Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5 - Chemicals For Consumers (Worksheet 04)
Uploaded by
Darren TaiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5 - Chemicals For Consumers (Worksheet 04)
Uploaded by
Darren TaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Student Name: Tai Zi Jun Student Number: 18078 Class: S2HE
Topic: SPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5: Chemicals for Consumers (Worksheet 04)
Date: 24-9-2022
SPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5: Chemicals for Consumers (Worksheet 04)
Uses of Food Additives
1. Food preservatives have been used since ancient times. Ancient civilisation used salt to
preserve meat and fish, herbs and spices to improve the flavour of food.
2. Food additives are chemicals that are added to food in small quantities for specific purposes
such as:
a. Making food last longer by preventing the growth of microorganisms;
b. Making food last longer by preventing the oxidation of fats and oils by oxygen in air
(rancidity);
c. Making food taste or smell better;
d. Improving the texture of food and to prevent food from becoming liquid;
e. Restoring the colour of food destroyed during food processing, and
f. Adding colouring to food so as to make the food look fresher, more interesting or
more appetising.
3. Drying fruits and meat is one of the oldest methods of food preservation. It is effective
because water is necessary for the growth of microorganisms.
4. Salt and sugar can also be used for food preservation because the dissolved salt and sugar
will cause water to flow by osmosis from the microorganisms to its surroundings.
The dehydration process stops the growth of microorganisms.
5. There are six types of food additives:
a. Preservatives
b. Antioxidants
c. Flavourings
d. Stabilisers
e. Thickeners
f. Dyes
6. Preservatives are chemicals that are added to food to retard or to prevent the growth of
microorganisms such as bacteria, mould or fungus so that the food can be stored for a
longer period.
7. In ancient times, food additives from natural sources such as salt, sugar and vinegar were
used to preserve food and to make the food taste better.
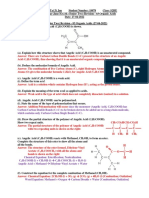
8. Types of preservatives and their uses:
Preservatives Molecular Formula Uses and Functions
To preserve meat, sausage, cheese and dried fish.
Sodium Nitrite NaNO2 To prevent food poisoning in canned foods.
Sodium Nitrate NaNO3 To maintain the natural colour of meat and to
make them look fresh.
Benzoic Acid C6H5COOH To preserve sauces (oyster, tomato or chilli),
Sodium Benzoate C6H5COONa fruit juice, jam and margarine.
Used as bleaches and antioxidants to prevent
Sulphur Dioxide SO2 browning in fruit juices.
Sodium Sulfite Na2SO3 Maintain the colour and freshness of vegetables.
To prevent the growth of microorganisms.
9. Antioxidants are chemicals that are added to food to prevent the oxidation of fats and oils
by oxygen in the air.
a. Food containing fats or oils are oxidised and become rancid when exposed to air.
This makes the food unfit for consumption. The rancid products are volatile organic
compounds with foul odours (for example, butanoic acid, C3H7COOH).
10. Ascorbic acid, citric acid and sodium citrate are examples of antioxidants.
Student Name: Tai Zi Jun Student Number: 18078 Class: S2HE
Topic: SPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5: Chemicals for Consumers (Worksheet 04)
Date: 24-9-2022
11. There are two types of flavouring agents: artificial flavours and flavour enhancers. They
are added to food to make them taste better.
a. Flavour enhancers have little or no taste of their own.
i. They are chemicals that are added to food to bring out the flavours or to
enhance the tastes of food. An example of a flavour enhancer is monosodium
glutamate (MSG).
b. Artificial flavours include sweeteners and other flavours such as peppermint or
vanilla.
i. Aspartame and saccharin are examples of artificial sweeteners.
ii. However, the use of saccharin is banned in many countries because it is a
suspected carcinogen.
iii. Many esters have fruity odours and tastes and are used as artificial flavours.
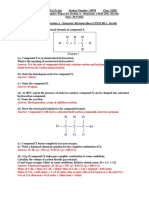
Ester Benzyl Ethanoate Octyl Ethanoate Ethyl Butanoate
Flavour Strawberry Orange Pineapple
12. Stabilisers and thickening agents improve the texture and the blending of food.
a. Stabilisers are chemicals that are used to enable oil and water in the food to mix
together properly in order to form an emulsion.
i. Examples of stabilisers are gelatin, acacia gum, lecithin and pectin.
b. Stabilisers are added to improve the texture of food.
i. For example, stabilisers are added to ice cream and peanut butter to keep
them smooth and creamy.
c. Thickening agents are chemicals that are added to food to thicken the liquid and to
prevent the food from liquefying.
i. Thickening agents (also called thickeners) absorb water and thicken the
liquid in food to produce a jelly-like structure.
ii. Most thickening agents are natural carbohydrates.
Gelatin and pectin are added to help jams and jellies set.
13. Dyes (colouring agents) are chemicals that are added to food to give them colour so as to
improve their appearance.
14. The food industry uses synthetic food colours to:
a. Restore the colour of food lost during food processing;
b. Enhance natural colours, so as to increase the attractiveness of food;
c. Give colour to food that do not have colour.
15. Some dyes are natural plant pigments while others are synthetically prepared.
16. The synthetic colours used in food are azo and triphenyl compounds.
a. Both these compounds are organic compounds.
17. Azo compounds are organic compounds containing the diazo group, –N=N–, and are
usually yellow, red, brown or black in colour. Triphenyl compounds are organic compounds
containing three phenyl groups, –C6H5, and are usually green, blue or purple in colour.
You might also like
- Food Preservatives Class 12th ProjectDocument14 pagesFood Preservatives Class 12th ProjectAnil87% (62)
- Botulinum Toxin Injection GuidDocument207 pagesBotulinum Toxin Injection Guidtextremist90% (10)
- Food AdditivesDocument15 pagesFood AdditivesrameshbptlNo ratings yet
- UFC-85 Plants For Urea Fertilizer Projects: Recommended DosageDocument8 pagesUFC-85 Plants For Urea Fertilizer Projects: Recommended Dosagevaratharajan g rNo ratings yet
- Alcolor DampeningDocument30 pagesAlcolor DampeningSaranovicu Krsto100% (3)
- Food Additives Folio ChemistryDocument8 pagesFood Additives Folio ChemistryFareez Aiman IlyasNo ratings yet
- Food AdditivesDocument10 pagesFood AdditivesMuhammad IlmanuddinNo ratings yet
- Food Additives and Its ClassificationDocument10 pagesFood Additives and Its ClassificationBaishaliNo ratings yet
- TLE FoodProcessing8 Q2M3Weeks4 5 OKDocument11 pagesTLE FoodProcessing8 Q2M3Weeks4 5 OKAmelita Benignos Osorio100% (1)
- HE6 Module - Food Additives and PreservativesDocument11 pagesHE6 Module - Food Additives and PreservativesJandrick MalapoteNo ratings yet
- Uses of Food Preservatives and Artificial Sweetening AgentsDocument11 pagesUses of Food Preservatives and Artificial Sweetening AgentsjacobandreialfantaNo ratings yet
- 07042020180851food AdditivesDocument79 pages07042020180851food Additivesdesamek647No ratings yet
- 2 Grade 9 - STE - Consumer Chemistry - Q2 - Wk1 - GLAKDocument20 pages2 Grade 9 - STE - Consumer Chemistry - Q2 - Wk1 - GLAKHela WilsonNo ratings yet
- Food Industry - 0Document8 pagesFood Industry - 0Saad and ObaidNo ratings yet
- Correction SeminarDocument4 pagesCorrection SeminarQüàñtîùm Stâmîñà Jr.No ratings yet
- 2 - Marks Unit - 1: List Out The Class - 1 and Class - 2 PreservativesDocument23 pages2 - Marks Unit - 1: List Out The Class - 1 and Class - 2 PreservativesDharmendraNo ratings yet
- Food AdditivesDocument78 pagesFood AdditivesNaveenNo ratings yet
- Food AdditivesDocument58 pagesFood AdditivesJithin JasinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food AdditivesDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Food AdditivesDavid UribeNo ratings yet
- Pickling Vinegar Salting Sweets Sulfur Dioxide Wines: Food AdditivesDocument4 pagesPickling Vinegar Salting Sweets Sulfur Dioxide Wines: Food AdditivesManjunatha HRNo ratings yet
- 2 Grade 9 - STE - Consumer Chemistry - Q2 - Wk2 - GLAKDocument16 pages2 Grade 9 - STE - Consumer Chemistry - Q2 - Wk2 - GLAKHela WilsonNo ratings yet
- Curing Meat the Right WayDocument39 pagesCuring Meat the Right Wayivy bontrostroNo ratings yet
- TLE QUARTER 3 Food Processing (Salting - Curing Mixtures and Solutions)Document9 pagesTLE QUARTER 3 Food Processing (Salting - Curing Mixtures and Solutions)Lovely Adellia Ventura JacildoneNo ratings yet
- Food AdditivesDocument2 pagesFood AdditivesNaomi OlympioNo ratings yet
- Ingles para Trabajos EscritosDocument4 pagesIngles para Trabajos EscritosCerda TurmequeNo ratings yet
- Food AdditiveDocument6 pagesFood AdditiveGaetano MinardiNo ratings yet
- Food Additives JffftftydydfdtrufyruytrrDocument7 pagesFood Additives JffftftydydfdtrufyruytrrGolmolNo ratings yet
- Non-Bulk Ingredients GuideDocument20 pagesNon-Bulk Ingredients GuideRoma Diane AvigueteroNo ratings yet
- AdditivesDocument2 pagesAdditivesElliot BorekNo ratings yet
- Food AdditivesDocument21 pagesFood AdditivesHarish Srinivasan100% (1)
- Learning Module: Surigao State College of TechnologyDocument5 pagesLearning Module: Surigao State College of TechnologyRegine YuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in The Dining RoomDocument11 pagesChemistry in The Dining RoomEllah Marie P. LimpangogNo ratings yet
- Oê Oê Oê Oê Oê Oê Oê OêDocument5 pagesOê Oê Oê Oê Oê Oê Oê OêzulhaizadNo ratings yet
- q2 l3 Food PreservativesDocument70 pagesq2 l3 Food PreservativesDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- food preserveDocument21 pagesfood preserveriza loveresNo ratings yet
- Food Preservatives and AdditivesDocument52 pagesFood Preservatives and AdditivesSean Gabriel LacambraNo ratings yet
- Academic Reading and Writing-10.10Document34 pagesAcademic Reading and Writing-10.10Logeswaran TangavelloNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document6 pagesGroup 1Print HubNo ratings yet
- Food AdditiveDocument55 pagesFood AdditiveYit Juan100% (1)
- ERT 426 Food Engineering Semester 1 Academic Session 2017/18Document32 pagesERT 426 Food Engineering Semester 1 Academic Session 2017/18nas radziNo ratings yet
- MF203 Fhs LNT 007Document30 pagesMF203 Fhs LNT 007PikuNo ratings yet
- sec-b food additives and adulterants and xenobioticsDocument29 pagessec-b food additives and adulterants and xenobioticssuman palNo ratings yet
- Zat AditifDocument17 pagesZat Aditifpuspita8967628No ratings yet
- Food Preservatives TestingDocument4 pagesFood Preservatives TestingJuliannie LinggayoNo ratings yet
- Con. Chem 9 QiiDocument13 pagesCon. Chem 9 QiiFrancheska de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Food AdditivesDocument2 pagesModule 3 Food AdditivesATHIRA MNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project 2019-2020Document18 pagesChemistry Project 2019-2020amirtha varshiniNo ratings yet
- Chemicals in Food: Additives, Colors, Sweeteners and PreservativesDocument18 pagesChemicals in Food: Additives, Colors, Sweeteners and Preservativesamirtha varshiniNo ratings yet
- Food Additives Guide: Preservatives, Flavourings, Colours and MoreDocument91 pagesFood Additives Guide: Preservatives, Flavourings, Colours and MoreshishirchemNo ratings yet
- Food AdditivesDocument20 pagesFood AdditivesGisela Olga KurniawanNo ratings yet
- RangkumanDocument14 pagesRangkumanfabianibrahimovic08No ratings yet
- Preservation by Food AdditivesDocument23 pagesPreservation by Food Additivesnoman_sheeraz7455No ratings yet
- Food Additives: Types, Uses and EffectsDocument91 pagesFood Additives: Types, Uses and EffectsWidia AprilianiNo ratings yet
- PreservativeDocument40 pagesPreservativeKrishnan vijayNo ratings yet
- Food Additives 1Document17 pagesFood Additives 1Ade Rizki AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Food PreservativeDocument2 pagesFood PreservativeNaharia RangirisNo ratings yet
- Aditivos Alimentarios PDFDocument38 pagesAditivos Alimentarios PDFANTHONY FARID CABEZAS GUEVARANo ratings yet
- Learning Module: Surigao State College of TechnologyDocument4 pagesLearning Module: Surigao State College of TechnologyAntonette DacuyaNo ratings yet
- AdditivesDocument12 pagesAdditivesFatima ZafarNo ratings yet
- PreservativesDocument10 pagesPreservativesAtanacia IlaganNo ratings yet
- Food Additives To SendDocument4 pagesFood Additives To SendElishah Ben AvrahamNo ratings yet
- 2022 May-June IGCSE (Senior Two) Revision - 02 Ammonia and Nitrates (25-04-2022)Document1 page2022 May-June IGCSE (Senior Two) Revision - 02 Ammonia and Nitrates (25-04-2022)Darren TaiNo ratings yet
- 2022 May-June IGCSE (Senior Two) Revision - 01 Alkenes (23-04-2022)Document1 page2022 May-June IGCSE (Senior Two) Revision - 01 Alkenes (23-04-2022)Darren TaiNo ratings yet
- 2022 May-June IGCSE (Senior Two) Revision - 03 Organic Acids (27-04-2022)Document1 page2022 May-June IGCSE (Senior Two) Revision - 03 Organic Acids (27-04-2022)Darren TaiNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry (Paper 02 - Section A - Structure) Revision Sheet (CPSM 2011 - Set 04)Document2 pagesSPM Chemistry (Paper 02 - Section A - Structure) Revision Sheet (CPSM 2011 - Set 04)Darren TaiNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5 - Chemicals For Consumers (Worksheet 01)Document1 pageSPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5 - Chemicals For Consumers (Worksheet 01)Darren TaiNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Revision Sheet on Calcium Phosphate, Fuel Cells and Organic CompoundsDocument3 pagesSPM Chemistry Revision Sheet on Calcium Phosphate, Fuel Cells and Organic CompoundsDarren TaiNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5 - Chemicals For Consumers (Worksheet 02)Document1 pageSPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5 - Chemicals For Consumers (Worksheet 02)Darren TaiNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5 - Chemicals For Consumers (Worksheet 03)Document2 pagesSPM Chemistry (Form 5) - Chapter 5 - Chemicals For Consumers (Worksheet 03)Darren TaiNo ratings yet
- Shete 2015Document10 pagesShete 2015riko setiawanNo ratings yet
- GK Technique (WWW - Admissionwar)Document41 pagesGK Technique (WWW - Admissionwar)Sahabur Rahman ShaonNo ratings yet
- Philippine Environmental Laws OverviewDocument34 pagesPhilippine Environmental Laws OverviewRadie ArnaldoNo ratings yet
- Hospira VincristineDocument9 pagesHospira VincristineIvenks EeNo ratings yet
- PerstorpDocument8 pagesPerstorpSundarNo ratings yet
- Mageba Bridge Bearings and Seismic Isolators - Inspection MaintenanceDocument32 pagesMageba Bridge Bearings and Seismic Isolators - Inspection MaintenanceJose Maria0% (1)
- Promag 10L1F PDFDocument36 pagesPromag 10L1F PDFAnonymous NR3qZ30No ratings yet
- Note - Attempt All The Following Questions. All Questions Carry Equal MarksDocument2 pagesNote - Attempt All The Following Questions. All Questions Carry Equal MarksMuhammadTanzeeLUsmanNo ratings yet
- SUINCO - Extramould Product SheetDocument1 pageSUINCO - Extramould Product SheetamunibfNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machines and HYdraulic MachinesDocument106 pagesFluid Machines and HYdraulic Machinesvamsi krishnaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Education Program: Department of Workforce ServicesDocument7 pagesNutrition Education Program: Department of Workforce ServicesRobert HartNo ratings yet
- Steel: Statistical Analysis of Steel FormabilityDocument12 pagesSteel: Statistical Analysis of Steel FormabilitynadhabindhuNo ratings yet
- Gardening) Growing Vegetables in Home GardensDocument24 pagesGardening) Growing Vegetables in Home GardenspiscarovNo ratings yet
- Appendix E PDFDocument9 pagesAppendix E PDFRammiris ManNo ratings yet
- PMMADocument7 pagesPMMAcuongtran_siegenNo ratings yet
- Direct Esterification of Olive Pomace Oil Using Mesopo - 2017 - Arabian JournalDocument6 pagesDirect Esterification of Olive Pomace Oil Using Mesopo - 2017 - Arabian Journallucian_lovNo ratings yet
- 24 Abad Thermo Praga-Abril-2015-Esteban AbadDocument35 pages24 Abad Thermo Praga-Abril-2015-Esteban AbadVulpoiulxNo ratings yet
- Explaining Product Data Sheet InformationDocument0 pagesExplaining Product Data Sheet InformationeraswastaNo ratings yet
- 3 Solution ConcentrationsDocument30 pages3 Solution ConcentrationsB R YNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Sunlight LiquidDocument2 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Sunlight Liquidgilang gilongNo ratings yet
- Manual Del GVMapper v3 3 PDFDocument102 pagesManual Del GVMapper v3 3 PDFguanatosNo ratings yet
- Guide No01 GRLs7th Issue Oct21Document13 pagesGuide No01 GRLs7th Issue Oct21hüseyinNo ratings yet
- AutoclaveDocument20 pagesAutoclaveNita Agarwal100% (1)
- Concrete NotesDocument4 pagesConcrete NotesdaleemaNo ratings yet
- Design Aeration XilenDocument180 pagesDesign Aeration XilenAlvaro HueteNo ratings yet
- Masti Oksidacija Lipidi Oksidacija Inicijacija Propagacija) TerminaijaDocument60 pagesMasti Oksidacija Lipidi Oksidacija Inicijacija Propagacija) TerminaijaAleksandar TeodovskiNo ratings yet