Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk Assessment Template 17 Aug 2015 - Final V7
Uploaded by
Nur kahnOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk Assessment Template 17 Aug 2015 - Final V7
Uploaded by
Nur kahnCopyright:
Available Formats
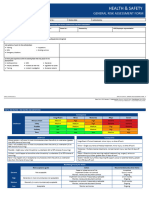
Health and Safety Risk Assessment
Activity / Task / Location: Reviewed / Approved By:
Signature and Date:
Consequence
Risk Assessment Developed by: Date:
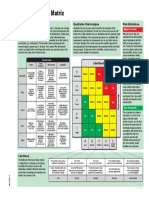
Risk Matrix Likelihood
N.B. For more details regarding use of this matrix / Almost
Rare Unlikely Possible Likely
definitions refer to final page of this document Certain
Severe
Eg. Potential Fatality or Injury or MEDIUM MEDIUM HIGH EXTREME EXTREME
Illness with permanent disability
Major
Eg. Potential Lost Time Injury (but LOW MEDIUM MEDIUM HIGH EXTREME
non-permanent disability)
Moderate
Eg. Potential Medical Treatment LOW LOW MEDIUM MEDIUM HIGH
injury or illness (but no lost time)
Minor
Eg. Potential First Aid injury LOW LOW LOW MEDIUM MEDIUM
Minimal
Eg. Hazard or near miss requiring LOW LOW LOW LOW LOW
reporting and follow up action
Actions required based on Risk Assessment
An “extreme” risk requires immediate assessment and senior staff consideration is required; a detailed mitigation plan must be developed, and consideration should be
Extreme given to ceasing the activity unless the risk can be reduced to a level of high or less; regular monitoring and reported on to the relevant management/steering committee;
Target resolution should be within 1 month.
A “high” risk may also require immediate assessment and senior staff consideration; a mitigation plan must be developed; regular monitoring and reported on to the
High
relevant management/steering committee. Target resolution (ideally reduction to medium or low level of risk) should be within 3 months.
Medium A mitigation plan must be developed; existing controls need to be reviewed. Target resolution (ideally reduction to low level of risk) should be within 1 year.
Low Risk is tolerable; manage by well established, routine processes/procedures and be mindful of changes to nature of risks.
For more information visit - http://www.newcastle.edu.au/current-staff/working-here/work-health-and-safety/managing-health-and-safety-risks
Health and Safety Risk Assessment
Control measures and Residual Risk Remaining
Hazard Identification and initial Risk Rating Actions required
Rating Hazards
What additional
Risk What control methods or Residual What hazard actions are
Rating measures will be used to Risk remains?
What are the steps of What are the required (by who
based reduce the likelihood Rating
the activity / items of potential on Risk based on and in what
and/or the consequence
equipment? hazards? Matrix Risk timeframe) to
of an illness or injury from
Matrix raise the level of
those hazards?
control?
For more information visit - http://www.newcastle.edu.au/current-staff/working-here/work-health-and-safety/managing-health-and-safety-risks
Health and Safety Risk Assessment
Summary of Requirements based on Risk Assessment Review Period / Date
Personal Protective
Equipment
Other Equipment and
Equipment Protection
Training Requirements
Procedures, SOPs etc
Relevant Legislation etc. WHS Act 2011 (NSW) & Regulations / Codes of Practice
Questions to ask in order to determine the hazards relating to the task:
A Could people be injured or made sick by things such as: D What could go wrong?
Noise What if equipment is misused?
Light What might people do that they shouldn’t
Radiation How could someone be killed?
Toxicity How could people be injured?
Infection What may make people ill?
High or low temperatures Are there any special emergency procedures required?
Electricity
Moving or falling things (or people) E Are procedures or organisational systems missing or
Flammable or explosive materials not being followed?
Things under tension or pressure (compressed gas or liquid; Standard Operating Procedures?
springs) Risk Assessments?
Any other energy sources or stresses Induction or training?
Biohazardous material Management of change?
Laser Safety Inspections?
Hazard reporting?
Contractor Management?
B Can workplace practices cause injury or sickness? F What kinds of injuries could possibly occur?
Are there heavy or awkward lifting jobs? Broken bones
Can people work in a comfortable posture? Eye damage
For more information visit - http://www.newcastle.edu.au/current-staff/working-here/work-health-and-safety/managing-health-and-safety-risks
Health and Safety Risk Assessment
If the work is repetitive, can people take breaks? Hearing problems
Are people properly trained? Strains or sprains
Do people follow correct work practices? Cuts or abrasions
Are there adequate facilities for the work being performed? Bruises
Are universal safety precautions for biohazards followed? Burns
Is there poor housekeeping? Look out for clutter Lung problems including inhalation injury/ infection
Torn or slippery flooring Skin contact
Sharp objects sticking out Poisoning
Obstacles Needle-stick injury
C Imagine that a child was to enter your work area? Psychological illness or injury
What would you warn them to be extra careful of?
What would do to reduce the harm to them?
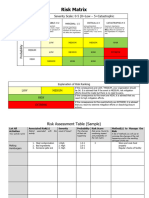
How to Assess Risk
Step 1 – Consider the Consequences Step 2 – Consider the Likelihood Step 3 – Calculate the Risk Rating
What are the potential consequences of an What is the likelihood of the consequence
incident occurring? identified in step 1 happening? A. Take Step 1 rating and select the correct column.
Consider what could reasonably happen as well
as what may actually happen. Consider this with the current controls in place. B. Take Step 2 Rating and select the correct line.
Look at the descriptions and choose the most Look at the descriptions and choose the most C. The calculated risk rating is where the two ratings
suitable Consequence. suitable Likelihood. cross
LIKELIHOOD
Consequence Likelihood Almost
Rare Unlikely Possibly Likely
Certain
Serious Potential Fatality or Injury or Illness with Almost The event could be expected to occur in most Serious
permanent disability Certain circumstances: “This is a common problem here”. MEDIUM MEDIUM HIGH EXTREME EXTREME
CONSEQUENCE
Potential Lost Time Injury requiring time off The event has a reasonable chance of occurring
Major Likely Major LOW MEDIUM MEDIUM HIGH EXTREME
work (but non-permanent disability) in usual conditions: “It has happened here before”.
Moderate Potential medical treatment Injury or Illness but The event might occur occasionally, has occurred Moderate
Possible sometime: “Has infrequently happened here before”. LOW LOW MEDIUM MEDIUM HIGH
no lost time
The event has a small chance of occurring. “It has
Minor Potential First Aid Injury Unlikely not happened here but has occurred elsewhere”. Minor LOW LOW LOW MEDIUM MEDIUM
No injury but hazard exists or near miss Very unlikely to occur. “It would be extremely rare
Minimal Rare for it to occur here”. Minimal LOW LOW LOW LOW LOW
occurred requiring reporting and follow up action
For more information visit - http://www.newcastle.edu.au/current-staff/working-here/work-health-and-safety/managing-health-and-safety-risks
Health and Safety Risk Assessment
Control Type Example
Eliminate Removing the hazard, eg taking a hazardous piece of equipment out of service.
Substitute Replacing a hazardous substance or process with a less hazardous one, eg substituting a hazardous substance with
a non-hazardous substance.
Engineering Redesign a process or piece of equipment to make it less hazardous, Isolating the hazard from the person at risk, eg
using a guard or barrier, or containing the hazard in an enclosure.
Administrative Adopting safe work practices or providing appropriate training, instruction or information.
Personal Protective The use of personal protective equipment could include using gloves, glasses, earmuffs, aprons, safety footwear,
Equipment (PPE) dust masks. NOTE: This is a last resort control and should be used in conjunction with higher level controls.
Controlling the Risk: Risk control is a method of managing the risk with the primary emphasis on controlling the hazards at source. For a risk that is assessed as “extreme” or “high”, steps
should be taken immediately to minimize risk of injury. The method of ensuring that risks are controlled effectively is by using the “hierarchy of controls”. The Hierarchy of Controls are:
For more information visit - http://www.newcastle.edu.au/current-staff/working-here/work-health-and-safety/managing-health-and-safety-risks
You might also like
- AWE Individual Risk Analysis 2Document10 pagesAWE Individual Risk Analysis 2Bibek Kandel100% (1)
- Risk Register - Trivia NightDocument1 pageRisk Register - Trivia Nightapi-514548596No ratings yet
- Bellak Tat Sheet2pdfDocument17 pagesBellak Tat Sheet2pdfTalala Usman100% (3)
- EHS Qualitative Risk Matrix Rev 2Document1 pageEHS Qualitative Risk Matrix Rev 2Didik SokoNo ratings yet
- Application of HIRAC ProcessDocument14 pagesApplication of HIRAC ProcessEric Valenzuela100% (2)
- Risk Assessment ReportDocument8 pagesRisk Assessment ReportHappi NessNo ratings yet
- Child Sexual Abuse Cover Up 2Document7 pagesChild Sexual Abuse Cover Up 2mikekvolpe100% (1)
- Hindustan Unilever PDFDocument63 pagesHindustan Unilever PDFSimran pokhriyalNo ratings yet
- 1 Colostomy and IleostomyDocument4 pages1 Colostomy and IleostomyAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Travel Risk Assessment Checklist - Security & SafetyDocument13 pagesTravel Risk Assessment Checklist - Security & SafetyHarisNo ratings yet
- HTLWHS002 AT4A Risk Assessment Control 0521Document6 pagesHTLWHS002 AT4A Risk Assessment Control 0521Soumyanil BabiNo ratings yet
- HAZID ModifiedDocument14 pagesHAZID Modifiedchem_taNo ratings yet
- Plumbing, Rev 011Document99 pagesPlumbing, Rev 011Suraj AmbekarNo ratings yet
- Risk AssesmentDocument48 pagesRisk AssesmentRie UsunNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Plan - Multiple HazardsDocument2 pagesRisk Management Plan - Multiple Hazardsali hamzaNo ratings yet
- RiskassessmenttemplateDocument4 pagesRiskassessmenttemplateJessel Ann MontecilloNo ratings yet
- Sample School Risk Register: Red Dot Primary School John Doe Red Dot Primary School, 1 Redding Road, RedvilleDocument13 pagesSample School Risk Register: Red Dot Primary School John Doe Red Dot Primary School, 1 Redding Road, RedvilleNina AzizNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Shaybah HSE DepartmentDocument20 pagesRisk Assessment: Shaybah HSE DepartmentMuhammad TariqNo ratings yet
- Scout Safe Risk AssessmentDocument1 pageScout Safe Risk Assessmentapi-348870392No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: India 8-Nov-2020 Low Cost Laptop Business by Super Comp System Brajendra Singh PatelDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment: India 8-Nov-2020 Low Cost Laptop Business by Super Comp System Brajendra Singh Patelbrajendra1020No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Template: Safety@edumail - Vic.gov - AuDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment Template: Safety@edumail - Vic.gov - AuEveNo ratings yet
- RiskassessmenttemplateDocument3 pagesRiskassessmenttemplatehmusallam4No ratings yet
- General Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesGeneral Risk Assessmentdeja_149547234No ratings yet
- Task 2.1 Job Safety Analysis Template 2Document6 pagesTask 2.1 Job Safety Analysis Template 2ridazainib06No ratings yet
- Table - Risk Assessment Matrix - Center For Campus InvolvementDocument5 pagesTable - Risk Assessment Matrix - Center For Campus InvolvementReduan ahimuNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Risiko K3 untuk Pencegahan KecelakaanDocument26 pagesManajemen Risiko K3 untuk Pencegahan KecelakaanAnnisaa MawarNo ratings yet
- Example Industry Hazard Register 2022Document5 pagesExample Industry Hazard Register 2022She-Ra Sha-Ju LaNo ratings yet
- General Risk Assessment FormDocument4 pagesGeneral Risk Assessment Formabhijeetmhetre12345No ratings yet
- Risk - Assessment - 2023 - Using FACS To Isolate ICC From Human Gastric TissueDocument5 pagesRisk - Assessment - 2023 - Using FACS To Isolate ICC From Human Gastric TissueSofia MoriamNo ratings yet
- Lab1 Risk AssessmentsDocument14 pagesLab1 Risk AssessmentsalwkilmunirhNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Dr. Khidir Faisal Abu Bakr MD (DPH)Document24 pagesRisk Assessment: Dr. Khidir Faisal Abu Bakr MD (DPH)ardesh abdille100% (1)
- Risk Assessment Form-DECADocument3 pagesRisk Assessment Form-DECAHill CordialNo ratings yet
- 04 Identifikasi Bahaya Dan Hirarki Kontrol PDFDocument84 pages04 Identifikasi Bahaya Dan Hirarki Kontrol PDFFitNo ratings yet
- Quality Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesQuality Risk ManagementA VegaNo ratings yet
- Manage health and safety risks in 4 stepsDocument4 pagesManage health and safety risks in 4 stepsMae Mae Marcelo-BautistaNo ratings yet
- HSE Risk ManagementDocument3 pagesHSE Risk ManagementAhmed GaafarNo ratings yet
- Master Risk Assessment FormDocument4 pagesMaster Risk Assessment FormKirana RoonnaphaiNo ratings yet
- Module U3 - Risk Management V2Document12 pagesModule U3 - Risk Management V2ryujindanceNo ratings yet
- RiskassessmenttemplateDocument4 pagesRiskassessmenttemplatekumar kannanNo ratings yet
- CONTROL RISKS WITH HIRARCDocument15 pagesCONTROL RISKS WITH HIRARCAwatifNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Form: Section A: Activity DetailsDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment Form: Section A: Activity DetailsJOAQUINFERNADO SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- RiskassessmenttemplateDocument4 pagesRiskassessmenttemplateLorena Vázquez VillafañaNo ratings yet
- BASELINE HSE RISK ASSESSMENT FOR EGYPRO EAST AFRICA LTDDocument25 pagesBASELINE HSE RISK ASSESSMENT FOR EGYPRO EAST AFRICA LTDRico100% (2)
- Risk Assessment Control Form - Happyville Home Care ServiceDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment Control Form - Happyville Home Care ServiceNatalia PetaiaNo ratings yet
- Field Work Risk Assessment FormDocument6 pagesField Work Risk Assessment FormLufias KeyNo ratings yet
- Hazard ManagementDocument22 pagesHazard Managementbrianwg2No ratings yet
- Hazard Assessment - V7Document8 pagesHazard Assessment - V7Anggi Gusti DewiNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessments Sample (HIRARC)Document8 pagesHazard Identification and Risk Assessments Sample (HIRARC)beriNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification & Assessment: Rehman Ali August, 2018Document20 pagesHazard Identification & Assessment: Rehman Ali August, 2018faraz shamimNo ratings yet
- BRHL Risk AssessmentDocument4 pagesBRHL Risk Assessmentmatuskova.lucie012No ratings yet
- JSA Job Safety AnalysisDocument7 pagesJSA Job Safety AnalysisLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Risk Matrix V 22Document4 pagesRisk Matrix V 22haikaltoro120101No ratings yet
- Introduction To Risk ManagementDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Risk Managementpikamau100% (1)
- Jsa FormDocument1 pageJsa FormStrauhs EquipamentosNo ratings yet
- METEC DESIGN & CONSTRUCTION RISK ASSESSMENTDocument235 pagesMETEC DESIGN & CONSTRUCTION RISK ASSESSMENTSamy KsNo ratings yet
- Notes On Risk ManagementDocument4 pagesNotes On Risk Managementcurlicue100% (2)
- BSBWHS401 Risk Management Procedures PDFDocument6 pagesBSBWHS401 Risk Management Procedures PDFdavidNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Template: Step 1: Identify The HazardsDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment Template: Step 1: Identify The HazardsMyolwinooNo ratings yet
- 04 RiskDocument4 pages04 Riskamin.tabeschNo ratings yet
- Johnston OESI Risk Management ForumDocument10 pagesJohnston OESI Risk Management ForumGermanNo ratings yet
- Risk Identification Sheet - TemplateDocument3 pagesRisk Identification Sheet - TemplatemrchimbavalaNo ratings yet
- 3 Risk AssessmentDocument31 pages3 Risk Assessmenta.pavloffskiyNo ratings yet
- Managing Operational RiskDocument40 pagesManaging Operational RiskkjNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Quality Risk Management: A Practical Approach to Effective Risk-Based ThinkingFrom EverandFoundations of Quality Risk Management: A Practical Approach to Effective Risk-Based ThinkingNo ratings yet
- MCC 34 DomperidoneDocument40 pagesMCC 34 DomperidoneAnonymous PTSx0GANo ratings yet
- No Timestamp Nama Lengkap Email Nomor Handphone OrganisasiDocument16 pagesNo Timestamp Nama Lengkap Email Nomor Handphone OrganisasiMeta WulandariNo ratings yet
- EKG Intermediate Tips Tricks ToolsDocument55 pagesEKG Intermediate Tips Tricks Toolsmayas bsharatNo ratings yet
- TriumphDebate SeptOct2021 OfficialBriefDocument134 pagesTriumphDebate SeptOct2021 OfficialBriefRebecca WardNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Information, LucknowDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Information, LucknowVipul GautamNo ratings yet
- Oil Sampling SOPDocument9 pagesOil Sampling SOPTorres Toledo JttNo ratings yet
- He Izard Heet: Wizard SchoolDocument3 pagesHe Izard Heet: Wizard SchoolItay OrgilNo ratings yet
- 2020年07月六级真题(全1套)Document12 pages2020年07月六级真题(全1套)六级真题及解析(1990-2022)No ratings yet
- Physical Fitness Test ResultsDocument28 pagesPhysical Fitness Test ResultsAshanti JavierNo ratings yet
- Health Guard Brochure Print76Document22 pagesHealth Guard Brochure Print76fhnNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument16 pagesNursing DiagnosisShemie TutorNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis MataDocument168 pagesDiagnosis Mata19. Moh Hidayatullah AL AhyaNo ratings yet
- Boys WH Swim Results 9.14Document4 pagesBoys WH Swim Results 9.14The LedgerNo ratings yet
- FCCS Course Advert 22.09.2022 - FinalDocument2 pagesFCCS Course Advert 22.09.2022 - FinalShaneabbas JafferNo ratings yet
- Department of Social Welfare and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesDepartment of Social Welfare and DevelopmentJhana May PayatNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Advantages and Disadvantages of VolunteeringDocument6 pagesDiscuss The Advantages and Disadvantages of Volunteeringaidil islamNo ratings yet
- A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Quetiapine and Paroxetine As Monotherapy in Adults With Bipolar Depression (EMBOLDEN II)Document12 pagesA Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Quetiapine and Paroxetine As Monotherapy in Adults With Bipolar Depression (EMBOLDEN II)HugoMattosNo ratings yet
- Detection of Marine Microalgae (Phytoplankton) Quality To Support Seafood Health: A Case Study On The West Coast of South Sulawesi, IndonesiaDocument8 pagesDetection of Marine Microalgae (Phytoplankton) Quality To Support Seafood Health: A Case Study On The West Coast of South Sulawesi, IndonesiaIndah AdeliaNo ratings yet
- Suicide Ideation and Attempts in A Pediatric Emergency Department Before and During COVID-19Document8 pagesSuicide Ideation and Attempts in A Pediatric Emergency Department Before and During COVID-19mikoNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Physical Fitness ActivitiesDocument27 pagesPhysical Education: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Physical Fitness ActivitiesKeith Tristan RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 1.BSBDIV501 Student Assessment Tasks RedoneDocument28 pages1.BSBDIV501 Student Assessment Tasks RedoneÇrox Rmg PunkNo ratings yet
- Mifepristone & MisoprostolDocument6 pagesMifepristone & MisoprostolnanimadallaNo ratings yet
- PED011 Final Req 15Document3 pagesPED011 Final Req 15macabalang.yd501No ratings yet
- Innovative Use of Virtual Reality in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Case-StudyDocument12 pagesInnovative Use of Virtual Reality in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Case-StudyomenpkuNo ratings yet
- Assignment: TopicDocument12 pagesAssignment: TopicAthul RNo ratings yet
- Nebosh Senirio Answer Guild FFDocument23 pagesNebosh Senirio Answer Guild FFTerry OghenerhovwoNo ratings yet