Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BLANK Everything You Need To Memorise: Part 3, Statistics PDF
Uploaded by
Francesco PiazzaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BLANK Everything You Need To Memorise: Part 3, Statistics PDF
Uploaded by
Francesco PiazzaCopyright:
Available Formats
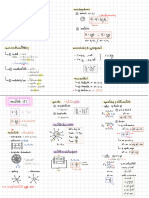
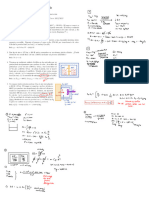
KNOW YOUR KNOW YOUR
Data Collection Location calculator !
Regression + Correlation calculator ! Discrete Uniform Distribution Hypothesis Testing
Keywords Mean Product Moment Correlation Coefficient Probabilities of outcomes all equal Definitions
Census : E. = ñ= PMCC ,r Ers ✗ is cloud cover measured inoalas Null
Hypothesis :
eg
.
Alternative Hypothesis
x
+ -
Listed Data Measures pc×=
:
LQ Med UQ
Significance
.
Level :
sampling
units :
position of Q,= Qe Qs= Regression Line
sampling frame :
Ifa decimal ,
Lineofbestfit Binomial Distribution One tailed Test :
-
Random Sampling If whole, ais ✗ ~ Two tailed Test
- :
i ) Simple Random Sampling Grouped Data bis FP(✗=r)=
✓
? Position of Q,= Qi Q}= interpolation :
When to use ? Correlation
Testing * updated from ✓ since
recording
Ñ
the video pis PMCC for
57thpercentile,P
✗
extrapolation F Ho : population
-
• ,
Percentiles
eg .
= :
rispmcctorsampk .
1- -
Deciles , 10% chunks , D. =
Exponential/Nonlinear Models F •
Hip p p
"
in If y=ab I with table
systematic sampling Doriot round, linear interpolation compare your r
•
use
REMEMBER
? Linear Interpolation T ↳
if your r is more extreme, context !
weight nearest
kg true class limits
frequency cumulative freq "
Cumulative Probabilities if your less extreme
.
is
Hy=ax
,
it ↳ r
,
Sg
lo -
iz ⇐ we
13-15 c- we
+ -
16-18 ⇐ w '
7
a,=
P(✗ < 5) =
KNOW Your
CALCULATOR !
iii stratified Sampling Qi-h.si P( ✗ > 3) =
Binomial
Testing
?
know Your
Probability
Venn
Plbcxeio)= Test Statistic :
Spread calculator ! Diagrams Inverse Probabilities •
Ho :
A' V13 Use tables ! Hi
'
+
lnterquartile Range
•
eg
-
.
* ,
Unions Assume Ho
Nou Random
Sampling 1QR=
F i. e.
+
•
i) Quota
sampling lnterperunlile Range Normal Distribution •
Find PLX > ore value in
question)
'
?
g.
10th to 90th / PR= * ☐
eg A' AB
.
Continuous Random Variable Y ,
And going remember
+ -
Variance ,o
'
/ standard Deviation,r Intersections Yu
• •
↳
if P< ✗ , context !
ii)
opportunity Sampling g- = MSMSM Point of inflection µ±r ↳ if P > ✗
,
µ
r
µtr
f.
-
µ
Tree Note, you should also be familiar with critical regions
? = Note :{fñ=kfxT Diagrams
+ -
A
B within of µ Actual significance level is
probability,P
Note there are other
advantages and
disadvantages B
'
Types of Data qualitative Coding Finding Probabilities and Inverse Normal
B
µ
KNOW Your
Normal
Testing
-
Sample Mean
quantitative either discrete If y=axtb eg.PH 1221,114<4--02 In
'
or continuous B >
calculator ! Sample Mean,
g- =
ry= Mutually Exclusive Standard Normal Distribution •
Ho :
Large Dataset '
4- Aand Bare mutually exclusive 2- ~ •
H, :
iwhen ? Representation
'
UK stations PIAAB)=
Coding
'
2- Assume Ho ,
z.ghth.g
* B =
i. e.
•
÷
.ee?..IMay-0ct'87and'15 Cumulative Frequency /Box Plots PIAVB)=
Missing µ,r both Find PIE > <
of sample taken)
•
or or mean
'
+ at
REMEMBER
i.
lowly 6 months Independence Use
coding andsimeq for both
>
.
✗
- ↳ if Pa ,
context !
,
;
International station,
÷
www.amawie, yawn , , are independent Approximating Binomial as normal ↳ ifp > a ,
1) Plants)=
Ifn
F
• can't tell
4 T-i.ir?...:. ÷! PLAIN
Histograms lfp
F =
Venn
•
from
iii. By at
Oct 87
'
3) Conditional
's
continuous data Probability µ= g- =
Data
nogaps
F
"
PIBIAI -_
Continuity Correction
Rainfall "tr
"
trace treat -025min calculations If approximating binomial normal
frequency density Reduce the whole
means as 0 in __ as
, ,
Ha area -_ spank A discrete →
Cloud cover
Comparisons Addition Law eg.PH/ss-)=Plyss.s--1!::et::::I:Y:ws values are incorrect in the video
.
.
Max Gust PIAUB)= P(3< £11 )=P(⇐ <
1) 2) F ✗
☒ updated from Oshie
recording of video .
You might also like
- Addictive Math Puzzles Grades 1 5 EbookDocument59 pagesAddictive Math Puzzles Grades 1 5 EbookNj Za100% (5)
- Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFDocument1 pageEverything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFTripleFireWingsNo ratings yet
- Eng Pipe DesignDocument12 pagesEng Pipe DesignEsapermana Riyan100% (1)
- Disney Animated Classics MedleyDocument22 pagesDisney Animated Classics MedleyGregorio Sanchez ArusNo ratings yet
- Syntorial NotesDocument13 pagesSyntorial NotesdanNo ratings yet
- Brock Planetary Declination SDocument6 pagesBrock Planetary Declination SDositheus Seth100% (2)
- Harc Snoop Test OperationDocument7 pagesHarc Snoop Test OperationMajdiSahnounNo ratings yet
- BLANK Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFDocument1 pageBLANK Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFVidhi SurekaNo ratings yet
- The Heat EquationDocument13 pagesThe Heat EquationRahulNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCheat Sheetthanagid423No ratings yet
- Fórmulas M.FluidosDocument3 pagesFórmulas M.FluidosJonathan RuizNo ratings yet
- Avida Towers Cebu Condominium: Key PlanDocument1 pageAvida Towers Cebu Condominium: Key PlanGrazel MDNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods: Multivariate AnalysisDocument1 pageStatistical Methods: Multivariate AnalysisJordan ChizickNo ratings yet
- MathDocument29 pagesMathIra CervoNo ratings yet
- 3 Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisDocument4 pages3 Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisNobel Vince Richillieu NoelNo ratings yet
- BICEN Maths Equation Revision SheetDocument1 pageBICEN Maths Equation Revision Sheetbruh bruhmanNo ratings yet
- Tema 6 - Derivación DiscretaDocument5 pagesTema 6 - Derivación DiscretaLuyi WangNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 1, Core Pure Year 1 PDFDocument1 pageEverything You Need To Memorise - Part 1, Core Pure Year 1 PDFBrain MasterNo ratings yet
- Oral Sur 2 MidtermDocument22 pagesOral Sur 2 Midtermnapat kidsanakaraketNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Tenses (Cae)Document1 pageGrammatical Tenses (Cae)ROBERTO DAVID HERRERA ROSILLONo ratings yet
- Math 2Document1 pageMath 2assal2007faisalNo ratings yet
- Bloemfontein MapDocument1 pageBloemfontein MapSiphumelele QithiNo ratings yet
- Studio Ghibli Medley-Violin 1Document3 pagesStudio Ghibli Medley-Violin 1jordi JimenezNo ratings yet
- Concertino: For Alto Sax and Orquesta OpersaxDocument2 pagesConcertino: For Alto Sax and Orquesta OpersaxDaniel DaLua SoviéticoNo ratings yet
- Zyston Roads & HousesDocument1 pageZyston Roads & HousesPradeep KumaraNo ratings yet
- MATH145 University of Waterloo Course NotesDocument38 pagesMATH145 University of Waterloo Course NotesokokNo ratings yet
- PM NB Gut Brain Axis STRY0042104 WebDocument3 pagesPM NB Gut Brain Axis STRY0042104 WebechidneNo ratings yet
- Figure 123a B Wildcats Habitat Suitability Model and Incidental Records PDFDocument2 pagesFigure 123a B Wildcats Habitat Suitability Model and Incidental Records PDFJhon SantosNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet HTDocument2 pagesCheatsheet HTAyam BakarNo ratings yet
- Week 2 VectorDocument1 pageWeek 2 VectorPhruek NatthaphatNo ratings yet
- Ded TrotoarDocument4 pagesDed TrotoarIndra AdriantoNo ratings yet
- Río Del Carrizal - Arroyo Seco 5+000 A 6+000Document1 pageRío Del Carrizal - Arroyo Seco 5+000 A 6+000David PaniaguaNo ratings yet
- IntegralesDocument1 pageIntegralesPaulaNo ratings yet
- Turing Machine RulebookDocument5 pagesTuring Machine RulebookAlexNo ratings yet
- Rules ENDocument5 pagesRules ENCos MinaNo ratings yet
- Calc Lec 1Document1 pageCalc Lec 1Nirved JainNo ratings yet
- Me 500Document17 pagesMe 500Marl SumaelNo ratings yet
- METRO Cash & Carry India - METRO 20th Anniversary ATL-1st July 2023-BangaloreDocument2 pagesMETRO Cash & Carry India - METRO 20th Anniversary ATL-1st July 2023-BangaloreThiru GnanamNo ratings yet
- Sector 20 Sector 23: Maruti Suzuki India LimitedDocument1 pageSector 20 Sector 23: Maruti Suzuki India Limitedbalaj iqbalNo ratings yet
- Lamina Agua Potable 1 de 2Document1 pageLamina Agua Potable 1 de 2Luis ReyesNo ratings yet
- ไฟฟ้าสถิต - แรง+สนาม+เกาส์Document2 pagesไฟฟ้าสถิต - แรง+สนาม+เกาส์peekpikbooNo ratings yet
- Henrietta .It#enursingmr:) Diagnostic ExpiatoryDocument9 pagesHenrietta .It#enursingmr:) Diagnostic ExpiatoryHNo ratings yet
- Internal Circulation of MuseumDocument1 pageInternal Circulation of MuseumSakhi BahetiNo ratings yet
- Correl 2 Hge NotesDocument21 pagesCorrel 2 Hge Notesromelio salumbidesNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument1 pageUntitled Notebookpixisom201No ratings yet
- Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire - WikipediaDocument1 pageTriangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire - WikipediaRamonita GarciaNo ratings yet
- ShieldGruppe Dashboard Model Work Task 1Document1 pageShieldGruppe Dashboard Model Work Task 1Charielle Esthelin BacuganNo ratings yet
- Legend: Smoke Detector Blank PlateDocument1 pageLegend: Smoke Detector Blank PlateGrazel MDNo ratings yet
- K06 16223006 Azzahra Raihana PR3Document3 pagesK06 16223006 Azzahra Raihana PR3Azzahra RaihanaNo ratings yet
- SubsDocument6 pagesSubsAverage Internet SurferNo ratings yet
- NIPS2019 TGAN Supplementary PDFDocument7 pagesNIPS2019 TGAN Supplementary PDFAmber SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4Shaurya JainNo ratings yet
- Stat Phys Exam Sample ProblemsDocument5 pagesStat Phys Exam Sample ProblemsReshamNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Definite Integrals PDFDocument3 pagesEvaluating Definite Integrals PDFJose Barrera GaleraNo ratings yet
- 중간고사 대비 A 풀이Document6 pages중간고사 대비 A 풀이민찬홍No ratings yet
- 19-Alignment Plan &profile KM 100-110Document1 page19-Alignment Plan &profile KM 100-110Tamrayehu KuremaNo ratings yet
- Tema 6Document2 pagesTema 6Marua AbselamNo ratings yet
- Audacity BrochureDocument2 pagesAudacity BrochureElvira Angela Gambini FernandezNo ratings yet
- House and Patrick Duet From Half-Wit PDFDocument1 pageHouse and Patrick Duet From Half-Wit PDFNicolae Ludvic Ionescu SánchezNo ratings yet
- Refer To The Attached Comment's Sheet: A-01B A-01BDocument1 pageRefer To The Attached Comment's Sheet: A-01B A-01BSyed Munawar AliNo ratings yet
- Arazi̇ Pafta 1Document1 pageArazi̇ Pafta 1sedra salemNo ratings yet
- Singer 478 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument74 pagesSinger 478 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- InTech-Batteries Charging Systems For Electric and Plug in Hybrid Electric VehiclesDocument20 pagesInTech-Batteries Charging Systems For Electric and Plug in Hybrid Electric VehiclesM VetriselviNo ratings yet
- Technical Methods and Requirements For Gas Meter CalibrationDocument8 pagesTechnical Methods and Requirements For Gas Meter CalibrationIrfan RazaNo ratings yet
- Rein RoundRobinModelling FSJ09Document30 pagesRein RoundRobinModelling FSJ09Noah RyderNo ratings yet
- Pi 0614 Hiblack f890b en WebDocument2 pagesPi 0614 Hiblack f890b en Web王偉仲No ratings yet
- Primakuro Catalogue Preview16-MinDocument10 pagesPrimakuro Catalogue Preview16-MinElizabeth LukitoNo ratings yet
- Faujifood Pakistan PortfolioDocument21 pagesFaujifood Pakistan PortfolioPradeep AbeynayakeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Reproduction PDFDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Reproduction PDFLmssvNo ratings yet
- Present Arlypon VPCDocument1 pagePresent Arlypon VPCErcan Ateş100% (1)
- 1 28701-FGC+101+3441+Router+6471+Datasheet+Rev+FDocument2 pages1 28701-FGC+101+3441+Router+6471+Datasheet+Rev+FВладимир ЕгоровNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Selectividad Acti9Document34 pages1.1 - Selectividad Acti9Bladimir MichelNo ratings yet
- TA1515VDocument4 pagesTA1515VLeo LeiNo ratings yet
- Vol07 1 PDFDocument275 pagesVol07 1 PDFRurintana Nalendra WarnaNo ratings yet
- Menstrupedia Comic: The Friendly Guide To Periods For Girls (2014), by Aditi Gupta, Tuhin Paul, and Rajat MittalDocument4 pagesMenstrupedia Comic: The Friendly Guide To Periods For Girls (2014), by Aditi Gupta, Tuhin Paul, and Rajat MittalMy Home KaviNo ratings yet
- 10 Q - Switching & Mode LockingDocument21 pages10 Q - Switching & Mode Lockingkaushik42080% (1)
- Calculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop Electrical Notes Articles PDFDocument10 pagesCalculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop Electrical Notes Articles PDFRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Microscope MaintenanceDocument2 pagesMicroscope MaintenanceCharlyn KeithNo ratings yet
- Electric Bike Monitoring and Controlling System Based On Internet of ThingsDocument8 pagesElectric Bike Monitoring and Controlling System Based On Internet of ThingsEarl PhamtonhiveNo ratings yet
- Med Chem Exam 2Document24 pagesMed Chem Exam 2cNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering and Technology TaxilaDocument5 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology TaxilagndfgNo ratings yet
- BHLP Year Long Plan Required English Medium 2023 24 Batch Final 991676721629413Document3 pagesBHLP Year Long Plan Required English Medium 2023 24 Batch Final 991676721629413A V GamingNo ratings yet
- The World S Finest Ideas in Cooling!: A Division ofDocument4 pagesThe World S Finest Ideas in Cooling!: A Division ofChiragNo ratings yet
- Visedo FPC-2016Document13 pagesVisedo FPC-2016Probonogoya Erawan SastroredjoNo ratings yet
- Wic ReflectionDocument3 pagesWic Reflectionapi-307029735No ratings yet
- Leta-Leta CaveDocument5 pagesLeta-Leta CaveToniNo ratings yet
- High Performance Dialysis GuideDocument28 pagesHigh Performance Dialysis GuideRoxana ElenaNo ratings yet
- Flash Memoir RevisedDocument3 pagesFlash Memoir Revisedapi-511179803No ratings yet
- Aerodrome Advisory Circular: AD AC 04 of 2017Document6 pagesAerodrome Advisory Circular: AD AC 04 of 2017confirm@No ratings yet