Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cerebelum
Uploaded by
aisyahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cerebelum
Uploaded by
aisyahCopyright:
Available Formats
state the roles of the each structure
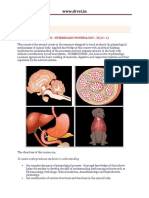
The cerebellum is located behind the top part of the brain stem where the spinal cord meets the
brain. It is a quite small portion of the brain. About ten percent of the total weight but it contains
roughly half of the brain's neurons that specialized cells that transmit information via electrical
signals (The Human Body: Cerebellum, 2015). The cerebellum with its two hemispheres, look like a
miniature version of the cerebrum. It is covered by the cerebellar cortex and has a set of deep
cerebellar nuclei. These nuclei receive projections from the cerebellar cortex and themselves send
projections out of the cerebellum to other parts of the brain. Each hemispheres of the cerebellum is
attached to the dorsal surface of the pons by bundle of axons which is the superior, middle and
inferior cerebellar peduncles (Carlson & Birkett, 2017).
In addition, Carlson and Birkett (2017) mentioned that the cerebellum receives visual, auditory,
vestibular and somatosensory information. It also receives information about individual muscles
movements being directed by the brain. The cerebellum integrates this information and modified
the motor outflow, exerting a coordinating and smoothing effect on the movements.The cerebellum
also receives information from the spinal cord, and other parts of the brain and then regulates
motor movements. The cerebellum coordinates voluntary movements such as posture, balance,
coordination, and speech, resulting in smooth and balanced muscular activity. It is also important for
learning motor behaviors (The Human Body: Cerebellum, 2015).
In addition, Llinas and Negrello (2015) the cerebellum is part of a system that involves four main
components. The largest component is the cerebellar cortex which is a tightly folded layer of neural
tissue attached to the dorsal side of the pons with white matter underneath. The next component is
a set of cerebellar nuclei that lying within the white matter underneath the cortex. The inferior
olivary nucleus, a convoluted structure lying within the medulla oblongata and sending projections
known as climbing fibers to the cerebellar cortex and cerebellar nuclei also the part of the main
component of a cerebellum. Lastly, a large collection of inputs known as mossy fibers impinging on
the cerebellum from various brain regions and sending projections to the cerebellar cortex and
cerebellar nuclei
Function of cerebellum- Coordinator of precise movement by continually comparing the output of
motor area of cerebral cortex with the proprioceptive information received from the site of muscle
action, it is able to bring about adjustment by influencing the activity of the lower motor neuron It
also sends back information to the motor cortex to inhibit the agonist muscle & stimulate the
antagonist muscle thus limiting the extent of voluntary movement
Fundamentally the cerebellar system (including the inferior olive and the cerebellar nuclei) acquires
and implements sensorimotor “tactics” (how to) that contextualize the motor strategies (what,
where and when) generated by the forebrain.
Such tactics relate mostly to movement execution, timing, compensatory, and multi-limb
coordination.The basic transactions are implemented at the cerebellar nuclear level the output of
which blends strategy andtactics by combining incoming ascending spinal cord information with
descending motor commands initiated byintrinsic CNS activity and sensory input. Thus cerebellar
function must be considered within the context of therest of the nervous system, since it is not a
primary way station for sensory or motor function, but combinesboth, during learning and
execution. Though its destruction does not produce sensory deficits or paralysis, cerebellar lesion
produces devastating inability for movement coordination and execution, and in some
accounts,deficits in executive function (see Cerebellar Involvement in Cognition).
Bibliography
Carlson, N. R., & Birkett, M. A. (2017). Physiology of Behavior. England: Pearson Education Limited.
Llinas, R., & Negrello, M. N. (2015). Cerebellum. Scholarpedia.
The Human Body: Cerebellum. (2015, March 5). Retrieved from HealthLine:
https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/cerebellum#1
Carlson, N. R., & Birkett, M. A. (2017). Physiology of Behavior. England: Pearson Education Limited.
The Human Body: Cerebellum. (2015, March 5). Retrieved from HealthLine:
https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/cerebellum#1
From this 'Know Your Brain' booklet task, we can conclude that human brain is a very complex and
interesting organ in the human body. Brain is the most important organ as each region of the brain,
there are specific ones that have their main roles that help guide cognitive functions. This showed
that Allah creation is perfect and………………………tolong sambungkan kalau ada idea lagi hehe
You might also like
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
- Cerebellum: Movement Regulation and Cognitive Functions Course Title DateDocument16 pagesCerebellum: Movement Regulation and Cognitive Functions Course Title DateDanyNo ratings yet
- Generalities: Unit 15. CerebellumDocument8 pagesGeneralities: Unit 15. CerebellumMay ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Session #22 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document14 pagesSession #22 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)G INo ratings yet
- Acknowledgments: Gray's Anatomy, The Remarkable Work From Which Gray's Clinical Neuroanatomy IsDocument7 pagesAcknowledgments: Gray's Anatomy, The Remarkable Work From Which Gray's Clinical Neuroanatomy IsAndreea LăzăroiuNo ratings yet
- (16-17) Brain SummaryDocument57 pages(16-17) Brain SummarybartNo ratings yet
- SASDocument14 pagesSASNicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Essence of Brain Function: 1/8/13-1/9/13 Overview of Human AnatomyDocument61 pagesEssence of Brain Function: 1/8/13-1/9/13 Overview of Human Anatomyjustice88_639020831No ratings yet
- The Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportDocument7 pagesThe Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportOlatokunbo SinaayomiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Neuroanatomy Lange 29Th Edition Stephen Waxman Full ChapterDocument51 pagesClinical Neuroanatomy Lange 29Th Edition Stephen Waxman Full Chaptertim.morrison630100% (14)
- Motor Control Theories and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesMotor Control Theories and PhysiologyAaminah NawazNo ratings yet
- This Paper Can Be Used As A Guide But Must Be Changed To Avoid Plagerism. The Author of This Paper Is Aware That I Am Using ItDocument4 pagesThis Paper Can Be Used As A Guide But Must Be Changed To Avoid Plagerism. The Author of This Paper Is Aware That I Am Using ItGina Holcomb MorganNo ratings yet
- Overview: Functions of The CerebellumDocument17 pagesOverview: Functions of The CerebellumMohd Fitri ShahruddinNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument23 pagesModule 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorRoxie May Theresse AbagatnanNo ratings yet
- Ballon, Rosemarie E. Chapter 4Document3 pagesBallon, Rosemarie E. Chapter 4Rose Marie BallonNo ratings yet
- 121 Veterinary Physiology - II (Neuromuscular Digestive & Respiratory Systems)Document346 pages121 Veterinary Physiology - II (Neuromuscular Digestive & Respiratory Systems)Vaidika YadavNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument51 pagesCerebellumLiya ThaaraNo ratings yet
- Structure and FunctionDocument8 pagesStructure and FunctionHoney PrasadNo ratings yet
- The Brain Stem: Location and Basic PhysiologyDocument33 pagesThe Brain Stem: Location and Basic PhysiologyMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument27 pagesBraincviymqty7No ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy, Brainstem - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument13 pagesNeuroanatomy, Brainstem - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfKritika MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Rullida - EdullantesDocument36 pagesRullida - EdullantesJaleah Gwyneth Fernandez EdullantesNo ratings yet
- Dissection 2Document12 pagesDissection 2hadiqaasif01No ratings yet
- Cerebellum 4 - 5Document45 pagesCerebellum 4 - 5sridhar100% (1)
- Subject PsychologyDocument11 pagesSubject PsychologyTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Organization of The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 3: Organization of The Nervous SystemTaz_devil91No ratings yet
- Mind Blowing BrainDocument16 pagesMind Blowing BrainTrance CrossingNo ratings yet
- Axon - Long Slender Projection That Conducts Electrical Impulses Away From The Cell BodyDocument6 pagesAxon - Long Slender Projection That Conducts Electrical Impulses Away From The Cell BodyshashwatthegamerytNo ratings yet
- Functional NeuroanatomyDocument23 pagesFunctional NeuroanatomyDaniela GrigoraşNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination Grade 11Document30 pagesNeural Control and Coordination Grade 11Dr. Remya RanjithNo ratings yet
- Organization of The BrainDocument12 pagesOrganization of The BrainChiraz MwangiNo ratings yet
- Cnsbloodsupply NotesDocument4 pagesCnsbloodsupply Notescare3ashNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Khaleel Alyahya, PHD, Med King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelyaDocument31 pagesNervous System: Khaleel Alyahya, PHD, Med King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelyaSalem AlshahraniNo ratings yet
- Coordination PDFDocument14 pagesCoordination PDFShamini Segari GunasakaranNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy, Cerebellar Dysfunction: Gross AnatomyDocument5 pagesNeuroanatomy, Cerebellar Dysfunction: Gross AnatomyANISA RIFKA RIDHONo ratings yet
- The Brain: Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon)Document7 pagesThe Brain: Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon)Cedy L. CieloNo ratings yet
- Kepy 01 08 33 EtextDocument13 pagesKepy 01 08 33 Etextmradul guptaNo ratings yet
- The Neurological Bases of Human MovementDocument12 pagesThe Neurological Bases of Human MovementErvin Gil Del PilarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NeuroplasticityDocument6 pagesUnit 2 NeuroplasticityKhushi AroraNo ratings yet
- The Brain - NobaDocument21 pagesThe Brain - NobaMarNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum: Anungputriillahika, DR Laboratoriumanatomi FkummDocument43 pagesCerebellum: Anungputriillahika, DR Laboratoriumanatomi FkummHarmas Novryan FarezaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System BSC 20161Document45 pagesNervous System BSC 20161Arohi ParlikarNo ratings yet
- The Brain: Learning ObjectivesDocument16 pagesThe Brain: Learning Objectivessaswati biswalNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions ManualSamanthaStuartijgt100% (40)
- Wa0041Document161 pagesWa0041SULDAANUL CAASHIQIINNo ratings yet
- BONADocument4 pagesBONATucho YadetaNo ratings yet
- Histology - Nerve Tissue and The Nervous SystemDocument21 pagesHistology - Nerve Tissue and The Nervous SystemDan UvarovNo ratings yet
- Nervous System TTCDocument24 pagesNervous System TTCelber campos valdesNo ratings yet
- CoursematerialDocument14 pagesCoursematerialNiraj NiketNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Organization of Nervous System: Presented by Dr. Amen FatimaDocument37 pagesIntroduction and Organization of Nervous System: Presented by Dr. Amen FatimaShanailNo ratings yet
- Ectodermal Derivatives of Pig EmbryoDocument7 pagesEctodermal Derivatives of Pig EmbryoChristalie Bea FernandezNo ratings yet
- Rullida - EdullantesDocument36 pagesRullida - EdullantesJaleah Gwyneth Fernandez EdullantesNo ratings yet
- 16 Motor Control ACNRJF11Document3 pages16 Motor Control ACNRJF11dwi_ratridwirNo ratings yet
- SNC EEG MalmivuoDocument10 pagesSNC EEG MalmivuoAdam SamenezesNo ratings yet
- Práctica 0Document7 pagesPráctica 0Juan CamaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Brain - GeeksforGeeksDocument11 pagesAnatomy of The Brain - GeeksforGeeksopheokani2000No ratings yet
- Explain The Central Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesExplain The Central Nervous SystemZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Bilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationDocument26 pagesBilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- The Brain Unlocked: A Journey Through the Mysteries of NeuroscienceFrom EverandThe Brain Unlocked: A Journey Through the Mysteries of NeuroscienceNo ratings yet
- PANCREATITISDocument38 pagesPANCREATITISVEDHIKAVIJAYANNo ratings yet
- Section 08630 Metal-Framed SkylightDocument4 pagesSection 08630 Metal-Framed SkylightMØhãmmed ØwięsNo ratings yet
- T 1246784488 17108574 Street Lighting Control Based On LonWorks Power Line CommunicationDocument3 pagesT 1246784488 17108574 Street Lighting Control Based On LonWorks Power Line CommunicationsryogaaNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Troubleshooting ManualDocument15 pagesMotorcycle Troubleshooting ManualJan Warmerdam100% (1)
- The Field-Effect Transistor - August 1972 Popular ElectronicsDocument5 pagesThe Field-Effect Transistor - August 1972 Popular Electronicsmac9papNo ratings yet
- Biasing Opamps Into Class ADocument11 pagesBiasing Opamps Into Class AsddfsdcascNo ratings yet
- NDT Matrix 12-99-90-1710 - Rev.2 PDFDocument2 pagesNDT Matrix 12-99-90-1710 - Rev.2 PDFEPC NCCNo ratings yet
- Nurtured Womb e BookDocument22 pagesNurtured Womb e BookSteph's Desserts100% (1)
- North Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteDocument8 pagesNorth Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteAnalyn FielNo ratings yet
- Moldex Realty, Inc. (Linda Agustin) 2.0 (With Sound)Document111 pagesMoldex Realty, Inc. (Linda Agustin) 2.0 (With Sound)Arwin AgustinNo ratings yet
- Science7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Document26 pagesScience7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Ishi OcheaNo ratings yet
- Oasis AirlineDocument5 pagesOasis AirlineRd Indra AdikaNo ratings yet
- Air System Sizing Summary For NIVEL PB - Zona 1Document1 pageAir System Sizing Summary For NIVEL PB - Zona 1Roger PandoNo ratings yet
- DUPIXENT Doctor Discussion GuideDocument4 pagesDUPIXENT Doctor Discussion GuideTAP THANH CHAUNo ratings yet
- Buckthorpe Etal 23 Optimising Early Stage ACL Rehab ProcessDocument24 pagesBuckthorpe Etal 23 Optimising Early Stage ACL Rehab ProcessCole VincentNo ratings yet
- Types of WinesDocument91 pagesTypes of Winesrajanrld19880% (1)
- International Travel Insurance Policy: PreambleDocument20 pagesInternational Travel Insurance Policy: Preamblethakurankit212No ratings yet
- Developing Agility and Quickness (Etc.) (Z-Library) - 66Document2 pagesDeveloping Agility and Quickness (Etc.) (Z-Library) - 66guypetro6No ratings yet
- Good Practices in Tray DesignDocument7 pagesGood Practices in Tray Designmehul10941100% (2)
- Smith KJ Student Mathematics Handbook and Integral Table ForDocument328 pagesSmith KJ Student Mathematics Handbook and Integral Table ForStrahinja DonicNo ratings yet
- Instructor: DR - Ashok Kaushal: Orthogonal ViewsDocument49 pagesInstructor: DR - Ashok Kaushal: Orthogonal ViewsKristi GjokaNo ratings yet
- South Valley University Faculty of Science Geology Department Dr. Mohamed Youssef AliDocument29 pagesSouth Valley University Faculty of Science Geology Department Dr. Mohamed Youssef AliHari Dante Cry100% (1)
- Annie Ovenden Exibition 2017Document19 pagesAnnie Ovenden Exibition 2017Vitaliy ChuenkoNo ratings yet
- Plaquette - PRECASEM - CIMEC 2019 English VersionDocument18 pagesPlaquette - PRECASEM - CIMEC 2019 English VersionFranck BertrandNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Science and Environment: Brgy - Pampang, Angeles City, PhilippinesDocument65 pagesIntroduction: Science and Environment: Brgy - Pampang, Angeles City, PhilippinesLance AustriaNo ratings yet
- Application of Eye Patch, Eye Shield and Pressure Dressing To The EyeDocument2 pagesApplication of Eye Patch, Eye Shield and Pressure Dressing To The EyeissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- EndressHauser HART CommunicatorDocument1 pageEndressHauser HART CommunicatorGhafur AgusNo ratings yet
- Fe jkj101Document5 pagesFe jkj101ApezAnuarNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris PATDocument10 pagesBahasa Inggris PATNilla SumbuasihNo ratings yet
- No Client Too Far: Flexible Antenna Options TDMA GPS Sync ClientDocument2 pagesNo Client Too Far: Flexible Antenna Options TDMA GPS Sync ClientFelix MartinezNo ratings yet