Professional Documents
Culture Documents
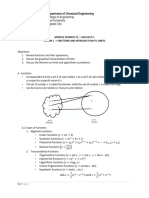
Tut (KUZ) Ind Integral
Uploaded by
Nguyen Lam Uyen FX12223Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tut (KUZ) Ind Integral
Uploaded by
Nguyen Lam Uyen FX12223Copyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial. Indefinite integral 14.04.21. Solutions.
Exercise 1 like on p.48:
Determine the antiderivative 𝐹(𝑥) of the following functions:
16
a) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥
− 3, 𝐹(𝑥) =
b) 𝑓(𝑥) = 10(𝑥 − 2) = 10𝑥 − 20, 𝐹(𝑥) =
8
c) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑒 𝑥 , 𝐹(𝑥) =
d) 𝑓(𝑥) = 5𝑒 𝑥 + 4 sin 𝑥 , 𝐹(𝑥) =
3
e) 𝑓(𝑥) = − , 𝐹(𝑥) =
√4−𝑥 2
5𝑙𝑛5
f) 𝑓(𝑥) = − 2𝑥, 𝐹(𝑥) =
𝑥
1 1
1 1
g) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 −3 − 𝑥 −4 , 𝐹(𝑥) =
3 4
h) 𝑓(𝑥) = √𝑥 + 𝑠𝑒𝑐 2 (𝑥), 𝐹(𝑥) =
2
i) 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑙𝑛2)𝑥 + 𝑥 −3 , 𝐹(𝑥) =
1
2𝑥 1
j) 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑙𝑛2) + 3 𝑥 −3 , 𝐹(𝑥) =
3
2 1
k) 𝑓(𝑥) = − (𝑙𝑛2) 𝑥 2 − 4 𝑥 −2 , 𝐹(𝑥) =
1
1 1
l) 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑙𝑛4) + 2 𝑥 2 , 𝐹(𝑥) =
8
m) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 4 , 𝐹(𝑥) =
𝑥2
n) 𝑓(𝑥) = 2
, 𝐹(𝑥) =
o) 𝑓(𝑥) = −8 sin 𝑥, 𝐹(𝑥) =
Tutorial. Indefinite integral 14.04.21. Solutions.
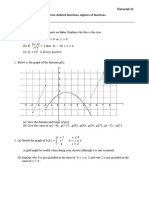
Exercise 2 like on p. 49:
sin 5𝑥
a) Prove that 𝐹(𝑥) = 5
is the antiderivative of the function 𝑓(𝑥) = cos 5𝑥
1
b) Prove that 𝐹(𝑥) = 2 (3𝑥 − 1)2 is the antiderivative of the function 𝑓(𝑥) = 9𝑥 −
3
1 3
c) Prove that 𝐹(𝑥) = 2 𝑒 3𝑥−2 is the antiderivative of the function 𝑓(𝑥) = 2 𝑒 3𝑥−2
2
d) Prove that 𝐹(𝑥) = ln(1 − 2𝑥) is the antiderivative of the function 𝑓(𝑥) =
2𝑥−1
𝑥2
e) Determine the antiderivative 𝐹(𝑥) of the function 𝑓(𝑥) = − 1, for which
2
𝐹(1) = 1.
2𝑥−1
f) Determine the antiderivative 𝐹(𝑥) of the function 𝑓(𝑥) = 4 ∗ 2 , for which
1
𝐹(0) = 3 ln 2
.
g) Determine the antiderivative 𝐹(𝑥) of the function 𝑓(𝑥) = 3 cos 3𝑥, for which
𝜋
𝐹 ( 2 ) = 1.
𝜋
h) Determine the antiderivative 𝐹(𝑥) of the function 𝑓(𝑥) = − sin ( − 𝑥), for
4
3𝜋
which 𝐹 ( ) = −1.
4
You might also like
- Cameron Francis - What It Isn'tDocument14 pagesCameron Francis - What It Isn'tKeith Porter75% (4)
- Scope 090312 DebateDocument2 pagesScope 090312 Debateapi-255074047No ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam - Gen Math - FinalDocument3 pages1st Quarter Exam - Gen Math - FinalAgnes RamoNo ratings yet
- Tally Erp 9 Shortcuts in PDFDocument5 pagesTally Erp 9 Shortcuts in PDFAmit Baviskar100% (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SGV Tieng Anh5 - Tap 1Document136 pagesSGV Tieng Anh5 - Tap 1trivanthNo ratings yet
- Mathematics I 12 Week 1Document4 pagesMathematics I 12 Week 1aybukealp59No ratings yet
- 04 - HW Derivatives ProblemsDocument3 pages04 - HW Derivatives ProblemsMaxNo ratings yet
- Deribatuak 1Document6 pagesDeribatuak 1loreaxiangcanceloNo ratings yet
- AMT108 Functions QuestionsDocument6 pagesAMT108 Functions QuestionsBilal NassarNo ratings yet
- Applied1 Unit5 2011ECDocument44 pagesApplied1 Unit5 2011ECTadesse100% (1)
- General Rules of Derivatives: Lecturer: Hakima Kh. AhmedDocument10 pagesGeneral Rules of Derivatives: Lecturer: Hakima Kh. AhmedKasar nagib 2002No ratings yet
- 5.1 Indefinite Integrals: Chapter 5: Integrals and Their ApplicationsDocument46 pages5.1 Indefinite Integrals: Chapter 5: Integrals and Their ApplicationsMilki Mesay100% (1)
- Lista 01 - DerivadasDocument3 pagesLista 01 - Derivadasrafa16kkNo ratings yet
- PreCal HO7 AlgebraOfFunctions WoExerciseDocument3 pagesPreCal HO7 AlgebraOfFunctions WoExerciseluluhbelle cruzNo ratings yet
- Homework Diff 5Document12 pagesHomework Diff 5Kking ChungNo ratings yet
- Relations and Functions Q-8Document3 pagesRelations and Functions Q-8ankitbhumika23No ratings yet
- Mat 221p Practice QuestionsDocument1 pageMat 221p Practice QuestionsIsulu PeNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 MTH102 PDFDocument1 pageAssignment2 MTH102 PDFjanazayatNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 MTH102 PDFDocument1 pageAssignment2 MTH102 PDFjanazayatNo ratings yet
- DT Turunan FixDocument1 pageDT Turunan Fixrenata.yolanda renata.yolandaNo ratings yet
- WEEK6Document11 pagesWEEK6Crius DiomedesNo ratings yet
- More On Functions 2 REDONE 2022Document11 pagesMore On Functions 2 REDONE 2022Lazy BanditNo ratings yet
- Examples of DerivativesDocument6 pagesExamples of DerivativesHamza HanaBhaiNo ratings yet
- Exam Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesExam Review QuestionsLoje LabNo ratings yet
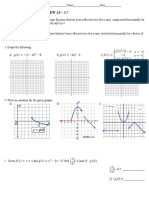
- ggE67x8EoHX3Jh9nreci5g-1.5 - 1.7 Test REVIEWDocument2 pagesggE67x8EoHX3Jh9nreci5g-1.5 - 1.7 Test REVIEWIllu SieveNo ratings yet
- Ficha de DerivadasDocument1 pageFicha de DerivadasSilvia Pañeda GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Inverse Function 1Document10 pagesInverse Function 1Jerom Lexther Mission EsposoNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chapter 1: FunctionsDocument5 pagesForm 4 Chapter 1: FunctionsSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Working With Functions1 1Document8 pagesChapter 2.1 Working With Functions1 1Enkhjin OtgonbatNo ratings yet
- TD FunctionsDocument8 pagesTD FunctionsMR NOBODYNo ratings yet
- Chap 5A - Orthogonal Functions and Fourier SeriesDocument13 pagesChap 5A - Orthogonal Functions and Fourier Seriesanatisyamimi03No ratings yet
- FASE 2 - Puntos - 4.5.6.7Document2 pagesFASE 2 - Puntos - 4.5.6.7victor alfonso jaimes torresNo ratings yet
- Relations and Functions Q-6Document3 pagesRelations and Functions Q-6ankitbhumika23No ratings yet
- 2.2 Partial DerivativesDocument12 pages2.2 Partial Derivativesshamarplummer0923No ratings yet
- Mathematics For Natural Sciences Math 1011 Worksheet On Chapters 3 and 4Document2 pagesMathematics For Natural Sciences Math 1011 Worksheet On Chapters 3 and 4Eyob LakewNo ratings yet
- Review Arithmetic and FunctionsDocument5 pagesReview Arithmetic and FunctionsAdrianus RioNo ratings yet
- ABCALC Exponential and Log Derivatives HomeworkDocument2 pagesABCALC Exponential and Log Derivatives HomeworkLOLNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document10 pagesLecture 1navrajk022No ratings yet
- IV.-Hallar Y' (X) para La Curva Dada en Forma Paramétrica X G (T), y y F (T), Donde: 1.-g (T) 2t-1 y F (T) Sen T 2. - G (T) y F (T) Sen3tDocument1 pageIV.-Hallar Y' (X) para La Curva Dada en Forma Paramétrica X G (T), y y F (T), Donde: 1.-g (T) 2t-1 y F (T) Sen T 2. - G (T) y F (T) Sen3tPAUL OWUEN MOYA SILENCIONo ratings yet
- Math 11: Calculus I Differential CalculusDocument9 pagesMath 11: Calculus I Differential CalculusKors Min YeolNo ratings yet
- P3 Revision Worksheet (AUGUST 20) : P3: Chapter 1 and 2 (Up To Inverse Function)Document2 pagesP3 Revision Worksheet (AUGUST 20) : P3: Chapter 1 and 2 (Up To Inverse Function)Bibi Marium SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- 348 - 38835 - BA101 - 2017 - 4 - 1 - 1 - A5 Math1 Fall 2017-Dr. Mostafa ElogailDocument3 pages348 - 38835 - BA101 - 2017 - 4 - 1 - 1 - A5 Math1 Fall 2017-Dr. Mostafa ElogailAyman Hesham El-AttarNo ratings yet
- Material Aula 7Document3 pagesMaterial Aula 7Vitoria MirandaNo ratings yet
- Relations and Functions Q-2Document3 pagesRelations and Functions Q-2ankitbhumika23No ratings yet
- Microlink Information Technology College Mekelle Branch APPLIED MATHEMATICS-I (MATH-281) Assignment Maximum Marks (35%)Document1 pageMicrolink Information Technology College Mekelle Branch APPLIED MATHEMATICS-I (MATH-281) Assignment Maximum Marks (35%)mer gerNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Revision SP22-Final AnswersDocument8 pagesExam 2 Revision SP22-Final AnswersAisha ANo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Functions and Introduction To LimitsDocument5 pagesLesson 1 - Functions and Introduction To Limitskylahernandez2022No ratings yet
- GenMath - LESSON 3Document1 pageGenMath - LESSON 3Russell AngelesNo ratings yet
- 3.1 The Chain Rule: NotesDocument5 pages3.1 The Chain Rule: NotesAzra OzenNo ratings yet
- 348 - 38835 - BA101 - 2017 - 4 - 1 - 1 - A7 Calculus1 Fall 2017-Dr. Mostafa ElogailDocument5 pages348 - 38835 - BA101 - 2017 - 4 - 1 - 1 - A7 Calculus1 Fall 2017-Dr. Mostafa ElogailAyman Hesham El-AttarNo ratings yet
- Samplenote Formula Sheet of Continuity & Differentability 1462984037 57335d6563f4c 42040Document3 pagesSamplenote Formula Sheet of Continuity & Differentability 1462984037 57335d6563f4c 42040Ashmita GoyalNo ratings yet
- MAT2018 Problem Sheet #2Document1 pageMAT2018 Problem Sheet #2romonedyer3No ratings yet
- Lect. 1Document18 pagesLect. 1jfbv549No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4.: Functions, Their Domains and Ranges, Graphs of FunctionsDocument3 pagesTutorial 4.: Functions, Their Domains and Ranges, Graphs of FunctionsKevon BvunzaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1yahyayaqoob2006No ratings yet
- GM M11GM-Ia-3 Q1Document6 pagesGM M11GM-Ia-3 Q1Ernesto Cabuyadao100% (1)
- Total No. of Printed Pages-2: Ii Sem Mthg1Document2 pagesTotal No. of Printed Pages-2: Ii Sem Mthg1Shudhangshu SarmahNo ratings yet
- AP Calcab Derviatives CW HW 2014-12-07Document33 pagesAP Calcab Derviatives CW HW 2014-12-07Max CorteziNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Continuity and DiffrentiabilityDocument1 pageWorksheet Continuity and DiffrentiabilityPristy JoyisNo ratings yet
- 04 - HW Derivatives SolutionsDocument7 pages04 - HW Derivatives SolutionsMaxNo ratings yet
- Exercise Calculus 2021 PhanXuanThanhDocument10 pagesExercise Calculus 2021 PhanXuanThanhPhong ÂuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 11Document2 pagesTutorial 11carlsandy1234No ratings yet
- Exam July2021Document5 pagesExam July2021Nguyen Lam Uyen FX12223No ratings yet
- OscillationsDocument4 pagesOscillationsNguyen Lam Uyen FX12223No ratings yet
- Chapter (15.2) Doppler EffectDocument10 pagesChapter (15.2) Doppler EffectNguyen Lam Uyen FX12223No ratings yet
- Sound Waves and Doppler EffectsDocument7 pagesSound Waves and Doppler EffectsNguyen Lam Uyen FX12223No ratings yet
- Physics Singapore AnswerDocument83 pagesPhysics Singapore AnswerNguyen Lam Uyen FX12223No ratings yet
- Chapter (15.1) Traveling WavesDocument18 pagesChapter (15.1) Traveling WavesNguyen Lam Uyen FX12223No ratings yet
- Chapter (14), OscillationsDocument14 pagesChapter (14), OscillationsNguyen Lam Uyen FX12223No ratings yet
- Topic 2 MCDocument23 pagesTopic 2 MCNguyen Lam Uyen FX12223No ratings yet
- LP SymbioticDocument3 pagesLP SymbioticRica AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Edgardo Ortega Martinez, - MARSSGDocument7 pagesEdgardo Ortega Martinez, - MARSSGChilly07No ratings yet
- Multiple-Voltage-Vector Model Predictive Control With Reduced Complexity For Multilevel InvertersDocument12 pagesMultiple-Voltage-Vector Model Predictive Control With Reduced Complexity For Multilevel InvertersNassima BekhouchaNo ratings yet
- KidsBox PreA1 Starters Practice TestDocument14 pagesKidsBox PreA1 Starters Practice TestMonika GodlewskaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Lab 1 Moles Molecules and GramsDocument4 pagesUnit 4 Lab 1 Moles Molecules and Gramsapi-239473897No ratings yet
- Whs Project Proposal TawilaDocument19 pagesWhs Project Proposal TawilaLawrence WatssonNo ratings yet
- Docshare - Tips - Seismic Processing and Interpretation PDFDocument102 pagesDocshare - Tips - Seismic Processing and Interpretation PDFGhassen LaouiniNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Question? Contact PhilipsDocument14 pagesUser Manual: Question? Contact PhilipsPopescuNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument5 pagesDocxJere Mae MarananNo ratings yet
- Basic Fuse Terminology: Fuse: Fuse Elements: Rated Current: Fusing Current: Fusing FactorDocument3 pagesBasic Fuse Terminology: Fuse: Fuse Elements: Rated Current: Fusing Current: Fusing FactorPralay RoyNo ratings yet
- Name and Section: Score:: V P Constant V T Constant P V Constant PV ConstantDocument4 pagesName and Section: Score:: V P Constant V T Constant P V Constant PV ConstantJohnnard BelenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2B Entrepreneurial ManagementDocument10 pagesLesson 2B Entrepreneurial ManagementErica Mae GacayonNo ratings yet
- 8 Wastes of LeanDocument6 pages8 Wastes of LeanAmey WarudeNo ratings yet
- C-More CableDocument31 pagesC-More CableWinston diaz valeraNo ratings yet
- Plan of Lectures and Lab MEC610 (March-Jul 2023)Document2 pagesPlan of Lectures and Lab MEC610 (March-Jul 2023)Aimi AireezNo ratings yet
- Windows Commands Abused by Threat ActorDocument14 pagesWindows Commands Abused by Threat Actoresmail ahmedNo ratings yet
- How To Configure Mail Proxy Settings in Outlook Express For GmailDocument34 pagesHow To Configure Mail Proxy Settings in Outlook Express For GmailSuman RoyNo ratings yet
- TYH - TYA-Inverter Ducted PAC - CatalogueDocument4 pagesTYH - TYA-Inverter Ducted PAC - CatalogueNguyễn Thành ChungNo ratings yet
- Roles Responsibilities in Engineering PDFDocument2 pagesRoles Responsibilities in Engineering PDFPratiksha PradhanNo ratings yet
- 2021 JPJC J2 H1 EC MYE (Annotated QP)Document8 pages2021 JPJC J2 H1 EC MYE (Annotated QP)PROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- Karjiker Opensource 2013Document389 pagesKarjiker Opensource 2013Richard ShayNo ratings yet
- Sikadur 31 PlusDocument5 pagesSikadur 31 Plusghazi.tcmarineNo ratings yet
- Get Started With GAWK: AWK Language FundamentalsDocument23 pagesGet Started With GAWK: AWK Language FundamentalsPranav PrakashNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignments Chapter-6: Alkyl Halides-Substitution and Elimination ReactionsDocument14 pagesHomework Assignments Chapter-6: Alkyl Halides-Substitution and Elimination ReactionsandrewNo ratings yet
- A New Strategic PlanDocument9 pagesA New Strategic PlanHezekia KiruiNo ratings yet
- Log Periodic Antennas - LPA-LPD SeriesDocument79 pagesLog Periodic Antennas - LPA-LPD SeriesMarco OlazabalNo ratings yet