Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GenMath MIDTERMS
Uploaded by
PK Adelantar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesSTEM
Original Title
GenMath-MIDTERMS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSTEM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesGenMath MIDTERMS
Uploaded by
PK AdelantarSTEM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
General Mathematics Intercepts- are the points of intersection of
RATIONAL FUNCTIONS the graph of a function and an axis.
Rational equations- An equation that The y-intercept of the graph of a rational
contains rational expressions is referred to function 𝑟(𝑥), if it exists, occur at 𝒓(𝟎),
as rational equation. provided that 𝒓(𝒙) is defined at 𝒙 = 𝟎
Rational Inequality- An inequality that The x-intercept of the graph of a rational
contains rational expressions is referred to function 𝑟 𝑥 , if it exist, occurs at the zeros of
as rational inequality. the numerator that are not zeroes of the
Rational Functions-A rational functions, denominators.
𝑟(𝑥), is a function of the form 𝑟 𝑥 = 𝑝(𝑥)/𝑞(𝑥)
Where 𝑝(𝑥) and 𝑞(𝑥) are polynomial Asymptotes
functions, and 𝑞 𝑥 ≠ 0 Zero of a rational function- zero of the
The domain of 𝑟(𝑥) is the set of real numerator but not zero of the denominator
numbers such that 𝑞 𝑥 is not zero.
Asymptote-an imaginary line to which a
In dealing with the a rational function, it is graph gets closer and closer as it increases
often helpful to find values for which the or decreases its value without limit
rational function is undefined. One will find Vertical asymptote-find the zeroes of the
that the graph of the rational function denominator that are not zeroes of the
approaches lines that contains these values numerator
for which the rational function is undefined; Horizontal asymptote-compare the degree
hence the graph does not cross these lines. of the numerator 𝑛 and the degree of the
denominator 𝑑.
Ex. The function 𝑓 𝑥 = 1/𝑥 which can be If 𝑛 < 𝑑, the horizontal asymptote is 𝑦 = 0
represented by the equation 𝑦 = 1/𝑥 is not If 𝑛 = 𝑑, the horizontal asymptote is 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑛/𝑎𝑑
defined when 𝑥 = 0. The graph of the .
equation line 𝑥 = 0 will not be crossed by the If 𝑛 > 𝑑, there is no horizontal asymptote
graph of 𝑓 𝑥 = 1/𝑥
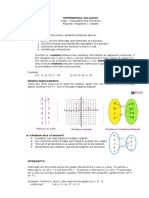
Domain-A rational function, which is ratio of INVERSE FUNCTION
two polynomials functions in many cases, is A function y = f(x) with domain D is
not a polynomial functions. Unlike a one-to-one on D if and only if for every x1
polynomial function which is defined for and x2 in D, f(x1 ) = f(x2 ) implies that x1 =
every real number, a rational function is x2 .
defined only when the its denominator is not
equal to zero. This implies that the domain Function- a mapping from its domain to its
of a rational function is the set of all real range so that each element, x, of the
numbers, except those that make the domain is mapped to one, and only one,
denominator zero element, f(x), of the range
Range-The range can be determined by
replacing 𝑓(𝑥) by 𝑦 and solving 𝑥 in terms and A function is one-to-one if each element
then find the restrictions f(x) of the range is mapped from one, and
only one, element, x, of the domain
EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS
Horizontal Line Test-A function y = f(x) is Exponential- often associated with any
one-to-one if and only if no horizontal line phenomenon characterized by rapid growth
intersects the graph of y = f(x) in more than with alarming consequences.
one point
Every function y = f(x) has an inverse
relation x = f(y). An exponential function is defined by the
rule: 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑎^𝑥 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑎 > 0 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑎 ≠ 1
The domain of the inverse relation is the a is the base and x is the exponent.The
range of the original function. The range of exponent must be a variable
the inverse relation is the domain of the
original function Exponential function-an equation having a
variable in the exponent.
For a function y = f(x), the inverse relation
of f is a function if and only if f is The property for exponential equations
one-to-one. Let a, b and c be real numbers and a≠ 0 .
For a function y = f(x), the inverse relation Then, 𝑎^ 𝑏 = 𝑎^ 𝑐. If and only if b=c.
of f is a function if and only if the graph of f
passes the horizontal line test. Exponential inequality-An equality in one
If f is one-to-one, the inverse relation of f is variable having a variable in the exponent
a function called the inverse function of f. Rules for solving an exponential
The inverse function of y = f(x) is written y = inequality
f^-1 (x) i. If the same real number is added to or
subtracted from both sides of an inequality,
To find the inverse of a relation the sense of the inequality is not changed.
algebraically, interchange x and y and ii. If both sides of an inequality are multiplied
solve for y. Change the function notation by or divided by the same positive real
number, the sense of inequality is not
Composition of a function and its changed.
inverse iii. If both sides of an inequality are
properties: multiplied by or divided by the same
i. 𝑓 −1 ∘ 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 for all 𝑥 in the domain of 𝑓, negative real number, the sense of the
and inequality is changed
ii. 𝑓 ∘ 𝑓 −1 𝑥 = 𝑥 for all 𝑥 in the domain of 𝑓 −1
• The inverse of the ordered pairs (x, y) is
the set of all ordered pairs (y, x).
• The Domain of the function is the range of
the inverse and the Range of the function is
the Domain of the inverse.
• Symbol: 1 f x( )
− In other words, switch the x’s and y’s!
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- PERTEMUAN III EVEN AND ODD FUNCTIONSDocument11 pagesPERTEMUAN III EVEN AND ODD FUNCTIONSMadinahNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics PowerPointDocument20 pagesGeneral Mathematics PowerPointMarie DirmaNo ratings yet
- GenMath ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenMath Reviewerinayeon797No ratings yet
- Module 4 - Inverse FunctionDocument14 pagesModule 4 - Inverse FunctionkayiNo ratings yet
- Mate VocabDocument1 pageMate VocabRiccardo LopezNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument5 pagesDifferentiationIH MarufNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 Operations On FunctionsDocument11 pagesLesson 1.3 Operations On FunctionsJomel RositaNo ratings yet
- MATHDocument29 pagesMATHInol DuqueNo ratings yet
- Function: Fernando Toding Bua' Ayu Andini Andry Yusdi Akidah Amaliah Jasrina Jumardi HasanDocument19 pagesFunction: Fernando Toding Bua' Ayu Andini Andry Yusdi Akidah Amaliah Jasrina Jumardi HasanFernando Toding BuaNo ratings yet
- Functions ExplainedDocument3 pagesFunctions ExplainedThe InvincibleNo ratings yet
- W#1 M#2 Types of FunctionsDocument10 pagesW#1 M#2 Types of FunctionsIsabel PerezNo ratings yet
- Logarithmic Functions Graphs and EquationsDocument22 pagesLogarithmic Functions Graphs and Equationscass dumpNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Functions Definitions:: 5. Determine Algebraically Whether Is Even, Odd, or NeitherDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of Functions Definitions:: 5. Determine Algebraically Whether Is Even, Odd, or NeitherJohn Angelo EraNo ratings yet
- Inverse Function: DefinitionsDocument11 pagesInverse Function: Definitionsjbahalkeh100% (1)
- Graphs of FunctionsDocument4 pagesGraphs of Functionsapi-174648067No ratings yet
- Gen MathDocument1 pageGen Mathreyn mendozaNo ratings yet
- Intercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Rational FunctionsDocument33 pagesIntercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Rational Functionsaiza100% (2)
- Polynomial FunctionsDocument31 pagesPolynomial FunctionsAdnan BukhariNo ratings yet
- 9 Elementary FunctionsDocument13 pages9 Elementary FunctionsinmaillanNo ratings yet
- Maths For Econ - Econ 1003 NotesDocument18 pagesMaths For Econ - Econ 1003 NotesamandaNo ratings yet
- Class 12th FormulaeDocument39 pagesClass 12th Formulaesushil tripathiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Gen MathDocument2 pagesReviewer in Gen MathTrina Venise BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- TRIGODocument7 pagesTRIGOizzatisafeeNo ratings yet
- 14 - Rational Function - MC - Guide and LabDocument13 pages14 - Rational Function - MC - Guide and LabElsa BrounsNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General MathematicsDocument6 pagesReviewer in General Mathematicskimseonwoo01130No ratings yet
- General Math 11 Q1 LAS Week3Document14 pagesGeneral Math 11 Q1 LAS Week3Ruben Rosendal De Asis100% (1)
- Math Written TaskDocument6 pagesMath Written TaskKanika KumarNo ratings yet
- So How Do We Find The Inverse of A Function?Document6 pagesSo How Do We Find The Inverse of A Function?sherryl v floresNo ratings yet
- IB Math AA HL Functions NotesDocument2 pagesIB Math AA HL Functions Notesmohammmed irshadNo ratings yet
- Summary (Preliminaries)Document16 pagesSummary (Preliminaries)Beyzanur BektaşNo ratings yet
- Steps On Finding Zeroes of Rational Functions and Graphing Rational FunctionsDocument29 pagesSteps On Finding Zeroes of Rational Functions and Graphing Rational FunctionsJeric ColumbinoNo ratings yet
- Section 3.4 Rational Functions: Example 1Document18 pagesSection 3.4 Rational Functions: Example 1api-362016104No ratings yet
- Math Week 6 NotesDocument3 pagesMath Week 6 Notesapi-490233660No ratings yet
- De La Salle University Senior High Math RequirementsDocument5 pagesDe La Salle University Senior High Math RequirementsAaron TingNo ratings yet
- The Graphical Interpretation of The Function Properties: Increasing, Decreasing, and Constant FunctionsDocument3 pagesThe Graphical Interpretation of The Function Properties: Increasing, Decreasing, and Constant FunctionsTavi FronieNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics ReviewerDocument2 pagesGeneral Mathematics ReviewerAechey FrandoNo ratings yet
- Rational FunctionDocument14 pagesRational Functionawyne nozulNo ratings yet
- Many FormulasDocument11 pagesMany FormulasDillep NandaNo ratings yet
- KEY CONCEPTS OF RATIONAL FUNCTIONSDocument10 pagesKEY CONCEPTS OF RATIONAL FUNCTIONSRobert John Basia BernalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 FunctionsDocument40 pagesLesson 2 Functionsagarao.kieshelynNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONSDocument2 pagesFUNCTIONSFlamerisse YoonNo ratings yet
- Inverse functions explainedDocument3 pagesInverse functions explainedRodante P Hernandez Jr.No ratings yet
- General Mathematics - Q1 Week 3Document8 pagesGeneral Mathematics - Q1 Week 3Johnson BautistaNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument2 pagesRelations and FunctionsCheMNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 0.4 Inverse Functions Inverse Trigonometric Functions of Mat 120 of MTMDocument7 pagesLecture 2 0.4 Inverse Functions Inverse Trigonometric Functions of Mat 120 of MTMSamiul Hasnat Taseen 2233054642No ratings yet
- FUNCTIONS & GRAPHSDocument4 pagesFUNCTIONS & GRAPHSJane Anonas100% (8)
- Chapter 1 AdvFun Notes Feb 1Document29 pagesChapter 1 AdvFun Notes Feb 1jackson maNo ratings yet
- Vertical AsymptoteDocument6 pagesVertical AsymptoteSarahNo ratings yet
- This Inverse May NOT Be A Function.Document5 pagesThis Inverse May NOT Be A Function.Apollo GumaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Exponential FunctionsDocument29 pagesLesson 4 - Exponential FunctionsFregie LerionNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS: Domains, Ranges, Intercepts and Asymptotes of FunctionsDocument11 pagesDIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS: Domains, Ranges, Intercepts and Asymptotes of FunctionsKarenNo ratings yet
- General Math Week 5 Review on Rational Functions and Inverse FunctionsDocument23 pagesGeneral Math Week 5 Review on Rational Functions and Inverse FunctionsL AlcosabaNo ratings yet
- Section1 2-FilledDocument9 pagesSection1 2-FilledSononameNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem MathDocument15 pages2nd Sem MathJayesh khachaneNo ratings yet
- Domain and Range FunctionsDocument17 pagesDomain and Range FunctionsRiot ShadowNo ratings yet
- Derivatives and Integrals EssayDocument13 pagesDerivatives and Integrals Essayapi-282374174No ratings yet
- Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument3 pagesExponential and Logarithmic FunctionsManel KricheneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Vocabulary ListDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Vocabulary ListLeetz123456No ratings yet
- Midterms Reviewer ORAL COM.Document4 pagesMidterms Reviewer ORAL COM.PK AdelantarNo ratings yet
- UCSP MidtermsDocument11 pagesUCSP MidtermsPK AdelantarNo ratings yet
- Midterms Reviewer P.E.Document3 pagesMidterms Reviewer P.E.PK AdelantarNo ratings yet
- Els MidtermsDocument9 pagesEls MidtermsPK AdelantarNo ratings yet
- PAGSAN-LC DirectoryDocument38 pagesPAGSAN-LC Directoryliezl vegaNo ratings yet
- Newton's MethodDocument3 pagesNewton's MethodRJ BedañoNo ratings yet
- Matlab Report File: Amity School of Engineering and TechnologyDocument8 pagesMatlab Report File: Amity School of Engineering and TechnologySagar WadhwaNo ratings yet
- TG-Basic Cal Q3 W22Document2 pagesTG-Basic Cal Q3 W22JohnNo ratings yet
- Arihant 41 Years MathsDocument625 pagesArihant 41 Years MathsBhavani Vuppuloju100% (1)
- Exponential Growth & Compound InterestDocument116 pagesExponential Growth & Compound InterestronnelNo ratings yet
- Exponential Functions: What I Need To KnowDocument44 pagesExponential Functions: What I Need To KnowManelyn TagaNo ratings yet
- 2203BPS - Final Exam2009 - Solutions (1) 2Document7 pages2203BPS - Final Exam2009 - Solutions (1) 2samNo ratings yet
- Winitzki - No Distributional Limit For Delta Function of Complex ArgumentsDocument2 pagesWinitzki - No Distributional Limit For Delta Function of Complex ArgumentswinitzkiNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Solving Exponential Equations: Essential QuestionDocument6 pages6.5 Solving Exponential Equations: Essential QuestionJoanna Marie BayleNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus G11 Q1 Mod2 The Derivative v5 4.editedlanguageDocument57 pagesBasic Calculus G11 Q1 Mod2 The Derivative v5 4.editedlanguageYevrah HarveyNo ratings yet
- Complex Number DefinitionDocument133 pagesComplex Number DefinitionKHaliD KareemiNo ratings yet
- TM1 - Turbo Integrator FuctionsDocument22 pagesTM1 - Turbo Integrator FuctionssomojyotiNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen Math Ems AnnuitiesDocument13 pagesDLL Gen Math Ems AnnuitiesFreyy Agad Maligot0% (1)
- Sasi NotesDocument80 pagesSasi Notess skNo ratings yet
- Population in China - SolutionDocument8 pagesPopulation in China - SolutionZikai WangNo ratings yet
- Basic MT F3 Notes PDFDocument297 pagesBasic MT F3 Notes PDFClemence TafitiNo ratings yet
- Senior High School General Mathematics MELCDocument5 pagesSenior High School General Mathematics MELCElle EtisegNo ratings yet
- Solve and graph exponential equations and inequalitiesDocument11 pagesSolve and graph exponential equations and inequalitiesBeatriceCarlisleNo ratings yet
- Table of SpecificationDocument6 pagesTable of SpecificationMark Jayson BacligNo ratings yet
- Laplace DistributionDocument2 pagesLaplace Distributionibrahim aboalazmNo ratings yet
- 05 Reliability of SystemsDocument11 pages05 Reliability of SystemsrogeriojuruaiaNo ratings yet
- Manual Sofistik Basics - 2022Document54 pagesManual Sofistik Basics - 2022JEMAYERNo ratings yet
- Computational Physics Course DescriptionDocument55 pagesComputational Physics Course DescriptionpticicaaaNo ratings yet
- Production Performance of HyCole New Zealand WhiteDocument9 pagesProduction Performance of HyCole New Zealand Whiteel KamalNo ratings yet
- Complex Analysis - Christian Berg PDFDocument192 pagesComplex Analysis - Christian Berg PDFHenry RojasNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Grade11 Syllabus PDFDocument11 pagesGeneral Mathematics Grade11 Syllabus PDFlip87% (15)
- Practice Problems Assignment Problems: NotesDocument8 pagesPractice Problems Assignment Problems: NotesNardo Gunayon FinezNo ratings yet
- Average Rate of Change Common Core Algebra 1 HomeworkDocument8 pagesAverage Rate of Change Common Core Algebra 1 Homeworktrrpeptif100% (1)
- College Algebra SyllabusDocument3 pagesCollege Algebra Syllabusapi-270071301No ratings yet