0% found this document useful (0 votes)
284 views1 pageEssential Divisibility Rules Explained
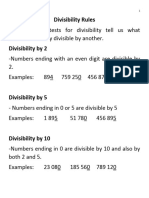
This document outlines divisibility rules for numbers 2 through 13. It provides tests to determine if a number is divisible by each factor based on the digits in the number, such as a number being divisible by 2 if its units digit is even. It also lists important points about divisibility, such as a number being divisible by a number's factors, and the sum or difference of two divisible numbers also being divisible.
Uploaded by
SashankCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
284 views1 pageEssential Divisibility Rules Explained
This document outlines divisibility rules for numbers 2 through 13. It provides tests to determine if a number is divisible by each factor based on the digits in the number, such as a number being divisible by 2 if its units digit is even. It also lists important points about divisibility, such as a number being divisible by a number's factors, and the sum or difference of two divisible numbers also being divisible.
Uploaded by
SashankCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd