Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Fall Semester 2 Final Exam Study Guide
Uploaded by
Lauren BeckerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Fall Semester 2 Final Exam Study Guide
Uploaded by
Lauren BeckerCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Fall Semester 2 Final Exam Study Guide
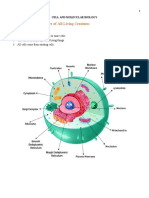
Unit 4: Ch. 8-10 – Cell Function
1. What kind of molecule is shown here? Where is the energy stored in this molecule?
2. What is an autotroph? A heterotroph? Give an example of each.
3. What are pigments? What is their role in photosynthesis?
4. How does chlorophyll affect the appearance of a plant?
5. What is the purpose of photosynthesis?
6. What are the products and reactants of photosynthesis?
7. What is the balanced equation for photosynthesis?
8. What are the factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis? (There are 3)
Chapter 9
9. How do organisms, such as humans, get the energy needed for their cells to survive?
10. What are the three reactions, in order, of aerobic (cellular) respiration?
11. How is cellular respiration different from fermentation?
12. What is the equation for cellular respiration?
13. What does aerobic mean? What does anaerobic mean? How do these terms relate to respiration
and fermentation?
14. How would you describe the relationship of photosynthesis and respiration? What affects
do they have on each other and the environment?
15. What organelle is responsible for carrying out respiration?
16. What is the first step in both cellular respiration and fermentation? What occurs during
this first step?
17. What follows glycolysis if oxygen is present? If it is absent?
18. During cellular respiration, how much ATP (approximately) is netted from each glucose?
19. What are the two main types of fermentation? What are their byproducts?
Chapter 10
20. How does diffusion affect large and small cells? How is this involved in cell division?
21. What is mitosis? What is the end result of mitosis?
22. What are chromosomes? Where are they found? When are they visible?
23. What are structures B in this diagram? What is structure A?
24. What are the phases of mitosis in order? What happens during each?
25. How does the number of chromosomes in the parent cell compare to the number of
chromosomes in the daughter cells during mitosis? How is this possible?
26. What is happening during stage “d” of the diagram
27. What is occurring during stage “a” of the diagram?
28. What stage is represented by the letter “b?” How about “e?”
29. What is shown in figure A above? What causes this?
Unit 5: Ch. 11-15 – Genetics & DNA
Chapter 11
30. What are genes? What are alleles? How are they different? Same?
31. What does homozygous mean? Heterozygous?
32. A breed of chicken shows codominance for feather color. One allele codes for black
feathers, another codes for white feathers. What color would a heterozygous chicken be?
33. What is diploid? What is haploid? Which is N? Which is 2N?
34. What is formed during meiosis? What can you say about the number of chromosomes in
the daughter cells at the end?
35. What phenotype would you expect to see in all of the offspring in the punnet square
shown here?
36. How many alleles do you get from each parent?
37. What process is shown here?
38. How many cells are formed at the end of meiosis? Are they identical?
39. Chapters 12 & 13
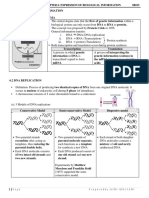
40. What structure/molecule is shown here? What is its shape?
41. What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
42. During replication, a DNA Polymerase reads the following DNA strand. Write in the
complementary strand that the DNA Polymerase would assemble.
43. ACTTGCGACGCGAGAATTCG
44. Is the strand of nucleic acid shown here DNA or RNA? How can you tell?
45. What are the functions of the three kinds of RNA? (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA)
46. What is protein synthesis? Walk through the steps from start to finish and identify the
molecules involved.
47. What is transcription? What is produced during transcription?
48. Using the key below, identify the amino acids coded for by each of the following codons.
a. GUC
b. CUC
c. UUG
d. UGA
e. UAG
f. UGG
49. What is translation? What is made? Where does it occur?
50. What information is coded for in your genes (DNA)?
51. What is the correct order of the following three terms? RNA, DNA, Proteins
52. What is a mutation?
Chapters 14 & 15
53. What is the probability that a child in humans will be male? Female?
54. Who is more likely to have a sex-linked trait on the X-chromosome? Why?
55. If the pedigree below shows the traits P and p, what is the genotype of individual 1?
Individual 3? Individual 8?
56. How many generations are shown in the pedigree above?
57. What is seen in this diagram?
58. What was the human genome project?
59. What is genetic engineering?
60. What is DNA fingerprinting and how does it work?
Unit 6: Ch. 16-19 - Evolution and Classification
Chapters 16-17
61. What is a gene pool?
62. What is a vestigial structure? What is a homologous structure? How are the two
similar/different?
63. How did Charles Darwin define fitness? How does that apply to natural selection?
64. What is a common ancestor? Why did Darwin claim all finches on the Galapagos came
from a common ancestor? How does this support evolution?
You might also like
- Sbi 4u Exam Review UpdateDocument2 pagesSbi 4u Exam Review UpdateKevin KocotNo ratings yet
- Bioscience Imp QuesDocument2 pagesBioscience Imp QuesdearsaswatNo ratings yet
- Histo Study Questions ListDocument2 pagesHisto Study Questions Listsayeda.raza24No ratings yet
- Biol 2110 Chapter 4 Study NotesDocument3 pagesBiol 2110 Chapter 4 Study NotesJunior HighNo ratings yet
- REVIEWDocument3 pagesREVIEWLovery BremNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions For Units 1 and 2: Unit 1Document7 pagesRevision Questions For Units 1 and 2: Unit 1api-26229242No ratings yet
- A Preap Fall Final ReviewDocument6 pagesA Preap Fall Final ReviewAsian PersonNo ratings yet
- Biology 101 Lab Exam 2 ReviewDocument4 pagesBiology 101 Lab Exam 2 ReviewSophie LimiNo ratings yet
- BIOL 3090 Study Guide for Exam 1Document5 pagesBIOL 3090 Study Guide for Exam 1anhminhandnamNo ratings yet
- Biology Midterm Exam Review Guide - The TOP 100 Questions Scientific Inquiry and Biological Principles (Chapter 1)Document4 pagesBiology Midterm Exam Review Guide - The TOP 100 Questions Scientific Inquiry and Biological Principles (Chapter 1)api-350761092No ratings yet
- AP Biology Name - Chapter 18 Guided Reading AssignmentDocument6 pagesAP Biology Name - Chapter 18 Guided Reading AssignmentRosenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Homework PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 9 Homework PDFRhonda JacobsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 AP Bio Study GuideDocument6 pagesChapter 18 AP Bio Study GuideHolly SullivanNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Name - Chapter 18 Guided Reading AssignmentDocument5 pagesAP Biology Name - Chapter 18 Guided Reading AssignmentJasonNo ratings yet
- Biology Important Questions: Tenth General ScienceDocument10 pagesBiology Important Questions: Tenth General ScienceNavyadeep SaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Key Concepts CH 5-8Document7 pagesUnit 2 Key Concepts CH 5-8Alvin AgollaNo ratings yet
- Biology Midterm Review 2023Document8 pagesBiology Midterm Review 2023beegirl954No ratings yet
- Cell Biology Questions: Functions, Structures & ProcessesDocument3 pagesCell Biology Questions: Functions, Structures & ProcessesSarah Mason100% (1)
- Bio 305 General Genetics Exam I ChecklisDocument2 pagesBio 305 General Genetics Exam I ChecklisChristian jade QuijanoNo ratings yet
- CHE 450 Biochemistry Final Exam Study GuideDocument8 pagesCHE 450 Biochemistry Final Exam Study Guidetlyons1188No ratings yet
- Syllabus in Biologyand Example Questions - Entrance Exam - TrakiaUniversity-2023Document4 pagesSyllabus in Biologyand Example Questions - Entrance Exam - TrakiaUniversity-2023Ruslana MilchevaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Cellular Energy and Cell Cycle Study Guide Honors BiologyDocument2 pagesUnit 3: Cellular Energy and Cell Cycle Study Guide Honors BiologyAakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ts SR Botany Imp QuestionsDocument5 pagesTs SR Botany Imp Questionssrneet555No ratings yet
- SBI4U0 Exam Review GuideDocument6 pagesSBI4U0 Exam Review GuideSukhvir AujlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Mia MistypuffNo ratings yet
- DNA's Code Through Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesDNA's Code Through Protein SynthesisCassandra KankamNo ratings yet
- 7th Science Final Exam Study GuideDocument8 pages7th Science Final Exam Study Guideapi-233736029No ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2008 Class - XII Subject - Biology: General InstructionsDocument3 pagesSample Paper - 2008 Class - XII Subject - Biology: General InstructionsChandan Kumar RoyNo ratings yet
- Biology 11thDocument5 pagesBiology 11thkaka849296No ratings yet
- 12th Bio Preboard 1 2023-24Document6 pages12th Bio Preboard 1 2023-24Mubashshir Al NahyanNo ratings yet
- Exam 6 GuideDocument5 pagesExam 6 Guidetalbw05No ratings yet
- Genetics and Evolution Unit NotesDocument19 pagesGenetics and Evolution Unit NotesJames OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 HomeworkDocument5 pagesChapter 1-3 HomeworkMatthew DriscollNo ratings yet
- 105期末Document7 pages105期末Rose FuNo ratings yet
- Biology: Cbse Class Xii - Board Exams 2021 Most Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesBiology: Cbse Class Xii - Board Exams 2021 Most Important QuestionsSwikritiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (Theory) : Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsDocument21 pagesBIOLOGY (Theory) : Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsWajahat AliNo ratings yet
- Final Term XI_26 marchDocument6 pagesFinal Term XI_26 marchavishank584No ratings yet
- Test 10 A Bio Q.paperDocument1 pageTest 10 A Bio Q.paperrahul kardakNo ratings yet
- Biology EOC Review GuideDocument13 pagesBiology EOC Review GuidedivaNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA, Cell Cycle, Mitosis & Meiosis ComparisonDocument3 pagesDNA, RNA, Cell Cycle, Mitosis & Meiosis ComparisonMaiki BodkinNo ratings yet
- Biology Eoc Study GuideDocument6 pagesBiology Eoc Study Guideapi-350761092No ratings yet
- Punjab College of Commerce Cantt Campus Golara Morr Assignment Ch.4 The CellDocument2 pagesPunjab College of Commerce Cantt Campus Golara Morr Assignment Ch.4 The CellMuhammad AtifNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Final Exam Study QuestionsDocument2 pagesComprehensive Final Exam Study QuestionsRonnieNo ratings yet
- Biology TestDocument5 pagesBiology TestVanshika BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Bio 6204 Quiz1,2&PrelimsDocument4 pagesBio 6204 Quiz1,2&PrelimsReynante RamosNo ratings yet
- 2710BBS Microbial Physiology Sem 1, 2003Document3 pages2710BBS Microbial Physiology Sem 1, 2003Mei MisakiNo ratings yet
- Genetics Study Guide Answers 1Document2 pagesGenetics Study Guide Answers 1KellyNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 - Principles of Inheritance - ASSIGNMENTDocument4 pagesCh-5 - Principles of Inheritance - ASSIGNMENTReet SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Collegedekho 240315 212806Document6 pagesCollegedekho 240315 212806Raja KumarNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1200: Human Biology Study Guide For EXAM 1 - Chapters 1 Through 3Document13 pagesBIOL 1200: Human Biology Study Guide For EXAM 1 - Chapters 1 Through 3emmaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 2 Fall 2011Document6 pagesStudy Guide 2 Fall 2011Raquel RenéNo ratings yet
- Biology Part 2 Short QuestionDocument7 pagesBiology Part 2 Short QuestionuzzikshaperNo ratings yet
- DAT Practice TestDocument75 pagesDAT Practice TestJustinTsui88% (8)
- Diagnostic Test Questions NewDocument74 pagesDiagnostic Test Questions NewRoi Patrick Albaladejo AponteNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument52 pagesScienceVannyNo ratings yet
- Bumdc 2015Document6 pagesBumdc 2015Saqib KhaskheliNo ratings yet
- Gamete cells undergo meiosisDocument2 pagesGamete cells undergo meiosisApichayaNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 6 Study Guide AnswersDocument3 pagesBiology Unit 6 Study Guide AnswersmisterbrownerNo ratings yet
- Ew Notes I Hate It HereDocument1 pageEw Notes I Hate It HereLauren BeckerNo ratings yet
- School dress codes often target females and limit self-expressionDocument1 pageSchool dress codes often target females and limit self-expressionLauren BeckerNo ratings yet
- BioDocument5 pagesBioLauren BeckerNo ratings yet
- Editor WilburDocument1 pageEditor WilburLauren BeckerNo ratings yet
- The Art of Being Yourself Despite CriticismDocument3 pagesThe Art of Being Yourself Despite CriticismLauren BeckerNo ratings yet
- CorruptionDocument3 pagesCorruptionLauren BeckerNo ratings yet
- But Time Moves On FasterDocument1 pageBut Time Moves On FasterLauren BeckerNo ratings yet
- DonDocument1 pageDonLauren BeckerNo ratings yet
- K'Nex DNA Replication Transcription Teacher GuideDocument46 pagesK'Nex DNA Replication Transcription Teacher GuideScience House100% (2)
- Python Exercises PDFDocument138 pagesPython Exercises PDFAna CardenasNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (1)
- HEC Revised Biotech SyllabusDocument56 pagesHEC Revised Biotech SyllabuswaheedgulNo ratings yet
- Bio 112 UBC MT2 Practice Exam Qs - Oct25th2013Document13 pagesBio 112 UBC MT2 Practice Exam Qs - Oct25th2013Cherica Oñate0% (1)
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument44 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceAnurag GautamNo ratings yet
- Compressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015Document10 pagesCompressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015SYAZWAN BIN MUSTAFA MoeNo ratings yet
- Theories of the Origin of LifeDocument3 pagesTheories of the Origin of LifeFelyn Roseann AretaNo ratings yet
- Biology EOC Review ALL StandardsDocument83 pagesBiology EOC Review ALL StandardsmspallardNo ratings yet
- DNA Molecule & Central DogmaDocument43 pagesDNA Molecule & Central DogmaJoanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- Chem 205 Lecture 5: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids (Derived From Voet, 2011)Document37 pagesChem 205 Lecture 5: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids (Derived From Voet, 2011)Rab BaloloyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Bozeman WorksheetsDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Bozeman Worksheetsa accountNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein: How Genes WorkDocument58 pagesFrom Gene To Protein: How Genes WorkGabe GallagherNo ratings yet
- Replication, Transcription, Translation QuizDocument4 pagesReplication, Transcription, Translation QuizAakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology Unit 1 Notes PDFDocument67 pagesEdexcel Biology Unit 1 Notes PDFbekoNo ratings yet
- Drugs in The Pipeline For HBVDocument21 pagesDrugs in The Pipeline For HBVMarius StancuNo ratings yet
- Booklet The Structures of LifeDocument66 pagesBooklet The Structures of LifeIrving EuanNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ChemistryDocument37 pagesDNA Structure and ChemistryDozdi100% (4)
- 6.2 D Protein Synthesis: ContosoDocument13 pages6.2 D Protein Synthesis: Contosoruva gundaNo ratings yet
- Students discuss biology and genetics concepts in an online classDocument8 pagesStudents discuss biology and genetics concepts in an online classXimenes VitalNo ratings yet
- Nssbio3e Sb1a Ch02 eDocument44 pagesNssbio3e Sb1a Ch02 emyaleung1221No ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document4 pagesChapter 03Teehee JonesNo ratings yet
- BioK DP Notes 2.7Document18 pagesBioK DP Notes 2.7Lal ÖzşahinNo ratings yet
- Molecular DiagnosticsDocument583 pagesMolecular DiagnosticsAnthony93% (14)
- EPISSAGE À LIRE Rogalska Et Al. Regulatation of pre-mRNA Splicing. Nat Rev Gen 2022Document19 pagesEPISSAGE À LIRE Rogalska Et Al. Regulatation of pre-mRNA Splicing. Nat Rev Gen 2022Léo VidoniNo ratings yet
- Essential Unani Medicines LRDocument57 pagesEssential Unani Medicines LRDrRaghvendra Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Bioteknologi B2-24 RapportDocument70 pagesBioteknologi B2-24 RapportPeter Nørgaard MortensenNo ratings yet
- DNA's Code Through Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesDNA's Code Through Protein SynthesisCassandra KankamNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument7 pagesGene ExpressionTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Regulation - Lactase - Gene - Click - Learn - WorksheetDocument3 pagesRegulation - Lactase - Gene - Click - Learn - WorksheetSophia BrannemanNo ratings yet