Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochem Quiz
Uploaded by
Nicole Malinao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the six main classifications of enzymes and provides examples of enzymes that fall within each classification. It also discusses the importance of enzymes in biological processes and classifies some key digestive enzymes. Specifically, it describes the six enzyme classifications as oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. It then explains the crucial role enzymes play in accelerating reactions necessary for functions like breathing, digestion, and muscle and nerve health. Finally, it lists and classifies several important digestive enzymes according to where they act in the digestive system.
Original Description:
dont give up
Original Title
biochem quiz
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the six main classifications of enzymes and provides examples of enzymes that fall within each classification. It also discusses the importance of enzymes in biological processes and classifies some key digestive enzymes. Specifically, it describes the six enzyme classifications as oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. It then explains the crucial role enzymes play in accelerating reactions necessary for functions like breathing, digestion, and muscle and nerve health. Finally, it lists and classifies several important digestive enzymes according to where they act in the digestive system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesBiochem Quiz
Uploaded by
Nicole MalinaoThe document summarizes the six main classifications of enzymes and provides examples of enzymes that fall within each classification. It also discusses the importance of enzymes in biological processes and classifies some key digestive enzymes. Specifically, it describes the six enzyme classifications as oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. It then explains the crucial role enzymes play in accelerating reactions necessary for functions like breathing, digestion, and muscle and nerve health. Finally, it lists and classifies several important digestive enzymes according to where they act in the digestive system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
RIA JOY M.
BASTISTIANA
BSN-1B
BIOCHEMISTRY
ACTIVITY/QUIZ (SEPT. 29, 2022)
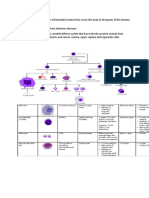
1. DESCRIBE THE 6 CLASSIFICATIONS OF ENZYMES. GIVE TWO EXAMPLES FOR EACH AND DISCUSS
THEIR FUNCTIONS RESPECTIVELY.
OXIDOREDUCTASES- catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions.
Ex. An alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation reaction of ethanol to form an
eldehyde.
Glucose oxidase known as notatin. Produced by certain species of fungi and insects and
displays antibacterial activity when oxygen and glucose are present
TRANSFERASES- catalyze transfer of functional group.
Ex. Acyl transferases that catalyze he transfer of acyl groups.
Riboflavin synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the final reaction of riboflavin
biosynthesis.
HYDROLASES- catalyze hydrolysis reactions
Ex. Phosphatases is an enzyme that removes a phosphate group from protein.
Glycosidases catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in complex sugars.
LYASES- catalyze addition or removal of functional group to form a double bond.
Ex. Citrate lyase- key enzyme of de novo fatty acid
Pectate lyase an enzyme involved in the maceration and soft rotting of plant tissue.
ISOMERASES- catalyze isomerization reactions
Ex. Triose phosphate isomerase involved in a critical energy-producing process known as
glycolysis.
Bisphosphoglycerate was primarily exists as a metabolic intermediate in both glycolysis
during respiration and the calvin cycle during photosynthesis.
LIGASES- Catalyze ligation reactions
Ex. Ubiquitin ligases-assist or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to
the protein substrate.
Pyruvate carboxylase catalyzes the physiologically irreversible carboxylation of pyruvate
to form oxaloacetate.
TRANSLOCASES- a protein that assists in moving another molecule, usually across a cell
membrane.
Ex. Ornithine translocase associated with ornithine translocase defiency.
Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase associated with carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase
deficiency.
2. DISCUSS BRIEFLY THE IMPORTANCE OF ENZYMES IN BIOLOGICAL EXISTENCE
In the human body, enzymes aid in accelerating chemical reactions. Among countless
other functions, they are crucial for breathing, food digestion, and the health of the
muscles and nerves. Numerous enzymes can be found inside each cell of the human
body. Each cell’s use of enzymes aids in facilitating chemical reactions.
3. IN A MORE SPECIFIC ROLE, CLASSIFY THE ENZYMES IN THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
SALIVARY AMYLASE (MOUTH) – breaks down starch into maltose.
PEPSIN (STOMACH) – breaks down proteins into dipeptides
AMYLASE (PANCREAS)- breaks down starch
TRYPSIN (PANCREAS)- breaks down proteins into dipeptides.
LIPASE (PANCREAS)- breaks down lipids.
MALTOSE (SMALL INTESTINE)- breaks maltose into glucose.
SUCRASE (SMALL INTESTINE)- breaks sucrose glucose.
LACTASE (SMALL INTESTINE)- breaks lactose into glucose
You might also like
- Module 6 in BiochemistryDocument19 pagesModule 6 in BiochemistryjeromeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1. Carbohydrates and Related CompoundsDocument8 pagesExperiment 1. Carbohydrates and Related CompoundsRalph Galano100% (4)
- NSTP2 Activity 3 COMMUNITY IMMERSIONDocument3 pagesNSTP2 Activity 3 COMMUNITY IMMERSIONNicole Malinao100% (2)
- Chapter 3 EnzymesDocument22 pagesChapter 3 EnzymesRam Charan100% (1)
- Biotransformation and Excretion of DrugDocument63 pagesBiotransformation and Excretion of DrugIzzuddin AhmadNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To EnzymesDocument25 pages1-Introduction To EnzymesMarwa Mohamed AminNo ratings yet
- Contoh Perhitungan DDD Excell - IRNADocument8 pagesContoh Perhitungan DDD Excell - IRNAMaya DamanikNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis RevisedDocument60 pagesNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Revisedemanuel coatesNo ratings yet
- Enzim&Protein RevDocument52 pagesEnzim&Protein Revkamilah rafaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry2 Past PaperDocument36 pagesBiochemistry2 Past PaperShamoon HaroonNo ratings yet
- Aoc 2 - BiocatalysisDocument22 pagesAoc 2 - BiocatalysisUsha gowdaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Learning AssessmentDocument9 pagesUnit 3 Learning AssessmentJay Lure Gomez BaguioNo ratings yet
- Classification of EnzymesDocument3 pagesClassification of EnzymesJett Matthew AquinoNo ratings yet
- HW5 EnzymesDocument4 pagesHW5 EnzymesLyleNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Catalytic ActionDocument13 pagesEnzymes: Catalytic ActionTemesgen MuletaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument28 pagesEnzymesGautamiNo ratings yet
- EmzymologyDocument17 pagesEmzymologySandeep AdapalaNo ratings yet
- Bio Essay 1Document1 pageBio Essay 1michellebest365No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMnotes 2Document3 pagesBIOCHEMnotes 2katNo ratings yet
- Copy of Copy of EnjymeDocument9 pagesCopy of Copy of Enjymeapi-327778003No ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument6 pagesBiological MoleculessanaullahNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - Notes For UPSC ExamDocument2 pagesEnzymes - Notes For UPSC ExamAltamashNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-xi-botany-RESPIRATION IN PLANTS-8Document7 pagesHsslive-xi-botany-RESPIRATION IN PLANTS-8diyakozhimalaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2NDDocument5 pagesGen Bio 2NDZyren Joy SamillanoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 WorksheetDocument10 pagesUNIT 5 WorksheetlorNo ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument16 pagesBiochem ReviewerHennessy PerezNo ratings yet
- TextDocument2 pagesTexthqpbh2zn79No ratings yet
- Las 3 ProteinsDocument2 pagesLas 3 ProteinsAntonio CharismaNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Bio f5Document8 pagesChapter5 Bio f5JiayingNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer (1) - CompressedDocument61 pagesBiology Reviewer (1) - CompressedkevinNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology: Digestion and AbsorptionDocument9 pagesA Level Biology: Digestion and AbsorptionSaeed AbdulhadiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry NCMA113 Midterm Notes PDocument3 pagesBiochemistry NCMA113 Midterm Notes PVaishnavi LoganathanNo ratings yet
- HW5 EnzymesDocument2 pagesHW5 EnzymesFATIMA AIRA LEGASPINo ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiochem ReviewerJOCY MARIE C. BOLONo ratings yet
- ENZYMES (Autosaved)Document12 pagesENZYMES (Autosaved)zaynab.z.sidNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument18 pagesEnzymesDRMEHUL DAVE100% (1)
- EnzymeDocument34 pagesEnzymeDanica SantosNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Mechanism of Enzyme ActionDocument6 pagesEnzymes Mechanism of Enzyme Actionkl42c4300No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Metabolism and EnzymesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Metabolism and Enzymes绿谷出久No ratings yet
- Unit 3 EnzymesDocument18 pagesUnit 3 Enzymeskamsjain6802No ratings yet
- Ncert Biology Chapter I4Document13 pagesNcert Biology Chapter I4sai arunNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document8 pagesTask 1maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledSyafrianda PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes (As Biology)Document42 pagesEnzymes (As Biology)Muhtasim FarhanNo ratings yet
- HWEnzymesDocument1 pageHWEnzymesKylie GatmaitanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes-G5 PPT NamenDocument23 pagesEnzymes-G5 PPT NamenMindi May AguilarNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument25 pagesEnzymesmymimi100% (1)
- Lecture 12. Liver Biochemistry. Pigmentary Metabolism. JaundicesDocument43 pagesLecture 12. Liver Biochemistry. Pigmentary Metabolism. JaundicesВіталій Михайлович НечипорукNo ratings yet
- EnzymologyDocument17 pagesEnzymologyqwerty123No ratings yet
- 2 What Lipids DoDocument12 pages2 What Lipids DocarlosNo ratings yet
- Metabolism 2017Document96 pagesMetabolism 2017aimaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes IntroDocument33 pagesEnzymes IntropragyasimsNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Vitamins NotesDocument14 pagesEnzymes and Vitamins NotesRealyn ZambasNo ratings yet
- PARAS, Mark Heinrich B. - Homework 3 - Lecture Biochemistry CHEM 40 BSN 1EDocument3 pagesPARAS, Mark Heinrich B. - Homework 3 - Lecture Biochemistry CHEM 40 BSN 1EMark Heinrich B. ParasNo ratings yet
- Enzyme 1Document115 pagesEnzyme 1fikaduNo ratings yet
- MCB 201 Biosynthesis of Biomolecules - MCB - 201Document10 pagesMCB 201 Biosynthesis of Biomolecules - MCB - 201Lena HasleyNo ratings yet
- PhmarmacogDocument8 pagesPhmarmacogMichelle CasilangNo ratings yet
- Compiled MetabolismDocument155 pagesCompiled MetabolismIced WatermelonNo ratings yet
- Metabolism and Metabolic Pathways in Bioprocessing Metabolism and Metabolic Pathways in BioprocessingDocument101 pagesMetabolism and Metabolic Pathways in Bioprocessing Metabolism and Metabolic Pathways in BioprocessingAhmadin BamudNo ratings yet
- Agri-501 Biochemistry 2021-2022: Doc. Regina P. ClavelDocument36 pagesAgri-501 Biochemistry 2021-2022: Doc. Regina P. ClavelIvan Jhon AnamNo ratings yet
- Enzymes (Plants, Fungi, and Animals)Document17 pagesEnzymes (Plants, Fungi, and Animals)John Mark SanchezNo ratings yet
- 1 - Biochemistry Notes by Dr. M A Bari Siddiqui: DrmentorsDocument3 pages1 - Biochemistry Notes by Dr. M A Bari Siddiqui: DrmentorsShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Activity 7Document3 pagesActivity 7Nicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Activity Management ScienceDocument3 pagesActivity Management ScienceNicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- NSTP2 Activity 5 Community ServicesDocument2 pagesNSTP2 Activity 5 Community ServicesNicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- NSTP2 Activity 4 PDFDocument3 pagesNSTP2 Activity 4 PDFNicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Output 2 ArtDocument3 pagesOutput 2 ArtNicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Soap SculptureDocument1 pageSoap SculptureNicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Cost of Accounting (Pre-Test)Document4 pagesCost of Accounting (Pre-Test)Nicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- 017 Spiritual Gifts and MinistriesDocument21 pages017 Spiritual Gifts and MinistriesNicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- P.E AssestmentDocument7 pagesP.E AssestmentNicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Cost of Accounting (Pre-Test)Document4 pagesCost of Accounting (Pre-Test)Nicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Antihyperuricemic Activity of Ficus Carica Leave Extract in Mus MusculusDocument16 pagesAntihyperuricemic Activity of Ficus Carica Leave Extract in Mus MusculusNeni HRNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy FamsDocument24 pagesPharmacognosy FamsAbdulyNo ratings yet
- Ora Recoltării: (Babesia SPP., Ehrlichia SPP., Anaplasma SPP., Haemobartonella SPP., Hepatozoon SPP., Dirofilaria SPP.)Document2 pagesOra Recoltării: (Babesia SPP., Ehrlichia SPP., Anaplasma SPP., Haemobartonella SPP., Hepatozoon SPP., Dirofilaria SPP.)Şnep Mihai AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Light-Dependent Herbicides - An OverviewDocument12 pagesLight-Dependent Herbicides - An OverviewCatherine TangNo ratings yet
- Kategori Obat VenDocument40 pagesKategori Obat Venmulla ali qoriNo ratings yet
- Catalog+OilGas+2020 +vfinal+-+ENGDocument17 pagesCatalog+OilGas+2020 +vfinal+-+ENGLucas Matias AriasNo ratings yet
- Biochem Midterm ReviewerDocument22 pagesBiochem Midterm Reviewerrentachin18No ratings yet
- How To Approach A Case of Dyslipidemia Y2!30!31Document10 pagesHow To Approach A Case of Dyslipidemia Y2!30!31MaisaraNo ratings yet
- Makassar Januari 2023Document147 pagesMakassar Januari 2023fatmawaty rachimNo ratings yet
- Dna RnaDocument2 pagesDna RnaralphNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Modification of FatDocument21 pagesEnzymatic Modification of FatLuis BejaranoNo ratings yet
- Rda Vitamins MineralsDocument1 pageRda Vitamins Mineralszeroena10No ratings yet
- Phytochemical Analysis of WeedsDocument4 pagesPhytochemical Analysis of WeedsvishcrimeNo ratings yet
- Specimen (IAL) QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelDocument22 pagesSpecimen (IAL) QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelCheung PhilaNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids-Unit 2Document19 pagesAlkaloids-Unit 2Gayatri SisodiyaNo ratings yet
- MEDICINASDocument2 pagesMEDICINASFARMADG CATIANo ratings yet
- Nomenclature Bansal Iit Jee Organic PDFDocument24 pagesNomenclature Bansal Iit Jee Organic PDFa143deendayal0% (2)
- Kris Alfred Delarmente - q1 Module 2 Answer SheetDocument6 pagesKris Alfred Delarmente - q1 Module 2 Answer SheetElla geangaNo ratings yet
- Co and CohDocument22 pagesCo and Cohapi-289060519No ratings yet
- 5 - Biochemistry MCQs Cetric Acid CycleDocument9 pages5 - Biochemistry MCQs Cetric Acid CycleSantosh Bhandari100% (1)
- SP Prekursor BaruDocument7 pagesSP Prekursor BaruMaria Yolanda KehiNo ratings yet
- Polyester Polyols For Rigid Polyurethane FoamsDocument16 pagesPolyester Polyols For Rigid Polyurethane Foamskureshi27No ratings yet
- CI SSCK1623 Organic Chemistry For Engineering 20192020-2 PDFDocument5 pagesCI SSCK1623 Organic Chemistry For Engineering 20192020-2 PDFKavinesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Weekly Aug29Document238 pagesChemical Weekly Aug29Chaitanya AyyagariNo ratings yet
- Density Values of Several PlasticsDocument4 pagesDensity Values of Several PlasticsAbdullah Al AsikNo ratings yet
- Daftar Nama Obat SIMPUSDocument11 pagesDaftar Nama Obat SIMPUSsdk.achmad TubeNo ratings yet
- Chemproducts2003 PDFDocument1 pageChemproducts2003 PDFA MahmoodNo ratings yet