Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 2topic1 - EDC-W2
Uploaded by
rithu varshanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2topic1 - EDC-W2
Uploaded by
rithu varshanCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3
AC Machines
Module2 :Topic 1,2
Three Phase Induction
motor- Construction and
operation
Dr. M. Nirmala /AP-III
Department of Electrical & Electronics
Engineering
Three Phase Induction motor
• The three phase induction motor is the most widely used electrical motor.
• Almost 80% of the mechanical power used by industries is provided by
three phase induction motors
• Advantages of three phase induction motors
• simple and rugged construction,
• low cost,
• good operating characteristics,
• the absence of commutator
• good speed regulation.
❖ In three phase induction motor, the power is transferred from stator to
rotor winding through induction. Hence it is called as rotating transformer.
❖ The induction motor is also called asynchronous motor as it runs at a
speed other than the synchronous speed.
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 2
Construction of 3 phase I.M
• A 3 phase induction motor is constructed from two main parts, namely the rotor and stator:
• Stator: As its name indicates stator is a stationary part of induction motor. A three phase stator
winding is placed in the stator of induction motor and the three phase supply is given to it.
• Rotor: The rotor is a rotating part of induction motor. The rotor is connected to the mechanical
load through the shaft
• The stator of the three-phase induction motor consists of three main parts : Stator frame, Stator
core, Stator winding
❖ Stator frame:
• It is the outer part of the three phase induction motor.
• Its main function is to support the stator core and the field winding.
• It acts as a covering, and it provides protection and mechanical strength to all the inner parts of
the induction motor.
• The frame is either made up of die-cast or fabricated steel. The frame of three phase induction
motor should be strong and rigid as the air gap length of three phase induction motor is very
small.
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 3
• Stator core
• The main function of the stator core is to carry the alternating flux. In order to reduce the eddy
current loss, the stator core is laminated.
• These laminated types of structure are made up of stamping which is about 0.4 to 0.5 mm thick.
• All the stamping are stamped together to form stator core, which is then housed in stator frame. The
stamping is made up of silicon steel, which helps to reduce the hysteresis loss occurring in the motor.
• Stator Winding
• The slots on the periphery of the stator core of the three-phase induction motor carry three phase
windings. Three phase ac supply is applied to this three-phase winding. It is wound for definite
number of poles.
• The three phases of the winding are connected either in star or delta depending upon which type of
starting method.
• The winding wound on the stator of three phase induction motor is also called field winding, and
when this winding is excited by three phase ac supply, it produces a rotating magnetic field.
• The choice of number of poles depends on the speed of the rotating magnetic field required. The
radial ducts are provided for the cooling purpose.
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 4
Rotor of the three phase induction
motor
• Depending upon the type of rotor construction used the three phase
induction motor are classified as:
1. Squirrel cage induction motor
2. Slip ring induction motor or wound induction motor or phase wound
induction motor.
❖ Squirrel cage induction rotor
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 5
Squirrel cage induction rotor
• The rotor core is cylindrical and slotted on its periphery.
• The rotor consists of uninsulated copper or aluminium bars called rotor conductors
• The bars are placed in the slots. These bars are permanently shorted at each end with the
help of conducting copper ring called end ring.
• The bars are usually brazed to the end rings to provide good mechanical strength.
• The entire structure looks like a cage, forming a closed electrical circuit. So the rotor is
called squirrel cage rotor.
• As the bars are permanently shorted to each other through end ring, the entire rotor
resistance is very very small. Hence this rotor also called short circuited rotor.
• As rotor itself is short circuited, no external resistance can have any effect on the rotor
resistance. Hence no external resistance can be introduced in the rotor circuit.
• So slip ring and brush assembly is not required for this rotor. Hence the construction of
this rotor is very simple.
• In this type of rotor, the slots are not arranged parallel to the shaft axis but are skewed.
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 6
Advantages of skewing of rotor slots
1. A magnetic hum i.e. noise gets reduced due to skewing hence skewing makes the motor
operation quieter.
2. It makes the smooth motor operation.
3. The stator and rotor teeth may get magnetically locked. Such a tendency of magnetic
locking gets reduced due to skewing.
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 7
Slip Ring Rotor or Wound Rotor
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 8
Slip Ring Rotor or Wound Rotor
• In this type of construction, rotor winding is exactly similar to the stator.
• The rotor carries a three phase star or delta connected, distributed
winding, wound for same number of poles as that of stator.
• The rotor construction is laminated and slotted. The slots contain the
rotor winding.
• The three ends of three phase winding, available after connecting the
winding in star or delta, are permanently connected to the slip rings.
• The slip rings are mounted on the same shaft
• In this type of rotor, the external resistances can be added with the help of
brushes and slip ring arrangement, in series with each phase of the rotor
winding.
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 9
Compare squirrel cage and wound
rotor constructions of induction motor.
S.No Wound or Slip ring rotor Squirrel cage rotor
1 Rotor consists of a three phase winding Rotor consists of bars, which are shorted at the
similar to the stator winding. ends with the help of end rings.
2 Construction is complicated. Construction is simple
3 Resistance can be added externally As permanently shorted, external resistance
cannot be added
4 Slip rings and brushes are present to add Slip rings and brushes are absent
external resistance.
5 Frequent maintenance is necessary Maintenance free
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 10
6 Rotors are costly Rotors are cheap
7 High starting torque can be Moderate starting torque
obtained
8 Rotor must be wound for same The rotor automatically adjusts itself for
number of poles the same number of poles as that of
stator
9 Rotor resistance starter can be used Rotor resistance starter cannot be used
.Speed control by rotor resistance is .Speed control by rotor resistance is not
possible possible
10 Rotor copper losses are high hence Rotor copper losses are les s hence
efficiency is less efficiency is high
11. Used for lifts, hoists, cranes, Used for lathes, drilling machines, fans,
elevators, compressors etc. blowers, waterpumps, grinders, printing
machines etc.
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 11
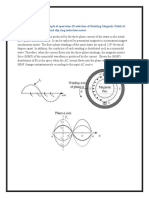
Working of three phase Induction motor
• When a three phase supply is given to the three phase stator winding, a rotating
magnetic field of constant magnitude is produced. The speed of this rotating
magnetic field is synchronous speed, Ns r.p.m.
• The R.M.F. gets cut by rotor conductors as R.M.F. sweeps over rotor conductors.
• Whenever conductor cuts the flux, e.m.f. gets induced in it according to Faraday’s
Law of electro-magnetic induction.
• As rotor forms closed circuit, induced e.m.f. circulates current through rotor called
rotor current whose direction is given by Lenz’s law.
• According to Lenz’s law the direction of induced current in the rotor is so as
oppose the cause producing it.
• The cause of rotor current is the induced e.m.f. which is induced because of
relative motion present between the rotating magnetic field and the rotor
conductors.
•
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 12
• Hence to oppose the relative motion i.e. to reduce the relative
speed, the rotor experiences a torque in the same direction as
that of R.M.F. and tries to catch up the speed of rotating magnetic
field.
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 13
Slip
• Slip of the induction motor is defined as the difference between the
synchronous speed (Ns) and actual speed of rotor i.e. motor (N) expressed
as a fraction of the synchronous speed (Ns). This is also called absolute slip
or fractional slip and is denoted as
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 14
• This is maximum value of slip s possible for induction motor which occurs
at start.
• While s = 0 gives us N = Ns which is not possible for an induction motor.
• So slip of induction motor cannot be zero under any circumstances.
• Practically motor operates in the slip range of 0.01 to 0.05 i.e. 1 % to 5 %.
• The slip corresponding to full load speed of the motor is called full load
slip.
27-04-2021 Dr.M.Nirmala AP-III/EEE 15
You might also like
- Practical-4 Aim: To study basic principle and construction of 3-ϕ induction motorDocument14 pagesPractical-4 Aim: To study basic principle and construction of 3-ϕ induction motorJay SathvaraNo ratings yet
- Practical-3 Aim: To study basic principle and construction of 3-ϕ induction motorDocument14 pagesPractical-3 Aim: To study basic principle and construction of 3-ϕ induction motorJay SathvaraNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument43 pagesInduction MotorAshvani ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-Ac Machines PDFDocument129 pagesUnit 3-Ac Machines PDFhotty pantsNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: by Ashvani Shukla Manager (C&I) BGR EnergyDocument15 pagesInduction Motor: by Ashvani Shukla Manager (C&I) BGR Energywondi BETNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Notes For GMEDocument165 pagesElectrical Machines Notes For GMESai CharanNo ratings yet
- Construction of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument6 pagesConstruction of Three Phase Induction MotorMuhammadZaydArattKhanNo ratings yet
- Single Phase AC Motor and Three Phase Induction Ac Motor PDFDocument28 pagesSingle Phase AC Motor and Three Phase Induction Ac Motor PDFmilan subediNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Induction Machines PDFDocument165 pagesChapter 5 Induction Machines PDFMillion GebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument28 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorNetaa sachinNo ratings yet
- P A G E 3 MC Emd-Three Phase Induction MotorDocument9 pagesP A G E 3 MC Emd-Three Phase Induction MotornikunjNo ratings yet
- Module-4a - Three Phase Induction Motor: By, Maria Sushma S Assistant Professor Dept of Eee, AtmeceDocument20 pagesModule-4a - Three Phase Induction Motor: By, Maria Sushma S Assistant Professor Dept of Eee, AtmeceDinesh Naik GNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Induction MotorDocument8 pagesUnit-2 Induction MotorJayantSharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument50 pagesElectrical MachinesTanvi SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Construction of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument13 pagesConstruction of Three Phase Induction MotorAttaUrRahmanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On - Induction MotorDocument15 pagesPresentation On - Induction MotorSri Hasthini AnnimallaNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Motor - 23!08!2016Document27 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor - 23!08!2016saravanan_KLUNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument20 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorKeshvan DhanapalNo ratings yet
- 2012 Chapter-4 (Induction Machine)Document104 pages2012 Chapter-4 (Induction Machine)mesfin snowNo ratings yet
- Module 3topic1,2 EDC W2Document11 pagesModule 3topic1,2 EDC W2Anand NirupNo ratings yet
- AC Machines-Three Phase Induction MotorsDocument8 pagesAC Machines-Three Phase Induction MotorsRinku SatapathyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Three Phase Induction MotorDocument87 pagesUnit 1 Three Phase Induction Motormahato741No ratings yet
- 3-Phase INDUCTION MOTORDocument6 pages3-Phase INDUCTION MOTORrgegNo ratings yet
- 3phase Induction MotorDocument36 pages3phase Induction MotorD_RAJNo ratings yet
- 1.what Are The Main Parts of Three-Phase Induction Motor?Document7 pages1.what Are The Main Parts of Three-Phase Induction Motor?Saiteja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Construction and OperationDocument36 pagesInduction Motor Construction and Operationkyaw winNo ratings yet
- 2.IM ConstructionDocument35 pages2.IM Constructionover allNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument3 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor780ANAY GUPTANo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument11 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorMohamed Ashraf Abd Elaazem Ali ٢٠١٥٠١٣٨٣No ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Motor: Prepared by D.Sharmitha AP/EEE Kumaraguru College of TechnologyDocument29 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor: Prepared by D.Sharmitha AP/EEE Kumaraguru College of TechnologySANJAYNo ratings yet
- Presentation On:: Induction MotorDocument29 pagesPresentation On:: Induction MotorashimaNo ratings yet
- Eliminating Rotor ProblemsDocument6 pagesEliminating Rotor Problemssuzette TabladaNo ratings yet
- EM 2 Lecture Notes Unit 1 2 3Document103 pagesEM 2 Lecture Notes Unit 1 2 3M ranganNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Basic Electrical - KtuQbankDocument23 pagesModule 6 - Basic Electrical - KtuQbankThahir TNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Presented by Pranesh KaDocument26 pagesInduction Motor: Presented by Pranesh KaPranesh KaNo ratings yet
- Machine LabDocument9 pagesMachine Labvikashyadavsy9No ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Motor ADocument2 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor AKantharaj ChinnappaNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Induction Motor - LongDocument63 pagesThree-Phase Induction Motor - LongTuhin techNo ratings yet
- AC MotorsDocument50 pagesAC MotorsDanzel SepilloNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument29 pagesInduction Motordumpy100% (1)
- Em 2 Chapter 3Document51 pagesEm 2 Chapter 3Sudhanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase IM Construction and WorkingDocument15 pages3-Phase IM Construction and Working19M647 - SRIRAM ANo ratings yet
- GRP No.1 El-P-MachineryDocument12 pagesGRP No.1 El-P-MachineryYasin OmaryNo ratings yet
- EE-101 (Unit-5)Document81 pagesEE-101 (Unit-5)Chauhan AyushmaanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 To 5 Induction Motor NotesDocument96 pagesUnit 3 To 5 Induction Motor Notesganesh ganeshNo ratings yet
- Bee Exp10Document4 pagesBee Exp10pranaybhandare765No ratings yet
- Electrical 3 Phase Motor Module 4 Part 2Document37 pagesElectrical 3 Phase Motor Module 4 Part 2Deeba Mushtaq AgaNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Em-Ii PDFDocument4 pagesExp 1 Em-Ii PDFabhay sharmaNo ratings yet
- P1: Explain The Working Principle of Operation (Production of Rotating Magnetic Field) of Three Phase Squirrel Cage and Slip Ring Induction MotorDocument4 pagesP1: Explain The Working Principle of Operation (Production of Rotating Magnetic Field) of Three Phase Squirrel Cage and Slip Ring Induction MotorSrinivasa PrabuNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument3 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorRaghu Jgfyc100% (2)
- Unit 5.1 Classification and ConstructionDocument16 pagesUnit 5.1 Classification and ConstructionArpit Personal 5No ratings yet
- Induction Motors Notes Wit Worked ExamplesDocument19 pagesInduction Motors Notes Wit Worked ExamplesFred RotichNo ratings yet
- A.C. MachineDocument32 pagesA.C. MachinehayikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Phase Induction MachinesDocument101 pagesChapter 3 Phase Induction Machineskelemyas ayalewNo ratings yet
- L3 - Three Phase Induction Motor-1Document52 pagesL3 - Three Phase Induction Motor-1Proshenjit BaruaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 IMSMDocument66 pagesModule 1 IMSMNIDHI A EEE20ANo ratings yet
- #5 Module 5Document52 pages#5 Module 5anishdeshmukh108No ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Motor 93138541001Document63 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor 93138541001Mce RegNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document12 pagesPresentation 2meghraj01No ratings yet
- Module II - Probability CompleteDocument47 pagesModule II - Probability Completerithu varshanNo ratings yet
- Module 3topic3 - W3 - Types of Single Phase I.MDocument11 pagesModule 3topic3 - W3 - Types of Single Phase I.Mrithu varshanNo ratings yet
- Asy1 - W2 - Capacitor Start IMDocument8 pagesAsy1 - W2 - Capacitor Start IMrithu varshanNo ratings yet
- Shaded Pole I.MDocument9 pagesShaded Pole I.Mrithu varshanNo ratings yet
- Asy2 - W2 - Capacitor Start-RunDocument9 pagesAsy2 - W2 - Capacitor Start-Runrithu varshanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Topic 1 - W2 - EDCDocument21 pagesModule 1 Topic 1 - W2 - EDCrithu varshanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Two Sweet Orange Cultivars Grafted On RootstockDocument11 pagesAssessment of Two Sweet Orange Cultivars Grafted On RootstockAhmad Hassan ChNo ratings yet
- 10.5 Functional Groups: Chapter 10 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: AlkanesDocument17 pages10.5 Functional Groups: Chapter 10 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: AlkanesYasarNo ratings yet
- Tool Set For Hobby Users in Plastic Box: Data SheetDocument2 pagesTool Set For Hobby Users in Plastic Box: Data SheetPutra KurniaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Thinking Dan Analisa Pengambilan KeputusanDocument47 pagesSistem Thinking Dan Analisa Pengambilan KeputusanyudiferiandiNo ratings yet
- Risk and ReturnDocument19 pagesRisk and ReturnRaju SainiNo ratings yet
- Kurva-S Arjasa - 2020 FebruariDocument57 pagesKurva-S Arjasa - 2020 FebruariIshaqNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Embedded Systems and Robotics PDFDocument67 pages1.introduction To Embedded Systems and Robotics PDFSK.FARAZ HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- MMW Chapter 3 Practice Activity - CAMACHO PDFDocument7 pagesMMW Chapter 3 Practice Activity - CAMACHO PDFJustin Maree CamachoNo ratings yet
- Finding The Greedy, Prodigal, and Suicidal Contracts at ScaleDocument14 pagesFinding The Greedy, Prodigal, and Suicidal Contracts at ScaleSaruul SaruulNo ratings yet
- OSI Model NotesDocument6 pagesOSI Model NotesBalajiPrabakarNo ratings yet
- Occurrences of Ore Minerals and Fluid Inclusion Study On The Kingking Porphyry Cu Au DepositDocument11 pagesOccurrences of Ore Minerals and Fluid Inclusion Study On The Kingking Porphyry Cu Au DepositLito Jay AntopuestoNo ratings yet
- (De Gruyter Stem) Dingyu Xue - Differential Equation Solutions With MATLAB - Fundamentals and Numerical Implementations (De Gruyter STEM) (2020, de Gruyter)Document454 pages(De Gruyter Stem) Dingyu Xue - Differential Equation Solutions With MATLAB - Fundamentals and Numerical Implementations (De Gruyter STEM) (2020, de Gruyter)adina crisanNo ratings yet
- Forces Worksheet #4 - Newton's Laws Problems: FrictionDocument2 pagesForces Worksheet #4 - Newton's Laws Problems: FrictionSTEVEN ST ANGELNo ratings yet
- Kony For SAP Tech Library 24.03Document2,352 pagesKony For SAP Tech Library 24.03suryananda sapbasis3No ratings yet
- Caixa ClaraDocument3 pagesCaixa ClaraDarioeNo ratings yet
- SSHTectia MigrationGuideDocument54 pagesSSHTectia MigrationGuideEquinoxe ChrissomallisNo ratings yet
- FH18 35(21)英文说明书Document16 pagesFH18 35(21)英文说明书ADM MTCNo ratings yet
- A 15 Resolution 601Document13 pagesA 15 Resolution 601mfazioliNo ratings yet
- Osiris MAP FeaturesDocument45 pagesOsiris MAP FeaturesNdèye Fatou SYNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Electronic DeviceDocument17 pagesIntelligent Electronic Devicesandeep_chauhan3770100% (1)
- MN Mining EngineeringDocument2 pagesMN Mining EngineeringsahithkumarNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Topology Optimization Upgrades Designs To Take Full Advantage of 3-D PrintingDocument3 pagesANSYS Topology Optimization Upgrades Designs To Take Full Advantage of 3-D PrintingAlexander Rueda OrduzNo ratings yet
- Manejo Cirúrgico de Doenças PancreáticasDocument75 pagesManejo Cirúrgico de Doenças PancreáticasSara KreboldNo ratings yet
- Design Plans For The " ": Advantage 10,000 Gallon Koi PondDocument19 pagesDesign Plans For The " ": Advantage 10,000 Gallon Koi PondMamad KoiNo ratings yet
- FIGL BI ExtractionDocument3 pagesFIGL BI ExtractionDurgesh Singh67% (3)
- Script To Calculate Your Sites Google SERP PositionDocument3 pagesScript To Calculate Your Sites Google SERP PositionDragos Florin LucianNo ratings yet
- Control Panel Space OptimizationDocument12 pagesControl Panel Space Optimizationyopy_yogieNo ratings yet
- Hitachi-12 Complete E CatalogDocument196 pagesHitachi-12 Complete E CatalogAcep KasepNo ratings yet