Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration Exercise
Uploaded by
Sacchin Cepal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThe document discusses respiration and how it relates to exercise. Respiration is the process by which organisms produce energy through the oxidation of glucose and release of carbon dioxide. During exercise, the heart rate and breathing rate increase to supply more oxygen to working muscles and remove more carbon dioxide from the blood. Exercise strengthens the heart and lungs to more efficiently circulate oxygen and remove waste throughout the body.
Original Description:
Original Title
Integrated Science Lab#2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses respiration and how it relates to exercise. Respiration is the process by which organisms produce energy through the oxidation of glucose and release of carbon dioxide. During exercise, the heart rate and breathing rate increase to supply more oxygen to working muscles and remove more carbon dioxide from the blood. Exercise strengthens the heart and lungs to more efficiently circulate oxygen and remove waste throughout the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesRespiration Exercise
Uploaded by
Sacchin CepalThe document discusses respiration and how it relates to exercise. Respiration is the process by which organisms produce energy through the oxidation of glucose and release of carbon dioxide. During exercise, the heart rate and breathing rate increase to supply more oxygen to working muscles and remove more carbon dioxide from the blood. Exercise strengthens the heart and lungs to more efficiently circulate oxygen and remove waste throughout the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Discussion:
A process in living organisms involving the production of energy, typically with
the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide from the oxidation of
complex organic substances.The word equation for aerobic respiration is: glucose +
oxygen → carbon dioxide + water (+ energy released) You need to be able to
recognise the chemical symbols: C 6H 12O 6 + 6O 2 → 6CO 2 + 6H 2O. Respiration is a
series of reactions, but this summarises the overall process.A rhythmical throbbing
of the arteries as blood is propelled through them, typically as felt in the wrists
or neck.Cellular respiration is this process in which oxygen and glucose are used
to create ATP, carbon dioxide, and water. ATP, carbon dioxide, and water are all
products of this process because they are what is created. Carbon dioxide is
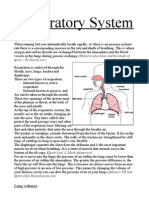
released as a gas when you exhale.A person's respiratory rate is the number of
breaths you take per minute. The normal respiration rate for an adult at rest is 12
to 20 breaths per minute. A respiration rate under 12 or over 25 breaths per minute
while resting is considered abnormal.The heart rate increases during exercise. The
rate and depth of breathing increases - this makes sure that more oxygen is
absorbed into the blood, and more carbon dioxide is removed from it. The rate of
breathing can be measured by counting the number of breaths in one minute.During
exercise there is an increase in physical activity and muscle cells respire more
than they do when the body is at rest. The heart rate increases during exercise.
The rate and depth of breathing increases - this makes sure that more oxygen is
absorbed into the blood, and more carbon dioxide is removed from it.During
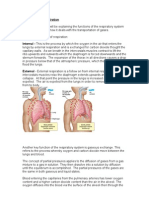
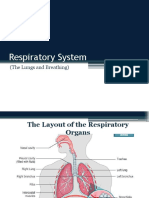
exercise, two of the important organs of the body come into action: the heart and
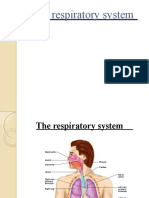
the lungs. The lungs bring oxygen into the body, to provide energy, and remove
carbon dioxide, the waste product created when you produce energy. The heart pumps
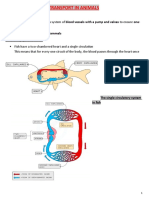
the oxygen to the muscles that are doing the exercise.The heart rate increases
during exercise. The rate and depth of breathing increases - this makes sure that
more oxygen is absorbed into the blood, and more carbon dioxide is removed from it.
The rate of breathing can be measured by counting the number of breaths in one
minute.Your heart, which is a muscular organ, gets a workout during exercise,
too.When you start your exercise, your muscles will start to work harder and demand
more oxygen. This demand will cause sympathetic nerves to stimulate the heart to
beat faster and with more force to increase overall blood flow.The heart must beat
faster during exercise because by increasing the heart rate, the body is able to
increase cardiac output and deliver the necessary blood flow to the muscles. During
exercise the body's muscles increase their activity level and consume more
oxygen.The best places to take your pulse are at your wrist, inside the elbow, at
the side of your neck or on the top of your foot, according to The American Heart
Association. You can also take your pulse at your groin, on your temple or behind
your knees. The pulse felt on the neck is called the carotid pulse.During exercise,
my pulse was very fast. But after when I relaxed it got back to its normal
beat.Your pulse is your heart rate, or the number of times your heart beats in one
minute. Pulse rates vary from person to person. Your pulse is lower when you are at
rest and increases when you exercise (more oxygen-rich blood is needed by the body
when you exercise).The lungs bring oxygen into the body when breathing in and send
carbon dioxide out of the body when breathing out. Carbon dioxide is a waste gas
produced by the cells of the body. ... The lungs add oxygen to the blood and remove
carbon dioxide in a process called gas exchange.Gas exchange takes place in the
millions of alveoli in the lungs and the capillaries that envelop them. As shown
below, inhaled oxygen moves from the alveoli to the blood in the capillaries, and
carbon dioxide moves from the blood in the capillaries to the air in the
alveoli.Just as exercise strengthens other muscles in your body, it helps your
heart muscle become more efficient and better able to pump blood throughout your
body. This means that the heart pushes out more blood with each beat, allowing it
to beat slower and keep your blood pressure under control.Daily physical activity
can help prevent heart disease and stroke by strengthening your heart muscle,
lowering your blood pressure, raising your high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels
(good cholesterol) and lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels (bad
cholesterol), improving blood flow, and increasing your heart's working capacity.
Optimizing each of these factors can provide additional benefits of decreasing the
risk for Peripheral Vascular Disease.Exercise has many benefits.Aerobic exercise
(which relies on the heart pumping oxygen to the muscles) can be beneficial for the
heart. It improves blood circulation, strengthens the heart muscle, reduces risks
of heart disease (by reducing abnormally high blood pressure) and can reduce some
symptoms of heart failure.An increase in preload results in an increased force of
contraction by Starling's law of the heart; this does not require a change in
contractility. An increase in afterload will increase contractility (through the
Anrep effect). An increase in heart rate will increase contractility (through the
Bowditch effect).It promotes good body structure and proper transportation of
blood.
Discussion 2 test:
A process in living organisms involving the production of energy, typically with
the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide from the oxidation of
complex organic substances.The word equation for aerobic respiration is: glucose
oxygen → carbon dioxide water ( energy released) You need to be able to recognise
the chemical symbols: C 6H 12O 6 6O 2 → 6CO 2 6H 2O. Respiration is a series of
reactions, but this summarises the overall process.A rhythmical throbbing of the
arteries as blood is propelled through them, typically as felt in the wrists or
neck.Cellular respiration is this process in which oxygen and glucose are used to
create ATP, carbon dioxide, and water. ATP, carbon dioxide, and water are all
products of this process because they are what is created. Carbon dioxide is
released as a gas when you exhale.A person's respiratory rate is the number of
breaths you take per minute. The normal respiration rate for an adult at rest is 12
to 20 breaths per minute. A respiration rate under 12 or over 25 breaths per minute
while resting is considered abnormal.The heart rate increases during exercise. The
rate and depth of breathing increases - this makes sure that more oxygen is
absorbed into the blood, and more carbon dioxide is removed from it. The rate of
breathing can be measured by counting the number of breaths in one minute.During
exercise there is an increase in physical activity and muscle cells respire more
than they do when the body is at rest.
You might also like
- Heart Rate and Breathing Lab 1 - AgsaldaDocument4 pagesHeart Rate and Breathing Lab 1 - AgsaldaEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Cyndy Trimm Healing PrayerDocument5 pagesCyndy Trimm Healing Prayermazzagra100% (3)
- NEJM Case Report 40-2017Document10 pagesNEJM Case Report 40-2017A. Rauf100% (1)
- Bioe 310 Project 3Document29 pagesBioe 310 Project 3api-364332579No ratings yet
- AerobicsDocument3 pagesAerobicsMark PetillaNo ratings yet
- Pen AerobicDocument3 pagesPen AerobicMiriam Saena EscarlosNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Exercise DefinitionDocument31 pagesAerobic Exercise Definitiontanishka SinghalNo ratings yet
- AerobicsDocument4 pagesAerobicsmyraturaNo ratings yet
- 11 Lung PhysiologyDocument14 pages11 Lung PhysiologyGlen UrbaniNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesEnhanced Science ReviewerJaqueline Benj OftanaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology PPT (27 September 2018)Document72 pagesExercise Physiology PPT (27 September 2018)Surya Diatmika100% (1)
- Changes of O2 Delievry To Muscle During ExerciseDocument21 pagesChanges of O2 Delievry To Muscle During Exercisealikhaqaan77No ratings yet
- Benefits of Training Camp_Yanovsky_1C CompletedDocument14 pagesBenefits of Training Camp_Yanovsky_1C CompletedteachernadiazaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Prelims ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience 9 Prelims ReviewergutierremilfordNo ratings yet
- Social and Preventative Medicine PresentationDocument10 pagesSocial and Preventative Medicine PresentationSarafina BowenNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ExerciseDocument13 pagesBenefits of ExerciseMukesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesRespiratory System Structure and FunctionRavi BhollahNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System During ExerciseDocument2 pagesCirculatory System During Exercisecassidy conchaNo ratings yet
- Science StudyDocument24 pagesScience Studypomeru.mandhadiNo ratings yet
- Analogy For Understanding The Regulation of Heart RateDocument4 pagesAnalogy For Understanding The Regulation of Heart RateTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Cardiorespiratory SystemDocument4 pagesUnderstanding the Cardiorespiratory SystemHeisel Hernandez LopezNo ratings yet
- Biology ScienceDocument9 pagesBiology SciencetalaNo ratings yet
- 9 RespirationDocument3 pages9 RespirationKavin ManimaranNo ratings yet
- MylesDocument9 pagesMylesMyless MukendiNo ratings yet
- Cardio Respiratory Endurance Mam PascoDocument13 pagesCardio Respiratory Endurance Mam PascoDavid GoliathNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Circulatory System P.EDocument10 pagesGroup 1 Circulatory System P.EGerardo CarreonNo ratings yet
- ST12P3 Taburnal, Marjorie Mae - PT 4.3 General Biology 2Document3 pagesST12P3 Taburnal, Marjorie Mae - PT 4.3 General Biology 2Marjorie Mae AmodiaNo ratings yet
- 2LO2Document3 pages2LO2Tan SinCosNo ratings yet
- 3 Blood Flow Calcs, Exercise - Metabolism HWDocument1 page3 Blood Flow Calcs, Exercise - Metabolism HWJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and BreathingDocument35 pagesThe Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and BreathingScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Human Body Evidence 2Document10 pagesHuman Body Evidence 2ashley UsNo ratings yet
- Respiration and BreathingDocument57 pagesRespiration and BreathingHarvagale BlakeNo ratings yet
- The Science of Running ExplainedDocument6 pagesThe Science of Running Explaineducing_33No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument25 pagesRespiratory SystemAnonymous 5hYhEkINo ratings yet
- Physiology WorkshopDocument63 pagesPhysiology WorkshopdegwiiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid gland and hormones regulate metabolismDocument21 pagesThyroid gland and hormones regulate metabolismJay Lure BaguioNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Document3 pagesBiology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Joy-Ann NuptialNo ratings yet
- How Exercise Improves the Cardiorespiratory SystemDocument15 pagesHow Exercise Improves the Cardiorespiratory SystemBASAVARAJ100% (1)
- Body Systems and ExerciseDocument15 pagesBody Systems and ExerciseMichael GuzikNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesTamisha JacobsNo ratings yet
- Assignment Respiratory During ExerciseDocument3 pagesAssignment Respiratory During Exercisedomhughes1093No ratings yet
- 8c Summary SheetsDocument2 pages8c Summary SheetslNo ratings yet
- Task Unit 12 - Group 1Document6 pagesTask Unit 12 - Group 1siti zaliaNo ratings yet
- Evens RespiortyDocument4 pagesEvens RespiortyamyhowarthNo ratings yet
- Heartrate and ExerciseDocument11 pagesHeartrate and ExerciseJay Queue JonnyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac and Circulatory Adaptation To ExerciseDocument31 pagesCardiac and Circulatory Adaptation To ExerciseShadow TiNo ratings yet
- Mutuc, Mariel M. (Pe-I)Document2 pagesMutuc, Mariel M. (Pe-I)MARIEL MUTUCNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-343368893No ratings yet
- How Exercise Boosts Health in Just 40 CharactersDocument17 pagesHow Exercise Boosts Health in Just 40 CharactersAminu IdrisNo ratings yet
- Breathing: Breathing Is The Process That Moves Air in and Out of The LungsDocument5 pagesBreathing: Breathing Is The Process That Moves Air in and Out of The LungsArief Rachman WiladisastraNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Breathing ExplainedDocument5 pagesMechanics of Breathing ExplainedMark Lyndon M OrogoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System NotesDocument3 pagesRespiratory System NotesNilar SanNo ratings yet
- Process of BreathingDocument3 pagesProcess of BreathingssmaddiNo ratings yet
- Human Breathing CirculatoryDocument4 pagesHuman Breathing CirculatoryRommel BauzaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pages4.2 - Respiratory SystemBenJenkinsNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Blood Pressure ReportDocument8 pagesMeasurement of Blood Pressure ReportESTHER WONG TZE YIING -No ratings yet
- Elesson 10 Bio 14mayDocument4 pagesElesson 10 Bio 14mayArchanaGuptaNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument19 pagesTransport in Animalsmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- The respiratory system: structures, functions, and diseasesDocument74 pagesThe respiratory system: structures, functions, and diseasesRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- The relationship between kidney disease, heart disease, and blood pressureDocument3 pagesThe relationship between kidney disease, heart disease, and blood pressurethe urvashiNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes During Aerobic ExerciseDocument19 pagesPhysiological Changes During Aerobic ExerciseAnand VaghasiyaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System and The Circulatory System SummaryDocument1 pageThe Respiratory System and The Circulatory System SummaryjohlumslumsmlNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cancer Is Not A Disease-But A SymptomDocument2 pagesCancer Is Not A Disease-But A Symptomelenaconstantin1No ratings yet
- Stability of Selected Biochemical Analytes in Plasma Samples Stored Under Different Time and Temperature ConditionsDocument4 pagesStability of Selected Biochemical Analytes in Plasma Samples Stored Under Different Time and Temperature ConditionsVincent ReyesNo ratings yet
- NUTRILITE ProteinPowder en UsDocument5 pagesNUTRILITE ProteinPowder en UsFauzan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Picture (CBP) Test Name Observed Values Units Biological Reference Intervals 12.1Document2 pagesComplete Blood Picture (CBP) Test Name Observed Values Units Biological Reference Intervals 12.1seravanakumarNo ratings yet
- 8 JunkfoodDocument10 pages8 JunkfoodLuminitaNo ratings yet
- Immuno 32 2 04Document52 pagesImmuno 32 2 04mmarquezsaNo ratings yet
- The Thromboelastogram (TEG®) : A Five-Minute Primer For The Emergency PhysicianDocument11 pagesThe Thromboelastogram (TEG®) : A Five-Minute Primer For The Emergency PhysicianMarcelliaNo ratings yet
- Analizador GP Getein 1100 ManualDocument2 pagesAnalizador GP Getein 1100 Manualbiomedico international0% (1)
- Blood Collection, Equipment, Additives, and Order of DrawDocument29 pagesBlood Collection, Equipment, Additives, and Order of DrawLyonTrioréNo ratings yet
- 10th Biology NotesDocument56 pages10th Biology NotesJYOTHI D100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/42 March 2021Document13 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/42 March 2021Inga NaranbatNo ratings yet
- (5E) Blood Magic Arcane SupplementDocument17 pages(5E) Blood Magic Arcane SupplementJason0% (1)
- Assign Immuno II HDNDocument4 pagesAssign Immuno II HDNNizam XNo ratings yet
- 10th Name The Following BiologyDocument11 pages10th Name The Following BiologyManoj ThakurNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism: Patient EducationDocument2 pagesPulmonary Embolism: Patient Educationyogurt100% (1)
- The Circulatory System:: BloodDocument101 pagesThe Circulatory System:: BloodAntonio MihaiNo ratings yet
- Plateletcrit As A Screening Tool For Detection of Platelet Quantitative DisordersDocument5 pagesPlateletcrit As A Screening Tool For Detection of Platelet Quantitative DisordersStephanie PattonNo ratings yet
- 6 Minute English The Wonder of BloodDocument4 pages6 Minute English The Wonder of BloodReza ShirmarzNo ratings yet
- KT - Ruling On The Types of WaterDocument12 pagesKT - Ruling On The Types of WaterAlamgir IslamNo ratings yet
- BT Case Scenario 1 (Group 1)Document3 pagesBT Case Scenario 1 (Group 1)Rej GarbosaNo ratings yet
- Essential Thrombocythemia: By: DR K.S.K Jusu Department of Haematology Comahs-UslDocument15 pagesEssential Thrombocythemia: By: DR K.S.K Jusu Department of Haematology Comahs-UslIdrissa John Sebeh ContehNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document-45Document6 pagesUntitled Document-45api-663741818No ratings yet
- List of Clotting Factors ExplainedDocument3 pagesList of Clotting Factors ExplainedMa Cheryll DueñasNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument6 pagesActivityandreskalikasansaraNo ratings yet
- Blood Cell Pathology GuideDocument12 pagesBlood Cell Pathology GuideRoman CoNo ratings yet
- Cdi ExamDocument41 pagesCdi ExamJeselyn MalaluanNo ratings yet
- HM 09 20155v2 Ruby Casebook 122010 PDFDocument91 pagesHM 09 20155v2 Ruby Casebook 122010 PDFFrankie LamNo ratings yet