Professional Documents
Culture Documents
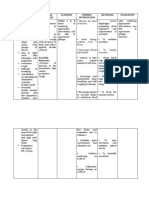
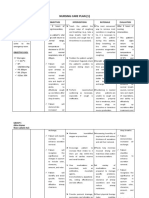
Nursing Interventions: Independent Intervention Dependent Intervention Rationale
Uploaded by
Vaniegrace Angel Balagon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageThis document summarizes nursing interventions for respiratory conditions. It lists independent nursing interventions such as elevating the head of the bed and teaching deep breathing techniques. It also lists dependent interventions like suctioning as needed and maintaining hydration. Rationales are provided for each intervention, such as how head elevation helps lung expansion and suctioning clears thick phlegm. Monitoring tools like chest x-rays and pulse oximetry readings are also mentioned to assess treatment effectiveness.
Original Description:
Original Title
Doc1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes nursing interventions for respiratory conditions. It lists independent nursing interventions such as elevating the head of the bed and teaching deep breathing techniques. It also lists dependent interventions like suctioning as needed and maintaining hydration. Rationales are provided for each intervention, such as how head elevation helps lung expansion and suctioning clears thick phlegm. Monitoring tools like chest x-rays and pulse oximetry readings are also mentioned to assess treatment effectiveness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageNursing Interventions: Independent Intervention Dependent Intervention Rationale
Uploaded by
Vaniegrace Angel BalagonThis document summarizes nursing interventions for respiratory conditions. It lists independent nursing interventions such as elevating the head of the bed and teaching deep breathing techniques. It also lists dependent interventions like suctioning as needed and maintaining hydration. Rationales are provided for each intervention, such as how head elevation helps lung expansion and suctioning clears thick phlegm. Monitoring tools like chest x-rays and pulse oximetry readings are also mentioned to assess treatment effectiveness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Nursing interventions
BY:Vaniegrace Angel Balagon
Independent Intervention Dependent Intervention Rationale
• Elevate the head of the • Suction as needed • Head elevation helps
bed, change position continuous coughing, improve the expansion of
frequently. The diaphragm unusual breath sounds, the lungs, enabling the
would be lowered, and desaturation caused patient to breathe more
allowing for chest by airway secretions. effectively.
expansion, aeration of lung Generates cough or clears
segments, mobilization, the airway manually in a • To help clear thick phlegm
and secretory purulence. patient who is unable to do that the patient is unable
so due to an inefficient to expectorate.
• Adequate deep-breathing cough or a reduced degree
techniques should be of consciousness.
taught and assisted to the • To assist in creating an
patient. • Maintain adequate accurate diagnosis and
hydration by forcing fluids monitor effectiveness of
to at least 3000 mL/day medical treatment.
• Demonstrate proper unless contraindicated
splinting of the chest and • To increase the oxygen
effective coughing while in • Promote ambulation level and achieve a value of
an upright position. Aids in the mobilization of at least 96%.
Encourage patient to do so secretions and the
often. reduction of atelectasis • To dilate or relax the
muscles on the airways. To
• Ensure that all bedridden • You can use humidified reduce the inflammation in
and preoperative patients oxygen or humidifier at the the lungs
practice deep breathing bedside. Increasing the
and coughing exercise on a humidity will decrease the
regular basis. Helps viscosity of secretions.
encourage complete
aeration and secretion • Monitor serial chest x-rays,
discharge. ABGs, pulse oximetry
readings
• Monitor patients breathing
pattern and Perform
treatments between meals
and limit fluids when
appropriate.
You might also like
- Thera Pulmo RehabDocument31 pagesThera Pulmo RehabMarcus VictaNo ratings yet
- Transcript Foundational Herbcraft Part 1Document32 pagesTranscript Foundational Herbcraft Part 1Stacey DianeNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument6 pagesOxygen Therapy11darnell100% (1)
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument29 pagesChest PhysiotherapyHari25885No ratings yet
- Breathing RetrainingDocument39 pagesBreathing RetrainingAishwarya PanchalNo ratings yet
- Promoting Oxygenation 2022Document86 pagesPromoting Oxygenation 2022AinaB ManaloNo ratings yet
- Breathing ExercisesDocument35 pagesBreathing ExercisesShubham KathareNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument15 pagesChest PhysiotherapyreconredulaNo ratings yet
- IGC-1 NotesDocument39 pagesIGC-1 Noteskhurram60% (5)
- NCP For AsthmaDocument1 pageNCP For AsthmaMelvin Martinez100% (1)
- CONSORT ChecklistDocument2 pagesCONSORT Checklistziana alawiyah75% (4)
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocument3 pagesDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJames Lozano83% (6)
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Hygiene or Airway Clearance TechniquesDocument139 pagesBronchial Hygiene or Airway Clearance TechniquesPiyush Salgaonkar100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanJose Mari F. Esguerra0% (1)
- NCP of PnuemoniaDocument13 pagesNCP of PnuemoniaFrando kenneth100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlansJayson Sumampong100% (1)
- MRS. Margaret Nursing CareplanDocument2 pagesMRS. Margaret Nursing CareplanCheran DeviNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentDyam MitchNo ratings yet
- NCP Surgical Ward #1Document1 pageNCP Surgical Ward #1Julie LesmorasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationFe DahunogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document1 pageNursing Care Plan 2JOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaSummer Ilu100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Collection of Mucus in The Airways (Pneumonia) andDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange Related To Collection of Mucus in The Airways (Pneumonia) andBetina De JesusNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument10 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Funda Lab Mod 5-7Document13 pagesFunda Lab Mod 5-7Liane BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions - RespiratoryDocument4 pagesNursing Interventions - Respiratorymanager.intelligentsolutionsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLolaLetNo ratings yet
- Copd - NCPDocument6 pagesCopd - NCPMonique Sacherow BacherNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Respi. Percussion VibrationDocument8 pages4.3 Respi. Percussion VibrationRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Objective Cues:: Ako," As Verbalized by The ClientDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment Objective Cues:: Ako," As Verbalized by The ClientMG CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and OxygenationDocument2 pagesNursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and Oxygenationlodeth100% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis (1) (1) .Finalgid NiyaDocument30 pagesNursing Diagnosis (1) (1) .Finalgid NiyaReadcast EFNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Document6 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Karissa GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Care ModalitiesDocument63 pagesRespiratory Care ModalitiesErica Clerigo LandichoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Sample 3Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Sample 3anon-333251No ratings yet
- Assisting A Client With Controlled Coughing and Deep BreathingDocument3 pagesAssisting A Client With Controlled Coughing and Deep BreathingKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument33 pagesPneumothoraxjamil aldasriNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Chest PhysiotherapyDocument25 pagesPediatric Chest PhysiotherapyShubha DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument3 pagesPneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Breathing BOP I AssignmentDocument23 pagesBreathing BOP I AssignmentSonia guptaNo ratings yet
- MSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyDocument3 pagesMSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Comprehensive ExaminationDocument8 pagesComprehensive ExaminationAnonymous dquW2YmO7No ratings yet
- Breathing Techniques During Labor (Lamaze Method) : Procedure Rationale Rating RemarksDocument4 pagesBreathing Techniques During Labor (Lamaze Method) : Procedure Rationale Rating Remarksadrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- Cptposturaldrainage 150627150049 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument29 pagesCptposturaldrainage 150627150049 Lva1 App6892 PDFBruce LeeNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument29 pagesChest PhysiotherapyPaul GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: (Related To Copious Tracheobronchial Secretions.)Document1 pagePneumonia: (Related To Copious Tracheobronchial Secretions.)Alyssa Mae DumularNo ratings yet
- Breathing Techniques During Labor (Lamaze Method) : Procedure Rationale Rating RemarksDocument4 pagesBreathing Techniques During Labor (Lamaze Method) : Procedure Rationale Rating RemarksHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Com +Nursing+Care+Plan+Community+Acquired+PneumoniaDocument4 pagesCom +Nursing+Care+Plan+Community+Acquired+Pneumoniadonnaluna203315No ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis ShubhaDocument32 pagesCystic Fibrosis ShubhaSuresh HalundeNo ratings yet
- CP FE - Transes.skillsDocument8 pagesCP FE - Transes.skillsmaaisley.yebanNo ratings yet
- OLA HA LecDocument4 pagesOLA HA LecBetina De JesusNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceMaria ArregoitiaNo ratings yet
- PTB 01Document2 pagesPTB 01Dianne ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRodmarc Corpuz BaranganNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument4 pagesChest Physiotherapyhakky gamyNo ratings yet
- Ayu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing CareDocument4 pagesAyu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Careson hyejooNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- 8vital SignsDocument15 pages8vital SignsVaniegrace Angel BalagonNo ratings yet
- DR Manual 2022Document17 pagesDR Manual 2022Vaniegrace Angel BalagonNo ratings yet
- Ethical Decision Making.1Document2 pagesEthical Decision Making.1Vaniegrace Angel BalagonNo ratings yet
- ANNOTATIONDocument2 pagesANNOTATIONVaniegrace Angel BalagonNo ratings yet
- Regular DietDocument5 pagesRegular DietVaniegrace Angel BalagonNo ratings yet
- REFLECTIONDocument2 pagesREFLECTIONVaniegrace Angel BalagonNo ratings yet
- 11medication Administration 1Document31 pages11medication Administration 1Vaniegrace Angel BalagonNo ratings yet
- Nurisng 101Document2 pagesNurisng 101Vaniegrace Angel BalagonNo ratings yet
- Competency Based TrainingDocument13 pagesCompetency Based TrainingPatrizia Isabel BlardonyNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Scheme - Cum Plan 2020 ... Naume MDocument168 pagesGrade 5 Scheme - Cum Plan 2020 ... Naume MDavid MazvidzsNo ratings yet
- Speech Outline - The Homeless in MalaysiaDocument3 pagesSpeech Outline - The Homeless in Malaysiaalisa IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Center Total Sessions Total No. of VursDocument8 pagesCenter Total Sessions Total No. of VursDDHS KANCHEEPURAMNo ratings yet
- Body Mass Index (BMI) : ObjectiveDocument13 pagesBody Mass Index (BMI) : Objectivenandan kumarNo ratings yet
- Growth 2x4 AssemblyDocument82 pagesGrowth 2x4 AssemblyrenatoNo ratings yet
- O2FLO1 Product Brochure-UpdateDocument3 pagesO2FLO1 Product Brochure-UpdateAli UnitedHospitalNo ratings yet
- Cfs Name Loma CFS Running Plan (March) CGMP / Iso (Notarization)Document3 pagesCfs Name Loma CFS Running Plan (March) CGMP / Iso (Notarization)Merry MardianaNo ratings yet
- Autohemotherapy - Treatment of SclerodermaDocument7 pagesAutohemotherapy - Treatment of SclerodermaOlivarNo ratings yet
- CYMEL NF2000A ResinDocument12 pagesCYMEL NF2000A ResinMohammed Tanjil Morshed remonNo ratings yet
- Encapsulado de Proioticos Con AlginatoDocument19 pagesEncapsulado de Proioticos Con AlginatoMoises Mancilla MejiaNo ratings yet
- Module 15 - Histology Lecture - LMSDocument15 pagesModule 15 - Histology Lecture - LMSJeridith M BaccayNo ratings yet
- Art03 PDFDocument13 pagesArt03 PDFMauricio Alfredo Mardones SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lembar Kerja/ Rencana Pengadaan Obat Apotek Wellhealth Farma Jalan Sultan Agung No 18BDocument3 pagesLembar Kerja/ Rencana Pengadaan Obat Apotek Wellhealth Farma Jalan Sultan Agung No 18BPSPA UB Angkatan 8No ratings yet
- Use of Soft Drinks and Its Effects Among High School Students of KottayamDocument6 pagesUse of Soft Drinks and Its Effects Among High School Students of Kottayamchinju shajanNo ratings yet
- A Case of Myocardial Bridging: Marco Guglielmo, MD, Feacvi, FSCCTDocument23 pagesA Case of Myocardial Bridging: Marco Guglielmo, MD, Feacvi, FSCCTRaul CincaNo ratings yet
- Final Written RevalidaDocument7 pagesFinal Written RevalidaRowena Lalongisip De LeonNo ratings yet
- En COVID 19 Laboratory Diagnosis 3Document3 pagesEn COVID 19 Laboratory Diagnosis 3Israa KashabaNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Test BankDocument21 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Test BankAdekunle Ologun100% (1)
- MSDS CallingtongDocument8 pagesMSDS CallingtongM Fajri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Item:: E L E EDocument7 pagesItem:: E L E Eshahbaz HazardousNo ratings yet
- Injury PreventionDocument16 pagesInjury PreventionSim BuenNo ratings yet
- Infections in Ear Are Very Common in Children. Children Are More Prone To Ear InfectionsDocument4 pagesInfections in Ear Are Very Common in Children. Children Are More Prone To Ear InfectionsbehrangNo ratings yet
- Social Contexts and Socioemotional Development: © 2008 Mcgraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights ReservedDocument44 pagesSocial Contexts and Socioemotional Development: © 2008 Mcgraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights ReservedafiqahNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - (Template) Understanding The Black Death Student MaterialsDocument4 pagesKami Export - (Template) Understanding The Black Death Student Materialscookniya1No ratings yet
- P Anisidine 99 5GDocument10 pagesP Anisidine 99 5GShazia BibiNo ratings yet