Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Blood Flow Calcs, Exercise - Metabolism HW
Uploaded by
Juan AnariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Blood Flow Calcs, Exercise - Metabolism HW
Uploaded by
Juan AnariCopyright:
Available Formats
BLOOD FLOW CALCULATIONS
1. What is meant by the term ‘heart rate’?
The amount of times the heart beats every minute, measured in beats per minute.
2. What is meant by the term ‘stroke volume’?
The volume of blood pumped out of the left ventricle per heartbeat.
3. What is meant by the term ‘cardiac output’?
The amount of blood pumped out of the heart, measured in litres per minute
4. How do you calculate cardiac output?
Stroke volume x Cardiac output.
5. A person’s heart beats 11 times in 10 seconds and each of their heart beats pumps 80 cm 3 of blood. What is this person’s
cardiac output? Show your working.
11 x 6 = 66
66 x 80 = 5280 litres per minute.
EXERCISE
1. What effect does exercising have on your heart rate and your breathing rate? Why?
Include the following key terms: muscle contraction, energy, respiration, muscle cells, supply, removal, heart rate, breathing
rate
Exercising increases your heart rate, as it requires more energy to carry out things such as muscle contraction, so
respiration occurs, which releases energy which is transported to the muscle cells. In order to carry out aerobic respiration,
breathing rate increases as the greater your breathing rate, the more oxygen is supplied to the body and your lungs,
allowing it to carry out aerobic respiration.
2. What is meant by the term ‘oxygen debt’? Why is there an oxygen debt? What effect does oxygen debt have on your heart
rate and breathing rate after exercise, and why?
Include the following key terms: oxygen, lactic acid, anaerobic respiration, heart rate, removes, liver, oxidised, glucose,
breathing rate, supply
Oxygen debt refers to the amount of oxygen required to replace the buildup of lactic acid aqquired through anaerobic
respiration with oxygen. This occurs after exercise as the body needs to carry out anaerobic respiration as it can no longer
carry out aerobic respiration without increasing the heart rate too much. Therefore, after exercise, especially long-distance
exercise, there is a buildup of lactic acid in the body as this is a product of anaerobic respiration. To get rid of it, lactic acid is
transported to the liver by the blood, where it is oxidised or converted into glucose. After a while the breathing rate will
return to normal, but this takes time as the lactic acid needs to be replaced first and the oxygen supply needs to be
increased again.
METABOLISM
1. What is meant by the term ‘metabolism’? (1)
The conversion of food and drink into energy.
2. What are some types of metabolic reactions? (4)
Catabolism, anabolism
You might also like
- Aerobics: Maximize Your Body Potential and Make Yourself More Attractive (The Essential Guide to Lose Weight Get a Lean and Toned Body While Having Fun Using Water Exercises)From EverandAerobics: Maximize Your Body Potential and Make Yourself More Attractive (The Essential Guide to Lose Weight Get a Lean and Toned Body While Having Fun Using Water Exercises)No ratings yet
- Pen AerobicDocument3 pagesPen AerobicMiriam Saena EscarlosNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Exercise DefinitionDocument31 pagesAerobic Exercise Definitiontanishka SinghalNo ratings yet
- AerobicsDocument4 pagesAerobicsmyraturaNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic respiration musclesDocument13 pagesAnaerobic respiration musclesImran IjazNo ratings yet
- AerobicsDocument3 pagesAerobicsMark PetillaNo ratings yet
- Respiration ExerciseDocument2 pagesRespiration ExerciseSacchin CepalNo ratings yet
- Body Systems and ExerciseDocument15 pagesBody Systems and ExerciseMichael GuzikNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate and Breathing Lab 1 - AgsaldaDocument4 pagesHeart Rate and Breathing Lab 1 - AgsaldaEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ExerciseDocument13 pagesBenefits of ExerciseMukesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Aerobic Exercise Improve Heart, Circulation & MoreDocument5 pagesBenefits of Aerobic Exercise Improve Heart, Circulation & MoreBongskie escalona0% (1)
- Social and Preventative Medicine PresentationDocument10 pagesSocial and Preventative Medicine PresentationSarafina BowenNo ratings yet
- Cardiac and Circulatory Adaptation To ExerciseDocument31 pagesCardiac and Circulatory Adaptation To ExerciseShadow TiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Relationship Between Left Ventricle VolumeggggggggggggggDocument1 pageWhat Is The Relationship Between Left Ventricle Volumeggggggggggggggbazz samNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology PPT (27 September 2018)Document72 pagesExercise Physiology PPT (27 September 2018)Surya Diatmika100% (1)
- What Is Aerobic Exercise?Document27 pagesWhat Is Aerobic Exercise?Zedy GullesNo ratings yet
- What Is Aerobic Exercise?Document27 pagesWhat Is Aerobic Exercise?sympatico0081No ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument7 pagesTransport in AnimalsGodfrey RugareNo ratings yet
- 3 StaminaDocument11 pages3 StaminaYago Piccin PoloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 BIODocument2 pagesChapter 12 BIODakshitaNo ratings yet
- Mutuc, Mariel M. (Pe-I)Document2 pagesMutuc, Mariel M. (Pe-I)MARIEL MUTUCNo ratings yet
- Body GeneratorsDocument16 pagesBody GeneratorsCassy Leighz BagonocNo ratings yet
- What is aerobic exerciseDocument27 pagesWhat is aerobic exerciseGab IlaganNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Circulatory System P.EDocument10 pagesGroup 1 Circulatory System P.EGerardo CarreonNo ratings yet
- Energy SystemDocument14 pagesEnergy SystemMaria Alyssa NaranjoNo ratings yet
- FORCEDocument14 pagesFORCEMaria Alyssa NaranjoNo ratings yet
- ST12P3 Taburnal, Marjorie Mae - PT 4.3 General Biology 2Document3 pagesST12P3 Taburnal, Marjorie Mae - PT 4.3 General Biology 2Marjorie Mae AmodiaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-343368893No ratings yet
- Aerobic: What Is Aerobic Exercise?Document4 pagesAerobic: What Is Aerobic Exercise?rajeevNo ratings yet
- Training and BreathingDocument6 pagesTraining and BreathingMIIIBNo ratings yet
- Aerobic RespirationDocument5 pagesAerobic RespirationDuncan C.MulengaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and BreathingDocument35 pagesThe Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and BreathingScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Syjc 2 Exercise Scientific ApproachDocument11 pagesSyjc 2 Exercise Scientific Approachamandesai0527No ratings yet
- Anaerobic vs Aerobic Respiration in Organisms & MusclesDocument16 pagesAnaerobic vs Aerobic Respiration in Organisms & MusclesrihanniNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Pe and HealthDocument16 pagesReviewer in Pe and HealthJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Aerobics and Anaerobic ExerciseDocument19 pagesAerobics and Anaerobic ExerciseKirin Ira VicenteNo ratings yet
- Respiration and BreathingDocument57 pagesRespiration and BreathingHarvagale BlakeNo ratings yet
- Example PowerpointDocument67 pagesExample Powerpointapi-321385393No ratings yet
- Physiological Changes During Aerobic ExerciseDocument19 pagesPhysiological Changes During Aerobic ExerciseAnand VaghasiyaNo ratings yet
- ACE's Essentials of Exercise Science For Fitness ProfessionalsDocument41 pagesACE's Essentials of Exercise Science For Fitness ProfessionalsLouis Trần100% (1)
- Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesRespiratory SystemShruti JhaNo ratings yet
- Changes of O2 Delievry To Muscle During ExerciseDocument21 pagesChanges of O2 Delievry To Muscle During Exercisealikhaqaan77No ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic TrainingDocument18 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic TrainingIzzat RedzuanNo ratings yet
- 2 Execise PhysiologyDocument41 pages2 Execise PhysiologyByronDiazNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION - Effect of Exercise On Breathing RateDocument1 pageRESPIRATION - Effect of Exercise On Breathing RateJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Exercise Benefits Your Heart, Lungs & MoreDocument3 pagesAerobic Exercise Benefits Your Heart, Lungs & MoreHonney Grace C. OpiñaNo ratings yet
- PE 101 FinalsDocument23 pagesPE 101 FinalsHazel EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Adaptation and Factors Affecting The Aerobic Training ResponseDocument2 pagesAerobic Adaptation and Factors Affecting The Aerobic Training ResponsekenjiyanasanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac and Circulatory Adaptation To ExerciseDocument25 pagesCardiac and Circulatory Adaptation To ExerciseGetahun TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Biology ScienceDocument9 pagesBiology SciencetalaNo ratings yet
- Respiration BiologyDocument32 pagesRespiration BiologyMuhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- P.E 1 Hand Outs 1quarterDocument9 pagesP.E 1 Hand Outs 1quarterArlyn S. Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Pe1 Essay For FinalsDocument2 pagesPe1 Essay For FinalsDean Jerick IgayaNo ratings yet
- ArobicDocument4 pagesArobicrishitNo ratings yet
- ResperationDocument5 pagesResperationaishabroNo ratings yet
- Respiration and The Respiratory SystemDocument41 pagesRespiration and The Respiratory Systemfrancis iduruNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Understanding Movement TaskDocument4 pagesYear 8 Understanding Movement TaskKomal SainiNo ratings yet
- Respiration 1 QPDocument6 pagesRespiration 1 QPtericetrwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 & 6 The Cardiovascular and The Respiratory SystemDocument26 pagesChapter 5 & 6 The Cardiovascular and The Respiratory SystemBernhard BrinkerNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Training Camp_Yanovsky_1C CompletedDocument14 pagesBenefits of Training Camp_Yanovsky_1C CompletedteachernadiazaNo ratings yet
- 04 A. Life in The Trenches QuestionsDocument4 pages04 A. Life in The Trenches QuestionsJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- 01 B. Review of Causes of WW1Document2 pages01 B. Review of Causes of WW1Juan AnariNo ratings yet
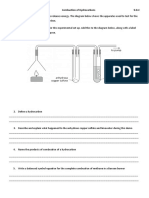
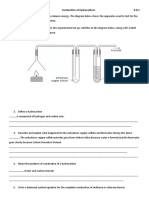
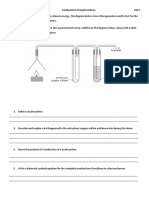
- 9.D.C - Practical Worksheet - Combustion of HydrocarbonsDocument1 page9.D.C - Practical Worksheet - Combustion of HydrocarbonsJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- SCHEDULE - Brick Lane Jazz FestivalDocument1 pageSCHEDULE - Brick Lane Jazz FestivalJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Recipes Containing CalciumDocument2 pagesRecipes Containing CalciumJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- 9.D.C - Practical Worksheet - Combustion of HydrocarbonsDocument2 pages9.D.C - Practical Worksheet - Combustion of HydrocarbonsJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Understanding wavesDocument4 pagesUnderstanding wavesJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Physics Revision ChecklistDocument32 pagesYear 9 Physics Revision ChecklistJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Combustion of Hydrocarbons 9.D.CDocument1 pageCombustion of Hydrocarbons 9.D.CJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- 11+ Art Scholarship TaskDocument5 pages11+ Art Scholarship TaskJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Holocaust Essay Planning 2021Document10 pagesHolocaust Essay Planning 2021Juan AnariNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Data Collation and Secondary DataDocument9 pagesQuestionnaire Data Collation and Secondary DataJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- P. G. Wodehouse - Aunts Aren't Gentlemen (Jeeves & Wooster)Document100 pagesP. G. Wodehouse - Aunts Aren't Gentlemen (Jeeves & Wooster)Prasad Shelake100% (3)
- Women's Suffrage RevisionDocument2 pagesWomen's Suffrage RevisionJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Ex SGGprepub S4 KDocument16 pagesEx SGGprepub S4 KJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- My Clean Air Superhero 2020Document1 pageMy Clean Air Superhero 2020Juan AnariNo ratings yet
- Creating Your Own DetectiveDocument2 pagesCreating Your Own DetectiveJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Read MeDocument1 pageRead MeJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- The Medieval KingsDocument11 pagesThe Medieval KingsJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Latin Homework p.50 Book 2Document1 pageLatin Homework p.50 Book 2Juan AnariNo ratings yet
- 1.2 John Upsets Everyone Notes SheetDocument1 page1.2 John Upsets Everyone Notes SheetJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Ex UBug Me U32Document17 pagesEx UBug Me U32Juan AnariNo ratings yet
- Does King John Deserve His Bad ReputationDocument1 pageDoes King John Deserve His Bad ReputationJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Ex Kid Who Ran For President K06Document21 pagesEx Kid Who Ran For President K06Juan AnariNo ratings yet
- Babette's Feast - EnhancedExcerpt PDFDocument56 pagesBabette's Feast - EnhancedExcerpt PDFJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Ex SGGprepub S4 KDocument16 pagesEx SGGprepub S4 KJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Text 9Document1 pageText 9Juan AnariNo ratings yet
- This Excerpt Is Available To Assist You in The Play Selection ProcessDocument22 pagesThis Excerpt Is Available To Assist You in The Play Selection ProcessJuan AnariNo ratings yet
- Ex Jackie and Me J66Document21 pagesEx Jackie and Me J66Juan AnariNo ratings yet
- Audienc SegmentationDocument3 pagesAudienc SegmentationFatima RoshniNo ratings yet
- 1 - PE 10PF-Ia-h-39Document2 pages1 - PE 10PF-Ia-h-39Shani Mabano100% (6)
- 6 Minute Walk Test ATS GuidelinesDocument7 pages6 Minute Walk Test ATS GuidelinescpradheepNo ratings yet
- BoxingandBarbellManual 1Document110 pagesBoxingandBarbellManual 1PhotoVideos BackupNo ratings yet
- Fitness For Life-3Document496 pagesFitness For Life-3Frank LeggNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s12603 020 1458 5Document5 pages10.1007@s12603 020 1458 5fathur rahma bahtiar ft2019No ratings yet
- Speaking B23 .Document22 pagesSpeaking B23 .Nguyễn Thị NgânNo ratings yet
- Bill Goldberg Workout Routine - Muscle and BrawnDocument4 pagesBill Goldberg Workout Routine - Muscle and BrawnTelemetric SightNo ratings yet
- Harmony of Exercise, Sport Physical Activity, Recreation and TourismDocument30 pagesHarmony of Exercise, Sport Physical Activity, Recreation and TourismSherwin Basan CelestialNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Adult ObesityDocument25 pagesNursing Care Plan for Adult ObesityAllyza Trixia Joyce VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Strength and Conditioning Considerations For Mixed Martial ArtsDocument12 pagesStrength and Conditioning Considerations For Mixed Martial ArtsmoaNo ratings yet
- ISSA Sports Performance Enhancement Main Course TextbookDocument615 pagesISSA Sports Performance Enhancement Main Course TextbookFANTAZTIC FITNEZZNo ratings yet
- 2 Quarter Summative Assessment 2 in Mapeh 10: Name: - Grade/Section: - ScoreDocument4 pages2 Quarter Summative Assessment 2 in Mapeh 10: Name: - Grade/Section: - ScoreKate MaryNo ratings yet
- Pe Exercise TableDocument1 pagePe Exercise TablenAndrei Paul MabatanNo ratings yet
- 11 Physical Education Study Material Session 2020 2021 Chapter 10Document16 pages11 Physical Education Study Material Session 2020 2021 Chapter 10Mantasa AfrinNo ratings yet
- Exercise Guidelines For PPSDocument2 pagesExercise Guidelines For PPSClaire BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document4 pagesModule 3Brafiel Claire Curambao LibayNo ratings yet
- Impaired MobilityDocument3 pagesImpaired MobilityYeana AlonNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Read The Questions Comprehensively and Choose The Letter That Best Correspond ToDocument5 pagesInstruction: Read The Questions Comprehensively and Choose The Letter That Best Correspond ToMaren PendonNo ratings yet
- 9 Tactics of Lifelong GeniusDocument4 pages9 Tactics of Lifelong GeniusApurv MehtaNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness Short Note (SPSC 1011) Unit One 1. 1. Concepts of Physical Fitness1 1.1. 1. Meanings and Definitions of Physical FitnessDocument62 pagesPhysical Fitness Short Note (SPSC 1011) Unit One 1. 1. Concepts of Physical Fitness1 1.1. 1. Meanings and Definitions of Physical Fitnesseyob astatkeNo ratings yet
- LA 3 PhilosophyDocument12 pagesLA 3 PhilosophyRuztom John TamayoNo ratings yet
- (FITT) Pinciples of TrainingDocument17 pages(FITT) Pinciples of TrainingCassandra Marie100% (1)
- TBA Advanced Euphonium Clinic San Antonio 2000Document20 pagesTBA Advanced Euphonium Clinic San Antonio 2000Nicholas Jones100% (20)
- Face ExerciseDocument6 pagesFace Exercisealekad65No ratings yet
- THESIS in NURSINGDocument47 pagesTHESIS in NURSINGkathy85% (40)
- GED0004, Physical Education 1Document4 pagesGED0004, Physical Education 1Gheoff RicareNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Training PrinciplesDocument24 pagesLesson 3: Training PrinciplesChen BalNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Hope 1 Midterms PDFDocument6 pagesModule 1 Hope 1 Midterms PDFEzekielNo ratings yet
- Pe & Health 11 - Module 1Document19 pagesPe & Health 11 - Module 1John Fritz LopezNo ratings yet