0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views6 pagesAISC 360-16 C-Section Analysis Guide
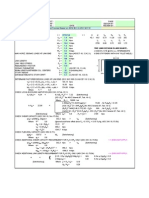
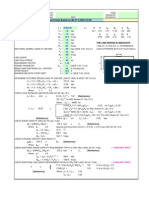
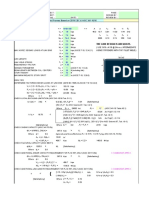
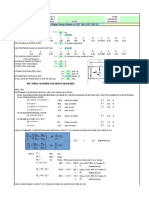
This document summarizes the structural analysis of a C-section channel. It includes:
1) Geometric properties of the cross-section like dimensions, areas, moments of inertia, product of inertia, radii of gyration, and shear center.
2) Calculations of the section's tension and compression capacities according to AISC 360-16 specifications, including yield tension, rupture tension, and flexural and torsional buckling capacities.
3) The section qualifies as non-slender and its buckling capacities are controlled by either elastic or inelastic buckling depending on the axis and applied load.
Uploaded by
inaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views6 pagesAISC 360-16 C-Section Analysis Guide
This document summarizes the structural analysis of a C-section channel. It includes:
1) Geometric properties of the cross-section like dimensions, areas, moments of inertia, product of inertia, radii of gyration, and shear center.
2) Calculations of the section's tension and compression capacities according to AISC 360-16 specifications, including yield tension, rupture tension, and flexural and torsional buckling capacities.
3) The section qualifies as non-slender and its buckling capacities are controlled by either elastic or inelastic buckling depending on the axis and applied load.
Uploaded by
inaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd