Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Energy and ATP
Uploaded by
Motie Kassab0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageChemical Energy and ATP
Uploaded by
Motie KassabCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Chemical Energy and ATP
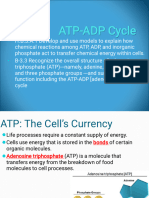
The chemical energy used for most cell processes is carried by ATP
ATP is a molecule that transfers energy from the breakdown of food molecules to
cell processes. Cells use ATP for functions such as building molecules and moving
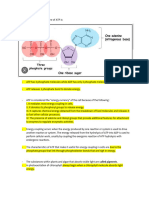
materials by active transport. The energy carried by ATP is released when a
phosphate group is removed from the molecule. ATP has three phosphate groups,
but the bond holding the third phosphate group is unstable and is very easily
broken. When the phosphate is removed, energy is released and ATP becomes
ADP. ADP is a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP by the
addition of a phosphate group.
Organisms break down carbon-based molecules to produce ATP
ATP molecules that are made from the breakdown of food is related to the
number of calories in food. The number of ATP molecules produced depends on
the type of molecule that is broken down-carbohydrate, lipid, or protein.
The breakdown of the simple sugar glucose yields about 36 molecules of ATP.
Lipids store most energy. Triglyceride can be broken down to make about 146
molecules of ATP.
A few types of organisms do not need sunlight and photosynthesis as
a source of energy.
Chemosynthesis is a process by which some organisms use chemical energy to
make energy-storing carbon-based molecules. These organisms still need ATP for
energy. Chemosynthesis organisms make their own food, but the raw materials
differ.
You might also like
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- ATP PPTDocument13 pagesATP PPTMA. HAZEL TEOLOGONo ratings yet
- ATP ADP SlidesDocument14 pagesATP ADP SlidesNorsaifah AbduljalalNo ratings yet
- ATP-ADP Cycle PowerpointDocument18 pagesATP-ADP Cycle PowerpointJohn Iderf LagardeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energy and ATPDocument7 pagesChemical Energy and ATPDaisy100% (1)
- Atp: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: - Aditya Sunil Nair - Class XI D - Roll No: 22Document10 pagesAtp: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: - Aditya Sunil Nair - Class XI D - Roll No: 22Aditya Sunil NairNo ratings yet
- ATP and Its Role in Living OrganismsDocument2 pagesATP and Its Role in Living OrganismsHayze Jones50% (2)
- AtpDocument10 pagesAtpSheba HernandezNo ratings yet
- ATP: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: ATP Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesATP: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: ATP Structure and FunctionCielo PepitoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Cycles - FermentationDocument13 pagesGen Bio Cycles - Fermentationyxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Karl Lohmann (1929) Discovered ATP in Muscle Cells. Fritz Lipmann and Herman Kalckar (1941) Were The First To Recognize The Role of ATP in Energy MetabolismDocument12 pagesKarl Lohmann (1929) Discovered ATP in Muscle Cells. Fritz Lipmann and Herman Kalckar (1941) Were The First To Recognize The Role of ATP in Energy Metabolismمحمد جانNo ratings yet
- ATP ADP CycleDocument14 pagesATP ADP CycleLalchan MiahNo ratings yet
- Atp EssayDocument3 pagesAtp EssayValeria PunzoNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument29 pagesCellular RespirationMaxxdlc 16No ratings yet
- ATP ProductionDocument2 pagesATP Productionpeach treeNo ratings yet
- Role of ATPDocument2 pagesRole of ATPWilliamNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformation - Atp-Adp CycleDocument33 pagesEnergy Transformation - Atp-Adp CyclePrincess EscandalloNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformation (N)Document56 pagesEnergy Transformation (N)Princess Lorreine GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Mitochondria ATPDocument5 pagesAerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Mitochondria ATPjatsugbNo ratings yet
- Coupled Reactions and Importance of Chloropyll and Other PigmentsDocument8 pagesCoupled Reactions and Importance of Chloropyll and Other PigmentsPerlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Q2Week-1 ATP ADP-CouplingDocument13 pagesQ2Week-1 ATP ADP-Couplingjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument12 pagesCellular RespirationJB - 10SS 731765 Harold M Brathwaite SSNo ratings yet
- lesson-4-Role-of-ATP-in-Energy-Coupling-and-Transfer (1) EnergyDocument10 pageslesson-4-Role-of-ATP-in-Energy-Coupling-and-Transfer (1) EnergyKivo ZoshikoroNo ratings yet
- Atp Group 5Document28 pagesAtp Group 5Dbez JonniNo ratings yet
- Questions: Notes:: 6CO + 6H O + Light Energy C H O + 6ODocument2 pagesQuestions: Notes:: 6CO + 6H O + Light Energy C H O + 6Oapi-300158846No ratings yet
- Energy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyDocument10 pagesEnergy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyManoj PantaNo ratings yet
- Energy Is A Way of Life ArticleDocument2 pagesEnergy Is A Way of Life Articleapi-262368188No ratings yet
- Atp Adp CycleDocument18 pagesAtp Adp CycleLyn Dela Cruz Fontila100% (1)
- MYP Cell Respiration PDFDocument23 pagesMYP Cell Respiration PDFRishar bokNo ratings yet
- Atp STR FinDocument16 pagesAtp STR FinNimsha KamalaNo ratings yet
- B 10 VRV 3081Document16 pagesB 10 VRV 3081api-283593849No ratings yet
- Energy and Life: 8.1 NotesDocument11 pagesEnergy and Life: 8.1 NotesLovely GreenNo ratings yet
- Metabolism:: Atp: ATP Is Produced by Almost All Living Things in Their Cell's OrganellesDocument3 pagesMetabolism:: Atp: ATP Is Produced by Almost All Living Things in Their Cell's OrganellesAngelo DecenaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 ATP and EnergyDocument10 pages4.2 ATP and EnergyShehbaaz SinghNo ratings yet
- Atp-Adp Cycle: Presentation By: Miranda, Morales, Morando, NietesDocument7 pagesAtp-Adp Cycle: Presentation By: Miranda, Morales, Morando, NietesYOSEF AZRIEL CONCEPCION MORALESNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationDocument20 pagesA2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationArnel100% (1)
- ATP - ADP CycleDocument13 pagesATP - ADP CycleDanessa Mina BalboaNo ratings yet
- Reactions That Produce and Consume ATPDocument7 pagesReactions That Produce and Consume ATPsittinginthecorner1No ratings yet
- Reviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2Document5 pagesReviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2alamagelyzaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisJoshua MeraNo ratings yet
- 9.1. Energy and LifeDocument19 pages9.1. Energy and Lifehanatabbal19No ratings yet
- 19 AtpDocument34 pages19 AtpSheena BautistaNo ratings yet
- Unit Five Last One Grade 11 Biology Energy TransformationDocument55 pagesUnit Five Last One Grade 11 Biology Energy TransformationaxumfunNo ratings yet
- All Cells Need Chemical Energy.: Key ConceptDocument15 pagesAll Cells Need Chemical Energy.: Key ConceptPrasanna Naresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Course Notes PDFDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course Notes PDFPRAJINIKUMARNo ratings yet
- GenbioDocument5 pagesGenbioYkhay ElfanteNo ratings yet
- Structure of An ATP Molecule: Atp + H O Adp + PiDocument3 pagesStructure of An ATP Molecule: Atp + H O Adp + PiIshaniNo ratings yet
- Adenosine TriphosphateDocument4 pagesAdenosine TriphosphateFizzah AshfaqNo ratings yet
- 2-Energy and RespirationDocument34 pages2-Energy and RespirationLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- Lee, Thonylet E. Mabinta, Dianne Melad, Maria FeDocument25 pagesLee, Thonylet E. Mabinta, Dianne Melad, Maria FeShivaveerakumar S. Chandrikimath100% (1)
- Atp CycleDocument4 pagesAtp CycleVignesh100% (1)
- Adenosine TriphosphateDocument1 pageAdenosine TriphosphateClement CharlesNo ratings yet
- PE Report - Output - Villanueva 1Document3 pagesPE Report - Output - Villanueva 1Rico Yan CanoNo ratings yet
- CHBH13 - Laboratory Manual 6Document17 pagesCHBH13 - Laboratory Manual 6Ysa DienteNo ratings yet
- Viernes BIOENERGETICS WorksheetDocument18 pagesViernes BIOENERGETICS WorksheetBelinda ViernesNo ratings yet
- Energy Systems PowerpointDocument27 pagesEnergy Systems PowerpointKellie Guest100% (1)
- Samantha Sealy 10/3/15 5 PeriodDocument2 pagesSamantha Sealy 10/3/15 5 PeriodsamanthasameNo ratings yet
- The ATP CycleDocument10 pagesThe ATP CyclePia FerrarisNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic Respiration MitochondriaDocument3 pagesGlycolysis Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic Respiration MitochondriaSofia Diane AbrahanNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 Energy and RespirationDocument34 pagesChap 12 Energy and RespirationGeorge ApidiNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes and MeiosisDocument2 pagesChromosomes and MeiosisMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- Cellualr Respiration in DetailDocument3 pagesCellualr Respiration in DetailMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesCell OrganellesMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane L3 CH3Document2 pagesCell Membrane L3 CH3Motie KassabNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathFrom EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)