Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MindMap Butterfly Anna-Mariya
Uploaded by
Anna-Maria LevenovaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MindMap Butterfly Anna-Mariya
Uploaded by
Anna-Maria LevenovaCopyright:
Available Formats
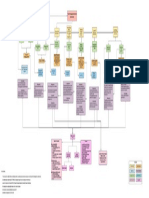
Mindmap
Hypothetical-
deductive inferences Ways of
Arguments manifesting
Intentions
Evidence
Demarcation through Context depending
falsification Preconceptions
Purpose
Unity of science
Specific time Plans
Empirically observable Prejudices and place
with human senses Dreams
Unbiased experimental
---- Pendulum
The Vienna circle ----
design Coherence Relations Lifeworld
---- Empirical studies Interpretations
Contextual Merleau-Ponty
Theory of truth
---- Fusion of horizons Manifestation
Strict application ---- Wilhelm Ditley Truth theory ways
Positivism & ---- Not value-free Hermeneutics Never be value-free
Critical rationalism ---- or objective Subjectivity
Rigorous scientific Genealogical
Heidegger
----
methods ----
----
Hermeneutics Sufficiency
---- Practical Knowledge from
----
---- Phenomenology consciousness First person
------
Manifestation Transparency Phenomenology ---- --- perspective
----------------
overlap ---- --- Good knowledge
----
----- Ensuring Credibility ----
Intersubjectivity - Human experience
--------------------------
Inclusion Epoche Truth theory ----- - Positivism &
-----
----- ---- Critical rationalism Truth of
- Reason
----- -- knowledge
KNOWLEDGE
Phenomenological ---
-----
reduction
Reflexive bracketing -----
----- ----- Factual/Scientific
knowledge
-- Absolute certainty
---
Biographical ----- --- Value-free
Group --- Objective
------
method ------ Application
Implicit discussion - Experience The Vienna circle
-
- issues --
----
------ ------
-
knowledge Thematic -
Scientific
-
-
opposition
-
literature Qualitative ------- Logos
-
Distance Doxa
--
Case analysis -Over-
--------
-
----
interview
-
---pragmatic
------ Constant
-
-
-- - ------- Methods redefinition
-
-
Theory-driven Confrontational ---
-
-
- - Selection of observable
----
questions Elements --- -------
--
----
Open questions - Challenges/ Time
--- ------- situation Opportunistic Open-
limitations
-
questions - -- Role definition ended
-
--- --------
---
-
-
--
----------------------
-
--
--
-- - --------- Everyday life
-
Elements -- ---
Problem-centred Data analysis Coincidence Inquiry
-
---
-
Semi-standardized ---- --
interview ----- Flexible
-
-
Formation of
-
-- -- -
-
interview -- Ethnographic
-
-
scientific theories - --- --
-
--
---
-------- -
-
-
Participant
-
interview
-
Human existence
-
-
Essential Challenges observation
-
-
---
-
statements
-
--
Challenges/
-
Reformulate - Observations
---
--
limitations -
Irritation Interviews Online
-
- Self-observation versus
-
Assesment -- interviews
-
Video observing others
-
-
-
---
--
- interviews Types of Virtual
-
Complexity --
-
ethnography
-
Interpretation - observation
---
-
Replace - Mismatching Roles of the
--
-
-
---
-
-
Expert and Objective researcher
---
--
-
- elite interview Focused facts?
---- Non- participant
-
Challenges/
---
Covert versus overt Ethnography
-
Eliminate Elite interview observation
Phases
--
Interviews limitations observation Distant
-
---
-
Situational
-
Participant-as-
-
-
-
competence observer
-
Extended observation
-
Privileged Characteristics Systematic vs
-
-
General
---
positions Researchers Setting Training unsystematic
Influence Expert Challenges/ Range observation methodological
knowledge
---
interviews limitations Non-direction Observer-as- “Unstructured” standards
participant data
---
Documentation
Decision- Theoretical
-
Status Theories “Right” experts Specificity Personal context Natural versus
making Capacity as saturation Methodological pragmatism
creation & depth Complete observer artificial situations
experts Descriptive
Retrospective observations Explicit
Broad Availability inspection Selective
Time Focused interpretation
network Complete observation
participant Initial observations
Context Exploration
collection Confidentiality Central
aspects
Relevance
You might also like
- Off the Bookshelf Coloring Book: 45+ Weirdly Wonderful Designs to Color for Fun & RelaxationFrom EverandOff the Bookshelf Coloring Book: 45+ Weirdly Wonderful Designs to Color for Fun & RelaxationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Play and PlayfulnessDocument60 pagesPlay and PlayfulnessMaggie YungNo ratings yet
- BLANK Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFDocument1 pageBLANK Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFVidhi SurekaNo ratings yet
- Inquiry Model 2Document10 pagesInquiry Model 2philipripNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods: Multivariate AnalysisDocument1 pageStatistical Methods: Multivariate AnalysisJordan ChizickNo ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade K: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade K: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- Adk Division C - Final ResultsDocument1 pageAdk Division C - Final Resultsapi-346863922No ratings yet
- Puso2019 FinalresultsDocument3 pagesPuso2019 Finalresultsapi-454740047No ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 5: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 5: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- Success by NumbersDocument2 pagesSuccess by NumberstinaeminiNo ratings yet
- Literature Analysis - A Mind Map of IdeasDocument1 pageLiterature Analysis - A Mind Map of IdeasRoger KnightNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesTable of Specifications: Objectivewanieramlie98No ratings yet
- Jsu T5 Bi K1Document1 pageJsu T5 Bi K1MOHD FAHMI BIN ABD ALIAN MoeNo ratings yet
- 2022 GA C Raw ScoresDocument1 page2022 GA C Raw ScoresooftNo ratings yet
- Nooscope PDFDocument1 pageNooscope PDFPacoMüllerNo ratings yet
- VUCA NotesDocument15 pagesVUCA NotesFilthy MemesNo ratings yet
- Roll Up Your Sleeve For Sputnik Jab: High Court Stays TS Ambulance OrderDocument10 pagesRoll Up Your Sleeve For Sputnik Jab: High Court Stays TS Ambulance OrderDggeffddfNo ratings yet
- Zone 1: 2010-2015 Zone 2: 2015-2020 Zone 3: 2020-2025 ZoneDocument1 pageZone 1: 2010-2015 Zone 2: 2015-2020 Zone 3: 2020-2025 Zoneapi-26008017No ratings yet
- Trends and Technology Timeline 2010Document1 pageTrends and Technology Timeline 2010Lynda KosterNo ratings yet
- Wang 2020 Cheat SheetsDocument13 pagesWang 2020 Cheat SheetsToàn Huỳnh ThanhNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Machinic Intelligence MDocument1 pageThe Evolution of Machinic Intelligence MMariana Campos CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- BLANK Everything You Need To Memorise: Part 3, Statistics PDFDocument1 pageBLANK Everything You Need To Memorise: Part 3, Statistics PDFFrancesco PiazzaNo ratings yet
- TOS Grade 2 MAPEH Diagnostic Test 2022 FINALDocument20 pagesTOS Grade 2 MAPEH Diagnostic Test 2022 FINALLeslie PadillaNo ratings yet
- Product Journey MapDocument1 pageProduct Journey MapGovarthanam KrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- Groin HerniasDocument1 pageGroin HerniasahmedNo ratings yet
- Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderDocument1 pagePost-Traumatic Stress DisorderJoan MonzonesNo ratings yet
- Long Intl Claim Resolution MethodologyDocument1 pageLong Intl Claim Resolution MethodologyPavanKumarNo ratings yet
- Actas Del Primer Parcial 2020-2021Document27 pagesActas Del Primer Parcial 2020-2021Xavier MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- (Analytic) (Dialectic) : A Posteriori A PrioriDocument1 page(Analytic) (Dialectic) : A Posteriori A PrioriDas Nichts PvoNo ratings yet
- Murtuza Indorewala PortfolioDocument43 pagesMurtuza Indorewala PortfolioMurtuzaNo ratings yet
- 291-Article Text-479-1-10-20200427Document16 pages291-Article Text-479-1-10-20200427خداداد مزملNo ratings yet
- Retail Attraction Towards IBC Stocks and The ABC of A Bad BetDocument12 pagesRetail Attraction Towards IBC Stocks and The ABC of A Bad BetY MuraliNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-01-03 at 09.58.50Document1 pageScreenshot 2024-01-03 at 09.58.50sagvantayebNo ratings yet
- Retrieval PracticeDocument2 pagesRetrieval PracticeAbu YahyaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Bay Area Regional Science Olympiad Tournament: # School Name (State)Document1 page2018 Bay Area Regional Science Olympiad Tournament: # School Name (State)Baguette BubblesNo ratings yet
- English 9 Q1 TOSDocument2 pagesEnglish 9 Q1 TOSJohnfil Ajeno JamolinNo ratings yet
- DFMEA PFMEA Control Plan LinkagesDocument1 pageDFMEA PFMEA Control Plan LinkagesSaul Montiel100% (2)
- Different Kinds of Obligation (Primary) : Section 6: Obligation With A Penal ClauseDocument1 pageDifferent Kinds of Obligation (Primary) : Section 6: Obligation With A Penal ClauseMarie Lourence AngelesNo ratings yet
- ADnD 1e Ability Scores v1.4Document1 pageADnD 1e Ability Scores v1.4Constantine PaleologusNo ratings yet
- Instruments de Mesure Selon Le MOHDocument1 pageInstruments de Mesure Selon Le MOHAymen DabboussiNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Nilai (Leger) Man Seram Masohi Kelas XI IPS-2 / Semester I (Satu) Tahun Pelajaran 2016/2017Document3 pagesKumpulan Nilai (Leger) Man Seram Masohi Kelas XI IPS-2 / Semester I (Satu) Tahun Pelajaran 2016/2017Saif Al SahabNo ratings yet
- Hapiness and VirtueDocument16 pagesHapiness and VirtueClaudia Pablos CruzNo ratings yet
- Contoh Competency Matrix Setiap DepartmentDocument430 pagesContoh Competency Matrix Setiap DepartmentKismiAzi100% (1)
- AspirationsDocument10 pagesAspirationsdr satnam kaurNo ratings yet
- Page 11Document1 pagePage 11amalNo ratings yet
- Set 3 - Jsu t5 Bi k3Document1 pageSet 3 - Jsu t5 Bi k3MOHD FAHMI BIN ABD ALIAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Oz SocialChart CompleteDocument1 pageOz SocialChart CompleteNathan DowNo ratings yet
- EstomihMtuiGreg 2012 Embryology ClinicalNeuroanatomyADocument6 pagesEstomihMtuiGreg 2012 Embryology ClinicalNeuroanatomyANastya PapounidouNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFDocument1 pageEverything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFTripleFireWingsNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and PR2Document11 pagesPhilosophy and PR2maeshengNo ratings yet
- KDRV - EngDocument1 pageKDRV - EngCenker YıldırımNo ratings yet
- Greensheet PrimaryDocument4 pagesGreensheet PrimaryIT Department BLS WORLD SCHOOLNo ratings yet
- 4 2012 06 05 PCINE Substructure Guide DetailsDocument12 pages4 2012 06 05 PCINE Substructure Guide Detailsmohamed samirNo ratings yet
- Traits & EthicsDocument1 pageTraits & EthicsKrishvasu99 KalaiNo ratings yet
- Jsu English RVDocument2 pagesJsu English RVQifaysVgNo ratings yet
- Dinotopia MapDocument2 pagesDinotopia MapNacho Caballero100% (5)
- Be YoutifulDocument9 pagesBe YoutifulAnna-Maria LevenovaNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument15 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsAnna-Maria LevenovaNo ratings yet
- Economic 041018Document7 pagesEconomic 041018Anna-Maria LevenovaNo ratings yet
- BachelorThesis OnlineCourses1Document8 pagesBachelorThesis OnlineCourses1Anna-Maria LevenovaNo ratings yet
- Tourism Specialization Exam AnnaMariya LevenovaDocument5 pagesTourism Specialization Exam AnnaMariya LevenovaAnna-Maria LevenovaNo ratings yet
- Service LawDocument6 pagesService LawAnna-Maria LevenovaNo ratings yet
- AI - Notes (Introduction To AI& AI Project Cycle)Document11 pagesAI - Notes (Introduction To AI& AI Project Cycle)Aabida Rafik ChikteNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics and Value ClarityDocument9 pagesBusiness Ethics and Value Clarityaditya himatsingkaNo ratings yet
- Ball - Against School - An Epistemological CritiqueDocument15 pagesBall - Against School - An Epistemological Critiquealexcypriano2No ratings yet
- What Is Child Psychology and Why Is It ImportantDocument3 pagesWhat Is Child Psychology and Why Is It ImportantLena StolerNo ratings yet
- Research Sleeping PatternsDocument18 pagesResearch Sleeping Patternsmnaem9999No ratings yet
- Back To Basics Qualitative ResearchDocument7 pagesBack To Basics Qualitative ResearchYina VanessaNo ratings yet
- Prabodhan First Round TaskDocument9 pagesPrabodhan First Round Taskvishwesh gautamNo ratings yet
- Ijerph 19 06484 v2Document20 pagesIjerph 19 06484 v2jembrison sentuf07No ratings yet
- (12..01.2016) Pierluigi Chiassoni - Legal Interpretation Without Truth PDFDocument24 pages(12..01.2016) Pierluigi Chiassoni - Legal Interpretation Without Truth PDFbargadoNo ratings yet
- WHLP Oral Communication - Week 1 v1Document1 pageWHLP Oral Communication - Week 1 v1Elenor May Chantal Messakaraeng100% (3)
- Silo - Pub Risk Crisis and Security ManagementDocument258 pagesSilo - Pub Risk Crisis and Security ManagementTafadzwa Kumani100% (1)
- Abnormal Psychology Plus New Mypsychlab 15th Edition Butcher Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesAbnormal Psychology Plus New Mypsychlab 15th Edition Butcher Solutions ManualMissKatherineGardnerfjcp100% (49)
- Secondary Level Volume Final 2Document202 pagesSecondary Level Volume Final 2Bonface KenaniNo ratings yet
- C 5 T R P: E O R D: Instructional GoalsDocument44 pagesC 5 T R P: E O R D: Instructional Goalskashan qamarNo ratings yet
- English Lesson Plan Year 5Document2 pagesEnglish Lesson Plan Year 5NORHAZLIZA BINTI HUSENNo ratings yet
- Script For COC 1Document9 pagesScript For COC 1louiced reno2129No ratings yet
- Kinds of Quantative Research Module 1Document13 pagesKinds of Quantative Research Module 1bmNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 RMDocument3 pagesLec 1 RMBarkatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Simulation With ANSYS Mechanical APDL: October 2016Document2 pagesIntroduction To Simulation With ANSYS Mechanical APDL: October 2016Shuo HaoNo ratings yet
- Image Processing and Machine VisionDocument2 pagesImage Processing and Machine VisionNaveenKumarLNo ratings yet
- Comparative Education Chapter 1Document20 pagesComparative Education Chapter 1kaboi mainaNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The Community School Culture and Organizational LeadershipDocument81 pagesThe Teacher and The Community School Culture and Organizational LeadershipJhon NavarroNo ratings yet
- JW 1 StgrclassactivityDocument6 pagesJW 1 Stgrclassactivityapi-632123997No ratings yet
- Creative Writing WHLPDocument4 pagesCreative Writing WHLPDavid DanaoNo ratings yet
- Cliquidity Adaptive Reasoning Assessment Brief Report - Jacolien Jansen Van VuurenDocument4 pagesCliquidity Adaptive Reasoning Assessment Brief Report - Jacolien Jansen Van VuurenjacolienjvvuurenNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept Mapcharlotte899No ratings yet
- Handouts - Eapp 1Document2 pagesHandouts - Eapp 1Christenz Anjonel M. CristobalNo ratings yet
- Introduction. Writing History With Animals: Quentin Deluermoz, François JarrigeDocument17 pagesIntroduction. Writing History With Animals: Quentin Deluermoz, François JarrigeEnson CcantoNo ratings yet
- Data Science Case Study Options 1.0Document2 pagesData Science Case Study Options 1.0omprakash padhiNo ratings yet
- Social Media Content Development FMS Flow ChartDocument3 pagesSocial Media Content Development FMS Flow Chartrashi sharmaNo ratings yet