Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transistor As A Delay Switch
Uploaded by
John Christian AgdamagOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transistor As A Delay Switch
Uploaded by
John Christian AgdamagCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTRICAL DEPARTMENT
Technological University of the Philippines
College of Industrial Technology
ELECTRICAL DEPARTMENT
Manila
Agdamag, John Christian A. April 3, 2022
Name: _____________________ Date: ___________________
BET-MECT 2A
Course, Yr. & Sec.: _____________ Monday, 12:00 pm – 3:00
Schedule: ________________
Mrs. Sherlie Bunag
Instructor: __________________ pm
Rating:
Transistor as a Delay Switch
I. Objectives:
This exercise should enable the student to:
Realize a switching delay, using a transistor
Explain the function of a stairway lighting circuit.
Calculate the time delay to off the circuit.
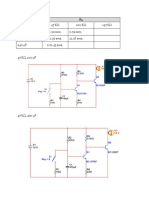
II. Circuit Diagram:
SDB Transistor as a Delay Switch
ELECTRICAL DEPARTMENT
III. Equipment
Name Qty.
Function generator with integral AC/DC power supply 1
Digital multimeter 1
Dual trace oscilloscope including probes 1
Test lead adapters, BNC / 4 mm 2
Universal panel 1
Capacitor, 100 µF 1
Capacitor, 470 µF 2
Resistor, 10 Ω 1
Resistor, 47 Ω 1
Resistor, 2.2 KΩ 1
Resistor, 47 KΩ 1
Resistor, 100 KΩ 1
Single-pole push-button switch 1
Lamp, 15V red 1
Transistor, BC107 1
Transistor, BC140 1
Set of connection cables 1
Connection plugs (jumpers) 2 mm / 7.5 mm
IV. Procedure:
1. Assemble the circuit shown in the diagram.
Ensure that the correct transistors are used.
2. The values of RX and CX on the circuit, are given in the table below.
Use the given combinations of R and C and for each combination, measure the time
constraint for the lamp to switch off after operating the switch. Use stopwatch to
measure the time.
RX
CX 47 KΩ 100 KΩ 147 KΩ
100 µF 00:03.48 00:05.45 00:06.72
470 µF 00:14.41 00:19.37 00:25.34
940 µF 00:30.86 00:50.65 01:07.07
Simulation:
SDB Transistor as a Delay Switch
ELECTRICAL DEPARTMENT
47 KΩ, 100 µF
47 KΩ, 470 µF
47 KΩ, 940 µF
SDB Transistor as a Delay Switch
ELECTRICAL DEPARTMENT
100 KΩ, 100 µF
100 KΩ, 470 µF
SDB Transistor as a Delay Switch
ELECTRICAL DEPARTMENT
100 KΩ, 940 µF
SDB Transistor as a Delay Switch
ELECTRICAL DEPARTMENT
147 KΩ, 100 µF
147 KΩ, 470 µF
SDB Transistor as a Delay Switch
ELECTRICAL DEPARTMENT
147 KΩ, 940 µF
What are the functions of the transistors, T1 and T2 in this exercise?
The capacitor Cx is initially uncharged, and the switch S1 is turned off. It signifies
that no current is flowing to the transistor's base and that the lamp is turned off.
When we press the S1 button, the capacitor Cx begins to charge. The capacitor's
charge rate is determined by the resistor Rx. The slower the capacitor charges,
the higher the Rx resistance. A voltage divider is implemented by the resistor-
capacitor (RC) filter. The voltage across the capacitor rises as the capacitor
charges. It indicates that the more charged the capacitor is, the more voltage is
applied to the transistor's base. The voltage provided to the transistor's base
eventually rises to the point where it can open the transistor. The transistor
begins to conduct current, and the lamp turns on. The delay can be adjusted by
changing the capacitance of the capacitor Cx and the resistance of the variable
resistor Rx.
What is the purpose of 100 Ω resistor connected in series with the switch S?
Resistors protect components from voltage spikes and guarantee that they receive
the right voltage by creating a voltage dip. A certain voltage is required for each
component in an electrical circuit, such as a light or a switch. A resistor will
provide a voltage drop if a component demands less voltage than the remainder
of the circuit, ensuring that the component does not receive too much electricity.
A voltage drop is created by slowing down, or resisting, electrons as they try to
pass through a resistor. A component may be destroyed or fail to perform
properly if it receives too much voltage.
SDB Transistor as a Delay Switch
ELECTRICAL DEPARTMENT
V. Conclusion
We may conclude from this action that a transistor can be used as a delay switch,
also that adjusting the resistance and capacitance can adjust the delay time of the
lamp turning off after the switch is shut off. When the lamp's resistance and
capacitance are both increased, the lamp's time constraint for turning off after
the switch is shut off is also increased. However, if the resistance and capacitance
both drop at the same time, the time it takes for the lamp to turn off is reduced.
SDB Transistor as a Delay Switch
You might also like
- Edc 2 Mumbai University Lab ManualDocument32 pagesEdc 2 Mumbai University Lab ManualXavier50% (4)
- Name: Date:: Experiment 03 Common Collector AmplifierDocument3 pagesName: Date:: Experiment 03 Common Collector AmplifierJuay Mae RianoNo ratings yet
- Ie 51Document51 pagesIe 51Ananya ChavanNo ratings yet
- 566 LIC Expt 2Document22 pages566 LIC Expt 2Hrivu Dasmunshi (RA1911004010566)No ratings yet
- Aust/Eee: Ahsanullah University of Science and TechnologyDocument27 pagesAust/Eee: Ahsanullah University of Science and Technologyruhul aminNo ratings yet
- Abad Dominguez Practica06Document22 pagesAbad Dominguez Practica06erick alavaNo ratings yet
- To Design The Automatc Night Lamp Using Logic CircuitDocument38 pagesTo Design The Automatc Night Lamp Using Logic CircuitSouvik PalNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 07 Name of The Experiment: Ob J E Cti V eDocument3 pagesExperiment No: 07 Name of The Experiment: Ob J E Cti V eAli MusaNo ratings yet
- V5 - 2022 - 23 MWOC Lab FinalDocument45 pagesV5 - 2022 - 23 MWOC Lab FinalCHINNI CHINNINo ratings yet
- Bec3l1 - Edc Lab NewDocument55 pagesBec3l1 - Edc Lab NewAhyen TambongNo ratings yet
- ECA ManualDocument50 pagesECA ManualkrajenderreddyNo ratings yet
- Rectification. 10 CO2 L3 Sol N.: Maharaja Institute of Technology MysoreDocument7 pagesRectification. 10 CO2 L3 Sol N.: Maharaja Institute of Technology MysoreSpoorthy HUNo ratings yet
- Nis Cie 2Document5 pagesNis Cie 2Manju BhuvanNo ratings yet
- Design-of-Astable-Multivibrator-Circuit - Mini Projects - Electronics Tutorial - Electronics TutorialDocument6 pagesDesign-of-Astable-Multivibrator-Circuit - Mini Projects - Electronics Tutorial - Electronics TutorialGangireddy SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering Experiments RGPVDocument28 pagesMicrowave Engineering Experiments RGPVYash JainNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits and Simulation LabDocument77 pagesAnalog Circuits and Simulation LableevasusanNo ratings yet
- Oscillator ManualDocument22 pagesOscillator ManualckooipgNo ratings yet
- Mulvaney Graham 352 Lab 1Document6 pagesMulvaney Graham 352 Lab 1api-125239608No ratings yet
- ET 4.3 Capacitors in Alternating Current Circuits: EquipmentDocument2 pagesET 4.3 Capacitors in Alternating Current Circuits: EquipmentMarvin Caballero ZelayaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 ManualDocument6 pagesExperiment 6 ManualAiden PierceNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Lab - Exp - 7 - Student - Manual (Summer 18-19)Document4 pagesElectronic Devices Lab - Exp - 7 - Student - Manual (Summer 18-19)MD MONIM ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Sardar Patel Institute of Technology: Experiment No. - 3Document7 pagesSardar Patel Institute of Technology: Experiment No. - 3Sreejit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Analysis of An RC Phase Shifter Circuit:: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesAnalysis of An RC Phase Shifter Circuit:: Objectiveayesha amjadNo ratings yet
- Probset 1 Questions 103Document5 pagesProbset 1 Questions 103Hazelle MamugayNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Facultad de Estudios Superiores Cuautitlán. Campo 4Document4 pagesUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Facultad de Estudios Superiores Cuautitlán. Campo 4Luis FigueroaNo ratings yet
- EEE 54 DP2 DocumentationDocument5 pagesEEE 54 DP2 DocumentationDarl John MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1.circuits and Simulation Integrated Laboratory 2013 RegulationDocument46 pages1.circuits and Simulation Integrated Laboratory 2013 RegulationNandha KumarNo ratings yet
- Ece481-Microwave and Optical Communication Laboratory ManualDocument44 pagesEce481-Microwave and Optical Communication Laboratory Manualeceklu100% (1)
- Expt 5 - Wein Bridge Oscillator (2020)Document3 pagesExpt 5 - Wein Bridge Oscillator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- Project 2018Document4 pagesProject 2018negikrishna9627No ratings yet
- Lab Manual EC II Format 2Document53 pagesLab Manual EC II Format 2nishavs100% (1)
- Design and Implementation of Variable Power SupplyDocument8 pagesDesign and Implementation of Variable Power SupplySoyebAhmed50% (2)
- HV Resonance CollectionDocument4 pagesHV Resonance CollectionfreiwildNo ratings yet
- Applied Electronics Lab 2Document9 pagesApplied Electronics Lab 2Rickel RoweNo ratings yet
- Study of Clipper and Clamper CircuitDocument5 pagesStudy of Clipper and Clamper Circuitmabrur nabilNo ratings yet
- Zulu James Lab 1 4157Document7 pagesZulu James Lab 1 4157James Jimmy JahNo ratings yet
- Expt 9 - Astable-Multivibrator (2020)Document5 pagesExpt 9 - Astable-Multivibrator (2020)samarth100% (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewDocument86 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Mosfets With A 8 Ohms Impedance Speaker Connected To It.: Audio Amplifier SystemDocument4 pagesMosfets With A 8 Ohms Impedance Speaker Connected To It.: Audio Amplifier SystemJ VikasNo ratings yet
- Wireless Power Transmission 2Document6 pagesWireless Power Transmission 2St. Anne's CET (EEE Department)No ratings yet
- Mwe&oc MannualDocument76 pagesMwe&oc MannualSajjala Poojith reddyNo ratings yet
- Wireless Power TransmissionDocument5 pagesWireless Power TransmissionNiranjan TawareNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Analog Circuits: PHYS 331: Junior Physics Laboratory IDocument6 pagesExercise On Analog Circuits: PHYS 331: Junior Physics Laboratory Iviso167No ratings yet
- Expt 11 - Bistable-Multivibrator (2020)Document4 pagesExpt 11 - Bistable-Multivibrator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- Microwave Manual 2017Document72 pagesMicrowave Manual 2017manjuri karNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 4 Wein-Bridge & RC Phase Shift OscillatorsDocument5 pagesLab Report 4 Wein-Bridge & RC Phase Shift OscillatorsAbdul Aziz ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- MWDC LabDocument105 pagesMWDC Labbchaitanya55No ratings yet
- Fpe (1) AkDocument39 pagesFpe (1) AkAnchal YewaleNo ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument94 pagesLIC Lab Manualmamathasuvarna1121No ratings yet
- NV6503Document45 pagesNV6503sandeep_226250% (2)
- A6 Relleta JamesDocument13 pagesA6 Relleta JamesLorenzo AbolarNo ratings yet
- 02-LVDT Trainer UITM-02 Range - 10mm NewDocument13 pages02-LVDT Trainer UITM-02 Range - 10mm Newhydromec_indiaNo ratings yet
- LC Lab Manual Svuce EceDocument116 pagesLC Lab Manual Svuce EcePMVamsiNo ratings yet
- DielectricDocument3 pagesDielectricJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- Certificate: Ushabai Deshmukh Jr. College - TheDocument24 pagesCertificate: Ushabai Deshmukh Jr. College - TheRxrdm ShubhamNo ratings yet
- EXP. 1-Filtered Power SupplyDocument4 pagesEXP. 1-Filtered Power SupplyJustine LentijasNo ratings yet
- Microwave&Optical Communications: Laboratory Manual (R10 Syllabus)Document43 pagesMicrowave&Optical Communications: Laboratory Manual (R10 Syllabus)Zareena Fathima100% (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- TYYYDocument13 pagesTYYYJohn Christian AgdamagNo ratings yet
- TRIAC CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesTRIAC CharacteristicsJohn Christian AgdamagNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Programmable Language of CNC - G and M Codes - (AGDAMAG)Document17 pagesUnderstanding The Programmable Language of CNC - G and M Codes - (AGDAMAG)John Christian AgdamagNo ratings yet
- CNC Lathe Program CyclesDocument2 pagesCNC Lathe Program CyclesJohn Christian AgdamagNo ratings yet
- FPN D Based Driver Smoking Behavior Detection MethodDocument11 pagesFPN D Based Driver Smoking Behavior Detection MethodJohn Christian AgdamagNo ratings yet
- Basic Science AssigDocument5 pagesBasic Science AssigdomromeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument21 pagesChapter 2 PDFMahdi BanjakNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Resistors in Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument2 pagesExperiment 5: Resistors in Series and Parallel CircuitsVictoria De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- October 2016 2Document16 pagesOctober 2016 2Tanvika AroraNo ratings yet
- Bump Grade Force On Wire Student-1Document3 pagesBump Grade Force On Wire Student-1Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Project Work Class 11Document17 pagesProject Work Class 11DipeshNo ratings yet
- h1 Styleclearboth Idcontentsection0the Only Guide To Commercial Fisheries Reviewh1jbfch PDFDocument14 pagesh1 Styleclearboth Idcontentsection0the Only Guide To Commercial Fisheries Reviewh1jbfch PDFgalleymark22No ratings yet
- Akshay Urja Full PDFDocument56 pagesAkshay Urja Full PDFNeelam Shrivastava100% (2)
- TanDocument8 pagesTanShourya RathodNo ratings yet
- Breathwork Fundamentals GuidebookDocument148 pagesBreathwork Fundamentals GuidebookJuliana RennerNo ratings yet
- Quantitative School of ManagementDocument3 pagesQuantitative School of ManagementVAIBHAV JAIN100% (1)
- Exp 3 Rahul Singh 2k20-A18-12Document8 pagesExp 3 Rahul Singh 2k20-A18-12Dummy Account-Rahul SinghNo ratings yet
- A Settlement Prediction Model Considering Tidal Loading and Traffic LoadingDocument14 pagesA Settlement Prediction Model Considering Tidal Loading and Traffic LoadingSandro GuedesNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics 2 Solutions UHSMCDocument5 pagesCombinatorics 2 Solutions UHSMCWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- English 900 - 01Document147 pagesEnglish 900 - 01Hnin Hnin AungNo ratings yet
- One-Dimensional Unconstrained Optimization: Example 1 Golden Section MethodDocument5 pagesOne-Dimensional Unconstrained Optimization: Example 1 Golden Section MethodMohamed MuayidNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Wb93r 5 Shop ManualDocument20 pagesKomatsu Wb93r 5 Shop Manualsandra100% (32)
- BYRGMv 3Document30 pagesBYRGMv 3tajsisNo ratings yet
- 6480 49 35800 2 10 20230801Document12 pages6480 49 35800 2 10 20230801samsidar nidarNo ratings yet
- Scaffold 2Document3 pagesScaffold 2Mahmoud Elsayed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Week 4 and 5 Non-Verbal Communication: 4.1 The Importance of Nonverbal CommunicationDocument8 pagesWeek 4 and 5 Non-Verbal Communication: 4.1 The Importance of Nonverbal CommunicationNovilia FriskaNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Tests For Job ApplicantsDocument30 pagesAptitude Tests For Job ApplicantsMboowa YahayaNo ratings yet
- Multifocal AntennaDocument5 pagesMultifocal AntennaLazni NalogNo ratings yet
- R.M. M, J. C, S.L. I S.M. H R C. M P J. M G : Aier Horover Verson AND Ayes Odney Aier and Eter C OldrickDocument1 pageR.M. M, J. C, S.L. I S.M. H R C. M P J. M G : Aier Horover Verson AND Ayes Odney Aier and Eter C OldrickPeter McGoldrickNo ratings yet
- Geography Worksheet 1 Rural SettlementsDocument14 pagesGeography Worksheet 1 Rural SettlementsLelethuNo ratings yet
- CulvertsDocument14 pagesCulvertsMatsobane LekalaksNo ratings yet
- 2347-Article Text-7179-1-10-20220922Document12 pages2347-Article Text-7179-1-10-20220922george weafriNo ratings yet
- AS Level Mathematics Statistics (New)Document49 pagesAS Level Mathematics Statistics (New)Alex GoldsmithNo ratings yet
- MonoSLAM Real-Time Single Camera SLAMDocument16 pagesMonoSLAM Real-Time Single Camera SLAMArmandoNo ratings yet
- Rosela Rowell, Carlos Rodriguez, Mark Salpeter, Chet Michals, Sarah KiddDocument5 pagesRosela Rowell, Carlos Rodriguez, Mark Salpeter, Chet Michals, Sarah KiddRosela De Jesus RowellNo ratings yet