Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Notebook Magnetism and Its Uses
Uploaded by
Camila Sanchez RodriguezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Notebook Magnetism and Its Uses
Uploaded by
Camila Sanchez RodriguezCopyright:
Available Formats
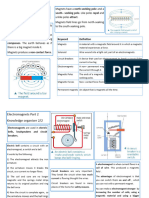
Magnetism and Its Uses
2 Electricity and Magnetism
REVIEW Recall the definition of the Review Vocabulary term.
VOCABULARY
electric current
electric current
NEW VOCABULARY Use your book to define each term.
electromagnetic force attractive or repulsive force between electric
electromagnetic force
electromagnetism charges and magnets
solenoid
interaction between electric charges and magnets
electromagnetism
electromagnet
galvanometer
single wire wrapped into a cylindrical wire coil
electric motor solenoid
temporary magnet created when there is a current
electromagnet
jn a wire coil
galvanometer device that uses an electromagnet to measure
electric current.
device that chanes electrical energy into mechanical
electric motor
energy
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education
Science Notebook • Magnetism and Its Uses
106
2 Electricity and Magnetism (continued)
Evaluate the magnetic fields that surround two identical pieces of
wire carrying the same electric current. One wire is straight, and the
other wire is coiled into a solenoid.
the magnetic field surround the solenoid is more strong than the
magnetic field surround the straight wire
Get It? Explain how the strength of the magnetic field around a
wire can be increased.
Cause the number of turns on coil increas.
Get It? Compare and contrast permanent magnets and
electromagnets.
the permanent magnet is any magnet whose domains remain aligned
without an external field.
a electro magnet is a temporary magnet created when there is a current in
wire coil.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education
Science Notebook • Magnetism and Its Uses
107
2 Electricity and Magnetism (continued)
Sequence the steps in the explanation of how electromagnets make
sound when you listen to a CD. Some terms from the word bank may
be used more than once.
amount current direction electromagnet
magnetic field repelled reproduces voltage
The CD player produces a .
The produces an electric in
the electromagnet next to the speaker cone.
The CD contains information that changes the of
current and its .
The changing electric current changes the direction and strength
of the around the electromagnet.
The electromagnet is attracted to or by the
permanent magnet.
The moving vibrates the speaker cone and
the sound recorded on the CD.
Get It? Summarize how a stereo speaker uses an electromagnet to
produce sound.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education
Science Notebook • Magnetism and Its Uses
108
2 Electricity and Magnetism (continued)
Model and label a galvanometer and describe how it works.
Sequence the steps an electric motor uses to change electrical
energy to mechanical energy. Make a sketch and label the motor.
1.
2.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education
3.
Science Notebook • Magnetism and Its Uses
109
2 Electricity and Magnetism (continued)
CHECK YOUR PROGRESS
8. Explain what happens when a magnet is placed near a current-carrying wire.
9. Infer A bar magnet is repelled when an electromagnet is brought close to it.
Describe how the bar magnet would have moved if the current in the
electromagnet had been reversed.
10. Define the term electromagnetic force. Give an example of a machine that uses
this force.
11. Describe two ways that you could increase the strength of the magnetic field
produced by an electromagnet.
12. Explain how a simple electric motor transforms electrical energy into mechanical
energy.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education
13. Predict How would an electromagnet’s magnetic field change if the iron core were
replaced by an aluminum core?
14. Math Connection The magnetic field around a current-carrying wire at a distance
of 1 cm is twice as strong as at 2 cm. How does the field strength at 0.5 cm
compare to the field strength at 1 cm?
Science Notebook • Magnetism and Its Uses
110
You might also like
- CH 11 Section 1 Reading EssentialsDocument5 pagesCH 11 Section 1 Reading EssentialsCAMERON MIZENo ratings yet
- Trilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsFrom EverandTrilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- c4 Electromagnetisme (Edited)Document26 pagesc4 Electromagnetisme (Edited)Aedlyn Hanny 403No ratings yet
- T02 - Electromagnetism (Complete)Document24 pagesT02 - Electromagnetism (Complete)rvjf8bwrj2No ratings yet
- Class10 Science Notes Chapter13Document5 pagesClass10 Science Notes Chapter13Anonymous skV4ao4No ratings yet
- 8 ElectrOMagnetism T April2016 PDFDocument69 pages8 ElectrOMagnetism T April2016 PDFDhatchana SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Unit1l2s - Magnetism - 30-04-01Document12 pagesUnit1l2s - Magnetism - 30-04-01amr abdellahNo ratings yet
- Current Can Produce Magnetism.: What Is The Source of Magnetism?Document7 pagesCurrent Can Produce Magnetism.: What Is The Source of Magnetism?Herleiy Jyne SmithNo ratings yet
- 427 431 PDFDocument5 pages427 431 PDFHerleiy Jyne SmithNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan of Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument3 pagesLesson Plan of Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentAditya Mathur67% (6)
- 2 StartersaDocument30 pages2 Startersaafiqah nasirNo ratings yet
- Electromagnets Part 2 Yr8Document4 pagesElectromagnets Part 2 Yr8saadNo ratings yet
- g10 Ntot Physics Electricity and MagnetismDocument36 pagesg10 Ntot Physics Electricity and MagnetismEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- 2 Starters ADocument30 pages2 Starters AJason MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- EE331-Introduction To Electromagnetics - Lectures 1-6Document31 pagesEE331-Introduction To Electromagnetics - Lectures 1-6azo1919zNo ratings yet
- Optical Devices Electricity and MagnetismDocument3 pagesOptical Devices Electricity and MagnetismKerwin TagumNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENTS WITH SPIRAL AND WANKEL MOTORS, With Ted Loder, Ph.D.Document46 pagesEXPERIMENTS WITH SPIRAL AND WANKEL MOTORS, With Ted Loder, Ph.D.Tedd St Rain100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Induction - Definition, Applications, Laws, VideosDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic Induction - Definition, Applications, Laws, VideoskrishnaNo ratings yet
- Observation of Force and Torque On A Current Loop Using A Simplified Electric MotorDocument3 pagesObservation of Force and Torque On A Current Loop Using A Simplified Electric Motorfrances leana capellan100% (2)
- Electricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument51 pagesElectricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismJun OrbitaNo ratings yet
- Electricity..class 7thDocument4 pagesElectricity..class 7thAyush Soni 7:- परिश्रम 3678No ratings yet
- Eric Palacios Definition FinalDocument9 pagesEric Palacios Definition Finalapi-534850962No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document32 pagesChapter 7Jenson HuangNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument5 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentShashank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mag ElectromagDocument38 pagesMag ElectromagJames Paul Micael GargantaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Class 10 Science Extra Questions With AnswersDocument9 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current Class 10 Science Extra Questions With AnswersGurinder SinghNo ratings yet
- General Physics2 Lesson 4 PDFDocument2 pagesGeneral Physics2 Lesson 4 PDFJohn Renzo MolinarNo ratings yet
- Extended AbstractDocument3 pagesExtended AbstractAlyssa Mary TogiNo ratings yet
- Science 4Document9 pagesScience 4Jaidyn LeeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5&6 - ElectromagnetsDocument19 pagesLesson 5&6 - Electromagnetsfirem0nkey.ggNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument22 pagesElectromagnetismhm3233003No ratings yet
- (L5) Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Class10 PDFDocument20 pages(L5) Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Class10 PDFRekha MishraNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Physics Group 5 3Document15 pagesMagnetism Physics Group 5 3Shanelle SantillanaNo ratings yet
- MagneticsDocument84 pagesMagneticsFuad MudesirNo ratings yet
- Physics: Unit 13: MagnetismDocument15 pagesPhysics: Unit 13: MagnetismNurulAinMatAronNo ratings yet
- Magnetism & ElectromagnetismDocument38 pagesMagnetism & ElectromagnetismganapathiNo ratings yet
- Science 10-Lesson 10Document34 pagesScience 10-Lesson 10afloresNo ratings yet
- Ac/Dc Machineries: A Study Guide and Module For Third Year BSME Students of SlsuDocument58 pagesAc/Dc Machineries: A Study Guide and Module For Third Year BSME Students of Slsuosas pasasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism: ConceptsDocument21 pagesLesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism: Conceptspauljkt1No ratings yet
- Ncert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 13Document11 pagesNcert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 13Aaryan KumarNo ratings yet
- CLASS-10 Subject: ScienceDocument62 pagesCLASS-10 Subject: ScienceZeonNo ratings yet
- 5.3 ElectromagnetDocument8 pages5.3 ElectromagnetYee Jiea PangNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 March 29 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument16 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 March 29 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Currentkramraj342No ratings yet
- Modeling The Magnetic Pickup of An Electric GuitarDocument8 pagesModeling The Magnetic Pickup of An Electric GuitarJosé GómezNo ratings yet
- G10 Ntot Physics Electricity and MagnetiDocument36 pagesG10 Ntot Physics Electricity and MagnetiqwertyNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETISMDocument11 pagesELECTROMAGNETISMSaiful NizamNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Slide Number DescriptionDocument4 pagesElectromagnetism: Slide Number DescriptionthegaiaprojectNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 KSSM ElectromagnetismDocument28 pagesChapter 4 KSSM ElectromagnetismJillian TanNo ratings yet
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0163971 A1Document10 pagesPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0163971 A1bluesurviverNo ratings yet
- Physics 72.1 Peer Review Final DraftDocument3 pagesPhysics 72.1 Peer Review Final Draftfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: What We Have Already LearntDocument14 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: What We Have Already LearntAnonymous pZp8uyNo ratings yet
- q3 Sci10 Lesson1 Pic1Document47 pagesq3 Sci10 Lesson1 Pic1Tash Marcelo Olo-anNo ratings yet
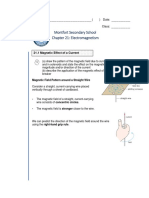
- Montfort Secondary School Chapter 21: Electromagnetism: Name: Date: ClassDocument12 pagesMontfort Secondary School Chapter 21: Electromagnetism: Name: Date: ClasssonghannNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field and Field Lines-FDocument20 pagesMagnetic Field and Field Lines-FjamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Elem EeDocument6 pagesElem EeShania MarieNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience ReviewerShaine RectoNo ratings yet
- 10th Magnetic Electric Current Test Paper-1Document6 pages10th Magnetic Electric Current Test Paper-1ashish gandreNo ratings yet
- Term 3 - 8. Magnet and Their UsesDocument12 pagesTerm 3 - 8. Magnet and Their UsescindyNo ratings yet
- Electric Current QuesDocument4 pagesElectric Current Queslomash.vijay.18No ratings yet
- Science 10 LASDocument11 pagesScience 10 LASJeyn T. Redoña IINo ratings yet
- Internship Report Mohammad AktharDocument39 pagesInternship Report Mohammad AktharJunaid KhanNo ratings yet
- MX5 NGS BrochureDocument2 pagesMX5 NGS BrochureHamatouty TottiNo ratings yet
- 4maint MGMT BIE2004 Wk4 2023Document39 pages4maint MGMT BIE2004 Wk4 2023aimanfznnnNo ratings yet
- Project 1Document23 pagesProject 1rock starNo ratings yet
- KC 11 A - Automatic Pipe CuttingDocument1 pageKC 11 A - Automatic Pipe CuttingMEGA BUANA UATAMA PERKASANo ratings yet
- Equipment Sump Pumps ScheduleDocument1 pageEquipment Sump Pumps ScheduleAnil RadheshwarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/12Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/12iman jamilNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Assessment of A Solar Thermal Collector: Sensitivity Analysis, Energy and Environmental BalancesDocument22 pagesLife Cycle Assessment of A Solar Thermal Collector: Sensitivity Analysis, Energy and Environmental Balancesjuan ceronNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: EpsolarDocument64 pagesOperation Manual: EpsolarZoki JevtićNo ratings yet
- Wind Diesel Hybrid Power System: Bachelor of TechnologyDocument11 pagesWind Diesel Hybrid Power System: Bachelor of Technologymadhu kotlaNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate and Measure Water Pump HorsepowerDocument10 pagesHow To Calculate and Measure Water Pump HorsepowerTanvir ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- LmnvswmmtdhspejexsylDocument70 pagesLmnvswmmtdhspejexsylsnehanshu12No ratings yet
- Low Speed Centrifuge LLS A54Document4 pagesLow Speed Centrifuge LLS A54VAN REPRESENTACIONES GENERALESNo ratings yet
- Hot Work PTWDocument2 pagesHot Work PTWVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- Marine Biofuels Costs and Emissions Study For The European Supply Chain Till 2030Document14 pagesMarine Biofuels Costs and Emissions Study For The European Supply Chain Till 2030sebas barbsoaNo ratings yet
- Reversed Carnot & VCR Cycle Part IIDocument23 pagesReversed Carnot & VCR Cycle Part IISumran ShahidNo ratings yet
- Numerical ProblemsDocument4 pagesNumerical Problemsvivek soniNo ratings yet
- Latchways - Fall ProtectionDocument6 pagesLatchways - Fall ProtectionNicky LimNo ratings yet
- Photocells: Installation InstructionsDocument2 pagesPhotocells: Installation Instructionssriramoju vishnusai sriramojuNo ratings yet
- Buccholtz Atus CatalogDocument4 pagesBuccholtz Atus Catalogindrajit mondalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 3 Phase AC CircuitsDocument47 pagesChapter 8 3 Phase AC CircuitsKì Hyö JüngNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument8 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectRoma BansalNo ratings yet
- Low-Cost Production of Renewable Diesel and SAF With BioFlux Hydrotreating TechnologyDocument24 pagesLow-Cost Production of Renewable Diesel and SAF With BioFlux Hydrotreating TechnologymacarenapurtichNo ratings yet
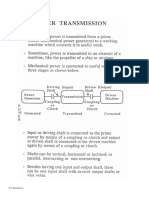
- 4 Power TransmissionDocument27 pages4 Power TransmissionMehmetNo ratings yet
- Miniature Circuit BreakersDocument44 pagesMiniature Circuit Breakersleandro sanchezNo ratings yet
- 942006-001 TQP-RS Manual Rev2Document40 pages942006-001 TQP-RS Manual Rev2week redNo ratings yet
- Gliders & Sailplanes: Geanta Bianca-Maria Grupa 914B Ingirerie AerospatialaDocument13 pagesGliders & Sailplanes: Geanta Bianca-Maria Grupa 914B Ingirerie AerospatialaGeanta BiancaNo ratings yet
- Impact Test Lab ReportDocument21 pagesImpact Test Lab Reporttariqlewis07No ratings yet
- Course: Smart Building: Dr.-Ing. Nguyen Van BinhDocument13 pagesCourse: Smart Building: Dr.-Ing. Nguyen Van BinhAnh Cao Minh NgocNo ratings yet
- Mikrotech BrochureDocument33 pagesMikrotech Brochureayiep1202No ratings yet