LuzadasNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Effects: Lidocaine (Subgroup 1B)Document1 pageCardiac Effects: Lidocaine (Subgroup 1B)rpascua123No ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Egao, Vanessa Jones C. Section: Block 260Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Egao, Vanessa Jones C. Section: Block 260Vanessa EgaoNo ratings yet
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDocument13 pagesNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- NEURO2 1.02C Hemorrhagic Stroke - Dr. HiyadanDocument2 pagesNEURO2 1.02C Hemorrhagic Stroke - Dr. HiyadanAra Diocos100% (1)
- Generic Name:: ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesGeneric Name:: ElectrolytesEleazar Desillarico GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DS Norepinephrine HydrocortisoneDocument4 pagesDS Norepinephrine HydrocortisoneReign RaineNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Brand Name Classification Dosage Indications Side/ Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Name Brand Name Classification Dosage Indications Side/ Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesRonald BurkeNo ratings yet
- Hypotensi On Gastroeph Ageal Reflux: Headache Dizziness Tachycar Dia FlushingDocument3 pagesHypotensi On Gastroeph Ageal Reflux: Headache Dizziness Tachycar Dia FlushingElle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Inotropes and Vasoactive Drugs in The PICUDocument2 pagesInotropes and Vasoactive Drugs in The PICULynda TsaiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PharmacologyDocument23 pagesCardiac PharmacologyRavi Kant IyerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 3Document5 pagesDrug Study 3jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Vasoactive Medication Mmre (Autosaved)Document31 pagesVasoactive Medication Mmre (Autosaved)mohamed rashadNo ratings yet
- DilitiazemDocument2 pagesDilitiazemYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Infection and Public HealthDocument3 pagesJournal of Infection and Public Healthtasneem abdallahNo ratings yet
- Polarity Analysis: Checklist of Reliable SymptomsDocument2 pagesPolarity Analysis: Checklist of Reliable SymptomssivakumarsarvananNo ratings yet
- Kesehatan Wisata 2020 UNIZAR-Prof TutiDocument56 pagesKesehatan Wisata 2020 UNIZAR-Prof Tutirinaldy IX9No ratings yet
- How Do Pregnancy Tests WorkDocument1 pageHow Do Pregnancy Tests WorkGeorge ArgyrouNo ratings yet
- SLMCDocument5 pagesSLMCDaniel Vergara ArceNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Safety: Precautions The Cancer Care Team Will TakeDocument5 pagesChemotherapy Safety: Precautions The Cancer Care Team Will TakelintangNo ratings yet
- Unit 08 Client Assessment Matrix Carl Fitt ProsDocument2 pagesUnit 08 Client Assessment Matrix Carl Fitt Prosapi-312576381No ratings yet
- 1.oral Infectious DiseasesDocument68 pages1.oral Infectious DiseasesDrMohamed AssadawyNo ratings yet
- Blast Injuries SlidesDocument67 pagesBlast Injuries SlidesManuela CormioNo ratings yet
- Research A2 Diabetes PDFDocument6 pagesResearch A2 Diabetes PDFbing bongNo ratings yet
- Relaxation ExercisesDocument3 pagesRelaxation ExercisesspdfbookNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain MedicineDocument26 pagesAnaesthesia Critical Care & Pain MedicineasiyazaidiaNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 SIDEnotes LeonorasDocument10 pagesNCM 116 SIDEnotes LeonorasChrizzha Mae Eredera EredianoNo ratings yet
- PhobiasDocument10 pagesPhobiasHafiza Rija ShahidNo ratings yet
- Historical Background of Cerebral PalsyDocument11 pagesHistorical Background of Cerebral PalsypraveenNo ratings yet
- Puberty (OBGYN Presentation #1)Document15 pagesPuberty (OBGYN Presentation #1)Alex KadirNo ratings yet
- 17Document3 pages17elvie21No ratings yet
- KinsellaDocument8 pagesKinsellaJessica SofianNo ratings yet
- TPT Talking Points BookletDocument9 pagesTPT Talking Points BookletNasasira BensonNo ratings yet
- Rubrics Normal DeliveryDocument3 pagesRubrics Normal DeliveryLia TuazonNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation-ChickenpoxDocument41 pagesCase Presentation-ChickenpoxShaliniNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryCaterina PrepelitaNo ratings yet
- Black Seed (Nigella Sativa) - Clark's NutritionDocument5 pagesBlack Seed (Nigella Sativa) - Clark's NutritionZoran BlamNo ratings yet
- Complementary Alternative MedicineDocument4 pagesComplementary Alternative Medicineapi-383773980No ratings yet