Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Language Comprehension
Uploaded by
Zidan Muhammad Rausyan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views14 pagesThe document discusses various theories about how language and the mind develop and interact, including that language allows communication of thought, language structure can determine mind structure, and that in childhood language and mind first develop independently before language is influenced by the mind. It also examines the cognitive processes involved in comprehending and producing language, such as perceiving linguistic units, retrieving word meanings, and determining syntactic patterns. Memory plays an important role in language and cognition by allowing people to remember past experiences, concepts, and words.
Original Description:
Original Title
3 LANGUAGE COMPREHENSION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various theories about how language and the mind develop and interact, including that language allows communication of thought, language structure can determine mind structure, and that in childhood language and mind first develop independently before language is influenced by the mind. It also examines the cognitive processes involved in comprehending and producing language, such as perceiving linguistic units, retrieving word meanings, and determining syntactic patterns. Memory plays an important role in language and cognition by allowing people to remember past experiences, concepts, and words.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views14 pages3 Language Comprehension
Uploaded by
Zidan Muhammad RausyanThe document discusses various theories about how language and the mind develop and interact, including that language allows communication of thought, language structure can determine mind structure, and that in childhood language and mind first develop independently before language is influenced by the mind. It also examines the cognitive processes involved in comprehending and producing language, such as perceiving linguistic units, retrieving word meanings, and determining syntactic patterns. Memory plays an important role in language and cognition by allowing people to remember past experiences, concepts, and words.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Processing & Disorder
Language: means whereby thought is
communicated
Mind: generated ideas formulated in
language
Humboldt: Language substance consists of
sound & thought
Sapir & Whorf: language structure
determines mind structure
Piaget: Mind formed language
Vygotsky: In childhood, language and mind
developed independently, before then
language is influenced by mind
1. Identify the words in the question ‘makan’
2. Organize the word into syntactic pattern
‘sudah makan’
3. Turn the question into proposition
‘offering’
4. Search memory for info ‘previous
experience’
5. Retrieve the info ‘already full’
6. Turn the info into words ‘thanks’
7. Utter the words ‘sound produced’
Perceptual: identify units of ling
message
Lexical: retrieve lexical
representation of words
Sentential: determine syntactic
pattern
Discourse: identify context
proceeding and following it
Perhatian -– Si -- Theodore -- Memiliki -- Ia --
Anak -- Masyarakat -- Ingin -- Upacara -- Sifat -–
Menghadiri –- Presiden -- Mendatangi -- Ingin --
Ketika –- Pengantin – Ingin -– Ia –- Amerika -–
Ambisius –- Ia –- Jenasah – Pusat – Roosevelt –
Pemakaman –- Menjadi –- Pesta -- Menjadi --
Pada -– Pernikahan –- Sang –- Saat –- Menjadi –
Serikat -- Namun
Anak Presiden Amerika Serikat
Theodore Roosevelt Memiliki Sifat
Ambisius. Ia Ingin Menjadi Pusat
Perhatian Masyarakat. Ketika
Menghadiri Pesta Pernikahan Ia Ingin
Menjadi Sang Pengantin. Namun
Pada Saat Mendatangi Upacara
Pemakaman Ia Ingin Menjadi Si
Jenasah
Memory is an integral part of human
existence that underlies language and mind.
Can you imagine if men cannot remember
past times, cannot save the entries they just
heard, and cannot remember what they did?
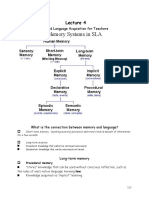
Short-term memory
long-term memory
First,The memory-related experience with
things of the past.
Second, The memory used to build a concept
based on the facts
Third, Remembers the words to form a
sound concept of the concept.
Memory can be categorized into two kinds of
declarative memory and non-declarative memory
There are many factors that lead to
declarative memory is acquired:
Frequency factor,
Relevance factors
Factor of significance
Factor of Preparation
Hereditary factors
Spoken Short-Term Language Comprehension
Language Memory Processor
Verbal Short-Term Language Comprehension
Information Memory Processor
= Clinical insight suggests these impairments are
due to:
•Attention to auditory stimuli
•Not understanding language as
meaningful/symbolic
•Fleeting nature of spoken language
•Language processor ‘broken’
•Combination of these
Bypassing Spoken Language Comprehension Using
Dynamic Scene Cues
(Moderate-Severe ASD)
Verbal
Information
Short-Term Imitation
Memory (as inferred from
dynamic scene cues)
Visual
Information
(dynamic scene cues)
You might also like
- ABA Language and Cognition PDFDocument377 pagesABA Language and Cognition PDFRaul Vaz ManzioneNo ratings yet
- 11-10 FINAL DICH NOI Bài Thu Ho CH EN47Document2 pages11-10 FINAL DICH NOI Bài Thu Ho CH EN47ngochuyenNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Process ModelsDocument36 pagesInterpreting Process ModelsJorge Franco100% (1)
- Thinking: Memory, Cognition, and Language: Group 5Document32 pagesThinking: Memory, Cognition, and Language: Group 5Kristine AquitNo ratings yet
- Language Processing: Otherwise Known As PsycholinguisticsDocument23 pagesLanguage Processing: Otherwise Known As PsycholinguisticswildaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 PsycholinguisticsDocument72 pagesChapter 9 PsycholinguisticsKurniawanNo ratings yet
- ELECTIVE 1 Module 1-FinalsDocument4 pagesELECTIVE 1 Module 1-FinalsMatteoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.2. Testing ListeningDocument16 pagesUnit 4.2. Testing ListeningUziel BeltranNo ratings yet
- Memory Systems in SLA: Second Language Acquisition For TeachersDocument5 pagesMemory Systems in SLA: Second Language Acquisition For TeachersHollós DávidNo ratings yet
- Two Languages in One Brain: Alliance Française de Nashville April 28, 2006Document38 pagesTwo Languages in One Brain: Alliance Française de Nashville April 28, 2006Bryan EcijaNo ratings yet
- Language & ThoughtDocument22 pagesLanguage & ThoughtAnkit RanaNo ratings yet
- The Teaching of ListeningDocument17 pagesThe Teaching of ListeningglennNo ratings yet
- Components of The Listening ProcessDocument33 pagesComponents of The Listening ProcessAfika NtandaNo ratings yet
- Dyslexia and Reading: RAVE-O Program.: A M U PDocument16 pagesDyslexia and Reading: RAVE-O Program.: A M U PVictoria KishchakNo ratings yet
- PrezentacjaDocument3 pagesPrezentacjaJakub BańduraNo ratings yet
- 20220704093918D6369 - Session 9. Informative SpeakingDocument21 pages20220704093918D6369 - Session 9. Informative SpeakingAngel GustasianaNo ratings yet
- Listening BackgroundDocument12 pagesListening Backgroundpandreop100% (4)
- Psycholinguistics Language Production and PerceptionDocument4 pagesPsycholinguistics Language Production and PerceptionBq HidiaNo ratings yet
- CoursDocument10 pagesCoursmelissandebantinNo ratings yet
- Listening Presentation 1Document9 pagesListening Presentation 1KROSDEVIL505No ratings yet
- Listening 1: Suzan Özgelen YılmazDocument33 pagesListening 1: Suzan Özgelen YılmazCPPE ARTENo ratings yet
- D 1.3 Use & Properties of LanguageDocument23 pagesD 1.3 Use & Properties of LanguageYuvaneswari ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Understanding Psychology 10th Edition Morris Solutions ManualDocument38 pagesUnderstanding Psychology 10th Edition Morris Solutions Manualeliasfmvargas100% (14)
- Psycho LinguisticsDocument21 pagesPsycho LinguisticsDonna Faith FajardoNo ratings yet
- Sentence ProductionDocument70 pagesSentence Productiongurjapsahota13No ratings yet
- Oral CompetencesDocument10 pagesOral Competencesjorbar02No ratings yet
- Speaking and Listening Skills: Reg. No.# S3F12ASOC0077Document21 pagesSpeaking and Listening Skills: Reg. No.# S3F12ASOC0077Faiza anwerNo ratings yet
- Definition of AttentionDocument8 pagesDefinition of AttentionZahra Kalsoom100% (1)
- The Five Characteristics of Language Are That It Is A SystemDocument4 pagesThe Five Characteristics of Language Are That It Is A SystemRupam8No ratings yet
- Jackendoff Patterns of The Mind - AnalysisDocument9 pagesJackendoff Patterns of The Mind - AnalysisDiego AntoliniNo ratings yet
- Language and Language SkillsDocument11 pagesLanguage and Language SkillsSafaa Mohamed Abou KhozaimaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Speaking: What Speakers Do and KnowDocument41 pagesTeaching Speaking: What Speakers Do and KnowJose Luis Gatillon SotoNo ratings yet
- Understanding ListeningDocument13 pagesUnderstanding ListeningAsmaaNo ratings yet
- Language Intelligence or Universal English: Remedy Your Speech Skills Book 3From EverandLanguage Intelligence or Universal English: Remedy Your Speech Skills Book 3No ratings yet
- TO BE Able To Teach Accurate PronunciationDocument1 pageTO BE Able To Teach Accurate PronunciationMustaqim AzizanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Language ProcessingDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Language ProcessingVere Veronica VereNo ratings yet
- Language Studies Group 5Document11 pagesLanguage Studies Group 5Rivaldo SiregarNo ratings yet
- Psycholinguistics INTRODUCTIONDocument7 pagesPsycholinguistics INTRODUCTIONDRISS BAOUCHE100% (1)
- Teaching of ListeningDocument107 pagesTeaching of ListeningAre KushiNo ratings yet
- ENG105 Course OutlineDocument8 pagesENG105 Course Outlineajwa telNo ratings yet
- tmp9CCD TMPDocument25 pagestmp9CCD TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Words, Meaning, Memory, RecognitionDocument11 pagesWords, Meaning, Memory, RecognitionEstee Rose AljoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document3 pagesChapter 7Evitania .pNo ratings yet
- English Language Assessment:: Meeting 6 and 7Document19 pagesEnglish Language Assessment:: Meeting 6 and 7Fadhlur RahmanNo ratings yet
- An Interactive Model of Listening Comprehension: Presented By: Zyrill Nathalie L. Digal, 3SE2 BSED-EnglishDocument13 pagesAn Interactive Model of Listening Comprehension: Presented By: Zyrill Nathalie L. Digal, 3SE2 BSED-EnglishMhonz LimbingNo ratings yet
- Are Fundamental Processes That Can Not Be Classified As: - Sensory - MotorDocument84 pagesAre Fundamental Processes That Can Not Be Classified As: - Sensory - Motornapoleon tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Handout - Week 3 - WedDocument17 pagesHandout - Week 3 - WedsohaNo ratings yet
- Psycog 2Document27 pagesPsycog 2Maria HazelNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 NLPDocument51 pagesUnit 4 NLPKumar SumitNo ratings yet
- Functions of Language - Revised 2015Document28 pagesFunctions of Language - Revised 2015Lorenz SmallNo ratings yet
- Listening Speaking SkillsDocument57 pagesListening Speaking Skillsธีมากร เสตถาNo ratings yet
- Title: 3A.1: Key Concepts in Processing Information Date: 05/05/2023 LI: Cognitive Approach To Understanding Behaviour. Starter TasksDocument38 pagesTitle: 3A.1: Key Concepts in Processing Information Date: 05/05/2023 LI: Cognitive Approach To Understanding Behaviour. Starter TasksreemNo ratings yet
- Listening Speaking SkillsDocument57 pagesListening Speaking Skillsธีมากร เสตถา100% (1)
- How To Master A Second Language?Document5 pagesHow To Master A Second Language?iraida sanchezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Memory - StudentDocument20 pagesChapter 6 Memory - StudentEmma StockleyNo ratings yet
- Professional Communication - Notes: Listening & Sounds of EnglishDocument10 pagesProfessional Communication - Notes: Listening & Sounds of EnglishRishavNo ratings yet
- Language AcquistionDocument11 pagesLanguage AcquistionDemeyNo ratings yet
- Stand and Themes of LingDocument3 pagesStand and Themes of LingMaria CristinaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Modern Grammar: The Language Faculty (Ii)Document9 pagesConcepts of Modern Grammar: The Language Faculty (Ii)a skeleton named MarvNo ratings yet
- Speech & LanguageqwdqdDocument20 pagesSpeech & LanguageqwdqdDaniel KohNo ratings yet
- The Language of Machines: Mastering Natural Language Processing AlgorithmsFrom EverandThe Language of Machines: Mastering Natural Language Processing AlgorithmsNo ratings yet
- Art 5 Do Children Learn From Prediction MistakesDocument25 pagesArt 5 Do Children Learn From Prediction MistakesZidan Muhammad RausyanNo ratings yet
- RPS KKNI PragmaticsDocument4 pagesRPS KKNI PragmaticsZidan Muhammad RausyanNo ratings yet
- Art. 1 Sentence ComprehensionDocument12 pagesArt. 1 Sentence ComprehensionZidan Muhammad RausyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.2 DatesDocument2 pagesChapter 3.2 DatesZidan Muhammad RausyanNo ratings yet
- Basic Versification RhytmDocument13 pagesBasic Versification RhytmZidan Muhammad RausyanNo ratings yet
- Urgent !! Harap Baca !!Document2 pagesUrgent !! Harap Baca !!Zidan Muhammad RausyanNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Reader Response ApproachDocument4 pagesThe Effectiveness of Reader Response ApproachCikika100% (1)
- A Feminist Study in Look Back in Anger by John Osborne IntroductionDocument5 pagesA Feminist Study in Look Back in Anger by John Osborne Introductionhelin rzgar111No ratings yet
- Communication Ethics: Dr. Naveen K MehtaDocument12 pagesCommunication Ethics: Dr. Naveen K MehtaromzNo ratings yet
- 170 TRẮC NGHIỆP VỀ COLLOCATIONS CƠ BẢN PDFDocument9 pages170 TRẮC NGHIỆP VỀ COLLOCATIONS CƠ BẢN PDFMAI VŨNo ratings yet
- Solomon 1998Document14 pagesSolomon 1998andris88No ratings yet
- S Announcement 33211Document1 pageS Announcement 33211Eunjina MoNo ratings yet
- Cup of TeaDocument7 pagesCup of Teadanyal khanNo ratings yet
- Pragmatism and Embodied Cognitive Science - From Bodily Intersubjectivity To Symbolic ArticulationDocument313 pagesPragmatism and Embodied Cognitive Science - From Bodily Intersubjectivity To Symbolic ArticulationNilton ClaraNo ratings yet
- არეოპაგიტული ძიებანიDocument230 pagesარეოპაგიტული ძიებანიDonCarlitoNo ratings yet
- Diss Study Guide 4th WeekDocument10 pagesDiss Study Guide 4th WeekRuth MadriagaNo ratings yet
- OB Unit 2.4 Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument29 pagesOB Unit 2.4 Perception and Individual Decision MakingNeggaz D MapeleNo ratings yet
- Diary EntryDocument5 pagesDiary EntryChetan NagarNo ratings yet
- Modern Medical Yoga StrugglingDocument28 pagesModern Medical Yoga StrugglingtihomihoNo ratings yet
- G.E. Moore'S Notion of Intrinsic Value of Goodness: A Disproof About The Three Core Values of Absolute Legal SeparationDocument9 pagesG.E. Moore'S Notion of Intrinsic Value of Goodness: A Disproof About The Three Core Values of Absolute Legal Separationjoselito ayoNo ratings yet
- Hard Choices Decision Making Under Unresolved Conflict (Isaac Levi) (Z-Library)Document262 pagesHard Choices Decision Making Under Unresolved Conflict (Isaac Levi) (Z-Library)Itzamna FuentesNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Answer ExamDocument5 pagesOral Com Answer ExamCijesNo ratings yet
- Married To The Eiffel TowerDocument8 pagesMarried To The Eiffel TowerPatrícia NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Reso BSWCDocument2 pagesReso BSWCrhenz villafuerteNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Mgt400-Dec 2018Document3 pagesAssignment 3 - Mgt400-Dec 2018Hasif YusofNo ratings yet
- SY 2020-2021 NDA GuidelinesDocument3 pagesSY 2020-2021 NDA GuidelinesNoli Antallan100% (1)
- Mauser MissionDocument9 pagesMauser Missionhakha.bazarganNo ratings yet
- Philosophy As The Parent Discipline Historical Background of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesPhilosophy As The Parent Discipline Historical Background of PhilosophyDouglasNo ratings yet
- Module Johntha (Autosaved)Document7 pagesModule Johntha (Autosaved)Tadyooss BalagulanNo ratings yet
- Reflection QuestionsDocument2 pagesReflection QuestionsANGEL JIYAZMIN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Orchids - Hazel Simmonds - MC Donald (ST Lucia)Document4 pagesOrchids - Hazel Simmonds - MC Donald (ST Lucia)Ariana EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Self-Reliance BookDocument20 pagesSelf-Reliance Bookহেল্পডেস্ক ইএলএল-আইআইইউসিNo ratings yet
- Carolyn Abbate Music Drastic or GnosticDocument33 pagesCarolyn Abbate Music Drastic or GnosticGarrison GerardNo ratings yet
- Assignment - The Age of Sensibility - Redwan Siddik - 1441Document2 pagesAssignment - The Age of Sensibility - Redwan Siddik - 1441REDWAN SIDDIKNo ratings yet
- Self Care For The Super WomanDocument25 pagesSelf Care For The Super WomanLorrie AyersNo ratings yet