Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3c Indonesia - Maja Wallengren
Uploaded by
Orlando Gonçalves BritoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3c Indonesia - Maja Wallengren
Uploaded by
Orlando Gonçalves BritoCopyright:
Available Formats
Country: Indonesia
GTECs and Gquality Coffee Integration Meeting
Poços de Caldas, Minas Gerais, Brazil
© By Maja Wallengren
Independent Analyst and Global Coffee Reporter
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
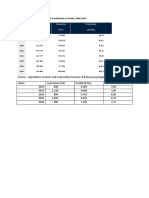
How important is Coffee compared to other local crops?
Of 23 mln hectares planted agricultural area (000 ha)
Crops Value Production Ha
(in mln $) (in 000 MT)
Rice 17,935 66,412 11.9 mln
Palm oil 9,369 21,534 7.2 mln
Natural Rubber 3,189 2,788 3.5 mln
Cassava 2,451 23,909 n/a
Coconuts 2,284 20,655 1.78 mln
Corn 1,798 18,364 3.2 mln
Banana 1,638 5,815 74,750
Tropical fruit 896.3 2,193 n/a
Sugar 870.2 26,500 478,200
Coffee 860.1 801 1.34 mln
Source: FAO, ICO
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Main coffee growing regions
Indonesia’s coffee regions
Aceh
Mandheling
Sulawesi
Borneo
Lampung
Java
Bali
Timor
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
How do growing regions and farmers look like?
Pictures of the origin
(pictures that represent the regions and farm types)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
How do growing regions and farmers look like?
Pictures of the origin
(pictures that represent the regions and farm types)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee In Indonesia - Overview
Year Production Area Yield Domestic Consumption
(starting) (000 60-kg bags) (000 Ha) (Bags/ha) (in 000 60-kg bags)
1990 7 400 950,000 7.8 1.242
2002 6 700 1 100 000 6.0 1 779
2003 6 400 1 100 000 6.0 1 833
2004 7 550 1 150 000 7.0 2 000
2005 9 150 1 150 000 8.0 2 500
2006 7 500 1 200 000 6.5 2 833
2007 6 250 1 200 000 5.2 3 333
2008 9 600 1 250 000 7.7 3 333
2009 11 380 1 300 000 8.8 3 400
2010 9 150 1 340 000 7.0 3 500
2011 8 750 1 340 000 6.5 3 600
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee “robusta” production – historic data
Year Production
(starting) (000 60-kg bags)
1990 6 700
2002 6 000
2003 5 650
2004 6 500
2005 8 150
2006 6 600
2007 5 450
2008 8 250
2009 9 730
2010 7 750
2011 7 400
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee “arabica” production: historic data
Year Production
(starting) (000 60-kg bags)
1990 700
2002 700
2003 750
2004 1 050
2005 1 100
2006 900
2007 800
2008 1 350
2009 1 650
2010 1 400
2011 1 350
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
How do growing regions and farmers look like?
Pictures of the origin
(pictures that represent the regions and farm types)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
How do growing regions and farmers look like?
Pictures of the origin
(pictures that represent the regions and farm types)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
How do growing regions and farmers look like?
Pictures of the origin
(pictures that represent the regions and farm types)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
How do growing regions and farmers look like?
Pictures of the origin
(pictures that represent the regions and farm types)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
How do growing regions and farmers look like?
Pictures of the origin
(pictures that represent the regions and farm types)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee farms profiles
Planted Area Number of Total
(ha) farmers Hectares % of total area
0.5-1 2.0 mln 500,000 37%
1-5 1.6 mln 500,000 37%
5-10 200,000 200,000 15%
10-50 200,000 100,000 7.5%
100-2000 5-10 4-5000 3.5%
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
How do growing regions and farmers look like?
Pictures of the origin
(pictures that represent the regions and farm types)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
How do growing regions and farmers look like?
Pictures of the origin
(pictures that represent the regions and farm types)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
How do growing regions and farmers look like?
Pictures of the origin
(pictures that represent the regions and farm types)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Technology Level
Coffee plantations age: 20 to 30 years
Main varieties: Canephora, typica, catimor
3*3 meters, average tree density
Planting spacing: 1200-1500 trees/ha
Pruning types and frequency: Stumping but no regular frequency
Fertilizers Dosage / ha / year
78 kilograms per hectare in cases
where fertilizer is used but less
than 10% of farmer use fertilizer
Mechanization Irrigation
Farms don’t use mechanization Irrigation is not used in Indonesia
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee Certification
% of coffee produced that is certified:
less than 5 percent and mostly in the arabica
Main Certifications organizations:
Rainforest Alliance
UtzKapeh
Fair Trade
Key requirements for certification:
Same as required by certifing agents for all other producers
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Commercialization
• The Commercialization is still involving many
intermediaries
• Most producers are forced to sell to private buyers
that will make the trip to the producing region
• Even though local infrastructure is good for a
developing country the distances travelled are often
long
• Indonesia does not have a strong co-op culture
• As a result the real purchasing price paid to
producers is still significantly below the market price
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee classification X Average earnings in 2011
Classification/types of coffee Average prices paid to growers in 2011
Grade 1: 11 defects per 300 gr $1.10-$130/lb for naturals-60-80 c/lb for robusta
Grade 2: 12-25 defects per 300 gr
Grade 3: 26-44 defects per 300 gr
Grade 4a: 45-60 defects per 300 gr
Grade 4b: 61-80 defects per 300 gr
Grade 5: 81-150 defects per 300 gr
Grade 6: 151-225 defects per 300 gr
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Sources of funds used in the coffee production
% Growers: There is no real funding available to growers
% Banks: Some banks provide small loans
% Incentives
• Government:
• NGOs: A few NGOs are involved in Aceh
• Importing countries
• Others: Some pre-harvesting financing from exporters
Are there any government incentives or programs to induce planted
area growth or quality improvements? Please describe
• The Indonesian Coffee Exporters Association has continued to
promote increasing arabica coffee to account for 20 percent of
the total production. Focus is on renovation rather than new areas
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee Crop Production Swot Analysis
Strengths Weaknesses
*Unique Arabica quality *Disorganized
*Established export market *Inconsistent
*Low population growth 1.07% *Un-ambitious
*Good rural infrastructure *Low productivity, small plots
Opportunities Threats
*Huge local market *Industrial growth
*Increasing middle class *Pressure on land
*Market demand *Competition for labor
*Tourism industry *Tourism industry
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Trends for medium/long term (Up to 2020)
Planted area: 1.3 mln ha to 1.5 mln ha if prices remain
high
Technology level: To remain relatively low across Indonesia
• Replanting: 10% to 20%
• Fertilizers: 10% to 50% if prices remain high
• Pruning: 20% to 50%
• Agrochemicals: 10% to 20%
• Mechanization: None seen in development, not likely to
change
• Irrigation: None seen in development, not likely to
change
Beverage quality: Continuing to improve in bean quality and
variety
Domestic consumption: Continuing to grow at 3-4%
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
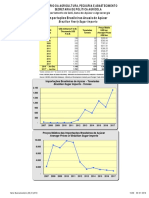
Trends for medium/long term (Up to 2020)
Domestic consumption: Continuing to grow at 3-7% a year for
next 5-10 years
A very similar story to that of Brazil but with a considerable
larger consumption of 240 million people
More than 25% are people below 25 years of age
Consumption is likely to rise to between 4 million and 5
million bags by 2020 from about 3.5 million bags today.
• Coffee shops have increased by 5-10% a year since 2008
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Coffee harvest and drying
(Describe the processes used)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Country: Indonesia
GTECs and Gquality Coffee Integration Meeting
Poços de Caldas, Minas Gerais, Brazil
© By Maja Wallengren
Independent Analyst and Global Coffee Reporter
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Main coffee growing regions
Indonesia’s coffee regions
Aceh
Sulawesi
Mandheling Borneo
Lampung
Java
Bali
Timor
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Production Costs - Robusta
Item % of total cost
Labor
Fertilizers
Agrochemicals
Maintenance (pruning, replanting, etc)
Transportation
Electrical Power
Depreciation
Coffee processing
Other operations
Mechanization
Taxes
Others (..........)
Total Cost (U$ / bag or Ton)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Production Costs - Arabica
Item % of total cost
Labor
Fertilizers
Agrochemicals
Maintenance (pruning, replanting, etc)
Transportation
Electrical Power
Depreciation
Coffee processing
Other operations
Mechanization
Taxes
Others (..........)
Total Cost (U$ / bag or Ton)
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
Plant Protection Issues and Management
Technology Level
Number of applications/
Main Diseases Products used to control year
Number of applications/
Main Pests (Insects) Products used to control year
GTECs Café e Gquality Integration March 7 – 9, 2012 / Poços de Caldas - MG
You might also like
- 3f Africa - Maina RuoDocument31 pages3f Africa - Maina RuoOrlando Gonçalves BritoNo ratings yet
- Global Cheesemaking Technology: Cheese Quality and CharacteristicsFrom EverandGlobal Cheesemaking Technology: Cheese Quality and CharacteristicsNo ratings yet
- Adipic Market 2Document39 pagesAdipic Market 2John Leonard FazNo ratings yet
- Plantation Crops Industry: Presenter: Manish Singhal Mba (Ab) 1 Year. Iabm BikanerDocument43 pagesPlantation Crops Industry: Presenter: Manish Singhal Mba (Ab) 1 Year. Iabm Bikanermanish_iabm3222No ratings yet
- Coffee Value Chain Analysis and Market Access Indonesia CaseDocument48 pagesCoffee Value Chain Analysis and Market Access Indonesia CaseBereket Teka TeshomeNo ratings yet
- 03 Presentation Adriana RoldanDocument33 pages03 Presentation Adriana RoldanJoshMooreNo ratings yet
- Sugar Presentation by Anuj AgarwalDocument31 pagesSugar Presentation by Anuj Agarwalanuj988No ratings yet
- 2 Pengeluaran Koko Di Malaysia PDFDocument72 pages2 Pengeluaran Koko Di Malaysia PDFHakimEngineerEmasNo ratings yet
- Cocoa - DDjajusman - IndonesiaDocument15 pagesCocoa - DDjajusman - IndonesiaSouvia RahimahNo ratings yet
- 2018S1POV Tab4 Adjko v2Document14 pages2018S1POV Tab4 Adjko v2Jacket TralalaNo ratings yet
- GDP: Growth: Real GDP: Yoy: Select This Link and CLDocument6 pagesGDP: Growth: Real GDP: Yoy: Select This Link and CLadityaNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: On-Going Schemes Water ManagementDocument5 pagesAgriculture: On-Going Schemes Water ManagementawaNo ratings yet
- Upah Minimum Provinsi Dan Inflasi Di DKI Jakarta, 1999-2020 Provincial Minimum Wages and Inflation at DKI Jakarta, 1999-2020Document3 pagesUpah Minimum Provinsi Dan Inflasi Di DKI Jakarta, 1999-2020 Provincial Minimum Wages and Inflation at DKI Jakarta, 1999-2020nurul husnaNo ratings yet
- Animal Feed Business in Indonesia: Australian Grains Industry ConferenceDocument10 pagesAnimal Feed Business in Indonesia: Australian Grains Industry ConferenceSita W. SuparyonoNo ratings yet
- Ashu Om 2Document3 pagesAshu Om 2imaashish5No ratings yet
- Sustainable Cacao Production 2021Document74 pagesSustainable Cacao Production 2021Pia Shannen OdinNo ratings yet
- Paparan - Kanya LakhsmiDocument21 pagesPaparan - Kanya Lakhsmiria indriatiNo ratings yet
- Company Name: Logo:: Amul (GCMMF)Document4 pagesCompany Name: Logo:: Amul (GCMMF)BhavNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem 2015 Poverty - Publication - 0Document44 pages1st Sem 2015 Poverty - Publication - 0mp dcNo ratings yet
- Presentation MarketReportTanzania 02Document11 pagesPresentation MarketReportTanzania 02ngobilegodwin121No ratings yet
- Sugar Manufacturing Industry. Mini Sugar Plant. Sugarcane Mill. - 11896Document68 pagesSugar Manufacturing Industry. Mini Sugar Plant. Sugarcane Mill. - 11896MahantNo ratings yet
- SPR Crop Prod 12 2018Document3 pagesSPR Crop Prod 12 2018Brittany EtheridgeNo ratings yet
- Sugar Annual Islamabad Pakistan 5-20-2010Document6 pagesSugar Annual Islamabad Pakistan 5-20-2010Shahzad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Name of The EnterpriseDocument19 pagesName of The EnterpriseRon Buecer CabeNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Byproduct Utilization - MNDocument22 pagesPresentation - Byproduct Utilization - MNMengistu NigussieNo ratings yet
- Harvested Area, Production Dan Produktivity of Paddy, 2008-2015Document1 pageHarvested Area, Production Dan Produktivity of Paddy, 2008-2015nilaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2: Market Study: Introduction To Feasibility Studies in AgricultureDocument8 pagesExercise 2: Market Study: Introduction To Feasibility Studies in AgricultureKristine Lea ClimacoNo ratings yet
- Mastat-1st-Assign-June-30-2018 (1) .XLSBDocument2 pagesMastat-1st-Assign-June-30-2018 (1) .XLSBKen-ken Chua GerolinNo ratings yet
- Manual Batch Records Mix Design ExcelDocument2 pagesManual Batch Records Mix Design ExcelReno Pratama Adi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Pemanfaatan Dan Konservasi Sumber Daya Alam Sumber Daya Alam Organik Annisa Rizka Wahid 15/379966/TK/43231Document6 pagesTugas 1 Pemanfaatan Dan Konservasi Sumber Daya Alam Sumber Daya Alam Organik Annisa Rizka Wahid 15/379966/TK/43231Yoel Dwi Putra GultomNo ratings yet
- Amul Priduct Ass - of MMDocument4 pagesAmul Priduct Ass - of MMsunilputusNo ratings yet
- Morning: Hot Drink CaféDocument7 pagesMorning: Hot Drink CaféKapish MahajanNo ratings yet
- Simulation Results - Industry Detail-3Document2 pagesSimulation Results - Industry Detail-3Ivneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Atbsp Map-Abcd 070218 PDFDocument113 pagesAtbsp Map-Abcd 070218 PDFGsp ChrismonNo ratings yet
- Emi Calculator AdvanceDocument8 pagesEmi Calculator AdvanceRana BiswasNo ratings yet
- PolyFlow BrochureDocument6 pagesPolyFlow BrochurejwochNo ratings yet
- Mango Road MapDocument37 pagesMango Road MapsamuelNo ratings yet
- Statistik TomatDocument2 pagesStatistik TomatfrisilNo ratings yet
- NR StatsDocument29 pagesNR StatshumayriNo ratings yet
- STP, ETP and CETP TreatmentDocument10 pagesSTP, ETP and CETP TreatmentDominic FerraoNo ratings yet
- Design, Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of A Maize ShellerDocument13 pagesDesign, Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of A Maize ShellerPeter AjewoleNo ratings yet
- Eastern Province: Funds Allocations To The ProvinceDocument3 pagesEastern Province: Funds Allocations To The ProvinceTharindu PriyanathNo ratings yet
- 07 2018 Power Statistics As of 29 March 2019 Annual LVM Peak Demand PDFDocument1 page07 2018 Power Statistics As of 29 March 2019 Annual LVM Peak Demand PDFDominic SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Textiles Gran Fe TextileDocument17 pagesTextiles Gran Fe TextileCanche Adriano DiazNo ratings yet
- 2018 Power Statistics - Final - As of 29 March 2019 - 7. Annual Peak Demand Per GridDocument1 page2018 Power Statistics - Final - As of 29 March 2019 - 7. Annual Peak Demand Per GridRenier Joseph Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- RCBC 112-6 Bank Reconciliation 2013Document1,598 pagesRCBC 112-6 Bank Reconciliation 2013Renniel DimalantaNo ratings yet
- No. Designation Qualification Basic Salary Per Month Production StafDocument3 pagesNo. Designation Qualification Basic Salary Per Month Production StafJai SanquilosNo ratings yet
- RCBC 112-6 Dec 31, 2015Document40 pagesRCBC 112-6 Dec 31, 2015Renniel DimalantaNo ratings yet
- Textiles Sector Cotton Sep19 PDFDocument9 pagesTextiles Sector Cotton Sep19 PDFSVP Group CottonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document10 pagesAssignment 2ADITYA BANSALNo ratings yet
- Project of Industrial Traning 'Document17 pagesProject of Industrial Traning 'Ritesh shuklaNo ratings yet
- Nothing To See Pls QiiuteDocument3 pagesNothing To See Pls QiiuteJingle BellNo ratings yet
- HOR 211 Production Technology of Fruits, Spices and Plantation Crops (2+1)Document38 pagesHOR 211 Production Technology of Fruits, Spices and Plantation Crops (2+1)KavieswarNo ratings yet
- Varieties and Production of Bananas in The PhilippinesDocument29 pagesVarieties and Production of Bananas in The PhilippinesMeow YoongiNo ratings yet
- MyFAST DataDocument3 pagesMyFAST DatadkdavorkalcNo ratings yet
- Copy13 of 25 ImpacanualDocument1 pageCopy13 of 25 ImpacanualFernando SalomãoNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document2 pagesBook 1Asim SaifullahNo ratings yet
- Sec A - Quiz 2 - 069 - AnweshaDocument18 pagesSec A - Quiz 2 - 069 - AnweshaAshish ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2-Converted-CompressedDocument10 pagesAssignment 2-Converted-CompressedADITYA BANSALNo ratings yet
- Study On E-Commerce in India & Madhya Pradesh As A StateDocument4 pagesStudy On E-Commerce in India & Madhya Pradesh As A StateishanhbmehtaNo ratings yet
- The Roaring TwentiesDocument2 pagesThe Roaring TwentiesBHARATH TRADERSNo ratings yet
- Birch Paper Case Study Solution - Performance MeasurementDocument2 pagesBirch Paper Case Study Solution - Performance MeasurementPiotr Bartenbach100% (3)
- A Raging Fire 14 - 02 - 24Document68 pagesA Raging Fire 14 - 02 - 24sadiqsamNo ratings yet
- FTX3044F Tutorial 1Document2 pagesFTX3044F Tutorial 1vrshaf001100% (1)
- Case in Point: The Filipino Farmer and GATT Quo Vadis?Document3 pagesCase in Point: The Filipino Farmer and GATT Quo Vadis?Chrisun CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- OM - Roll Out of CSSM-PMKVYDocument9 pagesOM - Roll Out of CSSM-PMKVYShallu ManchandaNo ratings yet
- China Construction BankDocument10 pagesChina Construction BankFRANCIS JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Project Synopsis On "Future of India-China Bilateral Trade Relations"Document8 pagesDissertation Project Synopsis On "Future of India-China Bilateral Trade Relations"rohanNo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument10 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceYeshwanth SunkaraNo ratings yet
- Flipkart Vs Amazon India: Who Won The Indian Ecommerce Battle in 2018?Document3 pagesFlipkart Vs Amazon India: Who Won The Indian Ecommerce Battle in 2018?Vivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Health Care System in Sri LankaDocument5 pagesHealth Care System in Sri LankaTanyaNo ratings yet
- Year 1 - 2021 Year 2 - 2022 Year 3 - 2023 Year 4-2024 Year 5 - 2025 Year 6 - 2026 85Document2 pagesYear 1 - 2021 Year 2 - 2022 Year 3 - 2023 Year 4-2024 Year 5 - 2025 Year 6 - 2026 85Francis BordonNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) : Simplified byDocument14 pagesGoods and Services Tax (GST) : Simplified byMohan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument44 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceYaswitha SadhuNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Musharraf's Era: Maaz IsmailDocument37 pagesAnalysis of Musharraf's Era: Maaz IsmailBushra NaumanNo ratings yet
- Muat TurunDocument3 pagesMuat TurunMelvina mousinNo ratings yet
- TYBCOM SEM 5 Export Marketing Nov 2019Document2 pagesTYBCOM SEM 5 Export Marketing Nov 2019Esha MuruganNo ratings yet
- Petunjuk DGT Per 25 PJ 2018Document2 pagesPetunjuk DGT Per 25 PJ 2018RJF HsbnNo ratings yet
- Foreigb ExchangeDocument2 pagesForeigb ExchangeruponNo ratings yet
- Tugas 30 Maret Surga Pasmod A - Kelompok 27Document17 pagesTugas 30 Maret Surga Pasmod A - Kelompok 27Sumitro SalimNo ratings yet
- Poverty Eradication in PakistanDocument4 pagesPoverty Eradication in PakistanBilal KhalidNo ratings yet
- 2-The Global EconomyDocument8 pages2-The Global EconomyWynnie RondonNo ratings yet
- Jenis Transaksi (Type Transaction) : Lima Puluh Juta Lima Ribu Rupiah Pembayaran DP MobilDocument2 pagesJenis Transaksi (Type Transaction) : Lima Puluh Juta Lima Ribu Rupiah Pembayaran DP MobilWilly TeguhNo ratings yet
- Lazaro Hernandez Roque 6751 W Indian School RD PHOENIX, AZ 85033Document2 pagesLazaro Hernandez Roque 6751 W Indian School RD PHOENIX, AZ 85033Rielzaruxo Ka Rioelzarux Ko XNo ratings yet
- 3 Piece Men SuitDocument1 page3 Piece Men Suitmdasifkhan2013No ratings yet
- Form-C para 10 See Chapter 5Document2 pagesForm-C para 10 See Chapter 5Farkat SakibNo ratings yet
- Chap06Mankiw - The Open EconomyDocument66 pagesChap06Mankiw - The Open EconomyopankbukanNo ratings yet
- PMC ScamDocument9 pagesPMC ScamSneha100% (1)
- 0469 MihamaDocument1 page0469 Mihamasaurav royNo ratings yet