Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Music Activity
Uploaded by
Armanderico B. Fernando0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageOriginal Title
Music activity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageMusic Activity
Uploaded by
Armanderico B. FernandoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
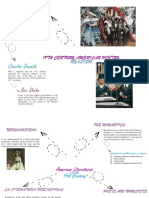
a literary, artistic, and philosophical movement originating in the 18th century,
characterized chiefly by a reaction against neoclassicism and an emphasis on the
imagination and emotions, and marked especially in English literature by sensibility
and the use of autobiographical material, an exaltation of the primitive and the
common man, an appreciation of external nature, an interest in the remote, a
predilection for melancholy, and the use in poetry of older verse forms
In the 1760s and ’70s a number of
British artists at home and in Rome,
including James Barry, Henry DEFINITION Musical romantism was marked by
Fuseli, John Hamilton Mortimer,
emphasis on originality and
and John Flaxman, began to paint
individuality, personal emotional
subjects that were at odds with the
expression, and freedom and
strict decorum and classical
experimentation of form. Ludwig
historical and mythological subject
van Beethoven and Franz Schubert
matter of conventional figurative
bridged the Classical and Romantic
art. These artists favoured themes
that were bizarre, pathetic, or ARTS
ROMANTISM MUSIC
periods, for while their formal
musical techniques were basically
extravagantly heroic, and they
Classical, their music’s intensely
defined their images with tensely
personal feeling and their use of
linear drawing and bold contrasts
programmatic elements provided an
of light and shade. William Blake,
important model for 19th-century
the other principal early Romantic
Romantic composers.
painter in England, evolved his
own powerful and unique visionary
images. LITERATURE
the publication Lyrical Ballads by Wordsworth and Coleridge.
the composition Hymns to the Night by Novalis.
poetry by William Blake.
poetry by Robert Burns.
Rousseau's philosophical writings.
"Song of Myself" by Walt Whitman.
the poetry of Samuel Taylor Coleridge.
You might also like
- Q1Document32 pagesQ1Jamshaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Actividad LiteraturaDocument2 pagesActividad LiteraturaFrank HuallaNo ratings yet
- Cave Art Egyptian Art Classical Period - Early Greek Art: and Consistency. PotteryDocument4 pagesCave Art Egyptian Art Classical Period - Early Greek Art: and Consistency. PotteryKarl BelasaNo ratings yet
- Late 18th and Early 19thDocument82 pagesLate 18th and Early 19thGrace CordelinNo ratings yet
- All Sub ReviewersDocument34 pagesAll Sub ReviewersLouie MagbojosNo ratings yet
- Review Questions Pg. 260Document2 pagesReview Questions Pg. 260Eamon Barkhordarian100% (1)
- LitCrit Week6 PradasDocument11 pagesLitCrit Week6 PradasRaquel Remolar FlorNo ratings yet
- British: Historical and Social BackgroundDocument13 pagesBritish: Historical and Social Backgroundfederico astorriNo ratings yet
- Romanticism: Romanticism (Also Known As The Romantic Era) Was An ArtisticDocument35 pagesRomanticism: Romanticism (Also Known As The Romantic Era) Was An ArtisticRohayu -No ratings yet
- The Caught Image: Figurative Language in the Fiction of Henry JamesFrom EverandThe Caught Image: Figurative Language in the Fiction of Henry JamesNo ratings yet
- 18 Century LiteratureDocument14 pages18 Century LiteratureSarah Mahmoud EsmaelNo ratings yet
- The Romantic Period: Sturm Und Drang French RevolutionDocument12 pagesThe Romantic Period: Sturm Und Drang French RevolutionHiya ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Presentazione IngleseDocument14 pagesPresentazione IngleseMichele Filippo PaluzziNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument18 pagesIntroductionSarahNo ratings yet
- L1 - Introducing The Music of The Romantic PeriodDocument23 pagesL1 - Introducing The Music of The Romantic PeriodJane JasaNo ratings yet
- Tennyson's PoetryDocument1 pageTennyson's PoetryMajeed JadweNo ratings yet
- ELT-313-2nd-exam-reviewerDocument7 pagesELT-313-2nd-exam-reviewerkylamendiola543No ratings yet
- Symbolismo LocochónDocument12 pagesSymbolismo LocochónFernandoNo ratings yet
- Курсова William ShakespeareDocument18 pagesКурсова William ShakespeareОксана КречковськаNo ratings yet
- The Characteristics of Romantic PoetryDocument5 pagesThe Characteristics of Romantic PoetryMuhammad Maad RazaNo ratings yet
- American & British LiteratureDocument2 pagesAmerican & British LiteratureJohanna Faith CapoyNo ratings yet
- The Romantic Age. The Meaning of The Term "Romantic" in The Romantic AgeDocument7 pagesThe Romantic Age. The Meaning of The Term "Romantic" in The Romantic AgeОльга СайчукNo ratings yet
- Erlich 1964 The Maker and The SeerDocument28 pagesErlich 1964 The Maker and The SeerSb__No ratings yet
- 11 - Chapter 4 PDFDocument17 pages11 - Chapter 4 PDFpriyashree jaiswalNo ratings yet
- SSC Art Integration ActvityDocument1 pageSSC Art Integration ActvityAnvita sameerNo ratings yet
- ELT-313-3rd-exam-reviewer-1Document8 pagesELT-313-3rd-exam-reviewer-1kylamendiola543No ratings yet
- Romanticism Movement in European Art and LiteratureDocument31 pagesRomanticism Movement in European Art and LiteratureIbtissam La100% (1)
- Romanticism Movement in European Art, Literature & PhilosophyDocument31 pagesRomanticism Movement in European Art, Literature & PhilosophyloklkioNo ratings yet
- LIT-5 ActivitiesDocument25 pagesLIT-5 ActivitiesEsperanza BuwatNo ratings yet
- Pre-Romantic PoetryDocument4 pagesPre-Romantic PoetryTehneat Arshad100% (2)
- Laurente Grade 9 Music Lesson 2 LPDocument17 pagesLaurente Grade 9 Music Lesson 2 LPRYAN LAURENTENo ratings yet
- Romanticism and The Industrial RevolutionDocument2 pagesRomanticism and The Industrial RevolutionBrianNo ratings yet
- Anglo-Saxon ModernismDocument11 pagesAnglo-Saxon ModernismArlette HernandezNo ratings yet
- Modern British Poetry Movements & InfluencesDocument76 pagesModern British Poetry Movements & InfluencesShahid AarfiNo ratings yet
- American LiteratureDocument2 pagesAmerican LiteratureKeesha Mae Urgelles TimogNo ratings yet
- Symbolism PDFDocument11 pagesSymbolism PDF畏100% (1)
- Music Quarter 3 Module 1Document1 pageMusic Quarter 3 Module 1EDWIN SIBUGALNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism ReviewerDocument2 pagesLiterary Criticism ReviewerAldrin BallaNo ratings yet
- New York School MovementDocument4 pagesNew York School MovementRussell anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Major Periods British American LitDocument3 pagesMajor Periods British American LitZarah Joyce SegoviaNo ratings yet
- The Romantic Period in Visual ArtsDocument31 pagesThe Romantic Period in Visual Artsjessa histaNo ratings yet
- Romanticism Vs RealismDocument1 pageRomanticism Vs RealismAni GlezNo ratings yet
- Greeks on Greekness: Viewing the Greek Past under the Roman EmpireFrom EverandGreeks on Greekness: Viewing the Greek Past under the Roman EmpireDavid KonstanNo ratings yet
- List of Literary Movements - WikipediaDocument11 pagesList of Literary Movements - Wikipediasnehasish PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- History and Evolution of Rhetoric and Stylistic AnalysisDocument2 pagesHistory and Evolution of Rhetoric and Stylistic Analysisdigger and aprilNo ratings yet
- The Screaming Skull and Other Classic Horror StoriesFrom EverandThe Screaming Skull and Other Classic Horror StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- 05 43 Victorian LiteratureDocument11 pages05 43 Victorian LiteratureAlessia GuardoneNo ratings yet
- 02.01 Literary CriticismDocument2 pages02.01 Literary CriticismYahia RifaiNo ratings yet
- Realism - Conceptual Art: Art Movements and StylesDocument18 pagesRealism - Conceptual Art: Art Movements and StylesKhyla DonatoNo ratings yet
- HH Arnason - Abstract Expressionism and The New American Art (Ch. 19)Document36 pagesHH Arnason - Abstract Expressionism and The New American Art (Ch. 19)KraftfeldNo ratings yet
- Unit1 PDFDocument5 pagesUnit1 PDFMonalisa DethaNo ratings yet
- American Literary History Timeline and Movements BDocument3 pagesAmerican Literary History Timeline and Movements BEricNo ratings yet
- Helit Group WorkDocument3 pagesHelit Group WorkAsih SunarsihNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument9 pagesArt AppreciationKimberly PuddefootNo ratings yet
- Notes 2Document2 pagesNotes 2Sulfur DioxideNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Lesson 3 and 4 SDG 9-17Document57 pagesQ3 - Lesson 3 and 4 SDG 9-17Armanderico B. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Lhs Blended Learning-Contract Sy2022-2023Document3 pagesLhs Blended Learning-Contract Sy2022-2023Armanderico B. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Journal - Fernando, Alexandria NicoleDocument16 pagesJournal - Fernando, Alexandria NicoleArmanderico B. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Cooling system components and functionsDocument1 pageCooling system components and functionsArmanderico B. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Fe Del Mundo: First Female Pediatrician in the PhilippinesDocument2 pagesFe Del Mundo: First Female Pediatrician in the PhilippinesArmanderico B. FernandoNo ratings yet
- GDRIVE LINK - Evangelou GatchalianDocument1 pageGDRIVE LINK - Evangelou GatchalianArmanderico B. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Reclaiming The Human Self - Redemptive Suffering and Spiritual SerDocument165 pagesReclaiming The Human Self - Redemptive Suffering and Spiritual SerTamilaruvi100% (1)
- Calvino in Postmodern LiteratureDocument10 pagesCalvino in Postmodern LiteratureAnthony Read100% (2)
- Quizizz - Device BasesDocument4 pagesQuizizz - Device BasesPratistha BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Cinarding Lesson Lesson 7Document36 pagesCinarding Lesson Lesson 7Maribel UmbaoNo ratings yet
- Audience and Purpose: 2analytical Tools ("The Big 5")Document3 pagesAudience and Purpose: 2analytical Tools ("The Big 5")faithNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of 21st Century Philippines LiteratureDocument6 pagesA Brief History of 21st Century Philippines LiteratureLeigh Nathalie LealNo ratings yet
- A Thing of Beauty: John Keats' Poem ExplainedDocument9 pagesA Thing of Beauty: John Keats' Poem Explainedkanak jeengarNo ratings yet
- Eason Rec Letter Music ScholarshipDocument4 pagesEason Rec Letter Music ScholarshipAres KampanosNo ratings yet
- Pride and Prejudice: Art of CharacterizationDocument3 pagesPride and Prejudice: Art of CharacterizationRizwan Rao100% (2)
- Bluest Eye Winter QuestionsDocument1 pageBluest Eye Winter QuestionsCaroline Rhude100% (1)
- Epic Conventions 2Document3 pagesEpic Conventions 2TikvahNo ratings yet
- Indian English Literature: Weavers, The Feather of The Dawn, in The Bazaars of Hyderabad EtcDocument2 pagesIndian English Literature: Weavers, The Feather of The Dawn, in The Bazaars of Hyderabad EtcGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- The Ocean of Story 09 PDFDocument352 pagesThe Ocean of Story 09 PDFIbirHassimNo ratings yet
- 4 5a Bookmark Poems Sing To Me ClimbDocument2 pages4 5a Bookmark Poems Sing To Me Climbapi-115513756No ratings yet
- Understanding Shelley's PoetryDocument1 pageUnderstanding Shelley's PoetrytonishiagNo ratings yet
- A Historical Survey of Literary CriticismDocument4 pagesA Historical Survey of Literary CriticismKring RosseNo ratings yet
- Edwin A R Trout - Some Writers On Concrete - The Literature of Reinforced Concrete, 1897-1935-Whittles (2013) PDFDocument321 pagesEdwin A R Trout - Some Writers On Concrete - The Literature of Reinforced Concrete, 1897-1935-Whittles (2013) PDFJ.G.PaikNo ratings yet
- Tuck Everlasting Chapter Questions WebDocument14 pagesTuck Everlasting Chapter Questions Web9602428100% (1)
- Metaphors and Myths of Deformity: A General SurveyDocument36 pagesMetaphors and Myths of Deformity: A General Surveyscooterkid5No ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Unit 4 Lesson 2 New and Emerging Literary GenresSDocument22 pages21st Century Literature Unit 4 Lesson 2 New and Emerging Literary GenresSCathyleen MontañezNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Children's LiteratureDocument3 pagesBenefits of Children's LiteratureRaji musharafNo ratings yet
- Comparative World LiteratureDocument10 pagesComparative World LiteratureLuis Martínez-Falero GalindoNo ratings yet
- LP - G8 LITERATURE - Free Verse and Blank VerseDocument6 pagesLP - G8 LITERATURE - Free Verse and Blank VerseJL SonNo ratings yet
- New Criticism: Novelties and LimitationsDocument5 pagesNew Criticism: Novelties and LimitationsIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument2 pagesExamHao Li MinNo ratings yet
- Chaucer ContributionDocument3 pagesChaucer ContributionFauzia ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Literary ArchetypesDocument8 pagesLiterary ArchetypesRaine CarrawayNo ratings yet
- Beginnings and Endings in NovelsDocument22 pagesBeginnings and Endings in NovelsHumphrey Chimpden EarwickerNo ratings yet
- Campos Haroldo de in Conversation PreviewDocument18 pagesCampos Haroldo de in Conversation PreviewManuel ColinaNo ratings yet