Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pointers To Review 1st PT Physics 1
Uploaded by
Jennis Nicole Crisostomo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThis document provides a review of key topics for a general physics exam, including:
1) Measurement concepts like density, systematic and random error, and scientific notation.
2) Vector concepts like components, finding the resultant, and determining direction.
3) Motion topics like position-time and velocity-time graphs, free fall, and projectile motion.
4) Circular motion and explanations of motion by Aristotle, Galileo, and Newton including their theories on inertia and Newton's laws of motion.
Original Description:
Original Title
Pointers-to-Review-1st-PT-Physics-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a review of key topics for a general physics exam, including:
1) Measurement concepts like density, systematic and random error, and scientific notation.
2) Vector concepts like components, finding the resultant, and determining direction.
3) Motion topics like position-time and velocity-time graphs, free fall, and projectile motion.
4) Circular motion and explanations of motion by Aristotle, Galileo, and Newton including their theories on inertia and Newton's laws of motion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesPointers To Review 1st PT Physics 1
Uploaded by
Jennis Nicole CrisostomoThis document provides a review of key topics for a general physics exam, including:
1) Measurement concepts like density, systematic and random error, and scientific notation.
2) Vector concepts like components, finding the resultant, and determining direction.
3) Motion topics like position-time and velocity-time graphs, free fall, and projectile motion.
4) Circular motion and explanations of motion by Aristotle, Galileo, and Newton including their theories on inertia and Newton's laws of motion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Pointers to Review
First Periodical Test in General Physics 1
I. Measurement
- How is density computed? Volume?
- Systematic and Random Error
- Scientific Notation
II. Scalars and Vectors
- Components of vectors (x-component -> cosine, y-component – sine)
- Finding the resultant of vectors: √
- Direction of a vector: ( )
Reminder: If x and y are positive, Θ is in quadrant I
X = negative, y= positive, Θ is in quadrant II
X = negative, y = positive, Θ is in quadrant III
X = positive, y = negative, Θ is in quadrant IV
II. Motion along a Straight Line
- Position vs. Time graph -> slope represents speed/velocity
- Velocity vs. Time graph -> slope represents acceleration
III. Free Fall and Projectile Motion
-> if the object id dropped
Acceleration is constant g = - 9.8m/s2 going up, 9.8m/s2 going down
Describe the velocity and acceleration at the maximum height.
IV. Circular Motion
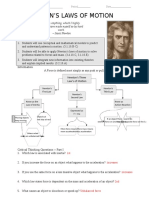
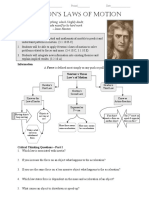
VI. Explanations of Motion:
Aristotle:
Natural Motion – based on the element (earth, fire, water, air) an object is
made of.
The heavier the object, the faster the fall.
Galileo:
In the absence of air resistance, objects with different mass fall at the same
time (constant acceleration).
Isaac Newton:
Newton’s Laws of Motion
Inertia – property of an object to resist changes in its state of motion.
First Law: An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in
motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by
an unbalanced force.
Second Law: The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net
force acting on it and is inversely proportional to its mass. a = F/m
Third Law: If an object exerts a force on a second object, the second object
exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object.
Inertial frame of reference – Newton’s first law holds true, a frame of
reference which is at rest or moving at constant velocity.
“Challenges are what makes life interesting and overcoming them is what
makes life meaningful.
You might also like
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyDocument13 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyMingNo ratings yet
- NewtonDocument2 pagesNewtonglueckwunsch.liebtNo ratings yet
- Subject Grade 10 Physics NotesDocument1 pageSubject Grade 10 Physics Notesjordan.shapiroNo ratings yet
- Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument1 pagePhysics - Newton's Laws of MotionCam MukaNo ratings yet
- Newtons 3rd LawDocument15 pagesNewtons 3rd LawcaitlyntreacyNo ratings yet
- GS104 - Exam I - ReviewDocument1 pageGS104 - Exam I - ReviewlonglistNo ratings yet
- LM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1Document40 pagesLM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Nkdievid 2Document10 pagesNkdievid 2nik100% (2)
- Laws of MotionDocument55 pagesLaws of MotionRalphNeilMarananNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Glenn Research Center NASADocument1 pageNewton's Laws of Motion Glenn Research Center NASAelenekalandadzeeeNo ratings yet
- Newtons 2nd Law Lesson 3Document19 pagesNewtons 2nd Law Lesson 3Aimee Gallego AngoluanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PhysciDocument124 pagesModule 3 Physciburner accNo ratings yet
- LM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1Document53 pagesLM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- NoteDocument2 pagesNoteSudhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit2keyconcepts 1Document4 pagesUnit2keyconcepts 1ansonng16888No ratings yet
- Dynamics: CausesDocument20 pagesDynamics: CausesperwinsharmaNo ratings yet
- Group-4'S Report: Leader: Chauncey Dale Pequiña Asst - Leader: Kristofer Cruz Sec - Alliah Garcia Jefel EcleoDocument26 pagesGroup-4'S Report: Leader: Chauncey Dale Pequiña Asst - Leader: Kristofer Cruz Sec - Alliah Garcia Jefel EcleoSheralyne Daz PequinaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument29 pagesNewton's Laws of Motionpbayes83% (6)
- Lecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)Document14 pagesLecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)verboseNo ratings yet
- 4 - Newton's Laws of Motion (Autosaved)Document20 pages4 - Newton's Laws of Motion (Autosaved)Saloni PatelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Laws of MotionDocument70 pagesLesson 2 Laws of MotionRonnie AbsalonNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion NotesDocument2 pagesForce and Motion NotesChaela ApplebyNo ratings yet
- The Laws of Motion: - Sir Isaac NewtonDocument51 pagesThe Laws of Motion: - Sir Isaac NewtonBrian NkhomaNo ratings yet
- 02 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovDocument16 pages02 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovKVP LyricsNo ratings yet
- Newtonian MechanicsDocument2 pagesNewtonian MechanicsJose AdrianoNo ratings yet
- The E Tutor - Laws of MotionDocument11 pagesThe E Tutor - Laws of Motioninfo5963No ratings yet
- Physical Science Unit 9Document2 pagesPhysical Science Unit 9Bluematwo TwoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Mechanics Part 2 2015-17Document92 pagesTopic 2 Mechanics Part 2 2015-17Byron JimenezNo ratings yet
- EportDocument6 pagesEportapi-295812958No ratings yet
- Newton's Mechanical Synthesis: Joseph Sebastian Dee, Danaan Portugal Villena, Tomy Paulino, John Darryl DyDocument44 pagesNewton's Mechanical Synthesis: Joseph Sebastian Dee, Danaan Portugal Villena, Tomy Paulino, John Darryl DyJoseph Sebastian DeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter DDocument14 pagesChapter DTerra DrakeNo ratings yet
- Primera Ley de Newton1Document9 pagesPrimera Ley de Newton1MelanieNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document5 pagesLecture 6Abdelaziz HijaziNo ratings yet
- Class Note 04Document1 pageClass Note 04userzeroNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws: Al-Basra University College of Engineering Department of MechanicsDocument12 pagesNewton's Laws: Al-Basra University College of Engineering Department of MechanicsZahra 9oNo ratings yet
- Final Term ReviewerDocument4 pagesFinal Term ReviewerNur-Aiza AlamhaliNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Lawsof Motion:: Velocity (An Acceleration) It Does Not Maintain The Velocity AsDocument4 pagesNewton's First Lawsof Motion:: Velocity (An Acceleration) It Does Not Maintain The Velocity AsIvan ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- 10physics2 2 PDFDocument6 pages10physics2 2 PDFSami NeriNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law's of MotionDocument19 pagesNewtons Law's of MotionAira YamuyamNo ratings yet
- بحث الفيزياDocument7 pagesبحث الفيزياrdcnqvv8szNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesLaws of MotionMarc Angel ValeraNo ratings yet
- Chap. 5: Three Forces Gravity Wind Force Water ForceDocument32 pagesChap. 5: Three Forces Gravity Wind Force Water ForceFranco FrecheroNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Gravity ForcesDocument28 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Forcesfelipee20No ratings yet
- محاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءDocument3 pagesمحاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءMahdiTahar BrahimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PhysicDocument5 pagesChapter 4 PhysicWaleska MendezNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceChaela ApplebyNo ratings yet
- PianoDocument1 pagePianoJack LoranNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument18 pagesMomentumfadi kimyaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2: MotionDocument2 pagesLESSON 2: MotionJamille Kate MedinaNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument8 pagesForcesapi-318478101No ratings yet
- Newton LawDocument5 pagesNewton Lawdva222No ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument8 pagesForce and MotionForsythe LearningNo ratings yet
- Newtons LawDocument7 pagesNewtons LawBrigette SanchezNo ratings yet
- Physics111 Lecture03Document22 pagesPhysics111 Lecture03Juliana MosqueraNo ratings yet
- Homework On The Laws of PhysicsDocument2 pagesHomework On The Laws of PhysicscnkrbkrNo ratings yet
- p6 Reviewr Ni MattDocument5 pagesp6 Reviewr Ni MattMatteo RazaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three Laws of MotionDocument28 pagesNewton's Three Laws of MotionDan Luigi TipactipacNo ratings yet
- Science 8 1Document18 pagesScience 8 1Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- F&MDocument1 pageF&MrhonNo ratings yet
- Technological and Legal ForcesDocument2 pagesTechnological and Legal ForcesJennis Nicole CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Kinship of Politics JNPCDocument3 pagesGroup 5 Kinship of Politics JNPCJennis Nicole CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- GenChem Lab 1.1MassConservationDocument1 pageGenChem Lab 1.1MassConservationJennis Nicole CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- GenChem Lab 1MassConservationDocument6 pagesGenChem Lab 1MassConservationJennis Nicole CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- NayarMarriage 1Document2 pagesNayarMarriage 1Jennis Nicole CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument27 pagesKinematicsme2742700No ratings yet
- Prac 1 ADocument2 pagesPrac 1 Apetkwo91No ratings yet
- From Classical To Quantum Field Theory (Davison Soper)Document12 pagesFrom Classical To Quantum Field Theory (Davison Soper)Rosemary Muñoz100% (2)
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Reading ActivityDocument2 pagesPotential and Kinetic Energy Reading Activityapi-269920605No ratings yet
- Physics DefinitionsDocument2 pagesPhysics DefinitionsElaine Neo Kai WenNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Notes - Unit 4, Part I: MagnetismDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Physics Notes - Unit 4, Part I: MagnetismAaron Kebede100% (1)
- DCH 215Document6 pagesDCH 215Vishal TanwarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in PhysicsDocument12 pagesLecture Notes in Physicsaslı tuncerNo ratings yet
- Dimensionless Quantity Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesDimensionless Quantity Fluid MechanicsAnakin SkywalkerNo ratings yet
- Newton and The Great World SystemDocument324 pagesNewton and The Great World Systemchilambu100% (1)
- XYZ Dairy EnggDocument7 pagesXYZ Dairy EnggBhuwesh PantNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Gravitational Potential Energy Using Calculus2Document7 pagesDerivation of Gravitational Potential Energy Using Calculus2W-d DomNo ratings yet
- Famous PhysicistsDocument11 pagesFamous PhysicistsPaul Mark PilarNo ratings yet
- Identification of 2H and 3R Polytypes of MoS2 Layered Crystals Using Photoluminescence SpectrosDocument7 pagesIdentification of 2H and 3R Polytypes of MoS2 Layered Crystals Using Photoluminescence SpectroswesleyNo ratings yet
- Grinding Errors and Possible SolutionsDocument6 pagesGrinding Errors and Possible SolutionsPinak ThankiNo ratings yet
- Literature Survey On M ShellDocument50 pagesLiterature Survey On M ShellMs ShehlaNo ratings yet
- NEMA Full Voltage Starters: Fast Shipment Program Cat. Nos. Are Printed inDocument4 pagesNEMA Full Voltage Starters: Fast Shipment Program Cat. Nos. Are Printed insoayNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2018 1Document393 pagesJEE Main 2018 1avinashno1No ratings yet
- Energy TransportDocument16 pagesEnergy TransportSarun NeamnomNo ratings yet
- 064 2012 02 02 051 Engl PDFDocument11 pages064 2012 02 02 051 Engl PDFHildebrando Santos100% (1)
- Hydro Borat I OnDocument198 pagesHydro Borat I OnEman MoustafaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsjfkdmfmdfNo ratings yet
- Chapt21 Lecture1Document25 pagesChapt21 Lecture1baig79No ratings yet
- FG29 fm1Document12 pagesFG29 fm1yassinebouazziNo ratings yet
- S TN HNG 001 PDFDocument11 pagesS TN HNG 001 PDFIhab El AghouryNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 02: Icet, University of The PunjabDocument9 pagesAssignment No. 02: Icet, University of The PunjabSalman HaroonNo ratings yet
- Htri FileDocument24 pagesHtri FileEalumalai Muthu100% (1)
- A Brief History of TimeDocument1 pageA Brief History of TimeCarlos Andres AndradeNo ratings yet
- Bruker Axs Saxs Webinar XRDDocument119 pagesBruker Axs Saxs Webinar XRDhafizalNo ratings yet