Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Internal Control System PDF Slides
Internal Control System PDF Slides
Uploaded by
Adeel Ahmad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views22 pagesOriginal Title
Internal Control System Pdf Slides
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views22 pagesInternal Control System PDF Slides
Internal Control System PDF Slides
Uploaded by
Adeel AhmadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Z\ Fla
a TA
»
a
=]
=]
Learning Objectives
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
+ Understand the basic definition of internal control.
+ Discuss why internal controls are important.
+ Distinguish between the different components of internal control.
+ Describe the elements of the control environment.
+ Evaluate how management's objectives are related to risk assessment.
+ Explain the effects of information and communication on the internal
control system.
+ Distinguish between the major types of control activities.
+ Give examples of major types of control activities.
+ Identify monitoring controls.
+ Know what is meant by design of controls.
Definition
Internal controls are a system consisting of specific policies and procedures designed to provide
management with reasonable assurance that the goals and objectives it believes important to
the entity will be met.
1. Reliability of Financial Reporting
2. Efficiency and Effectiveness of Operations
3. Compliance with Laws and Regulations
+ Internal Controls are put into place to Minimize Risk
MANAGEMENT AND AUDITORS RESPONSIBILITY FOR INTERNAL CONTROL
1, MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITIES 2. AUDITORS RESPONSIBILITIES FOR
UNDERSTANDING INTERNAL CONTROLS
1, REASONABLE ASSURANCE 1, CONTROL OVER RELIABILITY OF
2. INHERENT LIMITATIONS FINANCIAL REPORTING
2, CONTROL OVER CLASSES OF
TRANSACTIONS.
Transaction-Related Audit Objective—General
Form
1.Recorded transactions exist (occurrence).
2. Existing transactions are recorded (completeness).
3. Recorded transactions are stated at the correct
amounts (accuracy).
4, Recorded transactions are correctly included in
the master files and are correctly summarized.
(posting and summarization)
5. Transactions are correctly classified (classification),
6. Transactions are recorded on the correct dates
(timing).
Sales Transaction-Related Audit Objectives
‘Recorded sales are for shipments made to existing
customers.
2. Existing sales transactions are recorded.
3. Recorded sales are for the amount of goods shipped
and are correctly billed and recorded.
4, Sales transactions are correctly included in the master
files and are correctly summarized
5, Sales transactions are correctly classified.
6. Sales are recorded on the correct dates.
3. AUDITORS RESPONSIBILITY FOR TESTING OF CONTROLS
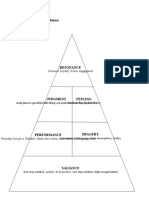
COSO Major Components of Internal Control
MONITORING RISK ASSESSMENT
INFORMATION AND ‘CONTROL ACTIVITIES
COMMUNICATION
Components of Internal Control
1. Control Environment:
Factors that set the tone of the organization, influencing the control
consciousness of its people. The seven factors ar
+ Integrity and ethical values,
+ Commitment to Competence,
+ Board of directors and audit committee
+ Management's philosophy and Operating style,
+ Organizational Structure.
+ Human Resource Policies and Practices
MAJOR COMPONENTS OF INTERNAL CONTROL
2. The Entity’s Risk Assessment
+ Management Must Identify the Risk
+ Identification
+ Significance of Risk
+ Assesses the likelihood of occurrence
+ Develop Actions and Policies
Major Components of Internal Control
3. CONTROL ACTIVITIES
Various policies and procedures that help to ensure those necessary actions
are taken to address risks affecting achievement of entity's objectives:
1. Adequate Separation of Duties
2. Proper Authorization of Transactions (General and Specific Authorization)
3. Adequate Documents and Records
4. Physical Controls over assets and records
5, Independent Checks on Performance
Major Components of Internal Control
4. ACCOUNTING INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION
Methods and policies established to record, process, summarize, and report
transactions and to maintain accountability of related assets and liabilities. Must
accomplish:
+ Identify and record all valid transactions.
+ Measure the value properly.
+ Record in the proper time period.
+ Properly present and disclose.
+ Communicate responsibilities to employees.
Major Components of Internal Control
5. MONITORING OF INTERNAL CONTROLS
+ Internal Control Over Times
Limitations of Internal Controls:
No matter how well internal controls are designed, they can only provide reasonable
assurance that objectives have been achieved. Some limitations are inherent in all
internal control systems. These include :
1, Judgment:
2. Breakdowns:
3, Management Override:
4. Collusion:
Resistant in Implementing Internal Controls or non-existent?
‘There is not enough staff to have adequate segregation of duties.
+ It is too expensive.
‘The employees are trusted and controls are not necessary.
OBTAIN AND DOCUMENT UNDERSTANDING OF INTERNAL
CONTROL (AUDITOR'S WORK)
rs
1. NARRATIVE
2. FLOW CHART
3. INTERNAL CONTROL
QUESTIONNAIRE
Risk Factors YouNo | T
EVALUATING INTERNAL CONTROL
IMPLEMENTATION
+ Update and Evaluate Auditor's Previous Experience with the Entity
+ Make Inquiries of Client Staff
+ Examine Documents and Records (Components)
+ Observe Entity Activities and Operations
+ Perform Walk troughs of the Accounting System
ASSESS CONTROL RISK (Class of Transactions)
1. ASSESS WHETHER FINANCIAL STATEMENTS ARE AUDIT ABLE OR NOT
+ Integrity of Management
+ Adequacy of Accounting Policies (Duplicate Sales Invoices)
+ Identify and Evaluate Control Deficiencies, Significant Deficiencies, and
Material Weaknesses
+ 1. Control deficiency.
+ 2. Significant deficiency
+ 3. Material weakness.
| ‘commUNtCATH
TEST OF CONTROLS
PROCEDURES FOR TEST OF CONTROLS
+ 1. Make inquiries of appropriate client personnel
+ 2, Examine documents, records, and reports
+ 3. Observe control-related activities
+ 4. Re-perform client procedures
EXTENT OF PROCEDURES
+ Reliance on Evidence from the Prior Year’s Audit
+ Testing of Controls Related to Significant Risks:
+ Testing Less Than the Entire Audit Period
REPORTING ON INTERNAL CONTROLS
1. Unqualified Opinion
2. Adverse Opinion
3. Qualified Opinion
4. Disclaimer of Opinion
You might also like
- IF Final AssignmentDocument41 pagesIF Final AssignmentAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Internalauditreportwriting 150526070325 Lva1 App6892Document18 pagesInternalauditreportwriting 150526070325 Lva1 App6892Adeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Audit Evidence New SlidesDocument20 pagesAudit Evidence New SlidesAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Decision MakingDocument34 pagesFoundation of Decision MakingAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Section: A Assignment: 1 Principles of Management: Name: Roll No: Section: ProgramDocument5 pagesSection: A Assignment: 1 Principles of Management: Name: Roll No: Section: ProgramAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics ProjectDocument4 pagesBusiness Statistics ProjectAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Audit Planning and Risk Assessment New SlidesDocument38 pagesAudit Planning and Risk Assessment New SlidesAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Creative and Persuasive Writing: Name: Adeel Ahmad Roll No: BBHM-F19-033 Class: BBA Section: 2ADocument3 pagesCreative and Persuasive Writing: Name: Adeel Ahmad Roll No: BBHM-F19-033 Class: BBA Section: 2AAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Name: Adeel Ahmad Roll Numb: BBHM-F19-033 Class: BBA (2A) Submitted To: Mam ShaziaDocument12 pagesName: Adeel Ahmad Roll Numb: BBHM-F19-033 Class: BBA (2A) Submitted To: Mam ShaziaAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Application of Estimation and Point Estimation in BiostatisticsDocument10 pagesApplication of Estimation and Point Estimation in BiostatisticsAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Brand Equity Model of Metro: Great Place To Get All The Little Things You NeedDocument5 pagesBrand Equity Model of Metro: Great Place To Get All The Little Things You NeedAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Organization CommunicationDocument27 pagesOrganization CommunicationAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Haier A.C Supply Chain Management Mid ProjectDocument12 pagesHaier A.C Supply Chain Management Mid ProjectAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Brand AudtingDocument27 pagesBrand AudtingAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Zain EnglishDocument4 pagesZain EnglishAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- History of ManagementDocument30 pagesHistory of ManagementAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Economics of PakistanDocument13 pagesEconomics of PakistanAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- What Is The Legislation Process ?Document2 pagesWhat Is The Legislation Process ?Adeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Punjab Public Service CommissionDocument2 pagesPunjab Public Service CommissionAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Development of Recipes and Estimation of Raw MaterDocument10 pagesDevelopment of Recipes and Estimation of Raw MaterAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Vision: MissionDocument9 pagesVision: MissionAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Bread Supply ChainDocument9 pagesBread Supply ChainAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)