Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lieberman - Upending The Expectations of Science
Uploaded by
Marilyn G0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageToumai, a 6-7 million year old skull found in Chad, upends previous assumptions about human evolution. While resembling a chimpanzee, Toumai has physical traits like smaller canines and a taller face that are more human-like than previous fossils. Its discovery in central Africa challenges the view that human divergence from chimpanzees occurred solely in East Africa. Toumai raises new questions and shows that scientific theories are incomplete and subject to revision as new evidence emerges.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lieberman - Upending the Expectations of Science
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentToumai, a 6-7 million year old skull found in Chad, upends previous assumptions about human evolution. While resembling a chimpanzee, Toumai has physical traits like smaller canines and a taller face that are more human-like than previous fossils. Its discovery in central Africa challenges the view that human divergence from chimpanzees occurred solely in East Africa. Toumai raises new questions and shows that scientific theories are incomplete and subject to revision as new evidence emerges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageLieberman - Upending The Expectations of Science
Uploaded by
Marilyn GToumai, a 6-7 million year old skull found in Chad, upends previous assumptions about human evolution. While resembling a chimpanzee, Toumai has physical traits like smaller canines and a taller face that are more human-like than previous fossils. Its discovery in central Africa challenges the view that human divergence from chimpanzees occurred solely in East Africa. Toumai raises new questions and shows that scientific theories are incomplete and subject to revision as new evidence emerges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
lO
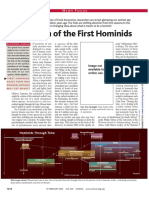
Upending the Expectations of Science
Does this mean Toumai, not Lucy, is assume a lack of evidence means the
verged sometime between five million believed humans first diverged from
a human ancestor? Perhaps, but we evidence doesn't exist, or that the evi:
By Daniel E. Lieberman and seven million years ago from a chimpanzees. dence we have is at all definitive. In
last common ancestor that was proba And Toumai's features also chal really have no clue.
lenge ourearlierunderstandingof this One delight of this discovery is that science, abirdinthehand is notworth
Cambridge, Mass. bly not much different from a chim
panzee. divergence.While Toumai is very like it raises more questions than it an two in the bush.
^ur earliest known homi- swers. Chiefamong these is what oth Michel Brunet and his French and
nid ancestor, Sahe- In most respects, Toumai looks like a chimpanzee, its face is more mod Chadian colleagues on the team that
a chimpanzee, with its small brain, ern, more human-like than that of any er species lived in central or West
lanthropus tchadensis, Africa that might be descendants of uncovered Toumai toiled in a harsh
wide front teeth, large canines and fossil we have from the four million
-was introduced to the
imposing brow ridge. But its cheek years that came after it Its face re- Toumai, ancestors of Homo, or both? part ofcentral Africa for more than 20
public last week under
teeth are a little bigger and thicker, its Toumai enlightens us becauseit dis years. Their efforts have rewarded us
the name Toumai,
canines are smaller and less pointy, proves our theories, and shows us with newInsights about human evolu
which means "hope of life" in the
its face is taller with less of a snout, again that we too often assume that tion, including in ways we don't yet
Goran language of the Sahel desert the data available to us contain all we comprehend. As we try to figure out
(The name is given to babies born
and it looks as if it might have walked
upright These features are typical of
An African skull need to" answer our questions. Before themeaning ofToumai, we should try
near the end of the dry season.) The the discovery of Toumai, forexample, to remember never to assume we've
skull, a portion of the jaw and tooth
later homiriids rather than apes.
Toumai's discovery — highly signif
alters our ideas on we confidentlytoldthe story of human learned enough to answer our ques
fragments are the only evidence of a evolution by looking throughtwo tiny tions. D
species that lived in central Africa
icant in the search for our evolution
ary origins — is equally significant
human evolution. windows: one in East Africa, the other
between six million and seven million for what it tells us about the nature of in South Africa.
years ago. The skull is unquestionably science. In science, one never pos Like the drunk in the old joke, We welcome comments and
cne of the most important fossil finds sesses the complete truth. One can searching for his keys under a lamp submissions to the editorial
in the last 100years, in part because it only look for what, at a given time,
sembles those of the earliest species post because the lightis better there, andOp^Ed pages. They maybe
provides the bestgllmpse-we'vehad of cannot-be-proved-ivrong.
of the genus Homo (to which we be we've focused on these two regions sent to the followinge-mail ad
the origins of the human lineage. Toumai, at one blow, has proved
long) rather than those of Australo because fossils preserve best there. dresses:
Toumai is vivid evidence of our many of our previous assumptions pithecus, the group of species from Yet Africa was a huge and complex EDITORIAL BOARD
close links with chimpanzees, with wrong. Toumai is older than many of East and South Africa that lived from place, full of diverse habitats that etUtorial@nyttmes.com
which we share almost 99 percent of us expected — by at least a million four million to two million years ago. might have been wonderful places to .
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
the same genetic code. Humans and years. Toumai is from a place 1,600 Australopithecines, including the fa be* a human ancestor — but where Ietters@nyttmes.com
chimpanzees almost certainly di- miles from the East African Rift Val mous skeleton Lucy, were always bones didn't fossilize welL
So one lesson of this great discovery OP-ED SUBMISSIONS
ley where almost all the earliest hu thought to be ancestral to Homo, yet oped@nytimes.com
Daniel E. Lieberman is a professor man fossil ancestors have been found, they have long, snouty faces — more — an old lesson, but always worth
of anthropology at Harvard. and where many scientists therefore like a chimpanzee's than Toumai's. relearning — is that we shouldnever
• -r—- "I i i•• ."I i • • t lj ' i • -*P i • • *• rrl i ,i • iii •• -f F i ii n' iisi \ • ,-^| i • •••'' -'^1 „M
You might also like
- Humankind History and Origins: A Short Guide on How we Came to beFrom EverandHumankind History and Origins: A Short Guide on How we Came to beNo ratings yet
- Heyokha Brothers Investment Report 3Q 2015 GeneralDocument11 pagesHeyokha Brothers Investment Report 3Q 2015 GeneralEdgar BrownNo ratings yet
- UNDSELF MidtermsDocument16 pagesUNDSELF MidtermsZOEZEL ANNLEIH LAYONGNo ratings yet
- In Search of The First Hominids: Image Not Available For Online UseDocument6 pagesIn Search of The First Hominids: Image Not Available For Online UseDRagonrougeNo ratings yet
- HUMAN EVOLUTION UNCOVERED AT RISING STAR CAVEDocument8 pagesHUMAN EVOLUTION UNCOVERED AT RISING STAR CAVEkoriNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Sienna Goodwin - NOVA - Evolution - Lab - Worksheets - Mission6 - uL2tHcoDocument6 pagesKami Export - Sienna Goodwin - NOVA - Evolution - Lab - Worksheets - Mission6 - uL2tHcoSienna GoodwinNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Early Humans in the Miocene PeriodDocument6 pagesEvolution of Early Humans in the Miocene PeriodManohar ReddyNo ratings yet
- One For All - SADocument4 pagesOne For All - SAmauoscuroNo ratings yet
- Homo sapiens PräsentationDocument23 pagesHomo sapiens Präsentationmp8b2v54ntNo ratings yet
- Donald C. Johanson: Founding Director, Institute of Human Origins, Arizona State UniversityDocument2 pagesDonald C. Johanson: Founding Director, Institute of Human Origins, Arizona State Universityart quaNo ratings yet
- U6 VG Transcript How Did Our Ancestors Evolve 10pages 2012Document5 pagesU6 VG Transcript How Did Our Ancestors Evolve 10pages 2012James JiangNo ratings yet
- BECOMING HUMAN - Transcript 2Document14 pagesBECOMING HUMAN - Transcript 2Scar ShadowNo ratings yet
- Human Evolution ppt1 Notes PDFDocument9 pagesHuman Evolution ppt1 Notes PDFDhiraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 13 Lecture OutlineDocument9 pagesModule 13 Lecture OutlineJose OrganistaNo ratings yet
- ET Civilizations - Germane: LyransDocument12 pagesET Civilizations - Germane: LyranssolomonblackNo ratings yet
- El Primer Hombre 5D Celeny Zegarra PorteroDocument2 pagesEl Primer Hombre 5D Celeny Zegarra PorteroDiana Zegarra PNo ratings yet
- EislerDocument7 pagesEislertimclarkdre100% (1)
- Guns Germs and Steel: Why Eurasian Plants, Animals Aided DevelopmentDocument2 pagesGuns Germs and Steel: Why Eurasian Plants, Animals Aided DevelopmentAubbrey MkNo ratings yet
- Tree of Origin What Primate Behavior Can Tell Us About Human Social Evolution (Frans B. M. de Waal, Richard Byrne Etc.)Document297 pagesTree of Origin What Primate Behavior Can Tell Us About Human Social Evolution (Frans B. M. de Waal, Richard Byrne Etc.)Arthur RimbaudNo ratings yet
- A Summary by Masood Ali ThahimDocument25 pagesA Summary by Masood Ali ThahimZahoor Tareen100% (2)
- Biology and Philosophy V. Intermission. Goethe As An AppetizerDocument6 pagesBiology and Philosophy V. Intermission. Goethe As An AppetizerValerie Rojas GNo ratings yet
- Ann Druyan Talks About Science, Religion, Wonder, Awe - . - and Carl Sagan - CSIDocument7 pagesAnn Druyan Talks About Science, Religion, Wonder, Awe - . - and Carl Sagan - CSIRubén Hernández GarcíaNo ratings yet
- From Monkey to Homo Sapiens A Journey Through the Stages that Led to HumankindFrom EverandFrom Monkey to Homo Sapiens A Journey Through the Stages that Led to HumankindRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Are You Smarter Than A Chimpanzee?: Test yourself against the amazing minds of animalsFrom EverandAre You Smarter Than A Chimpanzee?: Test yourself against the amazing minds of animalsNo ratings yet
- Story of LanguageDocument14 pagesStory of LanguagemkpraruNo ratings yet
- Werewolf Research PaperDocument7 pagesWerewolf Research Papervvgnzdbkf100% (1)
- Orpiada Daine P. 11 Stem A Ucsp Week 4Document6 pagesOrpiada Daine P. 11 Stem A Ucsp Week 4sarah jane lomaNo ratings yet
- Intro To EveloutionDocument9 pagesIntro To EveloutionJerik GarciaNo ratings yet
- Out of Africa Modern Human Origins Special FeatureDocument5 pagesOut of Africa Modern Human Origins Special FeatureDariebel Sab-itNo ratings yet
- Reptilian Aliens A Book of Memes: Reptilian Aliens a Book of MemesFrom EverandReptilian Aliens A Book of Memes: Reptilian Aliens a Book of MemesNo ratings yet
- Sample MonographDocument4 pagesSample MonographBucky_BallNo ratings yet
- The Science of Being Human: Why We Behave, Think and Feel the Way We DoFrom EverandThe Science of Being Human: Why We Behave, Think and Feel the Way We DoNo ratings yet
- Species of Homo: S S SapiensDocument4 pagesSpecies of Homo: S S SapiensAloyNo ratings yet
- Class 3 - Humans As PrimatesDocument48 pagesClass 3 - Humans As Primatescalebmakongoro01No ratings yet
- 2004.06.human - Origins Willima DembskiDocument26 pages2004.06.human - Origins Willima DembskiLeft Hook OlekNo ratings yet
- Desmond Morris - 1994 - The Human Animal - A Personal View of The Human SpeciesDocument218 pagesDesmond Morris - 1994 - The Human Animal - A Personal View of The Human SpeciesBruno VidovicNo ratings yet
- ASTERIX - Political Satire - MavoDocument3 pagesASTERIX - Political Satire - MavoMaviaNo ratings yet
- BonobosexandsocietyDocument7 pagesBonobosexandsocietyLuisa GaitanNo ratings yet
- January 2010Document1 pageJanuary 2010Eugene van PotchNo ratings yet
- Discoveries Challenge EvolutionDocument3 pagesDiscoveries Challenge EvolutionPochengShihNo ratings yet
- Selection in Relation To SexDocument3 pagesSelection in Relation To SexclaudiasulfitNo ratings yet
- Mother - Agenda.vol 01Document462 pagesMother - Agenda.vol 01shitNo ratings yet
- McFarlane Dragon Story Part OneDocument6 pagesMcFarlane Dragon Story Part OneLizzie ComiskeyNo ratings yet
- Different Stages of Human EvolutionDocument2 pagesDifferent Stages of Human EvolutionMAREEZ E ISHQ MAREEZ E ISHQNo ratings yet
- Golomb 1961Document4 pagesGolomb 1961SchlobinskiNo ratings yet
- The Complex and Complicated Human Family TreeDocument6 pagesThe Complex and Complicated Human Family TreeburhancimenNo ratings yet
- Go DocumentDocument7 pagesGo DocumentDiploma 2020No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Archeology Research 2002Document7 pagesMicrosoft Word - Archeology Research 2002wildlroverNo ratings yet
- Mocomi TimePass The Magazine - Issue 37Document14 pagesMocomi TimePass The Magazine - Issue 37Mocomi KidsNo ratings yet
- The Monkey in the Mirror: Essays on the Science of What Makes Us HumanFrom EverandThe Monkey in the Mirror: Essays on the Science of What Makes Us HumanRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Human Evolution GeneticsDocument8 pagesHuman Evolution GeneticsSoham MultaniNo ratings yet
- Ambang Tinambac Camarines SurDocument5 pagesAmbang Tinambac Camarines Surmark san andresNo ratings yet
- Sample Monograph FinalDocument4 pagesSample Monograph FinalBucky_Ball0% (3)
- Close-Up C1 CAE Practice Test AudioscriptDocument3 pagesClose-Up C1 CAE Practice Test AudioscriptCarmen PănuțăNo ratings yet
- 11.evolution by Human FinalDocument31 pages11.evolution by Human FinalThando MthethwaNo ratings yet
- Porter - War and The Rise of The State Ch.2Document12 pagesPorter - War and The Rise of The State Ch.2Marilyn GNo ratings yet
- Poggi - The Feudal System of RuleDocument11 pagesPoggi - The Feudal System of RuleMarilyn GNo ratings yet
- The Myth of Asia's Anti-Democratic Values: Culture is Not DestinyDocument7 pagesThe Myth of Asia's Anti-Democratic Values: Culture is Not DestinyMarilyn GNo ratings yet
- Markoff - Waves of DemocracyDocument10 pagesMarkoff - Waves of DemocracyMarilyn GNo ratings yet
- APES Erosion LabDocument3 pagesAPES Erosion Labawswenson13No ratings yet
- BASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 1Document4 pagesBASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 1Polee SheaNo ratings yet
- Viton A401CDocument8 pagesViton A401Crainer100% (1)
- The Plant Cell Wall A. IntroductionDocument6 pagesThe Plant Cell Wall A. IntroductionRizky EliandiNo ratings yet
- AIIMS May 2019 - PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAIIMS May 2019 - Physiologyshibira surendran vkNo ratings yet
- List of Nurseries - 2020Document52 pagesList of Nurseries - 2020Sadanand KumarNo ratings yet
- BacteriologyDocument14 pagesBacteriologyFrancene Ac-DaNo ratings yet
- Company C Inoc Harvest FinalDocument10 pagesCompany C Inoc Harvest FinalMubarak PatelNo ratings yet
- Laser Surface Treatment of Bio-Implant MaterialsDocument12 pagesLaser Surface Treatment of Bio-Implant MaterialsThe GantengNo ratings yet
- Bacterial StructureDocument72 pagesBacterial StructureKrittika ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormone Synthesis, Secretion, and TransportDocument5 pagesThyroid Hormone Synthesis, Secretion, and TransportAnonymous UTUWFODCEYNo ratings yet
- Breathe Strong, Perform Better by Alison McConnellDocument288 pagesBreathe Strong, Perform Better by Alison McConnellabacaterct100% (1)
- Btisnet: Objective, Structure &functionsDocument12 pagesBtisnet: Objective, Structure &functionssoumitaNo ratings yet
- List of Questions - HeredityDocument7 pagesList of Questions - Heredityshivani khareNo ratings yet
- Ecology Reading and ReviewDocument8 pagesEcology Reading and Reviewjohan preciadoNo ratings yet
- NPTEL CoursesDocument93 pagesNPTEL Coursestarun41873300No ratings yet
- Mastering English and Social StudiesDocument33 pagesMastering English and Social StudiesGalerya MarahuyoNo ratings yet
- USDA Forest Service Tree Seed ManualDocument162 pagesUSDA Forest Service Tree Seed ManualJulio Mora CastilloNo ratings yet
- Kryon Attributes of AscensionDocument15 pagesKryon Attributes of AscensionMeaghan Mathews100% (2)
- What Is Nervous System?: Presented By: TIP Grade 12 StudentDocument28 pagesWhat Is Nervous System?: Presented By: TIP Grade 12 StudentDreiza Patria SunodanNo ratings yet
- Hematologic EffectsDocument8 pagesHematologic EffectsGiralph NikkoNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural NetworkDocument9 pagesArtificial Neural Networkjyoti singhNo ratings yet
- Best Offer for EAMCET 2020 aspirantsDocument45 pagesBest Offer for EAMCET 2020 aspirantsrajaprasad2No ratings yet
- Worksheet in General Biology 2: Quarter 1 - Week 3: Theories of Evolution and The Development of Evolutionary ThoughtDocument10 pagesWorksheet in General Biology 2: Quarter 1 - Week 3: Theories of Evolution and The Development of Evolutionary ThoughtShastine ClaorNo ratings yet
- UKPAR COVID 19 Vaccine AstraZeneca 23.02.2021Document58 pagesUKPAR COVID 19 Vaccine AstraZeneca 23.02.2021SelenaNo ratings yet
- ANTHROPOLOGYDocument29 pagesANTHROPOLOGYPrincess Ann BalongaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MCQS WITH ANS (1) - CompressedDocument289 pagesPharmacology MCQS WITH ANS (1) - Compressed09Dhawal PatilNo ratings yet
- ESE200 Online TextbookDocument594 pagesESE200 Online TextbookSuren UlaganathanNo ratings yet
- Second MbbsDocument2 pagesSecond MbbsPriya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- CARY 100 BrochureDocument20 pagesCARY 100 BrochureNghia BiiNo ratings yet