Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photographs and Descriptions of Pressure Ulcers
Uploaded by
Claire Gido0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pagePhotographs and Descriptions of Pressure Ulcers
Uploaded by
Claire GidoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
AGING & DISABILITY SERVICES ADMINISTRATION
SKIN OBSERVATION PROTOCOL
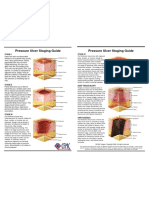
PHOTOGRAPHS & DESCRIPTIONS OF PRESSURE ULCERS
Stage I Stage II Stage III Stage IV
An observable pressure- Partial-thickness skin Full-thickness skin loss Full-thickness skin loss
related alteration of intact skin loss involving involving damage to or with extensive
with indicators as compared to epidermis, dermis, or necrosis of subcutaneous destruction, tissue
an adjacent or opposite area on both. The ulcer is tissue that may extend down necrosis, or damage to
the body. These indicators superficial and presents to, but not through, muscle, bone, or
may include changes in one or clinically as an underlying fascia. The ulcer supporting structures
more of the following: skin abrasion, blister, or presents clinically as a deep (e.g., tendon, joint
temperature, tissue shallow crater. crater with or without capsule). Undermining
consistency, and/or sensation. undermining of adjacent and sinus tracts may be
In lightly pigmented skin, the tissue. associated with Stage IV
ulcer appears as a defined area ulcers.
of persistent redness. In darker
skin, the ulcer may appear Stage 1 ulcers may not always be diagnosed reliably in patients with darkly
with persistent red, blue, or pigmented skin.
purple hues. When eschar is present, a pressure ulcer cannot be staged accurately until eschar
is removed.
Be alert to pressure-induced pain in patients with casts or support stockings.
Adapted from Statement on Pressure Ulcer Prevention Copyright, 1998. Used with
permission of National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel.
ADSA-CNC/NURSING SERVICES
APRIL 2003
You might also like
- ST ND RD THDocument8 pagesST ND RD THLuvleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Pressure UlcersDocument1 pagePressure UlcersnanaNo ratings yet
- 3 Pressure Ulcer (Bedsores) Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument12 pages3 Pressure Ulcer (Bedsores) Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsJOSHUA DICHOSONo ratings yet
- The Wound CareDocument51 pagesThe Wound CareIosefina DudeanuNo ratings yet
- NCP: Patient With A Pressure UlcerDocument2 pagesNCP: Patient With A Pressure UlcerICa Marlina100% (1)
- Chapter 48 - Skin Integrity and Wound CareDocument13 pagesChapter 48 - Skin Integrity and Wound CareHaji Raji100% (1)
- Impaired Skin DMDocument3 pagesImpaired Skin DMimnotdatsunny100% (1)
- NCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityFlauros Ryu Jabien90% (30)
- Wound Classification: Presented by Dr. Karen Zulkowski, D.N.S., RN Montana State UniversityDocument41 pagesWound Classification: Presented by Dr. Karen Zulkowski, D.N.S., RN Montana State UniversityDevasyaNo ratings yet
- Wound Care: Presentation For ACC Lab March 22, 2006Document19 pagesWound Care: Presentation For ACC Lab March 22, 2006heka_amrongNo ratings yet
- Mpaired Skin Integrity.Document8 pagesMpaired Skin Integrity.Tamil VillardoNo ratings yet
- META-Health Decoding Your Bodys Intelligence by Fisslinger, Johannes, RDocument196 pagesMETA-Health Decoding Your Bodys Intelligence by Fisslinger, Johannes, RTheo_96100% (2)
- Forensic Mycology - The Use of Fungi in Criminal Investigations.Document11 pagesForensic Mycology - The Use of Fungi in Criminal Investigations.Carlos MolinaNo ratings yet
- SJS NCPDocument4 pagesSJS NCPAira Alaro50% (2)
- Dr. John Stuart ReidENDocument2 pagesDr. John Stuart ReidEN刘育楠100% (1)
- NPIAP Staging PosterDocument2 pagesNPIAP Staging PosterDr. Hüseyin ŞAHİNNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin Integrity Related To Trauma or Infection: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesImpaired Skin Integrity Related To Trauma or Infection: Objectivesmhean azneitaNo ratings yet
- Skin Care PowerpointDocument52 pagesSkin Care Powerpointisapatrick812667% (3)
- NCP Impaired Skin IntergrityDocument3 pagesNCP Impaired Skin IntergrityGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- NCP CVDDocument5 pagesNCP CVDaejel1889% (9)
- Wound Documentation GuidelinesDocument2 pagesWound Documentation GuidelineslumitransNo ratings yet
- Pressure Injury Documentation and Assessment: A Guide To State-Of-The-Art Staging and Recording of PisDocument7 pagesPressure Injury Documentation and Assessment: A Guide To State-Of-The-Art Staging and Recording of PisAlexis TrivinoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcers Hand OutDocument52 pagesPressure Ulcers Hand OutAdiAri RosiuNo ratings yet
- Wounds Part OneDocument15 pagesWounds Part Onemei robiwidodoNo ratings yet
- Detecting Pressure Damage in People With Darkly Pigmented SkinDocument4 pagesDetecting Pressure Damage in People With Darkly Pigmented SkinShandz de RosasNo ratings yet
- Bed Sores WoundsDocument2 pagesBed Sores Woundspavni_rao6773No ratings yet
- Minggu I Miftahul Rauhan Bedah Plastik Ulkus DekubitusDocument25 pagesMinggu I Miftahul Rauhan Bedah Plastik Ulkus DekubitusmiftahulrauhanNo ratings yet
- Tissue ViabilityDocument5 pagesTissue Viabilitydezi981No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcomes Intervention Evaluation Nursing Interventions Rationale Resources RequiredDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcomes Intervention Evaluation Nursing Interventions Rationale Resources RequiredSiena KaleiNo ratings yet
- International PU Classification 2009Document2 pagesInternational PU Classification 2009metabolismeprotein100% (1)
- Skin Care and Management of Pressure UlcerDocument24 pagesSkin Care and Management of Pressure UlcerchellczyNo ratings yet
- Pressure Sores & ManagementDocument15 pagesPressure Sores & Managementmupt77No ratings yet
- Clinc Evidence 2020Document12 pagesClinc Evidence 2020Hari Prasath T RNo ratings yet
- WOUNDDocument6 pagesWOUNDLouie ParillaNo ratings yet
- Pressure UlcerDocument66 pagesPressure UlcerSwarnkar JayeshNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcer DR MirfatDocument50 pagesPressure Ulcer DR MirfatDrmirfat AlkashifNo ratings yet
- 2nd-Sem-Micro-Lab 2Document3 pages2nd-Sem-Micro-Lab 2Kristine Angie RamosNo ratings yet
- Pressure UlcersDocument36 pagesPressure UlcershylenshacNo ratings yet
- Approach To Debridement in Necrotizing Fasciitis: HowidoitDocument6 pagesApproach To Debridement in Necrotizing Fasciitis: HowidoitMc'onethree BrownNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcer DR MirfatDocument50 pagesPressure Ulcer DR MirfatDrmirfat AlkashifNo ratings yet
- Pressure UlcerDocument1 pagePressure UlcerIrish OrleansNo ratings yet
- Combine 3 Fitzpatricks Dermatology 9th Edition (PDF - Io)Document11 pagesCombine 3 Fitzpatricks Dermatology 9th Edition (PDF - Io)IcasiaYuseliNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcer StagesDocument3 pagesPressure Ulcer Stagesfreemind323No ratings yet
- Wound Assessment & CareDocument32 pagesWound Assessment & Caresami siddiqNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STG Independent STDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STG Independent STFrando kennethNo ratings yet
- Anti Decubitus Air Pump For Air Mattress SystemDocument7 pagesAnti Decubitus Air Pump For Air Mattress SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Staging and Management of Pressure-Induced Skin and Soft Tissue Injury - UpToDateDocument21 pagesClinical Staging and Management of Pressure-Induced Skin and Soft Tissue Injury - UpToDateNguyễn TrangtrangNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: STO: (Goal Met)Document4 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: STO: (Goal Met)Arian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcer Categorisation PosterDocument2 pagesPressure Ulcer Categorisation Posterdolcan.nicoletaNo ratings yet
- UNP-CN Do Not Reproduce: Learning Pocket DescriptionDocument37 pagesUNP-CN Do Not Reproduce: Learning Pocket DescriptionJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- Skin IntegrityDocument112 pagesSkin IntegrityHerlina NababanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Staging and Management of Pressure-Induced Skin and Soft Tissue Injury - UpToDateDocument31 pagesClinical Staging and Management of Pressure-Induced Skin and Soft Tissue Injury - UpToDatePriscillaNo ratings yet
- Burn IntroDocument2 pagesBurn IntroAllis RubioNo ratings yet
- Vigani2017 1Document15 pagesVigani2017 1Alexandra AvanuNo ratings yet
- Middle Age and Older AdultDocument2 pagesMiddle Age and Older AdultRAYANA UBASNo ratings yet
- Name: Score:: Tomas Claudio Memorial College College of NursingDocument31 pagesName: Score:: Tomas Claudio Memorial College College of NursingOng, IvanNo ratings yet
- 1.RagragPreventing Pressure Sore.1Document18 pages1.RagragPreventing Pressure Sore.1alsamixersNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Objective: Sto: DX: StoDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Objective: Sto: DX: StoJohn Ford VisoriaNo ratings yet
- The Dermatology Handbook: A Clinician's GuideFrom EverandThe Dermatology Handbook: A Clinician's GuideNeelam A. VashiNo ratings yet
- JOURNAL - Teaching Older Adult2Document3 pagesJOURNAL - Teaching Older Adult2Claire GidoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Evaluation of The HeartDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Evaluation of The HeartClaire GidoNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease of The HeartDocument3 pagesInfectious Disease of The HeartClaire GidoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Evaluation of The HeartDocument25 pagesDiagnostic Evaluation of The HeartClaire GidoNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgC-pzE5RQJIbCELZhV0cdk6ioDNIaJcmCjwqiRF DrvgVB6DZwpe H0xKtsQ-azwWzcoEmilNTpD-bIlbSmB5BUuUaB1XyQtaHmg4Ko6DsOFWTXCUb6HV9ROfpC cuspVp0vX5MLV8nPIBCDocument67 pagesACFrOgC-pzE5RQJIbCELZhV0cdk6ioDNIaJcmCjwqiRF DrvgVB6DZwpe H0xKtsQ-azwWzcoEmilNTpD-bIlbSmB5BUuUaB1XyQtaHmg4Ko6DsOFWTXCUb6HV9ROfpC cuspVp0vX5MLV8nPIBCClaire GidoNo ratings yet
- GerooonjournaldocDocument3 pagesGerooonjournaldocClaire GidoNo ratings yet
- REPORTDocument34 pagesREPORTClaire GidoNo ratings yet
- Vedantu Ncert PDF SheetDocument13 pagesVedantu Ncert PDF SheetKshreeNo ratings yet
- Orbulina Universa Globorotalia ConoideaDocument6 pagesOrbulina Universa Globorotalia Conoideawahyu robiulNo ratings yet
- Cancer Genetics-Genetic InstabilityDocument60 pagesCancer Genetics-Genetic InstabilityMadhu MithaNo ratings yet
- Azoospermia ThesisDocument8 pagesAzoospermia ThesisBuyCustomPapersOnlineUK100% (2)
- Medical Imaging and Pattern RecognitionDocument49 pagesMedical Imaging and Pattern RecognitionworkshoppeNo ratings yet
- Titin ProteinDocument40 pagesTitin ProteinAlexanderNo ratings yet
- IUCN Red List IndiaDocument66 pagesIUCN Red List Indiapratish100No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles: Classify Different Cell Types (Plant and Animal Tissues) and Specify The Functions of EachDocument42 pagesCell Organelles: Classify Different Cell Types (Plant and Animal Tissues) and Specify The Functions of EachTatingJainarNo ratings yet
- Coral Poaching in The Philippine: By: Aika Fore M. Garcia LLB 2CDocument16 pagesCoral Poaching in The Philippine: By: Aika Fore M. Garcia LLB 2CAika Fore GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Hatcheries in The Success or Failure of The Indian Shrimp IndustryDocument37 pagesThe Role of Hatcheries in The Success or Failure of The Indian Shrimp IndustryGlen ChoNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument23 pagesAppendicitisGina LositoNo ratings yet
- Dent 730Document15 pagesDent 730Noelia FernandezNo ratings yet
- 4 Progress Test A 7 RazredDocument4 pages4 Progress Test A 7 RazredMarijanaLazićNo ratings yet
- 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Ototoxicity in Adult Rats - Rapid Onset and Massive Destruction of Both Inner and Outer Hair Cells Above a Critical DoseDocument16 pages2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Ototoxicity in Adult Rats - Rapid Onset and Massive Destruction of Both Inner and Outer Hair Cells Above a Critical DosesovalaxNo ratings yet
- Jenis-Jenis Tumbuhan Suku Zingiberaceae Di Cagar Alam Pangi Binangga Sulawesi TengahDocument9 pagesJenis-Jenis Tumbuhan Suku Zingiberaceae Di Cagar Alam Pangi Binangga Sulawesi TengahFarida Nur AiniNo ratings yet
- SoilDocument4 pagesSoilYu HasNo ratings yet
- Biophysics Lecture 4 HemodynamicsDocument18 pagesBiophysics Lecture 4 HemodynamicsmalyaaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Rabun PDFDocument4 pagesJurnal Rabun PDFliana computerNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 7: Genetics Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageAP Biology Unit 7: Genetics Cheat Sheet: by ViaJ15No ratings yet
- Molecular-Docking Study of Malaria DrugDocument14 pagesMolecular-Docking Study of Malaria DrugJubairNo ratings yet
- Nicart, Jeric-Vincent C. - Genetics LaboratoryDocument3 pagesNicart, Jeric-Vincent C. - Genetics Laboratoryebenicart0No ratings yet
- Parasitism, Commensalism, and Mutualism: Exploring The Many Shades of SymbiosesDocument9 pagesParasitism, Commensalism, and Mutualism: Exploring The Many Shades of SymbiosesBen OusoNo ratings yet
- b8c2 PDFDocument193 pagesb8c2 PDFRhIdho POetraNo ratings yet
- Cucurbituril Homologues and Derivatives: New Opportunities in Supramolecular ChemistryDocument10 pagesCucurbituril Homologues and Derivatives: New Opportunities in Supramolecular Chemistrysanjay_dutta_5No ratings yet
- Zool 322 Lecture 4 2019-2020Document11 pagesZool 322 Lecture 4 2019-2020Timothy MutaiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report GCDocument8 pagesLab Report GCAyish MataNo ratings yet
- Grass Pea (Lathyrus Sativus L.) : Orphan Crop, Nutraceutical or Just Plain Food?Document18 pagesGrass Pea (Lathyrus Sativus L.) : Orphan Crop, Nutraceutical or Just Plain Food?ERYCK AZWARY ABRAHAM SURBAKTINo ratings yet