Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Macrolide Drug Study
Uploaded by
Emagra Azil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesMacrolide drug study
Original Title
Macrolide drug study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMacrolide drug study
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesMacrolide Drug Study
Uploaded by
Emagra AzilMacrolide drug study
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
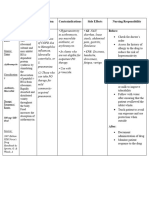
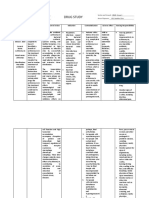
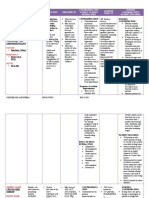
DRUG NAME DOSAGE MECHANISM INDICATION CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE NURSING
OF ACTION EFFECTS CONSIDERATIONS
Generic Availability: Binds to the Indicated Contraindicated in CNS: fatigue, Advise patient
Name: Injection: 500 mg 50S subunit of treatment for: patients headache, to avoid
Azithromycin Ophthalmic bacterial Acute bacterial hypersensitive to somnolence, excessive
(ay-zi-thro-MY-sin) solution: 1% ribosomes, worsening of azithromycin, dizziness. sunlight and to
Powder for oral blocking COPD caused erythromycin, or wear protective
Brand Name: suspension: 100 protein by Haemophilus other macrolide or CV: chest pain, clothing and use
Zithromax mg/5 mL, 200 mg/5 synthesis; influenzae, ketolide antibiotics palpitations. sunscreen when
Zithromax Tri- mL; 1,000 mg/single bacteriostatic Moraxella and in those with outside.
Pak dose packet or bactericidal, catarrhalis, or history of EENT: eye Tell patient to
Zithromax Z- Tablets: 250 mg, depending on Streptococcus cholestatic jaundice irritation report adverse
Pak 500 mg, 600 mg concentration. pneumoniae; or hepatic (ophthalmic). reactions
Zmax Uncomplicated dysfunction from promptly.
Chancroid skin and skin- prior use of GI: abdominal pain, Monitor patient
Classification: Adults: 1 g PO as a anorexia, diarrhea,
structure azithromycin. for
Anti-infective. single dose nausea, vomiting,
infections Serious cases of superinfection.
Belongs to the Pharyngitis, pseudomembranous
caused by allergic reactions, Drug may cause
class of drugs tonsillitis colitis, dyspepsia,
Staphylococcus including overgrowth of
known as Children age 2 and flatulence, melena.
aureus, angioedema, nonsusceptible
macrolide older: 12 mg/kg oral Streptococcus anaphylaxis, SJS, GU: candidiasis, bacteria or
antibiotics suspension pyogenes, or toxic epidermal nephritis, vaginitis. fungi.
(maximum, 500 mg) Streptococcus necrolysis, and Monitor patient
Route: Hepatic: cholestatic
PO daily for 5 days. agalactiae; DRESS syndrome for CDAD,
PO jaundice.
IV second-line have been reported, which may
Severe cholera therapy for some with fatalities. range in severity
OU Adults: 1 g PO as a Skin:
pharyngitis or Prolonged photosensitivity from mild
single dose tonsillitis observation and diarrhea to fatal
Forms: reactions, rash, pain
Pharmacokinetics
Injection Absorption: rapidly caused by S. symptomatic at injection site, colitis.
Ophthalmic absorbed pyogenes treatment may be pruritus. Consider full
Solution Peak: necessary. risk profile
Powder for PO : 2-5hr Infantile Other: when choosing
Oral Distribution: hypertrophic pyloric angioedema. appropriate
suspension Widely distributed stenosis has been antibiotic
Tablets throughout the body. reported after the therapy.
Metabolism: use of azithromycin Alternative
Metabolized in the in neonates macrolide or
liver (treatment up to 42 fluoroquinolone
Elimination: days of life). class drugs also
Eliminated and Don't use oral drug have the
unchanged in the in patients with potential to
feces via biliary pneumonia or in cause QT-
excretion and those with moderate interval
transintestinal to severe illness or prolongation
secretion risk factors (such as and other
Half Life: cystic fibrosis, significant
About 3 days. nosocomially adverse effects.
acquired infections, Monitor patient
known or suspected for allergic and
bacteremia; skin reactions.
hospitalized, elderly, Discontinue
or debilitated drug if reactions
patients; or patients occur. Be aware
with that allergic
immunodeficiency symptoms may
or functional recur when
asplenia). symptomatic
Use cautiously in therapy is
patients with discontinued;
impaired hepatic patient may
function or require
myasthenia gravis. prolonged
monitoring and
treatment.
Monitor patient
for jaundice,
hepatotoxicity,
and hepatitis.
Discontinue
drug
immediately if
signs and
symptoms
(yellowing of
skin or sclera,
abdominal pain,
nausea,
vomiting, dark
urine) occur.
You might also like
- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandToxic Epidermal Necrolysis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAzithromycin Drug StudyMelissa Marie Custodio100% (1)
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageAzithromycin Drug StudyChristine IbiasNo ratings yet
- BenadrylDocument2 pagesBenadrylsamfandood10No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (med ward)Document4 pagesDRUG STUDY (med ward)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJavie Bryant RedilNo ratings yet
- Bibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyDocument5 pagesBibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyCarlos LleverNo ratings yet
- 5 Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument4 pages5 Cefuroxime Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Clindamycin Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesClindamycin Nursing ResponsibilitiesDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.100% (1)
- Cephalexin Nursing GuideDocument2 pagesCephalexin Nursing GuideKatyana Cesar100% (1)
- Santiago, Gwyneth Julia B.-Bsn2-D-Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSantiago, Gwyneth Julia B.-Bsn2-D-Drug StudyGwyneth SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Trinity University of Asia Batch Asperion 2013 Drug StudyDocument5 pagesTrinity University of Asia Batch Asperion 2013 Drug StudysestablecidaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage and Route Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument7 pagesName of Drug Dosage and Route Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTon AgustinNo ratings yet
- Silver Sulfadiazine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSilver Sulfadiazine Drug StudyKenn Siasar100% (1)
- Polyomyelitis: Name: Ma Rupina B. Ponce Course: Bachelor of Science Major in Nursin Section: CDocument17 pagesPolyomyelitis: Name: Ma Rupina B. Ponce Course: Bachelor of Science Major in Nursin Section: CMaria Pina Barbado PonceNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Sulfate-Drug StudyDocument3 pagesGentamicin Sulfate-Drug StudyDaisy Palisoc82% (11)
- DRUG STUDY Bronchitis CorsigaDocument8 pagesDRUG STUDY Bronchitis CorsigaKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument2 pagesDrugthe_greatpasawayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- Document patient meds, effects, doses, and considerationsDocument1 pageDocument patient meds, effects, doses, and considerationsgeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- DrugStudy FluconazoleCasilaoDocument4 pagesDrugStudy FluconazoleCasilaoArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximeAbijah Leris SarmientoNo ratings yet
- GENTAMICINDocument2 pagesGENTAMICINlowell cerezoNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument6 pagesCefuroximeJoyce Joyx Joycee SalonoiNo ratings yet
- Update medication documentation in different color inkDocument1 pageUpdate medication documentation in different color inkgeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Drug Study With NCPDocument4 pagesDrug Study With NCPJoanne Kathleen SantolicesNo ratings yet
- Treating Pink Eye and Diarrhea SafelyDocument24 pagesTreating Pink Eye and Diarrhea SafelyCzarina Mae Lomboy100% (1)
- Drug Study Pedia WardDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pedia WardSyrelle GomezNo ratings yet
- Cleocin Clindamycin Hydrochloride: Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCleocin Clindamycin Hydrochloride: Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Leukupenia, Neutropenia, ThrombocytopeniaDocument3 pagesLeukupenia, Neutropenia, ThrombocytopeniaVANESSANo ratings yet
- Tetanus toxoid side effects and nursing responsibilitiesDocument10 pagesTetanus toxoid side effects and nursing responsibilitiesElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Sulfate Drug Study 1 2Document3 pagesGentamicin Sulfate Drug Study 1 2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Santiago, Gwyneth Julia B. - Drug MonographDocument1 pageSantiago, Gwyneth Julia B. - Drug MonographGwyneth SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin (Biaxin)Document1 pageClarithromycin (Biaxin)Jocelyn Rivera100% (1)
- Patient M. G Drug 1 - Ob MaxDocument5 pagesPatient M. G Drug 1 - Ob MaxGrace MellaineNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Adverse Effect Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Adverse Effect Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesJoshua Davantes100% (1)
- Drugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingDocument3 pagesDrugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingHazel Palomares100% (1)
- DRUGSTUDYDocument8 pagesDRUGSTUDYWinnie Salazar AriolaNo ratings yet
- Drug study nursing considerationsDocument4 pagesDrug study nursing considerationsMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- Gentamycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesGentamycin Drug StudyShin Guevara100% (3)
- Drug Study AZITHROMYCINDocument2 pagesDrug Study AZITHROMYCINDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Activity ErythromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study Activity ErythromycinNELL JOSHUA PANTIGNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- AmikacinDocument4 pagesAmikacinkristineK100% (1)
- AONBDocument4 pagesAONBNicole Rachelyn MartinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudySwag MasterNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indications/Contraindicati Ons Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations BeforeDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mode of Action Indications/Contraindicati Ons Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations BeforeMikko McDonie VeloriaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of CiprofloxacinDocument3 pagesDrug Study of CiprofloxacinZyra MendozaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy 20Document9 pagesDrugstudy 20MahledJoy EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- JM DrugDocument3 pagesJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDrug Study - CefuroximeErika Jane EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY ON CEFUROXIME AND HYOSCINE BUTYLBRROMIDEDocument5 pagesDRUG STUDY ON CEFUROXIME AND HYOSCINE BUTYLBRROMIDEGenierose YantoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RLEDocument8 pagesDrug Study RLEGenierose YantoNo ratings yet
- Patient Name: Room No.: Physician: Brand Name Mecahnism of Action Side Effects Contraindication Dosage Nursing Intervention InfusionDocument1 pagePatient Name: Room No.: Physician: Brand Name Mecahnism of Action Side Effects Contraindication Dosage Nursing Intervention InfusionEmber SaymanNo ratings yet
- To Reduce The Risk of Nsaid Induced Gastric Ulcers But Not Duodena L Ulcers in High-Risk PatientsDocument8 pagesTo Reduce The Risk of Nsaid Induced Gastric Ulcers But Not Duodena L Ulcers in High-Risk PatientsLouis Gabriel AdayaNo ratings yet
- Drud Study For DutyDocument9 pagesDrud Study For DutyAnonymous AlphaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Hydrocortisone)Document1 pageDrug Study (Hydrocortisone)Pauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Nursing drug study on mefenamic acidDocument2 pagesNursing drug study on mefenamic acidEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Tetracycline Drug StudyDocument5 pagesTetracycline Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin DRUGSTUDYDocument3 pagesVancomycin DRUGSTUDYEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Tinidazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTinidazole Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Penicillin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPenicillin Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Fluoroquinolone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFluoroquinolone Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Perception and Awareness of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Speciality Among Medical Postgraduate TraineesDocument5 pagesPerception and Awareness of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Speciality Among Medical Postgraduate TraineesAmadea EmanuelaNo ratings yet
- The God Within - BM HegdeDocument2 pagesThe God Within - BM HegdeSini AdvNo ratings yet
- Fetal Medicine Booklet 2023 ProgrammeDocument11 pagesFetal Medicine Booklet 2023 ProgrammeJuan TrianaNo ratings yet
- Liu 2017-Herbal Medicine For The Treatment of ObesityDocument17 pagesLiu 2017-Herbal Medicine For The Treatment of ObesityMas NuriNo ratings yet
- What Is SphigellosisDocument3 pagesWhat Is SphigellosisJulimaricon Rigucira BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Mental Health Forum (With Background)Document4 pages2nd Mental Health Forum (With Background)Aj CamachoNo ratings yet
- Epidemiologi Pasien Luka Bakar Di RSUP Sanglah Denpasar Tahun 2018-2019Document5 pagesEpidemiologi Pasien Luka Bakar Di RSUP Sanglah Denpasar Tahun 2018-2019Paris MirsanNo ratings yet
- Pig Farm and Health Plan v1 UKDocument15 pagesPig Farm and Health Plan v1 UKJerry WilliamNo ratings yet
- Goal 3&4Document20 pagesGoal 3&4sijal batoolNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Skeletal MusclesDocument27 pagesDiseases of Skeletal Musclesapi-3699361100% (1)
- Factors Responsible for Foodborne DiseasesDocument3 pagesFactors Responsible for Foodborne DiseasesSayp dNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Postoperative Healing Assessment Using Cannabinoids in Oral SurgeryDocument7 pages2019 - Postoperative Healing Assessment Using Cannabinoids in Oral SurgerycorcarolNo ratings yet
- G10 BiomoleculesDocument49 pagesG10 BiomoleculesMc AcebarNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 3-Ekofisiologi Manusia Dan KesehatanDocument78 pagesKuliah 3-Ekofisiologi Manusia Dan KesehatangardamdNo ratings yet
- Melinda Smith, M.A., Lawrence Robinson, and Jeanne Segal, PH.D, Sehar Shoukat, Sophia, Sarah, John M. Grohol, Psy.DDocument5 pagesMelinda Smith, M.A., Lawrence Robinson, and Jeanne Segal, PH.D, Sehar Shoukat, Sophia, Sarah, John M. Grohol, Psy.DZhang PeilinNo ratings yet
- Curcuma 2020 Fcell-08-00479Document10 pagesCurcuma 2020 Fcell-08-00479Jorge Luis Plasencia CubaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal assessment essentialsDocument91 pagesNeonatal assessment essentialsSHAFIQNo ratings yet
- Fellowship in Critical Care MedicineDocument12 pagesFellowship in Critical Care MedicinerajiNo ratings yet
- Final Oral Pathology ExamDocument5 pagesFinal Oral Pathology Examsolom islamNo ratings yet
- TFN Handouts Chapter 1Document5 pagesTFN Handouts Chapter 1Shanedy SumagangNo ratings yet
- Passmedicine MRCP Notes-Palliative Medicine and End of Life CareDocument5 pagesPassmedicine MRCP Notes-Palliative Medicine and End of Life CareMayar WaelNo ratings yet
- Cisplatin Versus Carboplatin For Patients With Metastatic Non - Small-Cell Lung Cancer - An Old Rivalry RenewedDocument2 pagesCisplatin Versus Carboplatin For Patients With Metastatic Non - Small-Cell Lung Cancer - An Old Rivalry RenewedFlorin RizicaNo ratings yet
- Aplastic Anemia Is A NormocyticDocument17 pagesAplastic Anemia Is A NormocyticAfrio ArismanNo ratings yet
- 678 FullDocument9 pages678 FullDarren WilliamNo ratings yet
- Addiction and Emotionally Focused Couple TherapyDocument218 pagesAddiction and Emotionally Focused Couple TherapyOlesya BoyerNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledJustinlloyd Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Rajkumari Amrit Kaur College of Nursing: Lesson Plan On Infection Prevention and Control MeasuresDocument18 pagesRajkumari Amrit Kaur College of Nursing: Lesson Plan On Infection Prevention and Control MeasuresIshwar Das100% (2)
- Bone tm3Document57 pagesBone tm3ZakiyahulfahdwNo ratings yet
- MCQ Final 1910Document20 pagesMCQ Final 1910JohnSonNo ratings yet
- CH 25 Respiration Study GuideDocument2 pagesCH 25 Respiration Study Guide99646qbkdwNo ratings yet