Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ULO-A
Uploaded by
Kenth VillanuenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ULO-A
Uploaded by
Kenth VillanuenaCopyright:
Available Formats
SELF CHECK:
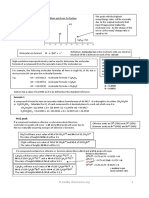
1. What are the compositions of air? 78% nitrogen, 20.95% Oxygen, 0.9% Argon
Gasses, Other gasses 0.17% and 0.03% Carbon Dioxide.
2. Differentiate climate from weather. Climate is the weather of a given place averaged
over a long period of time, whereas weather refers to short-term atmospheric
conditions.
3. What are examples of greenhouse gases? Discuss each.
Carbon Dioxide Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the primary
greenhouse gas emitted through human
activities.
Methane Its presence in the atmosphere affects
the earth's temperature and climate
system. Methane is emitted from a variety
of anthropogenic (human-influenced) and
natural sources.
Nitrous Oxide Nitrous oxide, more commonly known as
“laughing gas,” is a potent greenhouse
gas, 300 times more powerful than
carbon dioxide. Global emissions of N2O
are increasing as a result of human
activities that stimulate its production.
Chlorofluorocarbon-12 (CFC-12) CFC-12 (also known by the trade
name Freon or Freon-12) is an ozone-
depleting refrigerant and potent
greenhouse gas that was widely used in
air conditioners for automobiles and
trucks for over 30 years, up until the mid-
1990s.
LET’S ANALYZE:
1. It became trapped underground during the formation of fossil fuels and
sedimentary rocks.
2. Incomplete combustion had occurred because there was not enough oxygen.
3. Soot/particulate carbon because of the incomplete combustion occurred/not
enough oxygen present.
4. Green to red/orange because sulfur dioxide dissolves to form an acid/reference to
SO2 being a cause of acid rain.
5. Limewater goes cloudy due to the presence of carbon dioxide.
IN A NUTSHELL.
1. Transportation primarily come from burning fossil for vehicles. If your location is
just near to where you want to go, just walk. Try not to use vehicles, motorcycles
and other mode of transportation if it is just steps away from you.
2. Sulfur oxide is produced from the burning of fossil fuels (coal and oil) and the
smelting of mineral ores (aluminum, copper, zinc, lead, and iron) that contain
sulfur. It affects the respiratory system, particularly lung function, and can irritate
the eyes.
Nitrogen oxides are produced from the reaction of nitrogen and oxygen gases in
the air during combustion, especially at high temperatures. Thus, elevated levels
of nitrogen dioxide can cause damage to the human respiratory tract and
increase a person's vulnerability to, and the severity of, respiratory infections and
asthma. Long-term exposure to high levels of nitrogen dioxide can cause chronic
lung disease.
Particulate Carbon came from incomplete combustion of any fuel containing
carbon atoms. This can cause health problems for humans because it irritates
the lining of the lungs, can make asthma worse, and perhaps even cause cancer.
Particulate carbon can also cause global dimming, which may reduce rainfall.
You might also like
- Air Pollution: What Is Air Pollution and What Can We Do?Document6 pagesAir Pollution: What Is Air Pollution and What Can We Do?Leonor BagnosNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry Class-XiDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry Class-XiSatyaSaraswatNo ratings yet
- Resume Bab 3 13-5: A. Isu Pemanasan GlobalDocument6 pagesResume Bab 3 13-5: A. Isu Pemanasan GlobalAngesty PrawidyasariNo ratings yet
- Notes On Environmental PollutionDocument8 pagesNotes On Environmental PollutionUvaisNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry NotesDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry NotesharishNo ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument11 pagesEnvironmental PollutionrupeshNo ratings yet
- Environmental-Science-1 (1) - 52-96Document45 pagesEnvironmental-Science-1 (1) - 52-96aavvvNo ratings yet
- Module VI AEE Rev.1.0Document41 pagesModule VI AEE Rev.1.0Nikhil ShajiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - (Philoid IN) PDFDocument18 pagesUnit 1 - (Philoid IN) PDFKawshik RayNo ratings yet
- Some Pollutants in The Atmosphere Combine To Form Other PollutantsDocument71 pagesSome Pollutants in The Atmosphere Combine To Form Other PollutantsKasunNo ratings yet
- Assignment II PAT353Document5 pagesAssignment II PAT353fanhaoheNo ratings yet
- EVS UNIT-4 To 6Document91 pagesEVS UNIT-4 To 6tanakamuzira20No ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument11 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- Environmental ChemistryDocument40 pagesEnvironmental ChemistryharryNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Answer The Following Questions BelowDocument3 pagesActivity 3 Answer The Following Questions BelowMicca Ella VinoyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Climate Change, Ozone LossDocument59 pagesLesson 11 Climate Change, Ozone LossVinNo ratings yet
- ULO3 ADocument2 pagesULO3 AVainsNo ratings yet
- EEES UNIT 3 BBBB BBBDocument10 pagesEEES UNIT 3 BBBB BBBParvaNo ratings yet
- MinimalistDocument25 pagesMinimalistSeanette Manlatican CalapardoNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentphanhaibangNo ratings yet
- UNIT-14 Day-1Document16 pagesUNIT-14 Day-1kailash sharmaNo ratings yet
- Environmental ChemistryDocument19 pagesEnvironmental ChemistryNeeraj RathiNo ratings yet
- Science The Air Around Us: FolioDocument21 pagesScience The Air Around Us: FolioAfiqah NurhabreyahNo ratings yet
- Pollution: by Akram Hasan AlsultanyDocument27 pagesPollution: by Akram Hasan AlsultanySata AjjamNo ratings yet
- Global Warming & Green House EffectDocument32 pagesGlobal Warming & Green House EffectAbhijeeth NagarajNo ratings yet
- University of Calcutta: Environmental Science PROJECTDocument16 pagesUniversity of Calcutta: Environmental Science PROJECTSatyaki ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Enviormental Chemistry Class 11Document16 pagesEnviormental Chemistry Class 11prayasjindal281No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Class 11 Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry PDFDocument12 pagesChemistry Notes Class 11 Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry PDFAbbaas AlifNo ratings yet
- BCHE 111L - ULO3aDocument5 pagesBCHE 111L - ULO3aKaris DemetriaNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution SafetyDocument27 pagesAir Pollution Safetysirajudeen INo ratings yet
- Air EnvironmentDocument16 pagesAir EnvironmentMadeline Castro PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Science: Title: Pollution Unit 3.2 Teacher: Cik FatimahDocument35 pagesScience: Title: Pollution Unit 3.2 Teacher: Cik Fatimah한나No ratings yet
- Atmosphere RevisionDocument33 pagesAtmosphere RevisionChaos InsurgencyNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Occurs When Harmful SubstancesDocument9 pagesAir Pollution Occurs When Harmful SubstancesSourav Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (Pollution) Part 1Document53 pagesUnit 2 (Pollution) Part 1kumar.abhinav1015No ratings yet
- 17 Environmental Chemistry Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument2 pages17 Environmental Chemistry Formula Sheets QuizrrArjunNo ratings yet
- Dr. Suha M. Aabdeen: Mbbs UofkDocument96 pagesDr. Suha M. Aabdeen: Mbbs UofkshravaniNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tenaga Nasional: Mehb312 - Thermodynamics 2Document8 pagesUniversiti Tenaga Nasional: Mehb312 - Thermodynamics 2DcTur Stylo-pNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution: Study MaterialDocument7 pagesEnvironmental Pollution: Study MaterialHemu RaoNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument26 pagesAir PollutionAbhigya PoptaniNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument20 pagesAir PollutionElectrical EEENo ratings yet
- Ncert 12Document16 pagesNcert 12haarika1006No ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution (Final)Document25 pagesEnvironmental Pollution (Final)shreyaNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry Ch14: Environmental Chemistry TOP ConceptsDocument9 pagesClass XI Chemistry Ch14: Environmental Chemistry TOP ConceptsGurmeetNo ratings yet
- Ecology AirDocument21 pagesEcology Airarezoo bahramiNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric PollutionDocument2 pagesAtmospheric Pollutionanshvishwakarma674No ratings yet
- ESS Unit 6Document5 pagesESS Unit 6Ashrith SabhanamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Air Pollution - 6 - 2021Document45 pagesIntroduction To Air Pollution - 6 - 2021Andreas KanimeNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse GasDocument5 pagesGreenhouse Gastanzim444No ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument11 pagesChemistry ProjectHarishNo ratings yet
- Further Notes On Air PollutionDocument17 pagesFurther Notes On Air Pollutionwong zhi chengNo ratings yet
- Module For Climate ChangeDocument9 pagesModule For Climate ChangeReina DionsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Environmental ChemistryDocument7 pagesUnit 14 Environmental Chemistrygyogi1989No ratings yet
- AIR QUALITY AND POLLUTION (TKA 3301) LECTURE NOTES 12 - Global Air P ProblemDocument80 pagesAIR QUALITY AND POLLUTION (TKA 3301) LECTURE NOTES 12 - Global Air P Problemmamat88No ratings yet
- Acid Rain and OzoneDocument2 pagesAcid Rain and OzoneDevesh SawantNo ratings yet
- All About The Ozone Layer : Effects on Human, Animal and Plant Health - Environment Books | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandAll About The Ozone Layer : Effects on Human, Animal and Plant Health - Environment Books | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- ULO-CDocument1 pageULO-CKenth VillanuenaNo ratings yet
- ULO-BDocument2 pagesULO-BKenth VillanuenaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument12 pagesExercise 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusKenth VillanuenaNo ratings yet
- GE2 CompileDocument10 pagesGE2 CompileKenth VillanuenaNo ratings yet
- Villanueva SimDocument18 pagesVillanueva SimKenth VillanuenaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Back UpDocument4 pagesLaboratory Back UpKenth VillanuenaNo ratings yet
- Factors Tend To Increase and Derease DiversityDocument2 pagesFactors Tend To Increase and Derease DiversityKenth VillanuenaNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartDocument3 pagesFlow ChartKenth VillanuenaNo ratings yet
- FTM - HY110 with+REBARDocument13 pagesFTM - HY110 with+REBARRomyMohanNo ratings yet
- 2019 Jot FallDocument86 pages2019 Jot Fallahmed kabelNo ratings yet
- The Thermal Conductivity of Alumina Nanoparticles Dispersed in Ethylene GlycolDocument4 pagesThe Thermal Conductivity of Alumina Nanoparticles Dispersed in Ethylene GlycolShourya JainNo ratings yet
- LabEx No. 1 Wood Compression TestDocument10 pagesLabEx No. 1 Wood Compression TestianzkieeNo ratings yet
- The History of ConcreteDocument3 pagesThe History of ConcreteFer Rivas Nieto100% (1)
- Ethylene and Acetylene Plant PDFDocument405 pagesEthylene and Acetylene Plant PDFاحمد الدلالNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Test in Science V SY: 2018-2019 Table of Specifications Placement of Item/ Level Total No. of Test Items R U AP AN E CDocument4 pagesFirst Periodical Test in Science V SY: 2018-2019 Table of Specifications Placement of Item/ Level Total No. of Test Items R U AP AN E CCely Lopez Madriaga0% (1)
- 3 6 Candy MoleculesDocument4 pages3 6 Candy MoleculesVanessa JabagatNo ratings yet
- Mcqs of AASDocument3 pagesMcqs of AASfaisalNo ratings yet
- RohsDocument49 pagesRohssyladrianNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Kan-SUPRA Polyurethane FinishDocument3 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: Kan-SUPRA Polyurethane FinisholiviaNo ratings yet
- History of Gas Chromatography+Document11 pagesHistory of Gas Chromatography+Juliana SilvaNo ratings yet
- Supercast SW30 (UK)Document2 pagesSupercast SW30 (UK)Gry ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Admixture Pada Campuran BetonDocument54 pagesAdmixture Pada Campuran BetonDanny100% (2)
- CH 9 WorksheetsDocument5 pagesCH 9 Worksheetsadaglio001100% (1)
- Bend RestrictorsDocument2 pagesBend RestrictorsjiokoijikoNo ratings yet
- Msds OxysanzsDocument5 pagesMsds OxysanzsJorge AntonioNo ratings yet
- 11 KV Line Erection PracticesDocument90 pages11 KV Line Erection PracticesBoson FreelancerNo ratings yet
- Yellowing Behavior of TextilesDocument8 pagesYellowing Behavior of TextilesMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- "Production of Hydrogen Gas Using Gasification From BiomassDocument40 pages"Production of Hydrogen Gas Using Gasification From BiomassFaizNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0010854522004593 Main 2Document58 pages1 s2.0 S0010854522004593 Main 2Mys GenieNo ratings yet
- 09-04-2023 - Plumbing BOQ Without RatesDocument20 pages09-04-2023 - Plumbing BOQ Without RatesK. S. Design GroupNo ratings yet
- Union GalvasteelDocument25 pagesUnion GalvasteelJam67% (3)
- C-Mold GuideDocument188 pagesC-Mold GuideGuery SaenzNo ratings yet
- Products Product Filters: - All Industries - All ApplicationsDocument2 pagesProducts Product Filters: - All Industries - All ApplicationsSteven FryeNo ratings yet
- Experimental Analysis of Laser Drilling Impacts On Rock PropertiesDocument10 pagesExperimental Analysis of Laser Drilling Impacts On Rock PropertiesAngélica Acosta PérezNo ratings yet
- TDS GrilloDocument5 pagesTDS GrillomaxNo ratings yet
- 3.6 Revision Guide Organic Analysis AqaDocument3 pages3.6 Revision Guide Organic Analysis Aqashafiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Pivot-Table-Exercise PracticeDocument151 pagesPivot-Table-Exercise PracticePriyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Landfill Design ThesisDocument5 pagesLandfill Design Thesisdwsjyt34100% (2)