Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Origin of The Periodic Table ...
Uploaded by
Gabriela CamargoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Origin of The Periodic Table ...
Uploaded by
Gabriela CamargoCopyright:
Available Formats
Origin of the Periodic Table
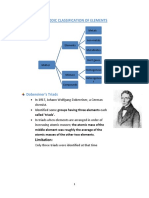
Between 1817 and 1829, the German chemist Johan Dobereiner classified some elements
into groups of three called triads, since they had similar chemical properties.
In 1863, the English chemist John Newlands classified the established elements into several
groups, proposing the Law of Octaves.
In 1869, the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev published his first periodic table of the
elements organized in increasing order of atomic mass.
At the same time, Lothar Meyer, a German chemist, published his own periodic table with
the elements arranged from lowest to highest atomic mass.
In 1913, an English chemist, Henry Moseley, by means of X-ray studies, determined the
nuclear charge of the elements, regrouping them in increasing order of atomic number.
Currently the current periodic table has 118 elements (94 of which occur naturally on
Earth).
Classification:
There are 2 classifications in the periodic table are metals and nonmetals.
In the metals there are:
Alkali
Transition
Alkaline earth
Post-transitional
Metalloids
Lanthanides
Actinides
In the nonmetals:
Halogens
Noble gases
- Hydrogen (H)1: Non-metals
- Helium (He)2 : Non-metals
- Lithium (Li)3: Alkali metals
- Beryllium (Be)4: Alkali earth metals
- Boron (B)5: Metalloids
- Carbon (C)6: Non-metals
- Nitrogen (N)7: Non-metals
- Oxygen (O)8: Non-metals
- Fluorine (F): 9 Halogens
- Neon (Ne): 10 Noble Gases
- Sodium (Na): 11 Alkali Metals
- Magnesium (Mg): 12 Alkaline Earth Metals
- Aluminum (Al): 13 Post-transitional
- Silicon (Si): 14 Metalloids
- Phosphorus (P)15 Non-metals
You might also like
- A Brief History of Element Discovery, Synthesis, and AnalysisFrom EverandA Brief History of Element Discovery, Synthesis, and AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Dmitri Mendeleev-Did He Really Deserve All The CreditDocument9 pagesDmitri Mendeleev-Did He Really Deserve All The CreditChriselda AkomahNo ratings yet
- Dmitri Mendeleev-Did He Really Deserve All The Credit?Document6 pagesDmitri Mendeleev-Did He Really Deserve All The Credit?Chriselda AkomahNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument13 pagesPeriodic TablesemantotanzimahmedNo ratings yet
- The History of The Periodic Table - DHDocument9 pagesThe History of The Periodic Table - DHDavid HallNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument14 pagesPeriodic TableJefferson Gaucho AyikaNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of The Development of The Periodic TableDocument1 pageA Brief History of The Development of The Periodic TableRaven QuiinNo ratings yet
- Johann Wolfgang DöbereinerDocument4 pagesJohann Wolfgang DöbereinerBaby Jean B. ZausaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Periodic TableDocument2 pagesNotes - Periodic TableIrene Sanchez100% (1)
- History of Periodic TableDocument2 pagesHistory of Periodic TableSukrit KhannaNo ratings yet
- History of The Modern Periodic TableDocument41 pagesHistory of The Modern Periodic TablecassNo ratings yet
- History of The Modern Periodic TableDocument41 pagesHistory of The Modern Periodic TableannakathirNo ratings yet
- Attempts Made by Johann Dobereiner and Johann NewlandsDocument21 pagesAttempts Made by Johann Dobereiner and Johann NewlandsJames MahNo ratings yet
- sANa OllDocument43 pagessANa OllPeejayNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument2 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsAlstroNo ratings yet
- History of The Modern Periodic TableDocument41 pagesHistory of The Modern Periodic TablephbhagwatNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table HistoryDocument5 pagesPeriodic Table HistoryMarybeth BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Scientist: The Contributions of The in The Development of The PeriodicDocument16 pagesScientist: The Contributions of The in The Development of The PeriodicSiti Nurul AmirahNo ratings yet
- Döbereiner, Johann Wolfgang (Germany, 1780-1849)Document6 pagesDöbereiner, Johann Wolfgang (Germany, 1780-1849)Andrea May IntiaNo ratings yet
- The History of Periodic Table RaianDocument2 pagesThe History of Periodic Table RaianRey SorianoNo ratings yet
- History of Periodic TableDocument24 pagesHistory of Periodic TableMaca RenaNo ratings yet
- History of Periodic Table DevelopmentDocument5 pagesHistory of Periodic Table Developmenthafizah_90No ratings yet
- Chem ProjectDocument6 pagesChem Projecthansinuthalapati2519No ratings yet
- Profile Picture of Maya Johnson: History of The Periodic Table TimelineDocument8 pagesProfile Picture of Maya Johnson: History of The Periodic Table TimelineLucas TinNo ratings yet
- CHEM Report - Periodic TableDocument3 pagesCHEM Report - Periodic TableLeah Rose Figueroa ParasNo ratings yet
- Antoine Lavoisier (1743 - 1794) : Chapter 4: Periodic Table of Elements - HistoryDocument2 pagesAntoine Lavoisier (1743 - 1794) : Chapter 4: Periodic Table of Elements - HistoryIzzat AziziNo ratings yet
- Tel/Fax No.: (047) 811-1683 The Historical Development of The Periodic TableDocument8 pagesTel/Fax No.: (047) 811-1683 The Historical Development of The Periodic TableCarl PaduaNo ratings yet
- Periodic TimelineDocument2 pagesPeriodic TimelineHannah BabidaNo ratings yet
- History of The Periodic TableDocument4 pagesHistory of The Periodic TableJennilyn LumacadNo ratings yet
- History of The Periodic Table - WikipediaDocument6 pagesHistory of The Periodic Table - WikipediazeeshanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table HistoryDocument1 pagePeriodic Table HistoryjavervalinoNo ratings yet
- History of TableDocument12 pagesHistory of TableKanat AmantaiulyNo ratings yet
- Classification of Element and Periodicity in PropertiseDocument27 pagesClassification of Element and Periodicity in PropertiseAditya chauhanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry (Pesonalities and Their Contributions)Document3 pagesGeneral Chemistry (Pesonalities and Their Contributions)Dean Mark AnacioNo ratings yet
- Mr. Shields Regents Chemistry U08 L01Document17 pagesMr. Shields Regents Chemistry U08 L01Remee CastroNo ratings yet
- Development of The Periodic TableDocument8 pagesDevelopment of The Periodic TableVernadette Camille RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner: TriadsDocument5 pagesJohann Wolfgang Döbereiner: TriadsMikeLesterCalolotNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Power PointDocument48 pagesPeriodic Table Power PointRanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- History of Peiodic Table - Gen ChemDocument2 pagesHistory of Peiodic Table - Gen ChemSai Adrienne RealubitNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of The Development of Periodic TableDocument2 pagesA Brief History of The Development of Periodic Tableantonetteporca100% (1)
- Periodic Table HistoryDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Historytawananyashatheodore495No ratings yet
- Hist. of PeriodicTableDocument30 pagesHist. of PeriodicTableRaisa Bint ZamanNo ratings yet
- Discovery of Elements and Development of The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument29 pagesDiscovery of Elements and Development of The Periodic Table of ElementsrayNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument38 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsLia Marlia100% (2)
- Chem ProDocument1 pageChem Proramykarim20082020No ratings yet
- Chapter 4:the Periodic Table of Elements: Group 1 - Afiq Rifqal - Nicole Ho - Raihan - Bharath - Tuck HoeDocument11 pagesChapter 4:the Periodic Table of Elements: Group 1 - Afiq Rifqal - Nicole Ho - Raihan - Bharath - Tuck HoeShafeeqah FadzilNo ratings yet
- The History of The Periodic Table of Elements: Gwyneth D. GocoDocument16 pagesThe History of The Periodic Table of Elements: Gwyneth D. GocoMelissa MalicdemNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements: MetalsDocument7 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements: MetalslucasNo ratings yet
- Hennig Brand: Persons Behind The Periodic TableDocument9 pagesHennig Brand: Persons Behind The Periodic Tablegeline joyNo ratings yet
- IM For Individual DemoDocument45 pagesIM For Individual DemoAndreiNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument19 pagesPeriodic Table of Elementsalexa de veraNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements PDFDocument8 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements PDFanjupal80% (5)
- Sci - 8 Elements of Periodic Table-Week 7-8Document37 pagesSci - 8 Elements of Periodic Table-Week 7-8SANTA ISABEL MERCADONo ratings yet
- History of ChemistryDocument4 pagesHistory of ChemistryHashir AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document58 pagesChapter 13oninNo ratings yet
- Development of The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument29 pagesDevelopment of The Periodic Table of ElementsEA CatalanNo ratings yet
- On Chemistry Sidpreet Singh Class XDocument24 pagesOn Chemistry Sidpreet Singh Class XSidpreet SandhuNo ratings yet