Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
11 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
Gagne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThe document discusses the switching characteristics of IGBTs using an inductive switching circuit model. It explains that IGBT switching waveforms are similar to power MOSFETs since the IGBT input stage is a MOSFET. However, the p-n-p output transistor affects switching, especially turn off. Another difference is IGBTs require a negative gate voltage when off to prevent latch up.
Original Description:
Original Title
11_L-7(DK)(PE) ((EE)NPTEL)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the switching characteristics of IGBTs using an inductive switching circuit model. It explains that IGBT switching waveforms are similar to power MOSFETs since the IGBT input stage is a MOSFET. However, the p-n-p output transistor affects switching, especially turn off. Another difference is IGBTs require a negative gate voltage when off to prevent latch up.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 page11 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
11 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneThe document discusses the switching characteristics of IGBTs using an inductive switching circuit model. It explains that IGBT switching waveforms are similar to power MOSFETs since the IGBT input stage is a MOSFET. However, the p-n-p output transistor affects switching, especially turn off. Another difference is IGBTs require a negative gate voltage when off to prevent latch up.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
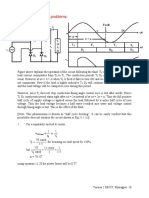
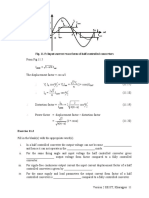
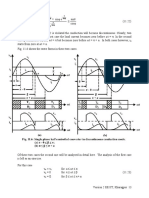
7.
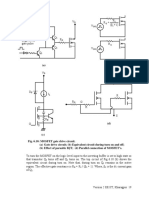
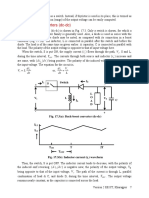
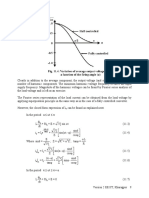
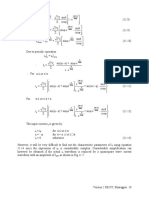
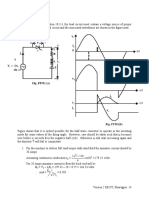
5 Switching characteristics of IGBT
Switching characteristics of the IGBT will be analyzed with respect to the clamped inductive
switching circuit shown in Fig 7.5(a). The equivalent circuit of the IGBT shown in Fig 7.5 (b)
will be used to explain the switching waveforms.
VCC
C
iL iD
DF D
iC + CGD
C VCE
Rg ig G Q1 G S
E CgE E
-
Vgg
(b)
(a)
Fig. 7.5: Inductive switching circuit using an IGBT
(a) Switching circuit; (b) Equivalent circuit of the IGBT
The switching waveforms of an IGBT is, in many respects, similar to that of a Power MOSFET.
This is expected, since the input stage of an IGBT is a MOSFET as shown in Fig 7.5(b). Also in
a modern IGBT a major portion of the total device current flows through the MOSFET.
Therefore, the switching voltage and current waveforms exhibit a strong similarity with those of
a MOSFET. However, the output p-n-p transistor does have a significant effect on the switching
characteristics of the device, particularly during turn off. Another important difference is in the
gate drive requirement. To avoid dynamic latch up, (to be discussed later) the gate emitter
voltage of an IGBT is maintained at a negative value when the device is off.
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 11
You might also like
- 9 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- IGBT MOSFET Gate Drive Optocoupler Application NotesDocument11 pagesIGBT MOSFET Gate Drive Optocoupler Application NotesJancyNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- A Low Investment Single-Phase To Three-Phase Converter Operating With Reduced LossesDocument6 pagesA Low Investment Single-Phase To Three-Phase Converter Operating With Reduced LossesSelamat Meliala, S.T.,MT Selamat Meliala, S.T.,MTNo ratings yet
- L-5 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 3Document5 pagesL-5 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 3GagneNo ratings yet
- EE352L Laboratory Experiment N # 4: 1.1 Pre-LabDocument5 pagesEE352L Laboratory Experiment N # 4: 1.1 Pre-LabYassine DjillaliNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Using IGBT Modules 4.1 Structure and Operation of IGBT ModuleDocument27 pages4.0 Using IGBT Modules 4.1 Structure and Operation of IGBT Modulerodruren01No ratings yet
- GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering Question PaperDocument15 pagesGATE 2009 Electrical Engineering Question PaperArjun MudlapurNo ratings yet
- Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor With Ultrafast Soft Recovery DiodeDocument17 pagesInsulated Gate Bipolar Transistor With Ultrafast Soft Recovery DiodeOlavo FelterNo ratings yet
- A Single Stage Integrated Bidirectional AC/DC and DC/DC Converter For Plug-In Hybrid Electric VehiclesDocument6 pagesA Single Stage Integrated Bidirectional AC/DC and DC/DC Converter For Plug-In Hybrid Electric VehiclesAli HussienNo ratings yet
- Exp 04Document3 pagesExp 04Captain Jack SparrowNo ratings yet
- BJT ProblemsDocument11 pagesBJT ProblemsRajesh PerlaNo ratings yet
- 22 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page22 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- L-5 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 2Document5 pagesL-5 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 2GagneNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of Data Conversion SystemsDocument45 pagesBuilding Blocks of Data Conversion SystemsGowthamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 TRDocument28 pagesLecture 14 TRMailly NewsNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument51 pagesPower Electronics Lab ManualArun DasNo ratings yet
- IGBT/MOSFET Gate Drive Optocoupler: Optocouplers and Solid-State RelaysDocument9 pagesIGBT/MOSFET Gate Drive Optocoupler: Optocouplers and Solid-State RelaysWilliam moreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Auto HCE Number PS H Fig Added Zo Corrected Edit 2Document59 pagesChapter 5 Auto HCE Number PS H Fig Added Zo Corrected Edit 2plabonNo ratings yet
- Infineon-IGBT Basics How Does An IGBT work-AdditionalTechnicalInformation-v01 00-ENDocument9 pagesInfineon-IGBT Basics How Does An IGBT work-AdditionalTechnicalInformation-v01 00-ENHernan CortezNo ratings yet
- An 9020Document25 pagesAn 9020Reshmi Parikal RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Manual of Experiments - Expt - 1Document2 pagesManual of Experiments - Expt - 1utkarshpatel.up04No ratings yet
- 7 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- IgbtDocument11 pagesIgbtRajeev VaranwalNo ratings yet
- An-7004 IGBT Driver Calculation Rev00Document8 pagesAn-7004 IGBT Driver Calculation Rev00Raghuram YaramatiNo ratings yet
- Fuji Elect Gate Drive CircuitsDocument11 pagesFuji Elect Gate Drive CircuitskristechnikNo ratings yet
- The Components and Control Methods For Implementation of InverterDocument9 pagesThe Components and Control Methods For Implementation of InverterIEA.BOD.I2 - Sơn, Vũ Văn - Giám đốc E&A - INTECH GROUPNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics WorkbookDocument54 pagesPower Electronics WorkbookPooja PandeyNo ratings yet
- Application Guide of IGBT DriverDocument17 pagesApplication Guide of IGBT DriverNam DoanNo ratings yet
- 1.2.4 New Developments in MOSFET and IGBT TechnologyDocument6 pages1.2.4 New Developments in MOSFET and IGBT Technologyjorge armando vega prietoNo ratings yet
- MOSFET QuestionsDocument23 pagesMOSFET QuestionsSure Avinash100% (2)
- Electronic Devices & Circuits (EDC) PE-124: Prepared By: Engr. Shafaq EjazDocument22 pagesElectronic Devices & Circuits (EDC) PE-124: Prepared By: Engr. Shafaq EjazShafaq EjazNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Circuits (EDC) PE-124: Prepared By: Engr. Shafaq EjazDocument22 pagesElectronic Devices & Circuits (EDC) PE-124: Prepared By: Engr. Shafaq EjazShafaq EjazNo ratings yet
- Slides Ch2 Devices PDFDocument28 pagesSlides Ch2 Devices PDFSatya SahaNo ratings yet
- LAB 5-PE-LabDocument7 pagesLAB 5-PE-LabLovely JuttNo ratings yet
- Chapter2-NewDocument39 pagesChapter2-NewIan Azarya AryantoNo ratings yet
- B BJT CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesB BJT CharacteristicskarthikarajaratnaNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment #1 Basic Converter Analysis Due at 10 Am MDT On Friday, September 7, 2017Document3 pagesHomework Assignment #1 Basic Converter Analysis Due at 10 Am MDT On Friday, September 7, 2017ollata kalanoNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 8: (Electronic Devices)Document7 pagesUnit Test 8: (Electronic Devices)padhi8480No ratings yet
- Semiconductor Power SwitchesDocument31 pagesSemiconductor Power SwitchesAswad AcademyNo ratings yet
- 11 Redução Harmonicos Baixa Frequencia Boost - Metodo Duty RatioDocument8 pages11 Redução Harmonicos Baixa Frequencia Boost - Metodo Duty RatioGleison SilvaNo ratings yet
- OP AMP AssignmentDocument8 pagesOP AMP AssignmentPradeep ChauhanNo ratings yet
- This Section Explains The Drive Circuit DesignDocument11 pagesThis Section Explains The Drive Circuit DesignSandeep SNo ratings yet
- EE 2009 GATE QuestionsDocument20 pagesEE 2009 GATE QuestionspraveeenkjNo ratings yet
- 2-EE-Objective Paper-II-2010 PDFDocument20 pages2-EE-Objective Paper-II-2010 PDFHarshit YadavNo ratings yet
- Transistor BiasingDocument54 pagesTransistor BiasingAma Serwaa YeboahNo ratings yet
- Band Gap ReferencesDocument115 pagesBand Gap ReferencesNam Luu Nguyen NhatNo ratings yet
- EE102 Electronic Engineering IIDocument29 pagesEE102 Electronic Engineering II211164 211164No ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual With LogoDocument69 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual With LogoPunith Gowda M BNo ratings yet
- 20 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page20 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- L-6 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 7Document3 pagesL-6 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 7GagneNo ratings yet
- PCGA200T65NF8Document1 pagePCGA200T65NF8Victor RichardNo ratings yet
- Assignment 05Document3 pagesAssignment 05Anchal Debnath ee21b017No ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document2 pagesTutorial 6Saransh MittalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Thyristors and TriacsDocument39 pagesLesson 4 Thyristors and TriacsChacko Mathew100% (1)
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to LSIFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to LSINo ratings yet
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxFrom EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Digital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsFrom EverandDigital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysNo ratings yet
- Digital Power Electronics and ApplicationsFrom EverandDigital Power Electronics and ApplicationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- 8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 22 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page22 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet